




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 205-215.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0282
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Received:2024-04-08
Accepted:2024-09-24
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2025-11-17
Contact:
Qing YANG
通讯作者:
杨清
作者简介:王雅婷 E-mail:18294165867@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yating WANG, Qing YANG. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Coupling Coordination of Cultivated Land “Production-living-ecological ”Space in Upper Reaches of Yellow River ——A Case Study of Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 205-215.
王雅婷, 杨清. 黄河上游耕地“三生”空间耦合协调时空演变特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(11): 205-215.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0282
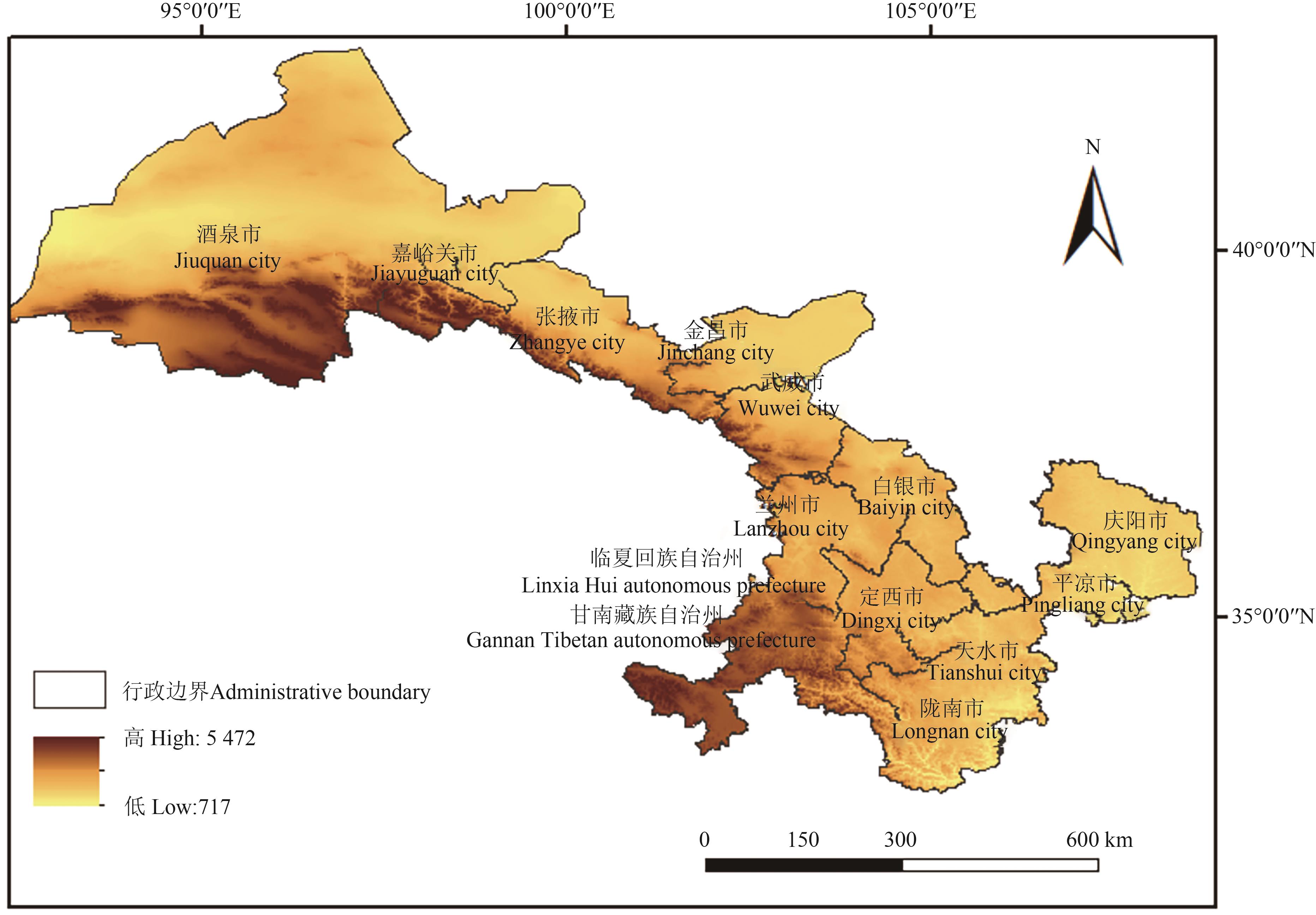
Fig. 1 Administrative divisions and elevation map of Gansu provinceNote:This map is based on the standard map No.GS(2022)1873 downloaded from the National Administrative Division Information Inquiry Platform of the official website of the Ministry of Civil Affairs, PRC. The base map has not been modified.
