




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 216-225.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0304
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Received:2024-04-17
Accepted:2024-10-31
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2025-11-17
Contact:
yong GAO
通讯作者:
高永
作者简介:袁嘉茂 E-mail:1277737185@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jiamao YUAN, yong GAO. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics of Soil Nutrients in Sand Area Tracking Photovoltaic Array Area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 216-225.
袁嘉茂, 高永. 沙区追踪式光伏阵列区域土壤养分空间分异特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(11): 216-225.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0304

Fig. 2 Temperature and humidity at different positions of photovoltaic panelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different locations in the photovoltaic field at P<0.05 level.
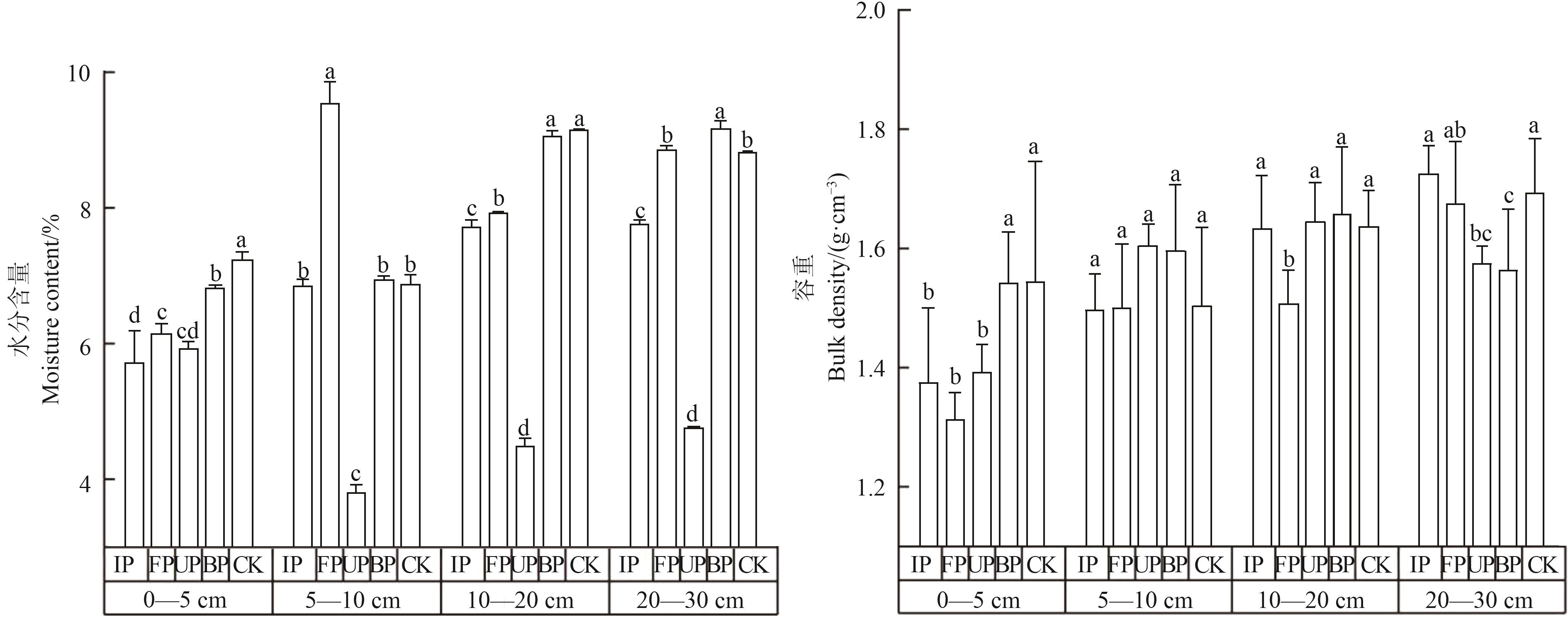
Fig. 3 Soil moisture and bulk density at different positions of photovoltaic panelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different locations in the photovoltaic field at P<0.05 level.
