




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 28-39.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0558
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yurong DENG1( ), Lian HAN1, Jinlong WANG1, Xinghan WEI1, Xudong WANG1, Ying ZHAO1,2, Xiaohong WEI1,2(
), Lian HAN1, Jinlong WANG1, Xinghan WEI1, Xudong WANG1, Ying ZHAO1,2, Xiaohong WEI1,2( ), Chaozhou LI1(
), Chaozhou LI1( )
)
Received:2022-07-05
Accepted:2022-10-08
Online:2024-01-15
Published:2024-01-08
Contact:
Xiaohong WEI,Chaozhou LI
邓玉荣1( ), 韩联1, 王金龙1, 韦兴翰1, 王旭东1, 赵颖1,2, 魏小红1,2(
), 韩联1, 王金龙1, 韦兴翰1, 王旭东1, 赵颖1,2, 魏小红1,2( ), 李朝周1(
), 李朝周1( )
)
通讯作者:
魏小红,李朝周
作者简介:邓玉荣 E-mail:2940834096@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yurong DENG, Lian HAN, Jinlong WANG, Xinghan WEI, Xudong WANG, Ying ZHAO, Xiaohong WEI, Chaozhou LI. Identification of SOD Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa and Their Response to Mixed Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 28-39.
邓玉荣, 韩联, 王金龙, 韦兴翰, 王旭东, 赵颖, 魏小红, 李朝周. 藜麦SOD家族基因的鉴定及其对混合盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 28-39.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0558
处理 Treatment | 盐分组成Salt composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氯化钠NaCl/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 硫酸钠Na2SO4/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸氢钠NaHCO3/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸钠Na2CO3/(200 mmol·L-1) | 硝普纳SNP/ (150 μmol·L-1) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - |
| B | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - |
| C | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | - |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| E | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | - |
| CK+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
| A+ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | + |
| B+ | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | + |
| C+ | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | + |
| D+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | + |
| E+ | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | + |
Table 1 Salt composition and molar ratio of different treatment
处理 Treatment | 盐分组成Salt composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氯化钠NaCl/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 硫酸钠Na2SO4/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸氢钠NaHCO3/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸钠Na2CO3/(200 mmol·L-1) | 硝普纳SNP/ (150 μmol·L-1) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - |
| B | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - |
| C | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | - |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| E | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | - |
| CK+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
| A+ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | + |
| B+ | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | + |
| C+ | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | + |
| D+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | + |
| E+ | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | + |
基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) | 退火温度 Tm/℃ | 产物长度 Amplicon size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqActin | CCCTCACCACTTTCCGATCT | TCCTCACCCTCACCCATTTT | 62.6 | 62 |
| CqSOD01 | ACTGGGAATGTCTCGGGTCT | GTAGCGGTACCATCATCCCC | 61.6 | 141 |
| CqSOD02 | AGGAGATGGCCCAACAACTG | GGCGAACTTCGTCTTCAGGA | 61.8 | 89 |
| CqSOD03 | TGCTGGTGGAAGATTGGCTT | TGTGGTGACTCGGTGAACTG | 62.7 | 107 |
| CqSOD04 | CGGAAGATGAAGTCCGGCAT | CACAAGGGCTCTACCGACAA | 61.9 | 138 |
| CqSOD05 | TTCAGAGAGACATGCGGGTG | CAGCATGCACCACAATAGCC | 62.3 | 111 |
| CqSOD06 | TCATCTCCGGCGCCAATAAC | GCCATGAAGACCAGGAGTGA | 62.0 | 87 |
| CqSOD07 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 63.1 | 125 |
| CqSOD08 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | CGGCTCCAAGGCATCAAATG | 63.5 | 86 |
| CqSOD09 | GGAGTCACATTGGGGAGAGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 62.2 | 90 |
| CqSOD10 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | ACATGACCTCCGCCATTGAA | 61.4 | 118 |
| CqSOD11 | GCTGGGCTTGGCTTGTTTAC | TGCTCCCAAACGTCGATAGT | 63.5 | 140 |
| CqSOD12 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | GATTCACATGACCTCCGCCA | 63.2 | 114 |
Table 2 qRT-PCR primers of CqSODs
基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) | 退火温度 Tm/℃ | 产物长度 Amplicon size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqActin | CCCTCACCACTTTCCGATCT | TCCTCACCCTCACCCATTTT | 62.6 | 62 |
| CqSOD01 | ACTGGGAATGTCTCGGGTCT | GTAGCGGTACCATCATCCCC | 61.6 | 141 |
| CqSOD02 | AGGAGATGGCCCAACAACTG | GGCGAACTTCGTCTTCAGGA | 61.8 | 89 |
| CqSOD03 | TGCTGGTGGAAGATTGGCTT | TGTGGTGACTCGGTGAACTG | 62.7 | 107 |
| CqSOD04 | CGGAAGATGAAGTCCGGCAT | CACAAGGGCTCTACCGACAA | 61.9 | 138 |
| CqSOD05 | TTCAGAGAGACATGCGGGTG | CAGCATGCACCACAATAGCC | 62.3 | 111 |
| CqSOD06 | TCATCTCCGGCGCCAATAAC | GCCATGAAGACCAGGAGTGA | 62.0 | 87 |
| CqSOD07 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 63.1 | 125 |
| CqSOD08 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | CGGCTCCAAGGCATCAAATG | 63.5 | 86 |
| CqSOD09 | GGAGTCACATTGGGGAGAGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 62.2 | 90 |
| CqSOD10 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | ACATGACCTCCGCCATTGAA | 61.4 | 118 |