一级指标 Primary index | 二级指标 Secondary index | 指标说明 Indicator specification | 属性 Attribute | 权重 Weight/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
生产空间 Productin space | 粮食单位面积产量 Grain yield per unit area/(kg·hm | 粮食总产量/粮食作物实际占用耕地面积 Total grain output/atual cultivated land occupied by grain crops | + | 6.943 6 |
耕地地均产值/(万元·hm Average output value of cultivated land/(104 yuan·hm | 农业总产值/耕地总面积 Total agricultural output value/total cultivated area | + | 8.572 9 | |
耕地种植指数 Cultivated land planting index/% | 年播种面积/耕地总面积 Annual sown area/total cultivated area | + | 9.339 7 | |
土地开垦率 Land reclamation rate/% | 耕地总面积/土地总面积 Total cultivated area/total land area | + | 6.708 8 | |
生活空间 Living space | 人均粮食保有量/(kg·人 Grain stock per capita/(kg·person | 粮食总产量/(总人口×400) Total grain production/(total population ×400) | + | 8.304 6 |
家庭农业收入占比 Share of household farm income/% | 家庭人均农业收入/农业人均可支配收入 Household per capita agricultural income/agricultural per capita disposable income | + | 25.694 8 | |
人均农业机械化水平/(kW·人 Agricultural mechanization level per capita/(kW·person | 农业机械总动力/总人口 Total power of agricultural machinery/total population | - | 6.593 8 | |
耕地地劳比/(hm2·人 Labor ratio of cultivated land/(hm2·person | 耕地总面积/总人口 Total cultivated area/total population | + | 4.691 4 | |
生态空间 Ecological space | 农田生态系统多样性 Farmland ecosystem diversity/% | + | 4.672 2 | |
耕地占生态用地比重 Proportion of cultivated land in ecological land use/% | 耕地总面积/(土地总面积-建设用地面积) Total cultivated area/(total land area-construction land area) | + | 6.450 1 | |
耕地利用化学负荷 Chemical load of cultivated land use/(kg·hm | 1/2×(化肥施用量+农用地膜覆盖量)/耕地总面积 1/2×(fertilizer application amount + agricultural mulch cover amount)/total cultivated area | - | 5.185 0 | |
耕地开发强度 Cultivated land development intensity/% | 建设用地面积/耕地总面积 Construction land area/total cultivated area | - | 6.843 0 |
Table 1 Index system of comprehensive evaluation of cultivated land “production-living-ecological”space
一级指标 Primary index | 二级指标 Secondary index | 指标说明 Indicator specification | 属性 Attribute | 权重 Weight/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
生产空间 Productin space | 粮食单位面积产量 Grain yield per unit area/(kg·hm | 粮食总产量/粮食作物实际占用耕地面积 Total grain output/atual cultivated land occupied by grain crops | + | 6.943 6 |
耕地地均产值/(万元·hm Average output value of cultivated land/(104 yuan·hm | 农业总产值/耕地总面积 Total agricultural output value/total cultivated area | + | 8.572 9 | |
耕地种植指数 Cultivated land planting index/% | 年播种面积/耕地总面积 Annual sown area/total cultivated area | + | 9.339 7 | |
土地开垦率 Land reclamation rate/% | 耕地总面积/土地总面积 Total cultivated area/total land area | + | 6.708 8 | |
生活空间 Living space | 人均粮食保有量/(kg·人 Grain stock per capita/(kg·person | 粮食总产量/(总人口×400) Total grain production/(total population ×400) | + | 8.304 6 |
家庭农业收入占比 Share of household farm income/% | 家庭人均农业收入/农业人均可支配收入 Household per capita agricultural income/agricultural per capita disposable income | + | 25.694 8 | |
人均农业机械化水平/(kW·人 Agricultural mechanization level per capita/(kW·person | 农业机械总动力/总人口 Total power of agricultural machinery/total population | - | 6.593 8 | |