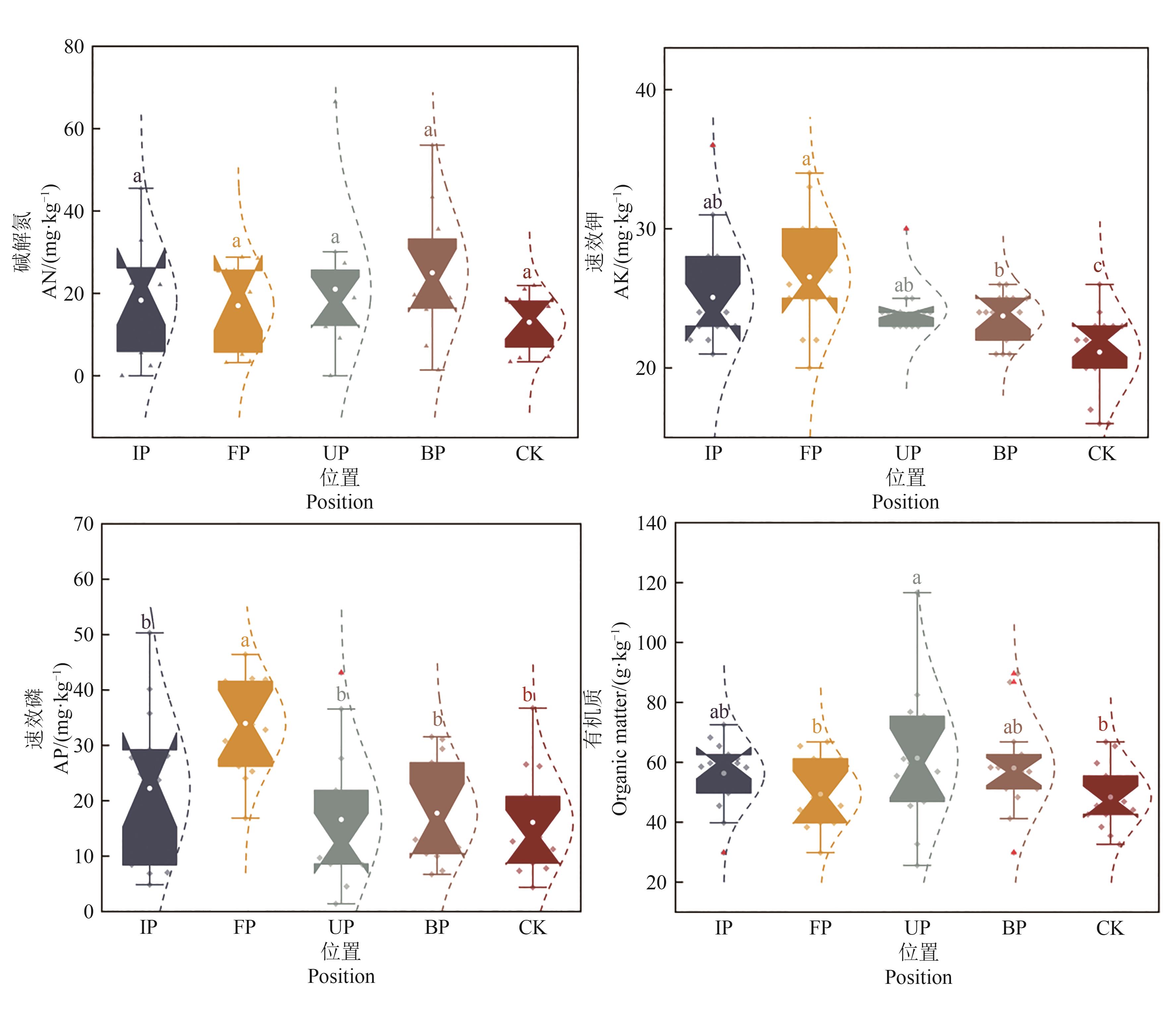
Fig. 4 Characteristic of soil nutrient content at different positions of photovoltaic panelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in soil nutrients between different locations in the photovoltaic field at P<0.05 level.
