




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 154-160.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0115
贾睿琪1( ), 郭子昂1, 姚晨1, 李璞2, 腊贵晓3, 陆夏梓1, 郭虹妤1, 李烜桢1(
), 郭子昂1, 姚晨1, 李璞2, 腊贵晓3, 陆夏梓1, 郭虹妤1, 李烜桢1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-21
接受日期:2022-04-12
出版日期:2022-08-15
发布日期:2022-08-22
通讯作者:
李烜桢
作者简介:贾睿琪 E-mail:jiaruiqi96@outlook.com;
基金资助:
Ruiqi JIA1( ), Ziang GUO1, Chen YAO1, Pu LI2, Guixiao LA3, Xiazi LU1, Hongyu GUO1, Xuanzhen LI1(
), Ziang GUO1, Chen YAO1, Pu LI2, Guixiao LA3, Xiazi LU1, Hongyu GUO1, Xuanzhen LI1( )
)
Received:2022-02-21
Accepted:2022-04-12
Online:2022-08-15
Published:2022-08-22
Contact:
Xuanzhen LI
摘要:
为探究低磷胁迫下小麦根系生理和形态的变化及其对镉的吸收能力的影响,以Ca3(PO4)2作为磷源,通过砂培试验研究了在低磷胁迫下小麦根系形态和分泌物变化特征,以及这些变化对难溶态镉(CdCO3)的活化与吸收的影响。结果表明,在低磷处理中,小麦地下部生物量显著低于对照,降幅为27.3%(P<0.05),根长度、根表面积和根体积均显著变小(P<0.05)。此外,低磷胁迫下小麦地上部和地下部磷含量均显著降低,降幅分别为35.4%和23.1%(P<0.05),但是显著促进了难溶态磷的溶解(P<0.05)。同时还发现低磷胁迫显著提高了小麦植株Cd含量和Cd的总活化量,增幅分别为190.8%和82.8%(P<0.05)。低磷胁迫下培养基pH降低了0.3,同时根中草酸根和苹果酸根含量显著升高,增幅分别为1 588.1%和37.7%(P<0.05),由此可见,低磷胁迫下小麦通过分泌质子和羧酸根促进了磷的活化,并促进了Cd的活化,进而导致小麦Cd吸收的增加。这些结果阐明了低磷胁迫影响小麦Cd吸收的机制。
中图分类号:
贾睿琪, 郭子昂, 姚晨, 李璞, 腊贵晓, 陆夏梓, 郭虹妤, 李烜桢. 低磷胁迫对小麦镉吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 154-160.