耕地地劳比/(hm2·人 Labor ratio of cultivated land/(hm2·person | 耕地总面积/总人口 Total cultivated area/total population | + | 4.691 4 | |
生态空间 Ecological space | 农田生态系统多样性 Farmland ecosystem diversity/% | + | 4.672 2 | |
耕地占生态用地比重 Proportion of cultivated land in ecological land use/% | 耕地总面积/(土地总面积-建设用地面积) Total cultivated area/(total land area-construction land area) | + | 6.450 1 | |
耕地利用化学负荷 Chemical load of cultivated land use/(kg·hm | 1/2×(化肥施用量+农用地膜覆盖量)/耕地总面积 1/2×(fertilizer application amount + agricultural mulch cover amount)/total cultivated area | - | 5.185 0 | |
耕地开发强度 Cultivated land development intensity/% | 建设用地面积/耕地总面积 Construction land area/total cultivated area | - | 6.843 0 |
耦合阶段 Coupling phase | 协调水平 Coordination level | 范围 Range |
|---|---|---|
高水平耦合阶段 High level coupling stage | 优质协调 High quality coordination | 0.8≤D≤1 |
磨合阶段 Run-in stage | 中度协调Moderate coordination 初级协调 Primary coordination 濒临失调 Borderline dysregulation | 0.7≤D<0.8 0.6≤D<0.7 0.5≤D<0.6 |
拮抗阶段 Antagonistic stage | 初级失调 Primary dysregulation | 0.3≤D<0.5 |
低水平耦合阶段 Low level coupling stage | 中度失调 Moderate dysregulation | D<0.3 |
Table 2 Division standard of coupling coordination degree of cultivated land “production-living-ecological”space
耦合阶段 Coupling phase | 协调水平 Coordination level | 范围 Range |
|---|---|---|
高水平耦合阶段 High level coupling stage | 优质协调 High quality coordination | 0.8≤D≤1 |
磨合阶段 Run-in stage | 中度协调Moderate coordination 初级协调 Primary coordination 濒临失调 Borderline dysregulation | 0.7≤D<0.8 0.6≤D<0.7 0.5≤D<0.6 |
拮抗阶段 Antagonistic stage | 初级失调 Primary dysregulation | 0.3≤D<0.5 |
低水平耦合阶段 Low level coupling stage | 中度失调 Moderate dysregulation | D<0.3 |
年份 Year | C:耦合度 Coupling degree | D:耦合协调度 Coupling coordination degree | 协调水平 Coordination level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 0.984 3 | 0.800 2 | 优质协调High quality coordination |
| 2014 | 0.993 5 | 0.794 0 | 中度协调Moderate coordination |
| 2015 | 0.787 8 | 0.534 6 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2016 | 0.849 0 | 0.593 5 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2017 | 0.870 6 | 0.567 0 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2018 | 0.860 9 | 0.591 6 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2019 | 0.827 4 | 0.610 1 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
| 2020 | 0.957 6 | 0.610 7 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
| 2021 | 0.940 1 | 0.645 2 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
| 2022 | 0.911 6 | 0.663 8 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
Table 3 Spatial coupling coordination level of cultivated land “production-living-ecological”space
年份 Year | C:耦合度 Coupling degree | D:耦合协调度 Coupling coordination degree | 协调水平 Coordination level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 0.984 3 | 0.800 2 | 优质协调High quality coordination |
| 2014 | 0.993 5 | 0.794 0 | 中度协调Moderate coordination |