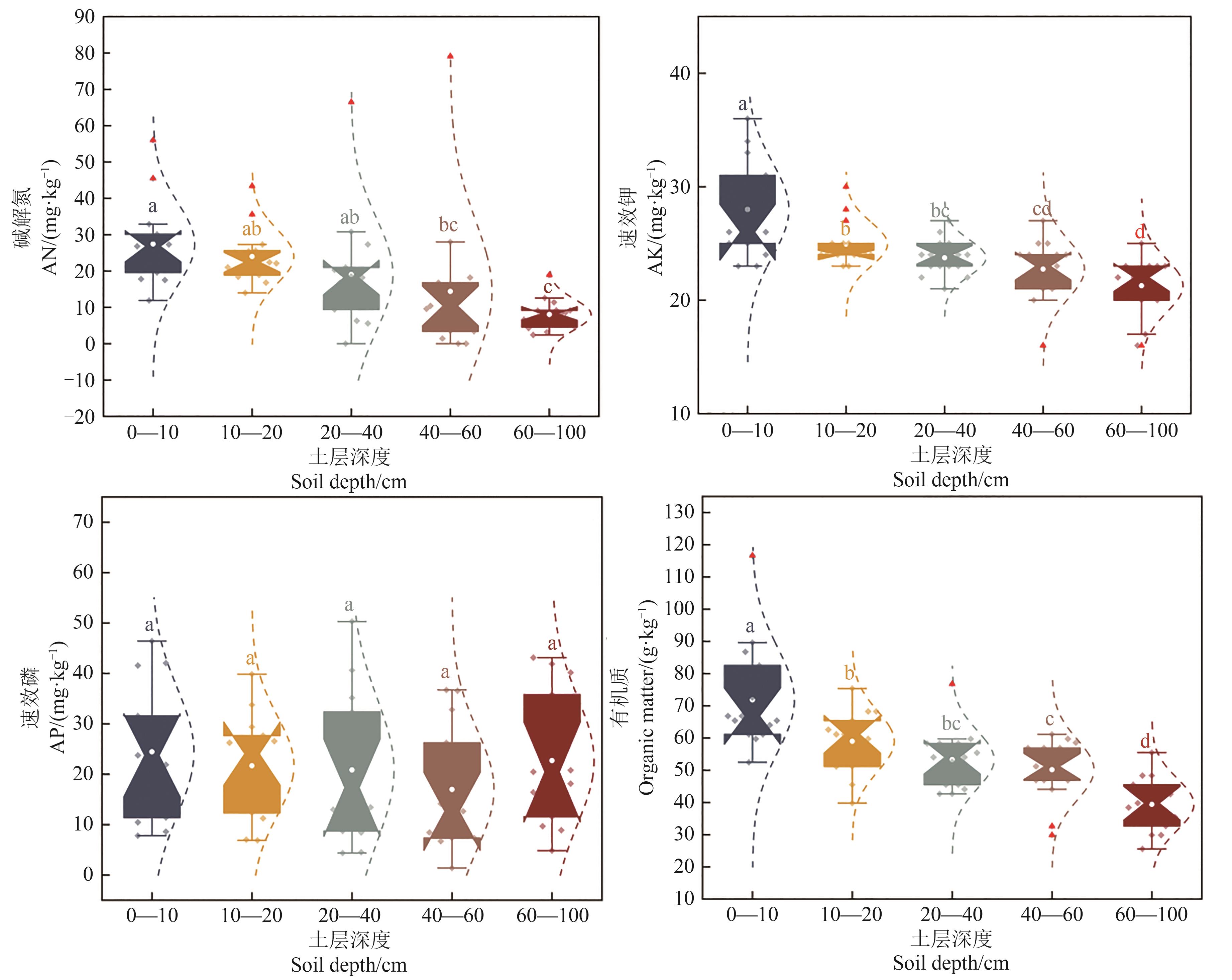
Fig. 5 Characteristic of soil nutrient content at different depths of photovoltaic panelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in soil nutrients between different depths in the photovoltaic field area at P<0.05 level.