Ruiqi JIA, Ziang GUO, Chen YAO, Pu LI, Guixiao LA, Xiazi LU, Hongyu GUO, Xuanzhen LI. Effect of Low Phosphorus Stress on Cadmium Uptake in Wheat[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 154-160.

图1 低磷胁迫对小麦干重及根系形态指标的影响注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 1 Effects of low phosphorus stress on wheat biomass and root morphological indicatorsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
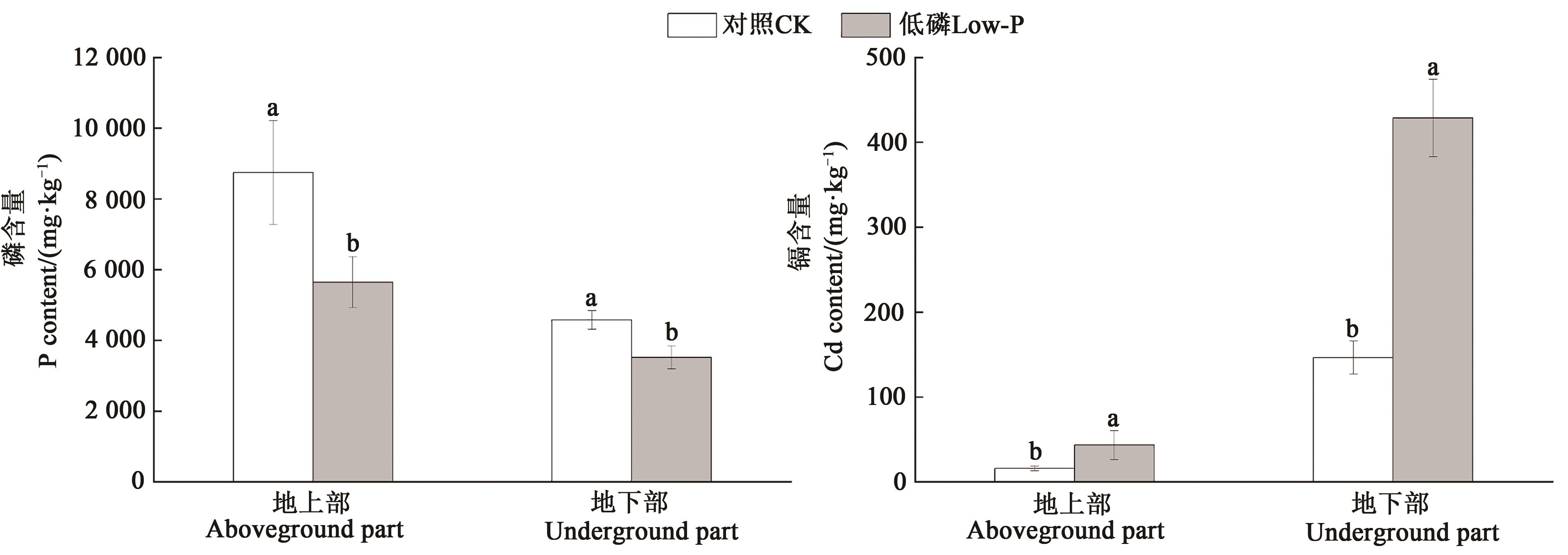
图2 低磷胁迫对小麦磷和镉含量的影响注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 2 Effect of low phosphorus stress on phosphorus and cadmium contents in wheatNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
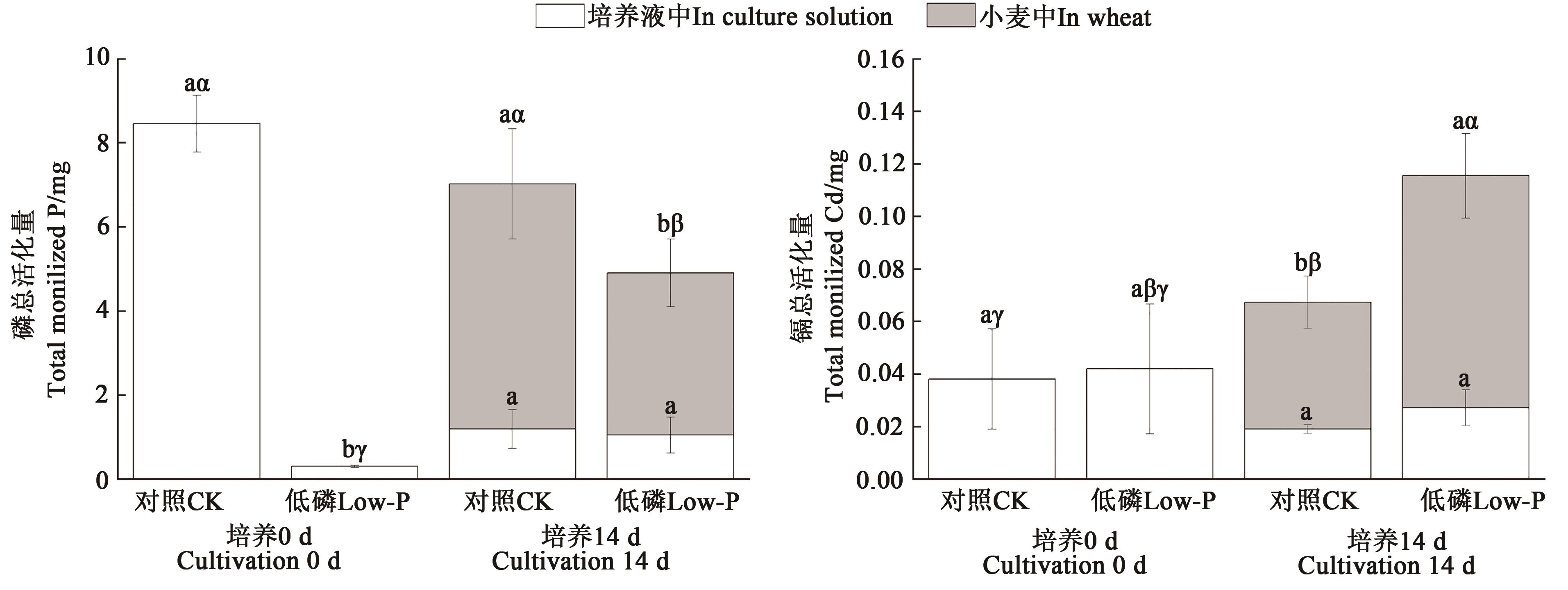
图3 低磷胁迫对小麦-培养基体系中磷和镉含量的影响注:不同英文字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),不同希腊字母表示总活化量间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 3 Effect of low phosphorus stress on the distribution of phosphorus and cadmium in wheat-culture medium systemNote:Different English letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05),different Greek letters indicate significant differences between total activation (P<0.05).
