




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 189-201.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0119
收稿日期:2021-02-01
接受日期:2021-04-15
出版日期:2022-05-15
发布日期:2022-06-06
通讯作者:
张智猛
作者简介:戴良香 E-mail:liangxiangd@163.com;
基金资助:
Liangxiang DAI( ), Guanchu ZHANG, Hong DING, Yang XU, Zhimeng ZHANG(
), Guanchu ZHANG, Hong DING, Yang XU, Zhimeng ZHANG( )
)
Received:2021-02-01
Accepted:2021-04-15
Online:2022-05-15
Published:2022-06-06
Contact:
Zhimeng ZHANG
摘要:
为研究有机肥和钙肥对盐碱地花生根际微生物群落结构和功能的影响,以不施肥为对照(CK)、设置施用钙肥(C)、有机肥(M)和有机肥+钙肥(CM)处理,通过构建细菌16S rRNA基因文库和高通量测序技术对不同处理下花生根际微生物进行测序。结果表明,施用有机肥、钙肥和有机肥钙肥配施均显著影响较轻度盐碱土壤花生根际微生物的多样性和丰富度,而对较重度盐碱土花生根际细菌的多样性和丰富度无显著影响。PCoA分析表明,样本OTUs多样性与土壤盐碱程度关系密切,施用钙肥处理花生根际微生物的菌群结构与其他处理间存在较大差异。两种滨海盐碱土花生根际微生物的种群结构均受施用有机肥、钙肥及其配施的影响,不同处理根际微生物均具有相同的优势菌群,但各优势菌群的相对丰度存在较大差异。在目和科水平上,有占总细菌76.3%~82.5%的新种OTUs未能注释,说明黄河三角洲滨海盐碱土花生根际蕴含大量微生物新种资源。16S rRNA功能预测分析表明,施用钙肥和有机肥处理均可显著提高2种土壤花生根际微生物碳水化合物代谢、氨基酸代谢、能量代谢、辅助因子和维生素的代谢、核苷酸代谢、翻译和膜运输等相关功能基因丰度。由此可见,施用钙肥和有机肥有利于改良盐碱土壤根际微生态环境,提高植物胁迫耐受性。
中图分类号:
戴良香, 张冠初, 丁红, 徐扬, 张智猛. 有机肥和钙肥对盐碱土花生根际细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 189-201.
Liangxiang DAI, Guanchu ZHANG, Hong DING, Yang XU, Zhimeng ZHANG. Effects of Organic Fertilizer and Calcium Fertilizer on Peanut Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Structure in Saline-alkali Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 189-201.
采样地点 Sampling site | 含盐量 Salt content/(g·kg-1) | 有机质含量 Organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potasium/ (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
利津毛坨 Maotuo of Lijin County | 5.17 | 6.45 | 0.612 | 54.35 | 9.82 | 115.17 | 8.6 |
垦利青坨 Qingtuo of Kenli County | 3.91 | 11.40 | 0.892 | 69.06 | 14.08 | 89.76 | 8.4 |
表1 供试土壤样品的理化性状
Table 1 Characteristics of soil samples for test
采样地点 Sampling site | 含盐量 Salt content/(g·kg-1) | 有机质含量 Organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potasium/ (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
利津毛坨 Maotuo of Lijin County | 5.17 | 6.45 | 0.612 | 54.35 | 9.82 | 115.17 | 8.6 |
垦利青坨 Qingtuo of Kenli County | 3.91 | 11.40 | 0.892 | 69.06 | 14.08 | 89.76 | 8.4 |
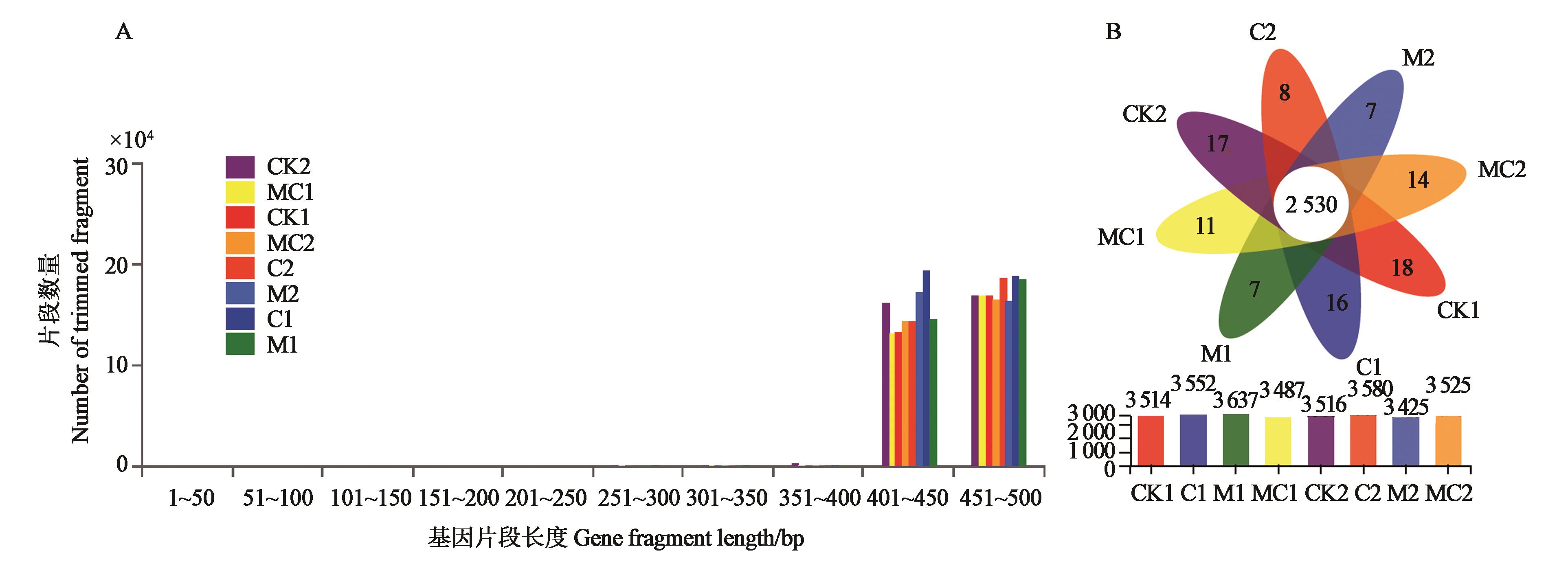
图1 花生根际土壤微生物群落测序数据A:序列长度分布;B: OTU数量维恩图
Fig. 1 Overall sequence data of bacterial communities in the peanut rhizosphereA: Length distribution of trimmed sequences; B: Venn diagram of OTUs
处理 Treatment | 丰富度 Community richness | 多样性 Community diversity | 覆盖度 Coverage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sobs | Chao | Ace | Shannon | Simpson | ||
| CK1 | 3 216.5 | 3 508.856 | 3 459.115 | 7.253 0 | 0.001 34 | 0.991 11 |
| C1 | 3 271.0 | 3 513.107 | 3 453.484 | 6.792 7 | 0.005 44 | 0.995 60 |