指标 Indicator | 主成分Principal component | 公因子方差Communality/% | 分组Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||
| 有机质Organic matter | -0.333 | 0.908 | 93.5 | 1 |
| 碱解氮AN | 0.166 | 0.940 | 91.1 | 1 |
| 速效钾AK | 0.851 | 0.375 | 86.5 | 1 |
| 速效磷AP | 0.955 | -0.199 | 95.2 | 1 |
| 土壤容重Soil bulk density | -0.186 | -0.179 | 6.7 | 2 |
| 土壤水分Soil moisture | -0.901 | 0.017 | 81.1 | 2 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 2.620 | 1.919 | ||
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate/% | 43.67 | 31.99 | ||
| 累积方差贡献率Accumulative variance contribution rate/% | 43.67 | 75.66 | ||
Table 1 Principal component analysis of soil fertility quality evaluation indexes
指标 Indicator | 主成分Principal component | 公因子方差Communality/% | 分组Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||
| 有机质Organic matter | -0.333 | 0.908 | 93.5 | 1 |
| 碱解氮AN | 0.166 | 0.940 | 91.1 | 1 |
| 速效钾AK | 0.851 | 0.375 | 86.5 | 1 |
| 速效磷AP | 0.955 | -0.199 | 95.2 | 1 |
| 土壤容重Soil bulk density | -0.186 | -0.179 | 6.7 | 2 |
| 土壤水分Soil moisture | -0.901 | 0.017 | 81.1 | 2 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 2.620 | 1.919 | ||
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate/% | 43.67 | 31.99 | ||
| 累积方差贡献率Accumulative variance contribution rate/% | 43.67 | 75.66 | ||

Fig. 6 Correlation analysis of air temperature, humidity and soil indicators in the photovoltaic field areaNote:* indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 level.
位置 Position | Y1得分 Y1 score | Y2得分 Y2 score | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IP | 2.34 | -0.84 | 0.75 | 1 |
| FP | -0.24 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 3 |
| UP | -1.36 | 0.84 | -0.32 | 4 |
| BP | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 2 |
| CK | -1.48 | -2.01 | -1.29 | 5 |
Table 2 Principal component score and comprehensive score
位置 Position | Y1得分 Y1 score | Y2得分 Y2 score | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IP | 2.34 | -0.84 | 0.75 | 1 |
| FP | -0.24 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 3 |
| UP | -1.36 | 0.84 | -0.32 | 4 |
| BP | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 2 |
| CK | -1.48 | -2.01 | -1.29 | 5 |
| [1] | 朱吉庆,宋雨昂.太阳能光伏发电技术发展现状与前景[J].对外经贸,2024(1):31-34, 131. |
| ZHU J Q, SONG Y A. Solar photovoltaic power generation technology and its development status and prospects [J]. Foreign Econ. Relations Trade, 2024 (1): 31-34, 131. | |
| [2] | 屈准,杨肃昌,肖建华.双碳背景下中国西北地区光伏电站建设现状与潜力分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2024,38(2):20-26. |
| QU Z, YANG S C, XIAO J H. Current situation and potential of photovoltaic power plant construction in northwestern China under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2024, 38(2): 20-26. | |
| [3] | 丁冠元,张军华.双碳背景下我国光伏行业碳排放数据库建设必要性分析[J].信息技术与标准化,2023(12):53-56. |
| DING G Y, ZHANG J H. Necessity analysis of carbon emission database construction in China’s photovoltaic industry under the dual carbon background [J]. Inf. Technol. Stand., 2023(12): 53-56. | |
| [4] | 王祯仪,汪季,高永,等.光伏电站建设对沙区生态环境的影响[J].水土保持通报,2019,39(1):191-196. |
| WANG Z Y, WANG J, GAO Y, et al.. Impacts of photovoltaic power station construction on ecology environment in sandy area [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 39(1):191-196. | |
| [5] | 田政卿,张勇,刘向, 等.光伏电站建设对陆地生态环境的影响:研究进展与展望[J].环境科学,2024,45(1):239-247. |