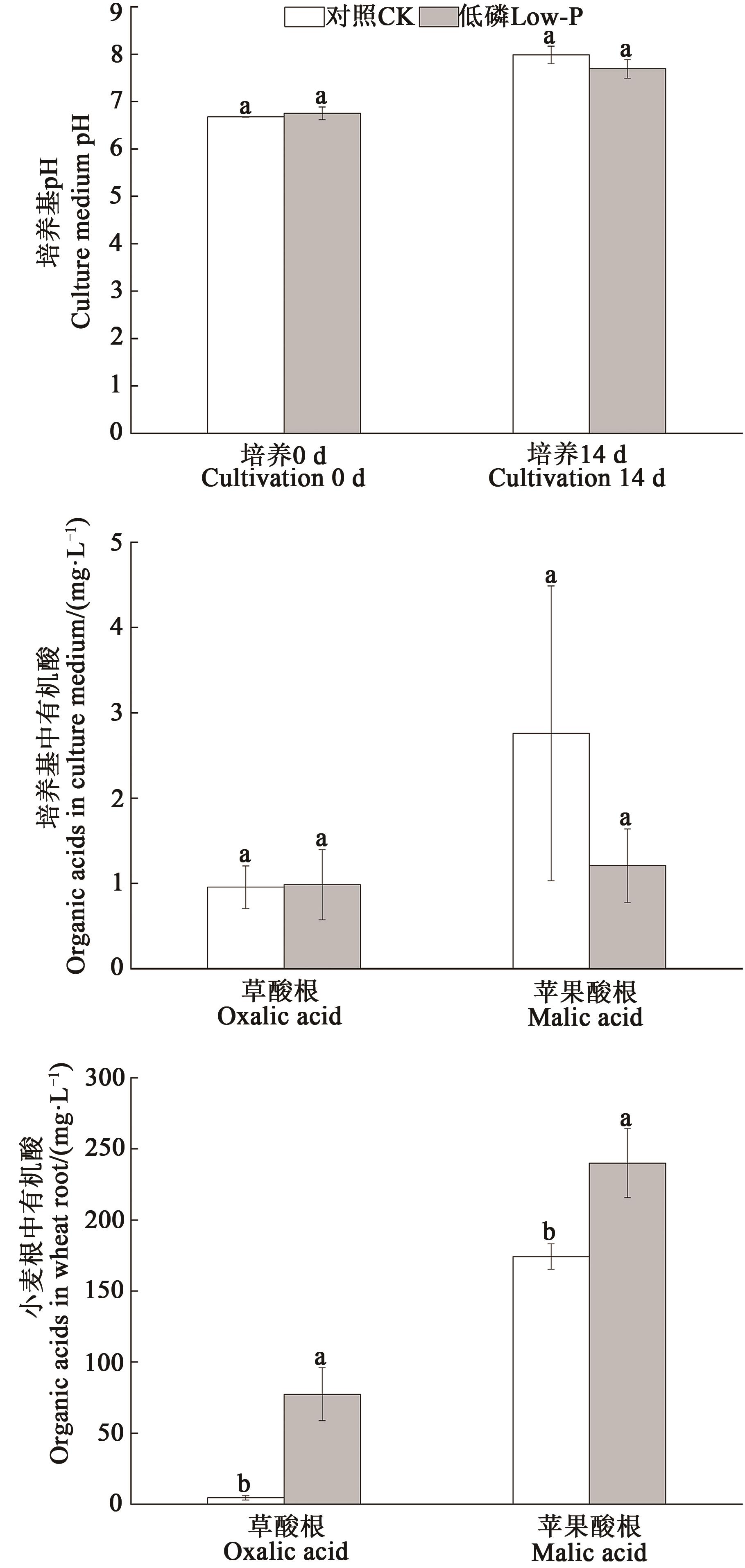
图4 低磷胁迫对培养基pH、有机酸含量及小麦根中有机酸含量的影响注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 4 Effect of low phosphorus stress on medium pH, organic acid and organic acids in wheat rootsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
| 1 | HUSSAIN B, ASHRAF M N, SHAFEEQ UR R, et al.. Cadmium stress in paddy fields: effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ. , 2021, 754: 142188 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 2 | ZHAO F J, MA Y, ZHU Y G, et al.. Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(2): 750-759. |
| 3 | SUN Y, XU Y, XU Y, et al.. Reliability and stability of immobilization remediation of Cd polluted soils using sepiolite under pot and field trials [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2016, 208: 739-746. |
| 4 | SHI T, MA J, WU X, et al.. Inventories of heavy metal inputs and outputs to and from agricultural soils: a review [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2018, 164: 118-124. |
| 5 | QIAO K, WANG F, LIANG S, et al.. New biofortification tool: wheat TaCNR5 enhances zinc and manganese tolerance and increases zinc and manganese accumulation in rice grains [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2019, 67(35): 9877-9884. |
| 6 | ZHANG L, ZHANG C, DU B, et al.. Effects of node restriction on cadmium accumulation in eight Chinese wheat (Triticum turgidum) cultivars [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ. , 2020, 725: 138358[2022-02-20]. . |
| 7 | LIANG X, STRAWN D G, CHEN J, et al.. Variation in cadmium accumulation in spring wheat cultivars: uptake and redistribution to grain [J]. Plant Soil, 2017, 421(1-2): 219-231. |
| 8 | LIU N, HUANG X, SUN L, et al.. Screening stably low cadmium and moderately high micronutrients wheat cultivars under three different agricultural environments of China [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125065 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 9 | RIZWAN M, ALI S, ABBAS T, et al.. Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2016, 130: 43-53. |
| 10 | GRUTER R, COSTEROUSSE B, MAYER J, et al.. Long-term organic matter application reduces cadmium but not zinc concentrations in wheat [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 669: 608-620. |
| 11 | ROMANYA J, BLANCO-MORENO J M, SANS F X. Phosphorus mobilization in low-P arable soils may involve soil organic C depletion [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017, 113: 250-259. |
| 12 | WEYERS E, STRAWN D G, PEAK D, et al.. Phosphorus speciation in calcareous soils following annual dairy manure amendments [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2016, 80(6): 1531-1542. |
| 13 | OBURGER E, LEITNER D, JONES D L, et al.. Adsorption and desorption dynamics of citric acid anions in soil [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci., 2011, 62(5): 733-742. |
| 14 | HU Y, GAO Z, HUANG Y, et al.. Impact of poplar-based phytomanagement on metal bioavailability in low-phosphorus calcareous soil with multi-metal contamination [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 686: 848-855. |