| CqSOD11 | GCTGGGCTTGGCTTGTTTAC | TGCTCCCAAACGTCGATAGT | 63.5 | 140 |
| CqSOD12 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | GATTCACATGACCTCCGCCA | 63.2 | 114 |
基因登录号 Gene accession No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸数 Size/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight /kD | 等电点 pI | 不稳定指数Instability index | 脂肪酸指数Aliphatic index | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 亚细胞定位Subcellular localization | 磷酸化位点数量Phosphorylation site number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUR62000929 | CqSOD01 | 152 | 15.26 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 14 |
| AUR62005041 | CqSOD02 | 152 | 15.27 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.21 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 11 |
| AUR62014976 | CqSOD03 | 287 | 29.96 | 8.34 | 41.28 | 78.61 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 77 |
| AUR62029152 | CqSOD04 | 246 | 25.26 | 6.02 | 28.11 | 85.28 | -0.01 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 56 |
| AUR62032030 | CqSOD05 | 157 | 16.01 | 6.38 | 22.92 | 87.52 | -0.18 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62032721 | CqSOD06 | 130 | 13.41 | 6.33 | 16.19 | 89.23 | -0.16 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62001685 | CqSOD07 | 262 | 29.89 | 8.33 | 38.29 | 81.15 | -0.35 | 微体Microbody | 36 |
| AUR62010480 | CqSOD08 | 280 | 31.65 | 6.19 | 35.50 | 69.71 | -0.46 | 微体Microbody | 25 |
| AUR62020097 | CqSOD09 | 262 | 30.00 | 7.73 | 39.44 | 82.63 | -0.33 | 微体Microbody | 34 |
| AUR62030413 | CqSOD10 | 281 | 31.66 | 6.40 | 36.42 | 70.85 | -0.47 | 微体Microbody | 31 |
| AUR62024917 | CqSOD11 | 295 | 32.43 | 8.80 | 37.17 | 93.63 | -0.12 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 46 |
| AUR62030627 | CqSOD12 | 233 | 25.89 | 6.79 | 39.36 | 87.98 | -0.35 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 30 |
Table 3 Basic physicochemical properties of CqSOD proteins
基因登录号 Gene accession No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸数 Size/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight /kD | 等电点 pI | 不稳定指数Instability index | 脂肪酸指数Aliphatic index | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 亚细胞定位Subcellular localization | 磷酸化位点数量Phosphorylation site number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUR62000929 | CqSOD01 | 152 | 15.26 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 14 |
| AUR62005041 | CqSOD02 | 152 | 15.27 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.21 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 11 |
| AUR62014976 | CqSOD03 | 287 | 29.96 | 8.34 | 41.28 | 78.61 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 77 |
| AUR62029152 | CqSOD04 | 246 | 25.26 | 6.02 | 28.11 | 85.28 | -0.01 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 56 |