| TIAN Z Q, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al.. Effects of photovoltaic power station construction on terrestrial environment: retrospect and prospect [J]. Environ. Sci., 2024, 45 (1):239-247. | |
| [6] | 崔杨,陈正洪.光伏电站对局地气候的影响研究进展[J].气候变化研究进展,2018,14(6):593-601. |
| CUI Y, CHEN Z H. Research progresses of the impacts of photovoltaic power plants on local climate [J]. Clim. Change Res., 2018, 14(6): 593-601. | |
| [7] | HERNANDEZ R R, EASTER S B, MURPHY-MARISCAL M L, et al.. Environmental impacts of utility-scale solar energy [J].Renewable Sustain. Energy Rev., 2015, 29: 766-779. |
| [8] | 杨丽薇,高晓清,吕芳,等.光伏电站对格尔木荒漠地区太阳辐射场的影响研究[J].太阳能学报,2015,36(9):2160-2166. |
| YANG L W, GAO X Q, LYU F, et al.. Study on the impact of large solar farm on radiation field in desert areas of Golmud [J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin., 2015, 36(9):2160-2166. | |
| [9] | CAMPBELL G S, NORMAN J M. An introduction to environmental biophysics second edition [M]. New York: Springer, 2000:15-23 |
| [10] | ARMSTRONG A, OSTLE N J, WHITAKER J. Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling [J/OL]. Environ. Res. Lett., 2016, 11(7):074016[2024-03-16]. . |
| [11] | 赵晶,张有新,李文龙,等.光伏电站内不同植被下土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J].中国土壤与肥料,2021(5): 21-26. |
| ZHAO J, ZHANG Y X, LI W L, et al.. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N and P under different vegetation in the photovoltaic power station [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2021(5): 21-26. | |
| [12] | 翟波,高永,党晓宏,等.内蒙古中部草原区光伏电站对土壤水分及其脉冲响应的作用机制[J].太阳能学报,2022,43(6):49-56. |
| ZHAI B, GAO Y, DANG X H, et al.. Mechanism of photovoltaic power station on soil moisture and its impulse response in grassland region of central Inner Mongolia [J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin., 2022, 43(6): 49-56. | |
| [13] | 王颖,李国庆,周洁,等.光伏阵列对土壤水分的影响研究[J].太阳能,2021(7):53-58. |
| WANG Y, LI G Q, ZHOU J, et al.. Research on influence of PV array on soil moisture [J]. Solar Energy, 2021(7):53-58. | |
| [14] | TSOUTSOS T, FRANTZESKAKI N, GEKAS V. Environmental impacts from the solar energy technologies [J]. Energy Policy, 2005, 33(3):289-296. |
| [15] | HASSANPOUR ADEH E, SELKER J S, HIGGINS C W. Remarkable agrivoltaic influence on soil moisture,micrometeorology and water-use efficiency [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(11):e0203256[2024-03-16]. . |
| [16] | TANNER K E, MOORE-O'LEARY K A, PARKER I M, et al.. Simulated solar panels create altered microhabitats in desert landforms [J/OL]. Ecosphere, 2020, 11(4):e03089 [2024-03-16].. |
| [17] | 贾瑞庭,袁立敏,蒙仲举.植物措施对沙漠光伏电站土壤的改良效应[J].中国农业科技导报,2023,25(10):182-188. |
| JIA R T, YUAN L M, MENG Z J. Effects of plant measures on soil improvement of desert photovoltaic power station [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(10):182-188. | |
| [18] | 刘文祥,万丹,甘国权,等.干热河谷区光伏电站建设的生态效应与植被恢复探讨[J].中国水土保持,2023(1):15-19. |
| [19] | 吴智泉,罗忠新,罗久富,等.石漠化光伏场区土壤肥力质量空间分异特征[J].生态学杂志,2023,42(11):2597-2603. |
| WU Z Q, LUO Z X, LUO J F, et al.. Spatial differentiation of soil fertility in a photovoltaic power station in rocky desertification zone [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2023, 42(11):2597-2603. | |
| [20] | 王涛.光伏电站建设对靖边县土壤、植被的影响研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2015. |