| 15 | CONG W F, SURIYAGODA L D B, LAMBERS H. Tightening the phosphorus cycle through phosphorus-efficient crop genotypes [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2020, 25(10): 967-975. |
| 16 | VANCE C P, UHDE-STONE C, ALLAN D L. Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource [J]. New Phytol., 2003, 157(3): 423-447. |
| 17 | POSTMA J A, DATHE A, LYNCH J P. The optimal lateral root branching density for maize depends on nitrogen and phosphorus availability [J]. Plant Physiol., 2014, 166(2): 590-602. |
| 18 | HALING R E, BROWN L K, STEFANSKI A, et al.. Differences in nutrient foraging among Trifolium subterraneum cultivars deliver improved P-acquisition efficiency [J]. Plant Soil, 2018, 424(1): 539-554. |
| 19 | HINSINGER P, PLASSARD C, TANG C X, et al.. Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review [J]. Plant Soil, 2003, 248(1): 43-59. |
| 20 | RICHARDSON A E, LYNCH J P, RYAN P R, et al.. Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture [J]. Plant Soil, 2011, 349(1): 121-156. |
| 21 | PANG J, BANSAL R, ZHAO H, et al.. The carboxylate-releasing phosphorus-mobilizing strategy can be proxied by foliar manganese concentration in a large set of chickpea germplasm under low phosphorus supply [J]. New Phytol., 2018, 219(2): 518-529. |
| 22 | 邢维芹, 张红毅, SCHECKEL Kirk G., 等. 铅冶炼污染区小麦籽粒镉含量及低积累品种筛选 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(10): 2039-2040. |
| XING W Q, ZHANG H Y, SCHECKEL K G, et al.. Grain Cd concentrations of 100 wheat(Triticum aestivum L.) varieties and strains grown on lead-smelting contaminated soils and screening for low Cd varieties [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(10): 2039-2040. | |
| 23 | MA S, NAN Z, HU Y, et al.. Phosphorus supply level is more important than wheat variety in safe utilization of cadmium-contaminated calcareous soil [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2022, 424: 127224 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 24 | LUO L, MA Y, SANDERS R L, et al.. Phosphorus speciation and transformation in long-term fertilized soil: evidence from chemical fractionation and P K-edge XANES spectroscopy [J]. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems, 2017, 107(2): 215-226. |
| 25 | 屈锋,牟世芬,侯小平,等. 小麦根系中有机酸的离子色谱法分析研究 [J]. 色谱, 1995(5): 395-397. |
| QU F, MOU S F, HOU X P, et al.. Determination of organic acids in wheat-root by lon chromatography [J]. Chin. J. Chromatography, 1995(5): 395-397. | |
| 26 | LAMBERS H, SHANE M W, CRAMER M D, et al.. Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits [J]. Ann. Bot., 2006, 98(4): 693-713. |
| 27 | SHEN J, YUAN L, ZHANG J, et al.. Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant [J]. Plant Physiol., 2011, 156(3): 997-1005. |
| 28 | MANSKE G, ORTIZ-MONASTERIO J, MVAN GINKEL, et al.. Traits associated with improved P-uptake efficiency in CIMMYT’s semidwarf spring bread wheat grown on an acid Andisol in Mexico [J]. Plant Soil, 2000, 221(2): 189-204. |