| AUR62032030 | CqSOD05 | 157 | 16.01 | 6.38 | 22.92 | 87.52 | -0.18 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62032721 | CqSOD06 | 130 | 13.41 | 6.33 | 16.19 | 89.23 | -0.16 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62001685 | CqSOD07 | 262 | 29.89 | 8.33 | 38.29 | 81.15 | -0.35 | 微体Microbody | 36 |
| AUR62010480 | CqSOD08 | 280 | 31.65 | 6.19 | 35.50 | 69.71 | -0.46 | 微体Microbody | 25 |
| AUR62020097 | CqSOD09 | 262 | 30.00 | 7.73 | 39.44 | 82.63 | -0.33 | 微体Microbody | 34 |
| AUR62030413 | CqSOD10 | 281 | 31.66 | 6.40 | 36.42 | 70.85 | -0.47 | 微体Microbody | 31 |
| AUR62024917 | CqSOD11 | 295 | 32.43 | 8.80 | 37.17 | 93.63 | -0.12 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 46 |
| AUR62030627 | CqSOD12 | 233 | 25.89 | 6.79 | 39.36 | 87.98 | -0.35 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 30 |
基因 Gene | 蛋白质二级结构Secondary structure of protein | 染色体定位 Chromosomal localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α螺旋α helix | 延伸链Extension chain | 无规则卷曲Random coil | ||
| CqSOD01 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr12 |
| CqSOD02 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr05 |
| CqSOD03 | 86 | 46 | 155 | Chr15 |
| CqSOD04 | 47 | 55 | 144 | Chr00 |
| CqSOD05 | 0 | 55 | 102 | Chr11 |
| CqSOD06 | 4 | 42 | 84 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD07 | 71 | 61 | 130 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD08 | 93 | 49 | 138 | Chr13 |
| CqSOD09 | 93 | 48 | 121 | Chr18 |
| CqSOD10 | 94 | 51 | 136 | Chr16 |
| CqSOD11 | 96 | 49 | 150 | Chr01 |
| CqSOD12 | 89 | 43 | 101 | Chr04 |
Table 4 Secondary structure and chromosomal localization
基因 Gene | 蛋白质二级结构Secondary structure of protein | 染色体定位 Chromosomal localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α螺旋α helix | 延伸链Extension chain | 无规则卷曲Random coil | ||
| CqSOD01 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr12 |
| CqSOD02 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr05 |
| CqSOD03 | 86 | 46 | 155 | Chr15 |
| CqSOD04 | 47 | 55 | 144 | Chr00 |
| CqSOD05 | 0 | 55 | 102 | Chr11 |
| CqSOD06 | 4 | 42 | 84 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD07 | 71 | 61 | 130 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD08 | 93 | 49 | 138 | Chr13 |
| CqSOD09 | 93 | 48 | 121 | Chr18 |
| CqSOD10 | 94 | 51 | 136 | Chr16 |
| CqSOD11 | 96 | 49 | 150 | Chr01 |
| CqSOD12 | 89 | 43 | 101 | Chr04 |
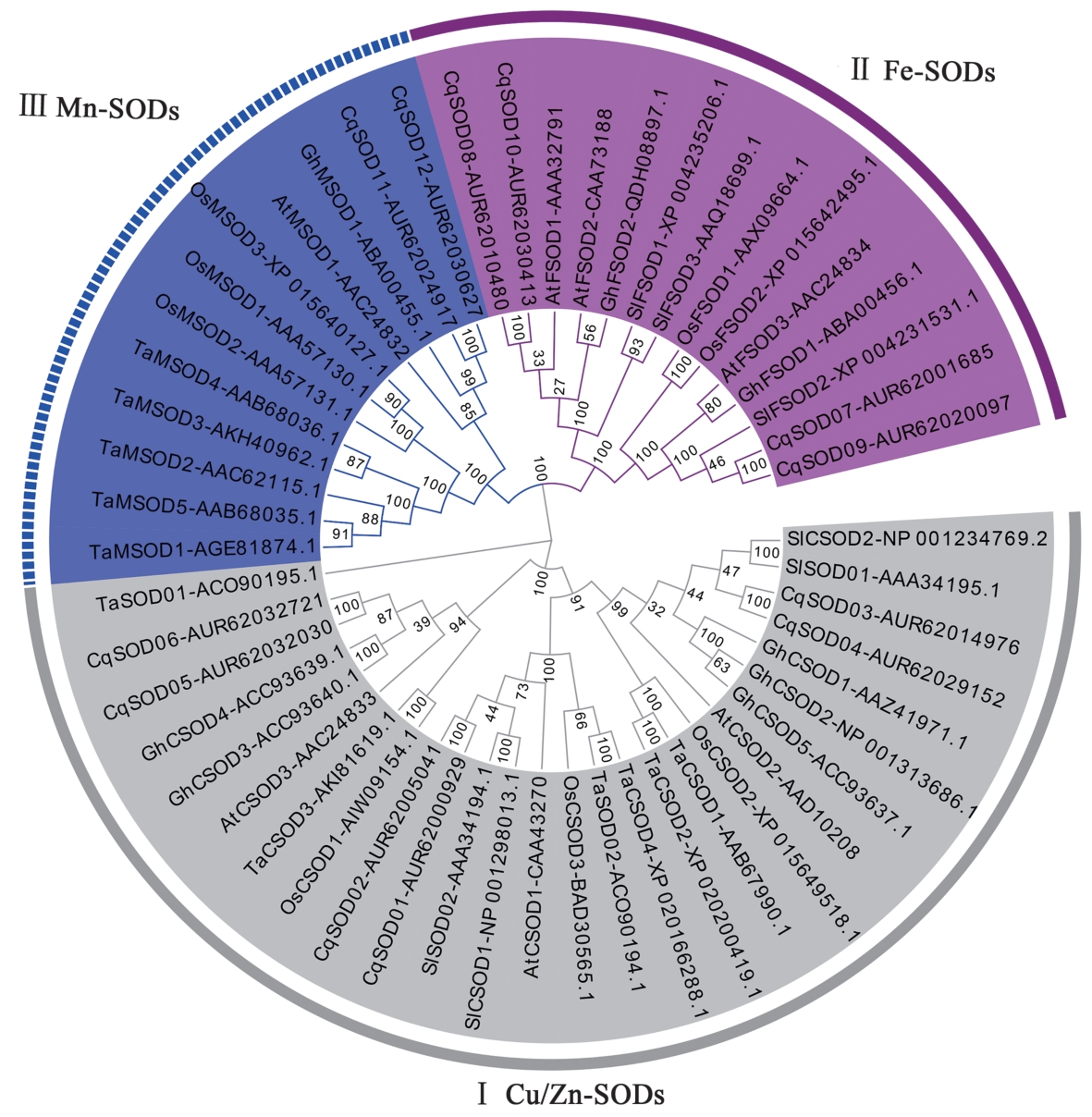
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic of SOD proteins from quinoa and other plantsNote: At—Arabidopsis; Ta—Triticum aestivum; Sl—Solanum lycopersicum;Cq-Chenopodium quinoa; Gh-Gossypium hirsutum; Os-Oryza sativa.