| WANG T. The impact of photovoltaic power construction on soil and vegetation in Jingbian county [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2015. | |
| [21] | 屈文娟.大型光伏电站区域环境要素时空变化特征及其影响研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2023. |
| QU W J. Study on the temporal and spatial variation characteristics of regional environmental elements of large-scale photovoltaic power plants and their impacts [D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Technology, 2023 | |
| [22] | CRISTINA M M, ROSITA M, LUISA M, et al.. Soil properties changes after seven years of ground mounted photovoltaic panels in Central Italy coastal area [J/OL]. Geoderma Reg., 2022, 29:00500 [2024-03-16]. . |
| [23] | WU C D, LIU H, YU Y, et al.. Ecohydrological effects of photovoltaic solar farms on soil microclimates and moisture regimes in arid Northwest China:a modeling study [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2022, 802:149946 [2024-03-16]. . |
| [24] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:34-201. |
| [25] | 赵鹏宇,高永,陈曦,等.沙漠光伏电站对空气温湿度影响研究[J].西部资源,2016(3):125-128. |
| [26] | 高晓清,杨丽薇,吕芳,等.光伏电站对格尔木荒漠地区空气温湿度影响的观测研究[J].太阳能学报,2016,37(11):2909-2915. |
| GAO X Q, YANG L W, LYU F, et al.. Observational study on the impact of the large solar farm on air temperature and humidity in desert areas of Golmud [J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin., 2016, 37(11):2909-2915. | |
| [27] | 翟波,党晓宏,陈曦,等.内蒙古典型草原区光伏电板降水再分配与土壤水分蒸散分异规律[J].中国农业大学学报,2020,25(9):144-155. |
| ZHAI B, DANG X H, CHEN X, et al.. Difference regularity of precipitation redistribution and soil water evapotranspiration in photovoltaic panels in typical steppe areas of Inner Mongolia [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2020, 25(9):144-155. | |
| [28] | 张萌,党晓宏,崔向新,等.风沙采煤塌陷区土壤水分空间分布特征[J].内蒙古林业调查设计,2020,43(5):94-98, 67. |
| ZHANG M, DANG X H, CUI X X, et al.. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil moisture in coal mining subsidence area in windy desert area [J]. Inner Mongolia For. Investig. Des., 2020, 43(5): 94-98, 67. | |
| [29] | 王思敏,张红丽,张恒硕,等.晋西黄土区典型小流域不同土层土壤容重分布特征及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志,2024,43(3):609-615. |
| WANG S M, ZHANG H L, ZHANG H S, et al.. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil bulk density at different soil layers in typical small watershed in loess region of western Shanxi province [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2024, 43(3):609-615. | |
| [30] | 孙志伟,梁越,喻金桃.长江上游流域土壤容重的空间分异特征[J].河南科学,2022,40(12):1927-1933. |
| SUN Z W, LIANG Y, YU J T. Spatial variation analysis of soil bulk density in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Henan Sci., 2022, 40(12):1927-1933. | |
| [31] | 周茂荣,王喜君.光伏电站工程对土壤与植被的影响——以甘肃河西走廊荒漠戈壁区为例[J].中国水土保持科学,2019,17(2):132-138. |
| ZHOU M R, WANG X J. Influence of photovoltaic power station engineering on soil and vegetation: taking the Gobi Desert area in the Hexi Corridor of Gansu as an example [J]. Sci. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 17(2):132-138. | |
| [32] | 王涛,王得祥,郭廷栋,等.光伏电站建设对土壤和植被的影响[J].水土保持研究,2016,23(3):90-94. |
| WANG T, WANG D X, GUO T D, et al.. The impact of photovoltaic power construction on soil and vegetation [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2016, 23(3):90-94. |