| 29 | TENG W, DENG Y, CHEN X P, et al.. Characterization of root response to phosphorus supply from morphology to gene analysis in field-grown wheat [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2013, 64(5): 1403-1411. |
| 30 | SHEN Q, WEN Z, DONG Y, et al.. The responses of root morphology and phosphorus-mobilizing exudations in wheat to increasing shoot phosphorus concentration [J/OL]. Aob Plants, 2018, 10(5): ply054 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 31 | LIU D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. |
| 32 | LIU B, LI H, ZHU B, et al.. Complementarity in nutrient foraging strategies of absorptive fine roots and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi across 14 coexisting subtropical tree species [J]. New Phytol., 2015, 208(1): 125-136. |
| 33 | CHEN W, KOIDE R T, ADAMS T S, et al.. Root morphology and mycorrhizal symbioses together shape nutrient foraging strategies of temperate trees [J]. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 2016, 113(31): 8741-8746. |
| 34 | LI H, LIU B, MCCORMACK M L, et al.. Diverse belowground resource strategies underlie plant species coexistence and spatial distribution in three grasslands along a precipitation gradient [J]. New Phytol., 2017, 216(4): 1140-1150. |
| 35 | MA Z, GUO D, XU X, et al.. Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits [J]. Nature, 2018, 555(7694): 94-97. |
| 36 | LAMBERS H, HAYES P E, LALIBERTE E, et al.. Leaf manganese accumulation and phosphorus-acquisition efficiency [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2015, 20(2): 83-90. |
| 37 | WANG Y, LAMBERS H. Root-released organic anions in response to low phosphorus availability: recent progress, challenges and future perspectives [J]. Plant Soil, 2020, 447(1): 135-156. |
| 38 | 刘胜亮, 朱舒亮, 李静, 等. 不同有机酸对磷酸三钙溶解能力的研究 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2017, 39(5): 1010-1016. |
| LIU S L, ZHU S L, LI J, et al.. A study on the ability of different organic acids to dissolve tricalcium phosphate [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2017, 39(5): 1010-1016. | |
| 39 | ROBIN A L, SANKHLA D. Essential Guide to Food Additives. [M]. 4th Ed n. London: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013: 44-64. |
| 40 | YANG P, CHEN H J, FAN H Y, et al.. Phosphorus supply alters the root metabolism of Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. varchinensis. utilis Tsen et Lee) and the mobilization of Cd bound to lepidocrocite in soil [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2019, 167: 103827 [2020-02-20]. . |
| 41 | EDAYILAM N, MONTGOMERY D, FERGUSON B, et al.. Phosphorus stress-induced changes in plant root exudation could potentially facilitate uranium mobilization from stable mineral forms [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52(14): 7652-7662. |
| 42 | MAGDZIAK Z, MLECZEK M, RUTKOWSKI P, et al.. Diversity of low-molecular weight organic acids synthesized by salix growing in soils characterized by different Cu, Pb and Zn concentrations [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2017, 39(6): 1-15. |