| 2015 | 0.787 8 | 0.534 6 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2016 | 0.849 0 | 0.593 5 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2017 | 0.870 6 | 0.567 0 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2018 | 0.860 9 | 0.591 6 | 濒临失调Borderline dysregulation |
| 2019 | 0.827 4 | 0.610 1 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
| 2020 | 0.957 6 | 0.610 7 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
| 2021 | 0.940 1 | 0.645 2 | 初级协调Primary coordination |
| 2022 | 0.911 6 | 0.663 8 | 初级协调Primary coordination |

Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of coupling coordination degree of cultivated land “production-living-ecological” space of Gansu provinceNote:This map is based on the standard map No.GS(2022)1873 downloaded from the National Administrative Division Information Inquiry Platform of the official website of the Ministry of Civil Affairs, PRC. The base map has not been modified.
| [1] | 中共中央 国务院关于建立国土空间规划体系并监督实施的若干意见[EB/OL].(2019-05-23)[2024-03-06]. . |
| [2] | 许伟. “三生空间”的内涵、关系及其优化路径[J].东岳论丛, 2022,43(5):126-134. |
| [3] | 江曼琦,刘勇. “三生”空间内涵与空间范围的辨析[J].城市发展研究, 2020, 27(4): 43-48, 61. |
| JIANG M Q, LIU Y. Discussion on the concept definition and spatial boundary classification of “production-living-ecological” space [J]. Urban Dev. Stud., 2020, 27(4): 43-48, 61. | |
| [4] | 鲁达非,江曼琦.中国城市“三生”空间高质量建设目标内涵解析[J].河北学刊,2024,44(3):147-156. |
| LU D F, JIANG M Q. Analysis on the connotation of the objectives under high-quality construction of “production-living-ecological” space in Chinese cities [J]. Hebei Acad. J., 2024, 44(3): 147-156. | |
| [5] | 董雅文,周雯,周岚,等.城市化地区生态防护研究——以江苏省、南京市为例[J].城市研究, 1999(2): 6-8, 10. |
| [6] | 邓红兵,陈春娣,刘昕,等.区域生态用地的概念及分类[J].生态学报,2009,29(3):1519-1524. |
| DENG H B, CHEN C D, LIU X, et al.. Conception and function classification of regional ecological land [J].Acta Ecol. Sin.,2009, 29(3):1519-1524. | |
| [7] | 李文娅,何勇,李聪聪,等.基于核心-边缘的重庆国土“三生”空间时空格局演变[J].智能城市,2023,9(9):48-51. |
| LI W Y, HE Y, LI C C, et al..The “production-living-ecologica” space of Chongqing’s land based on core edge evolution of spatiotemporal pattern [J]. Intelligent City, 2023,9(9): 48-51. | |
| [8] | 宋小青,欧阳竹.耕地多功能内涵及其对耕地保护的启示[J].地理科学进展,2012,31(7):859-868. |
| SONG X Q, OUYANG Z. Connotation of multifunctional cultivated land and its implications for cultivated land protection [J]. Progress Geogr., 2012,31(7):859-868. | |
| [9] | 邹永偲,兰安军,范泽孟,等. “三生空间”视角下贵州省景观生态安全评价及其耦合特征分析[J].水土保持研究,2024,31(3):432-442. |
| ZOU Y C, LAN A J, FAN Z M, et al.. Evaluation of landscape ecologica security and its coupling characteristics analysis in Guizhou province from the perspective of production-living-ecology space [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2024, 31(3):432-442. | |
| [10] | 杨健.基于“三生空间”的宁波市土地利用结构分析[J].测绘与空间地理信息,2023,46(10):203-206. |
| YANG J. Analysis of land use structure in Ningbo city based on“Sansheng Space” [J]. Geomatics Spatial Inform. Technol., 2023, 46(10): 203-206. | |
| [11] | 朱庆莹,陈银蓉,胡伟艳,等.中国土地集约利用与区域生态效率耦合协调度时空格局[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(4):234-243. |