基因 Gene | 激素响应元件 Phytohormone responsiveness element | 压力响应元件 Stress responsiveness element | 组织特异性表达元件 Tissue-specific expression element | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ABA响应元件 ABRE | CGTCA 基序 CGTCA-motif | P盒 P-box | TATC盒TATC-box | TCA 元件 TCA-element | TGACG基序TGACG-motif | TGA 元件 TGA-element | 低温应答元件 LTR | MYB结合位点 MBS | 富含TC的重复序列 TC-rich repeats | 厌氧诱导作用元件 ARE | CAT盒CAT-box | MYB 结合位点MBSI | O2位点 O2-site | |
| CqSOD01 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD02 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD03 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||
| CqSOD04 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| CqSOD05 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| CqSOD06 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| CqSOD07 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD08 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD09 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD10 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD11 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
Table 5 Cis-acting elements in the promoter region of CqSOD genes
基因 Gene | 激素响应元件 Phytohormone responsiveness element | 压力响应元件 Stress responsiveness element | 组织特异性表达元件 Tissue-specific expression element | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ABA响应元件 ABRE | CGTCA 基序 CGTCA-motif | P盒 P-box | TATC盒TATC-box | TCA 元件 TCA-element | TGACG基序TGACG-motif | TGA 元件 TGA-element | 低温应答元件 LTR | MYB结合位点 MBS | 富含TC的重复序列 TC-rich repeats | 厌氧诱导作用元件 ARE | CAT盒CAT-box | MYB 结合位点MBSI | O2位点 O2-site | |
| CqSOD01 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD02 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD03 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||
| CqSOD04 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| CqSOD05 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| CqSOD06 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| CqSOD07 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD08 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD09 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD10 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD11 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
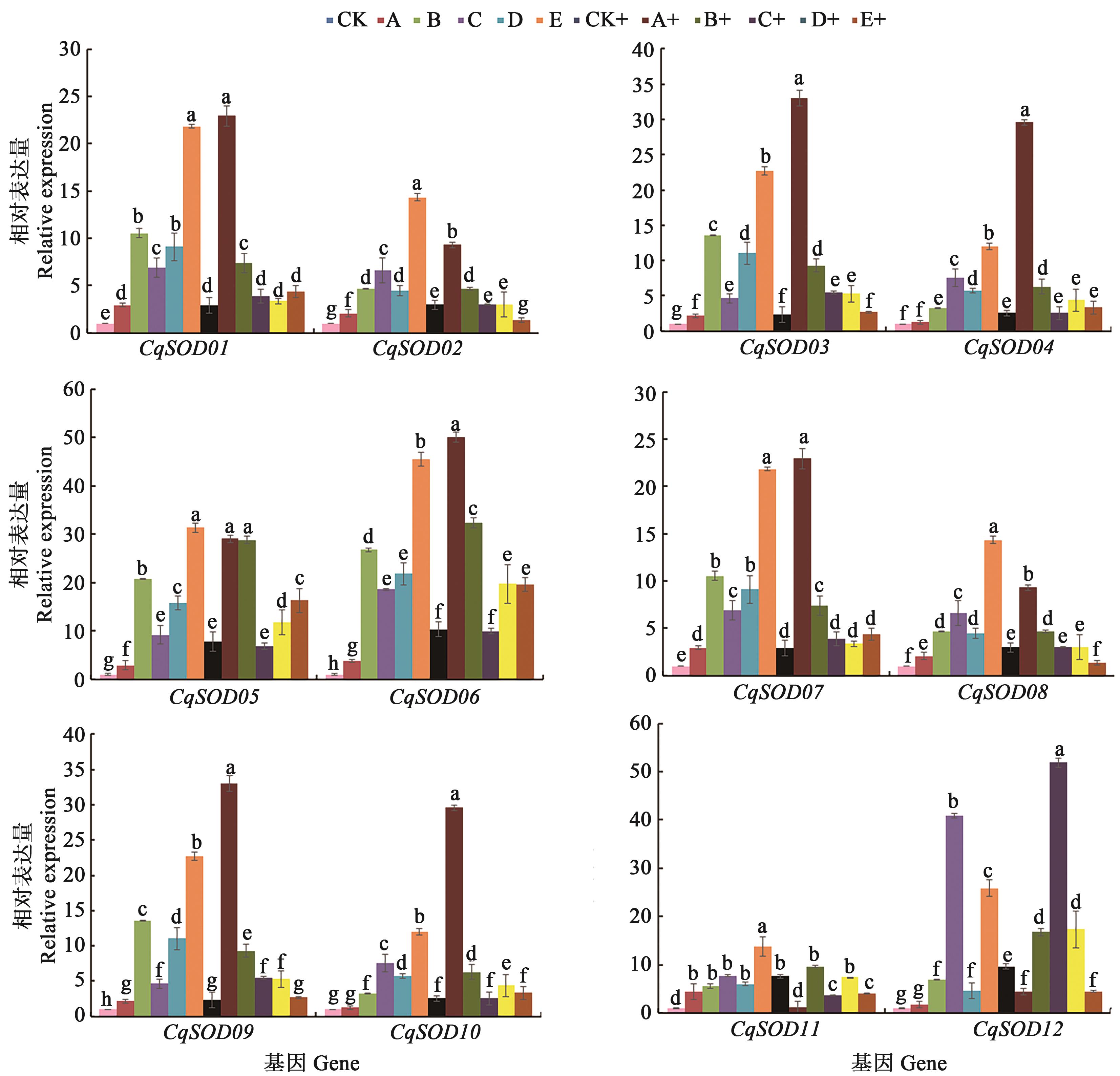
Fig. 5 qRT-PCR of CqSODs in response to mixed saline-alkali stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | MILLER A. Superoxide dismutases: ancient enzymes and new insights [J]. FEBS Lett., 2012, 586(5): 585-595. |
| 2 | MITTLER R. ROS are good [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2017, 22(1):11-19. |
| 3 | BAFANA A, DUTT S, KUMAR S, et al.. Superoxide dismutase: an industrial perspective [J]. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 2011, 31(1):65-76. |
| 4 | ZELKO I N, MARIANI T J, FOLZ R J. Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression [J]. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2002, 33(3):337-349. |
| 5 | TEPPERMAN J M, DUNSMUIR P. Transformed plants with elevated levels of chloroplastic SOD are not more resistant to superoxide toxicity [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 1990, 14(4): 501-511. |