| 43 | 刘桂华, 敖明, 柴冠群, 等. 低分子有机酸对贵州黄壤中镉释放及形态的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(6): 1473-1479. |
| LIU G H, AO M, CHAI G Q, et al.. Effects of organic acids with low molecular weight on the extraction and fractionations of cadmium in yellow soil of Guizhou [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2018, 49(6): 1473-1479. | |
| 44 | 胡浩, 潘杰, 曾清如, 等. 低分子有机酸淋溶对土壤中重金属Pb Cd Cu和Zn的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008 (4): 1611-1616. |
| HU H, PAN J, ZENG Q R, et al.. The effects of soil leaching with low molecular weight organic acids on Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2008(4): 1611-1616. | |
| 45 | 魏佳, 李取生, 徐智敏, 等. 多种有机酸对土壤中碳酸镉的活化效应[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(9): 5298-5306. |
| WEI J, LI Q S, XU Z M, et al.. Mobilization effects of various organic acids on cadmium carbonate in soil [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2017, 11(9): 5298-5306. |
| [1] | 黄焰新, 吴香, 曹艳, 闫旭宇, 李玲. 外源钙诱导植物应答镉胁迫的效应及作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 165-171. |
| [2] | 周峻宇, 谷雨, 吴海勇, 李明德, 刘琼峰, 周旋, 董春华. 柠檬酸强化籽粒苋修复镉污染土壤效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 215-223. |
| [3] | 刘一凡, 刘少帅, 臧瑞, 李洋, 刘薇, 李婷婷, 刘旦梅, 刘登才, 李爱丽, 毛龙, 王翔, 耿帅锋. 168份小麦种质资源品质性状分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 44-57. |
| [4] | 吕彩霞, 李永福, 信会男, 李娜, 赖宁, 耿庆龙, 陈署晃. 缓释氮肥对滴灌冬小麦产量及土壤硝/铵态氮的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 179-186. |
| [5] | 朱强, 车宗贤, 崔恒, 张久东, 包兴国. 绿肥替代氮肥对麦田温室气体的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 182-189. |
| [6] | 丁献华, 闫双堆, 闫明. 松木木屑加压烘焙制备高品质生物焦燃料及其特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 204-216. |
| [7] | 胡懿, 公杰, 赵玮, 程蓉, 柳忠玉, 高世庆, 杨亚珍. 小麦PHY基因家族鉴定及热胁迫下表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 30-43. |
| [8] | 呼斯乐, 包玉龙, 图布新巴雅尔null, 陶际峰, 郭恩亮. 基于无人机高光谱和集成学习的春小麦叶绿素含量反演[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 93-103. |
| [9] | 史硕, 冯宇, 李亮, 孟瑞, 章延泽, 杨秀荣. 印度梨形孢介导小麦抗纹枯病的转录组分析及关键基因筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 133-145. |
| [10] | 赵昕, 吴子龙, 韩超, 张浩, 宋炜, 李子怡. 丛枝菌根真菌对镉胁迫下狗尾草生长及镉富集的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 193-202. |
| [11] | 王子豪, 周雪, 张冬寒, 梁红怡, 王岩, 赵子昂, 陈清. 含腐植酸水溶肥料对玉米苗生长及土壤改良的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 209-220. |
| [12] | 马蓓, 公杰, 杜银柯, 甘雨薇, 程蓉, 朱波, 易丽霞, 马锦绣, 高世庆. 小麦花粉孔发育相关TaINP1基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 22-35. |
| [13] | 米春娇, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 张砚迪. 我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标和推荐施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [14] | 薛振宇, 张康康, 张元元, 闫强强, 姚立蓉, 张宏, 孟亚雄, 司二静, 李葆春, 马小乐, 王化俊, 汪军成. 优质抗旱小麦种质的筛选及功能基因检测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 35-49. |
| [15] | 周喜新, 袁世林, 杨柳, 夏滔, 张毅, 范伟. 连作烟草根系分泌物鉴定及潜在化感物质的筛选研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 136-146. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||