| ZHU Q Y, CHEN Y R, HU W Y,et al..Spatiotemporal pattern of coupling coordination degree between land intensive use and regional ecological efficiency in China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc.Agric. Eng., 2020, 36(4):234-243. | |
| [12] | 王欣然. “三生空间”背景下全域土地综合整治路径研究——以金寨县面冲村为例[C]//中国城市规划学会.人民城市,规划赋能——2022中国城市规划年会论文集(16乡村规划).安徽建筑大学,2023: 9. |
| [13] | 陈正发,史东梅,何伟,等. 1980—2015年云南坡耕地资源时空分布及演变特征分析[J].农业工程学报,2019,35(15):256-265. |
| CHEN Z F, SHI D M, HE W, et al..Spatio-temporal distribution and evolution characteristics of slope farmland resources in Yunnan from 1980 to 2015 [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2019, 35(15): 256-265. | |
| [14] | 张宇佳,蔡海生,张学玲,等.鄱阳湖平原耕地多功能时空演变及其驱动机制[J].水土保持通报,2023,43(3):245-253. |
| ZHANG Y J, CAI H S, ZHANG X L,et al..Multi-functional spatiotemporal evolution of cultivated land and its driving mechanisms in Poyang Lake Plain [J].Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2023, 43(3): 245-253. | |
| [15] | 冯瑛. 基于“三生空间”的玉州区国土空间优化方法探索[J].城市建设理论研究(电子版),2023(25):7-11. |
| [16] | 邹利林,李裕瑞,刘彦随,等. 基于要素视角的耕地“三生”功能理论建构与实证研究[J].地理研究,2021,40(3):839-855. |
| ZOU L L, LI Y R, LIU Y S, et al.. Theory building and empirical research of production-living-ecological function of cultivated land based on the elements [J].Geogr. Res., 2021,40(3):839-855. | |
| [17] | 刘俊祥,张蕾,刘格格,等. 湖北省国土空间“三生”功能权衡特征及影响因素分析[J].水土保持研究,2024,31(2):354‒366, 378. |
| LIU J X, ZHANG L, LIU G G, et al.. Analysis of the trade-off pattern and influencing factors among production-living-ecological functions of territorial space in Hubei province [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2024, 31(2):354-366. | |
| [18] | 罗莎莎,赖庆标,王旭东,等.基于多功能评价与权衡-协同关系的福建省耕地区划管控[J].农业工程学报,2023,39(13):271-280. |
| LUO S S, LAI Q B, WANG X D, et al.. Control and management of cropland regionalization in Fujian province of China using multi-functional evaluation and trade-off-synergy relationships [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2023, 39(13):271-280. | |
| [19] | 李凯迪,袁琳,胡晓,等.京津冀地区三生用地时空格局变化及其生态环境效应[J].生态科学,2023,42(5):94-102. |
| LI K D, YUAN L, HU X, et al..Spatiotemporal dynamics of production-living-ecological land and its impact on the environment in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region [J].Ecol. Sci.,2023, 42(5):94-102. | |
| [20] | 熊昌盛,张永蕾,王雅娟,等.中国耕地多功能评价及分区管控[J].中国土地科学,2021,35(10):104-114. |
| XIONG C S, ZHANG Y L, WANG Y J, et al..Multi-function evaluation and zoning control of cultivated land in China [J].China Land Sci., 2021, 35(10):104-114. | |
| [21] | 高鹏飞,杨朝现,信桂新,等. 三峡库区重庆段国土空间“三生”功能时空演变特征及格局优化[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2023, 39(9):1103-1113. |
| GAO P F, YANG C X, XIN G X, et al.. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and pattern optimization of production-living-ecological functions of territorial space in Chongqing section of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2023, 39(9): 1103-1113. | |
| [22] | 党慧,荣丽华,李伊彤,等.农牧交错区三生空间时空演变特征与影响因素——以内蒙古呼和浩特市为例[J].干旱区研究,2023, 40(10):1698-1706. |