| [1] | Xiyu ZHANG, Xing SHEN, Wei LI, Wenge XIE, Jie LI, Changhao YANG, Zhongping CHAI. Influence of Reduced Nitrogen Fertilizer Combined with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Bacterial Community Structure in Korla Pear Orchards [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 217-228. |
| [2] | Chenyang ZHANG, Minggang XU, Fei WANG, Ran LI, Nan SUN. Effects of Manure Application on Soybean Yield and Soil Nutrients in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [3] | Caiyan DU, Haiyan LU, Yanzhu XIONG, Xi SUN, Xiumei SUN, Jixiong PU, Naiming ZHANG. Effects of Combined Application of Biogas Slurry and Chemical Fertilizer on Peach Growth and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties for Two Consecutive Years [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| [4] | Rui XIAO, Lu TAN, Liang WU, Hao ZHANG, Jiayuan GUO, Haijun YANG. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil of Kochia scoparia Under Cd Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [5] | Jia YAO, Jiaxin LIU, Yan SU, Xiaojuan SU. Effects of Combined Application of Tobacco Stem Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizers on Corn Growth and Soil Properties in Seeding Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [6] | Tingting NIE, Yiqiang DONG, Helong YANG, Asitaiken Julihaiti, Shijie ZHOU, Shazhou AN. Effects of Enclosure on Plant and Soil Stoichiometric Characteristics in an Artemisia Desert [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 178-187. |
| [7] | Yunzhu ZHENG, Shuchen SUN. Effects of Straw Biochar and Straw on Soil Nutrients and Crop Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation System [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [8] | Chuang LU, Haitang HU, Yuan QIN, Heju HUAI, Cunjun LI. Delineating Management Zones in Spring Maize Field Based on UAV Multispectral Image [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 106-115. |
| [9] | Kuiyuan CHEN, Hui LIU, Wei DING. Effect of Glyphosate on Soil Nutrient and the Functional Enzyme Activities in Soybean Fields [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 180-188. |
| [10] | Zhenjia HE, Wangtao FAN, Yichun DU, Qilong WANG. Effects of Water and Fertilizer Coupling on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Rice Soil and Yield Based on Soil Organic Reconstruction [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 176-185. |
| [11] | Lijuan HE, Zhongju MENG, Xiaohong DANG, Tao LYU. Effects of Planting Glycyrrhizauralensis on Mechanical Composition and Nutrients of Aeolian Sandy Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [12] | Zhuwen LIU, Longfei YANG, Maolin LIU, Guotao JIA, Qian YAO, Yiqiong MA, Ting CUI, Xinling YANG, Yang CHEN, Liangkun CHENG. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Soil Nutrients and Inherent Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 190-198. |
| [13] | PU Quanming1, YANG Peng1*, DENG Yuchuan2, XIANG Chengyong1, LIN Bangmin1, LIU Lisha1, SHI Songmei3, HE Zemin1, YONG Lei1. Effects of Different Fertilization Methods on Soil Enzyme Activity, Soil Nutrients and Quality of Spring Cabbage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 130-139. |
| [14] | WU Xin-jia, WANG Hong, ZHANG Ai-jun, ZHANG Rui-fang, ZHOU Da-mai. Effect of Different Fertilizer Treatments on Nutrient and Enzymatic Activity of Soil in River Ancient Channel [J]. , 2009, 11(6): 118-122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号 