| M1 | 3 400.5 | 3 626.337 | 3 578.135 | 7.247 3 | 0.001 50 | 0.993 79 |
| MC1 | 3 211.5 | 3 484.869 | 3 442.857 | 7.171 5 | 0.001 62 | 0.991 75 |
| CK2 | 3 142.5 | 3 466.744 | 3 414.230 | 7.120 0 | 0.001 84 | 0.989 75 |
| C2 | 3 292.0 | 3 585.756 | 3 524.607 | 6.996 1 | 0.003 06 | 0.993 03 |
| M2 | 3 163.5 | 3 405.369 | 3 350.942 | 6.822 0 | 0.003 65 | 0.995 00 |
| MC2 | 3 227.5 | 3 497.223 | 3 448.287 | 6.745 6 | 0.006 47 | 0.993 16 |
表2 不同处理下根际土壤微生物的Alpha多样性指数
Table 2 Alpha diversity index of rhizosphere soil samples in each treatment
处理 Treatment | 丰富度 Community richness | 多样性 Community diversity | 覆盖度 Coverage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sobs | Chao | Ace | Shannon | Simpson | ||
| CK1 | 3 216.5 | 3 508.856 | 3 459.115 | 7.253 0 | 0.001 34 | 0.991 11 |
| C1 | 3 271.0 | 3 513.107 | 3 453.484 | 6.792 7 | 0.005 44 | 0.995 60 |
| M1 | 3 400.5 | 3 626.337 | 3 578.135 | 7.247 3 | 0.001 50 | 0.993 79 |
| MC1 | 3 211.5 | 3 484.869 | 3 442.857 | 7.171 5 | 0.001 62 | 0.991 75 |
| CK2 | 3 142.5 | 3 466.744 | 3 414.230 | 7.120 0 | 0.001 84 | 0.989 75 |
| C2 | 3 292.0 | 3 585.756 | 3 524.607 | 6.996 1 | 0.003 06 | 0.993 03 |
| M2 | 3 163.5 | 3 405.369 | 3 350.942 | 6.822 0 | 0.003 65 | 0.995 00 |
| MC2 | 3 227.5 | 3 497.223 | 3 448.287 | 6.745 6 | 0.006 47 | 0.993 16 |

图2 不同处理花生根际土壤微生物的多样性指数注:*和**分别表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 2 Diversity index of rhizosphere soil microorganism in different treatmentsNote: * and ** indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 贾敬敦,张富.依靠科技创新推进我国盐碱地资源可持续利用[J].中国农业科技导报,2014,16(5):1-7. |
| JIA J D, ZHANG F. Sustainable utilization of saline-alkali land resources through scientific and technological innovation in China [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2014, 16(5):1-7. | |
| 2 | 张智猛,慈敦伟,丁红,等.花生品种耐盐性指标筛选与综合评价[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(12):3487-3494. |
| ZHANG Z M, CI D W, DING H, et al.. Indices selection and comprehensive evaluation of salinity tolerance for peanut varieties [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2013, 24(12):3487-3494. | |
| 3 | 慈敦伟,张智猛,丁红,等.花生苗期耐盐性评价及耐盐指标筛选[J].生态学报,2015,35(3):805-814. |
| CI D W, ZHANG Z M, DING H,et al..Evaluation and selection indices of salinity tolerance in peanut seedling [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2015, 35(3):805-814. | |
| 4 | 张旭龙,马淼,吴振振,等.不同油葵品种对盐碱地根际土壤酶活性及微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J].生态学报,2017, 37(5):1659-1666. |
| ZHANG X L, MA M, WU Z Z, et al..Effects of Helianthus annuus varieties on rhizosphere soil enzyme activities and microbial community functional diversity of saline-alkali land in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(5):1659-1666. | |