| DANG H, RONG L H, LI Y T, et al.. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of production-living-ecological spaces in the farming-pastoral ecotone: taking Hohhot of Inner Mongolia as an example [J].Arid Zone Res., 2023, 40(10):1698-1706. | |
| [23] | 尹琴,黄娟,陈亚颦,等.西南地区“三生”空间功能耦合协调发展水平及时空分异特征[J].乐山师范学院学报,2023, 38(4):107-115. |
| YIN Q, HUANG J, CHEN Y P, et al.. On the coordinated development and space-time difference of PLES function coupling in southwest China [J]. J. Leshan Normal Univ., 2023, 38(4):107-115. | |
| [24] | 宋小青,吴志峰,欧阳竹.1949年以来中国耕地功能变化[J].地理学报,2014,69(4):435-447. |
| SONG X Q, WU Z F, OUYANG Z. Changes of cultivated land function in China since 1949 [J]. Acta Geogr. Sin.,2014, 69(4):435-447. | |
| [25] | 孙新章.新中国60年来农业多功能性演变的研究[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2010,20(1):71-75. |
| SUN X Z.Evolution of agricultural multifuncfionality since 1949 [J].China Popul. Resour. Environ.,2010, 20(1):71-75. | |
| [26] | WIGGERING H, DALCHOW C, GLEMNITZ M. Indicators for multifunctional land use Linking socioeconomic requirements with landscape potentials [J]. Ecol. Indicators, 2006, 6(1):238-249. |
| [27] | 张玥,代亚强,陈媛媛,等.中国耕地多功能耦合协调时空演变及驱动因素[J].农业工程学报,2023, 39(7):244-255. |
| ZHANG Y, DAI Y Q, CHEN Y Y, et al.. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of cultivated landmultifunctional coupling coordination development in China [J].Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2023, 39(7):244-255. | |
| [28] | 努尔比耶·奥布力艾散, 阿依吐尔逊·沙木西, 艾则买提江·麦麦提图尔荪.和田地区耕地时空演变的生产-生态效应研究[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2024, 41(1):36-48. |
| Ubulhasan Nurbiya, Xamxi Aytursun, Mamattursun Azimatjan. Spatiotemporal evolution of cultivated land production-ecological effects in Hotan Region [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2024, 41(1):36-48. | |
| [29] | 王成,彭清,唐宁,等. 2005—2015年耕地多功能时空演变及其协同与权衡研究:以重庆市沙坪坝区为例[J].地理科学,2018,38(4):590-599. |
| WANG C, PENG Q, TANG N, et al.. Spatio-temporal evolution and the synergy and trade-off relationship of cultivated land multi-function in 2005—2015:a case of Shapingba district,Chongqing city [J]. Sci. Geogr. Sin., 2018, 38(4):590-599. | |
| [30] | 甘肃省统计局, 国家统计局甘肃调查总队.甘肃发展年鉴(2014—2023)[R]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2023. |
| [31] | 甘肃农村年鉴编委会.甘肃农村年鉴(2014—2023)[R].北京:中国统计出版社,2023. |
| [32] | 姜广辉,张凤荣,孔祥斌,等.耕地多功能的层次性及其多功能保护[J].中国土地科学,2011,25(8):42-47. |
| JIANG G H, ZHANG F R, KONG X B, et al.. The different levels and the protection of multi-functions of cultivated land [J].China Land Sci., 2011, 25(8):42-47. |
| [1] | Shuting XIAO, An YAN. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon in Typical Natural Forests in Tianshan Mountains [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 227-238. |
| [2] | Jiajia SONG, Yunxia MA, Jingjie GUO, Baomengkenashun, Zhonghou GU, Kun LIU, Zhilong LI, Shengli HAN, Xia KANG, Rewadi. Spatial Pattern and Interspecific Association of Natural Platycladus orientalis Population in Loess Hilly Region of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 203-212. |