| 6 | SU W, RAZA A, GAO A, et al.. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under different hormones and abiotic stress conditions [J/OL]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, 10(8): 1182 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 7 | ABREU I A, CABELLI D E. Superoxide dismutases-a review of the metal-associated mechanistic variations [J]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2010, 1804(2): 263-274. |
| 8 | SONG J, ZENG L, CHEN R, et al.. In silico identification and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Medicago truncatula [J/OL]. 3 Biotech., 2018, 8(8): 348 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 9 | 魏婧, 徐畅, 李可欣, 等. 超氧化物歧化酶的研究进展与植物抗逆性[J].植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12): 2571-2584. |
| WEI J, XU C, LI K X, et al.. Progress on superoxide dismutase and plant stress resistance [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2020, 56(12):2571-2584. | |
| 10 | ASENSIO A C, GIL-MONREAL M, PIRES L, et al.. Two Fe-superoxide dismutase families respond differently to stress and senescence in legumes [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2012, 169(13):1253-1260. |
| 11 | HAN L M, HUA W P, CAO X Y, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza [J/OL]. Gene, 2020, 742:144603[2022-06-03]. . |
| 12 | ZHANG X, ZHANG L T, CHEN Y Y, et al.. Genome-wide identification of the SOD gene family and expression analysis under drought and salt stress in barley [J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2021, 94(1): 49-60. |
| 13 | FENG K, YU J H, CHENG Y, et al.. The SOD gene family in tomato: identification, phylogenetic relationships, and expression patterns [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016(7): 1279 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 14 | ZHOU Y, HU L F, WU H, et al.. Genome-wide identification and transcriptional expression analysis of cucumber superoxide dismutase (SOD) family in response to various abiotic stresses [J/OL]. Int. J. Genomics, 2017, 2017: 7243973 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 15 | MOLINA-RUEDA J J, TSAI C J, KIRBY E G. The Populus superoxide dismutase gene family and its responses to drought stress in transgenic poplar overexpressing a pine cytosolic glutamine synthetase (GS1a) [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e56421 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 16 | ZURITA-SILVA A, FUENTES F, ZAMORA P, et al.. Breeding quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): potential and perspectives [J]. Mol. Breed., 2014, 34(1): 13-30. |
| 17 | 赵颖, 魏小红, 李桃桃. 外源NO对混合盐碱胁迫下藜麦种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 92-101. |
| ZHAO Y, WEI X H, LI T T. Efferts of exogenous nitric oxide on seed Emination and seedling growth of Chenopodium quinoa under complex saline-alkali stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2020, 29(4): 92-101. | |
| 18 | 刘文瑜, 杨发荣, 黄杰, 等. NaCl 胁迫对藜麦幼苗生长和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2017, 37(9): 1797-1804. |
| LIU W Y, YANG F R, HUANG J, et al.. Response of seedling growth and the activities of antioxidant enzymes of Chenopodium quinoa to salt stress [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2017, 37(9):1797-1804. | |
| 19 | RUIZ K B, BIONDI S, MARTÍNEZ E A, et al.. Quinoa-a model crop for understanding salt-tolerance mechanisms in halophytes [J]. Plant Biosyst., 2016, 150(2): 357-371. |
| 20 | 李美丽, 宿俊吉, 杨永林, 等. 陆地棉COI家族基因鉴定及在干旱和盐胁迫下的表达分析[J].中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4):63-74. |
| LI M L, SU J J, YANG Y L, et al.. Identification of COl family genes and their expression in Gossypium hirsutum L. under drought and salt stress [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(4): 63-74. | |
| 21 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real-time quantitative PCR [J]. Methods, 2002, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 22 | WANG T, SONG H, ZHANG B H, et al.. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) [J/OL]. 3 Biotech., 2018, 8(12): 486 [2022-06-03].. |
| 23 | DEHURY B, SARMA K, SARMAH R, et al.. In silico analyses of superoxide dismutases (SODs) of rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 2013, 22(1): 150-156. |
| 24 | GOSAVI G U, JADHAV A S, KALE A A, et al.. Effect of heat stress on proline, chlorophyll content, heat shock proteins and antioxidant enzyme activity in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) at seedlings stage [J]. Indian J. Biotechnol., 2014, 13(13): 356-363. |
| 25 | XMHA B, QXC B, QI Y B, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of superoxide dismutase genes in Larix kaempferi [J]. Gene, 2019, 686: 29-36. |
| 26 | TANG Y H, BAO X X, ZHI Y L, et al.. Overexpression of a MYB family gene, OsMYB6, increases drought and salinity stress tolerance in transgenic rice [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2019(10): 168 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 27 | LIN Y L, LAI Z X. Superoxide dismutase multigene family in longan somatic embryos: a comparison of CuZn-SOD, Fe-SOD, and Mn-SOD gene structure, splicing, phylogeny, and expression [J]. Mol. Breeding, 2013, 32(3): 595-615. |
| 28 | WANG W, ZHANG X, DENG F, et al.. Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in Gossypium hirsutum [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2017,18(1):376 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 29 | FINK R C, SCANDALIOS J G. Molecular evolution and structure-function relationships of the superoxide dismutase gene families in angiosperms and their relationship to other eukaryotic and prokaryotic superoxide dismutases [J]. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2002, 399(1): 19-36. |
| 30 | XU G X, GUO C C, SHAN H Y, et al.. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, 109(4): 1187-1192. |
| 31 | GILL S S, TUTEJA N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2010, 48(12): 909-930. |
| 32 | FENG X, LAI Z X, LIN Y L, et al.. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the superoxide dismutase gene family in Musa acuminata cv.Tianbaojiao (AAA group)[J/OL]. BCM Genomics, 2015, 16:823 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 33 | HU X X, HAO C Y, CHENG Z M, et al.. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the grapevine superoxide dismutase (SOD) family [J/OL]. Int. J.Genomics, 2019:7350414 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 34 | PILON M, RAVET K, TAPKEN W. The biogenesis and physiological function of chloroplast superoxide dismutases [J]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2011, 1807(8): 989-998. |
| [1] | Zhining YANG, Xuke LU, Yapeng FAN, Yuping SUN, Xin YU, Liang WANG, Yongjian GAO, Gulijiayinashen Habuli, Gulishaxi Nasiyi, Wumuer Abudu, Hui HUANG, Menghao ZHANG, Lidong WANG, Xiao CHEN, Lei XIAO, Xinrui ZHANG, Shuai WANG, Xiugui CHEN, Junjuan WANG, Lixue GUO, Wenwei GAO, Wuwei YE. Response Mechanism of Cotton GhDMT7 Gene to 5-azacytidine [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 28-35. |