| [3] | Xiaohu YANG, Manyu ZHANG, Haichang YANG, Fenghua ZHANG, Yilin JIANG, Xiaolan YI. Inversion of Soil Salinity in Farmland of Manas River Basin Based on Combined Model [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 134-141. |
| [4] | LI Shuang, ZHANG Wei, WANG Li, LI Xiaojun, CUI Juntao. Effect of Straw Returning on Fertility and Stem Rot of Black Soil with Different Land Fertility [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 80-90. |
| [5] | LIU Xinghong, ZHANG Qingqing, ZHANG Guangpeng, LI Hong . Analysis of Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Plant Communities in the Lower Reaches of Tarim River [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(10): 131-144. |
| [6] | GAO Suhong1,2, WU Haiyan2, WEN Xiaolei2, LU Changkuan2, ZHAO Chunming2, ZHANG Qi2, DING Yuanyuan2. Spatial Distribution and Sampling Technique of the Overwintering Eggs of Apolygus lucorum in the Vineyard [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(8): 116-122. |
| [7] | XU Peng1, XU Weicheng2, LUO Yangfan2, ZHAO Zuoxi2*. Precise Classification of Cultivated Land Based on Visible Remote Sensing Image of UAV [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(6): 79-86. |
| [8] | FENG Xueying1, ZHANG Yibo2, HUANG Yucui1, GUO Mengran1, MENG Ye1, ZHANG Xiaoming3, XU Haiyun1*. Population Dynamics and Spatial Distribution of Bemisia tabaci in Xiongan New Area and Its Surrounding Areas [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(10): 115-124. |
| [9] | ZOU Mengmeng1, ZHOU Weihong1,2, ZHANG Jingjing1, LIU Ying1, . Heavy Metal Pollution of Cultivated Soil in Eastern China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(1): 117-124. |
| [10] | ZHAO Yingming1,2,3, LEI Yuancai4, YANG Wenbin1*, HAO Yuguang2,3, HUANG Yaru2,3, DONG Xue2,3, MA Yingbin2,3, LIU Yuting2,3. Spatial Distribution of Main Root Biomass of Farmland Shelterbelt [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(9): 86-94. |
| [11] | QIAN Guixia1, XIAO Min2, ZHAO Wenzhe1, ZHANG Qifeng1, PAN Yuehong3*. Spatial Distribution Change and Operation Status of Milk Collection Stations at Postcrisis Era ——A Case Study of Inner Mongolia [J]. , 2013, 15(4): 102-109. |
| [12] | YANG Li-ping1, GUO Hong-hai1, LI Xin-hua1, YANG Ping1, WAN Shu-bo2. Preliminary Studies on Spatial Distribution Prediction of Peanut Protein Content in China [J]. , 2010, 12(5): 92-97. |
| [13] | LIU Yu, MEN Ming-xin, XU Hao, LIU Shu-qing . Study on Calculation and Application of the Integrated Productive Capacity of Cultivated Land |——A Case Study of Bazhou City [J]. , 2008, 10(1): 87-92. |
| [14] | GUO Ya-jun,YAO Shun-bo, LI Hua . The analysis of the effect of the policy about returning forest from cultivated land on the comprehensive production of agriculture in wuqi county [J]. , 2007, 9(2): 116-120. |
| [15] | WANG Yue-xing . Study on Rational Utilization of Unused Cultivated Land [J]. , 2006, 8(6): 81-83. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号 