| [2] | Jinxian LIU, Lijuan WANG, Jie LIU, Xianyu FU, Guangheng WU. Identification and Expression Analysis of Calmodulin-binding Transcription Activator (CAMTA) Family Genes in Tea Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 71-82. |
| [3] | Xianguo LI, Qi DAI, Zepeng WANG, Zhaolong CHEN, Huizhuan YAN, Ning LI. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tomato CCCH-like Zinc Finger Protein Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [4] | Xiaorong GUO, Ying LIU, Jiazhen FAN, Tao HUANG, Rong ZHOU. Bioinformatics Analysis of Porcine CREBRF Gene and Its Expression Pattern [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 44-53. |
| [5] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [6] | Xinyue BAO, Hongmin CHEN, Weiwei WANG, Yimiao TANG, Zhaofeng FANG, Jinxiu MA, Dezhou WANG, Jinghong ZUO, Zhanjun YAO. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Wheat TaCOBL-5 Genes [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 11-21. |
| [7] | Yanhong ZHANG, Zhanbin GUO, Ruixiang LIU. Comprehensive Analysis and Evaluation of Agronomic Characters of 50 Chenopodium Quinoa Germplasm Resources [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 45-54. |
| [8] | Yang FENG, Fenggen GUO, Shiyu WANG, Zhengjie LIU, Wenhong LONG. Codon Bias and Evolution Analysis of CqGAI in Chenopodium quinoa [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 27-36. |
| [9] | Bo LIU, Wangtian WANG, Li MA, Junyan WU, Yuanyuan PU, Lijun LIU, Yan FANG, Wancang SUN, Yan ZHANG, Ruimin LIU, Xiucun ZENG. Identification and Characterization of IPT Gene Family in Brassica rapa L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 56-66. |
| [10] | Zhenwei ZHANG, Xiangshu DONG, Jing YANG, Xuejun LI, Meijun QI, Kuaile JIANG, Yonglin YANG, Butian WANG, Xuedong SHI, Junchao QIU, Zhihua CHEN, Yu GE. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Key Chlorophyll Synthesis Related Gene CaPOR in Coffea arabica [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 83-97. |
| [11] | Qiujing CHEN, Zhaodi YANG, Shiyu WANG, Fenggen GUO, Xiaoxue ZHAO, Fan CHEN, Yang FENG. Effects of Plant Growth Retarders on Lodging Resistance and Yield of Quinoa [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 42-48. |
| [12] | Jinfeng ZHAO, Aili YU, Yanfang LI, Yanwei DU, Gaohong WANG, Zhenhua WANG. Response Characteristics of SiCBL3 to Abiotic Stresses in Foxtail Millet [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 68-75. |
| [13] | Qinqin WANG, Xiugui CHEN, Xuke LU, Shuai WANG, Yuexin ZHANG, Yapeng FAN, Quanjia CHEN, Wuwei YE. Bioinformatics Analysis and Functional Verification of GhPKE1 inUpland Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 38-45. |
| [14] | LIU Zhengwen, WANG Xingfen, MENG Chengsheng, ZHANG Yan, SUN Zhengwen, WU Liqiang, MA Zhiying, ZHANG Guiyin. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of GH9 Gene Family in Gossypium barbadense L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(9): 30-45. |
| [15] | PU Quanming, YANG Peng, YONG Lei, DENG Yuchuan, HE Zihan, LIN Bangmin, SHI Songmei, XIANG Chengyong, FANG Fang. Studies on Pigment Content and Photosyntheic Characteristics of Purple-red Leaf Color Mutant in Radish [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 45-54. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号