| 5 | ZHANG Q, YU X. Allelopathy in replant problem in forest soil [J]. Allelopathy J., 2001, 8:51-64. |
| 6 | KUZYAKOV Y, RAZAVI B S. Rhizosphere size and shape: temporal dynamics and spatial stationarity [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2019, 135:343-360. |
| 7 | CORREA-GALEOTE D, BEDMAR E J, FERNÁNDEZ-GONZÁLEZ A J, et al.. Bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of amilaceous maize (Zea mays L.) as assessed by pyrosequencing [J/OL]. Frontiers Plant Sci., 2016, 7:1016 [2020-12-20]. . |
| 8 | SINGH A, SARMA B K, UPADHYAY R S, et al.. Compatible rhizosphere microbes mediated alleviation of biotic stress in chickpea through enhanced antioxidant and phenylpropanoid activities [J]. Microbiol. Res., 2013, 168(1):33-40. |
| 9 | HAW-KINS H J, LEW IS O A M. Effect of NaCl salinity, nitrogen form, calcium and potassium concentration on nitrogen uptake and kinetics in Triticum aestivum L. cv. gamtoos [J]. New Phytol., 1993,124:171-177. |
| 10 | CAINES A M, SHENNAN C. Interactive effects of Ca2+ and NaCl salinity on the growth of two tomato genotypes differing in Ca2+ use efficiency [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 1999, 37:569-576. |
| 11 | 李银鹏,林鹏.盐度对木榄幼苗某些金属元素累积的影响及钙的效应[J].应用生态学报,2000,11(2):177-180. |
| LI Y P, LIN P. Impact of salinity on accumulation of several metal elements in Bruguiera gymnorrhiza seedlings and Ca effect [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2000, 11(2):177-180. | |
| 12 | EHRHARDT D W, WAIS R, LONG S R. Calcium spiking in plant root hairs responding to Rhizobium nodulation signals [J]. Cell, 1996, 85:673-681. |
| 13 | CHIEN C T, SHETTY K, MORTIMER M, et al.. Calcium-induced salt tolerance in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovarviciae strain C124b [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1991, 83:219-224. |
| 14 | 孟磊,丁维新,蔡祖聪.长期定量施肥对土壤有机碳储量和土壤呼吸影响[J].地球科学进展,2005,20(6):687-692. |
| MENG L, DING W X, CAI Z C, et al.. Storage of soil organic C and soil respirationas effected by long-term quantitative fertilization [J]. Adv. Earth Sci., 2005, 20(6):687-692. | |
| 15 | WANG X L, REN Y Y, ZHANG S Q, et al.. Applications of organic manure increased maize (Zea mays L.) yield and water productivity in a semi-arid region [J]. Agric. Water Manage., 2017, 187:88-98. |
| 16 | 孙薇,钱勋,付青霞,等.生物有机肥对秦巴山区核桃园土壤微生物群落和酶活性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(5):1224-1233. |
| SUN W, QIAN X, FU Q X, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil microbial community and enzymes activities in walnut orchards of the Qinling-Bashan Region [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2013, 19(5):1224-1233. | |
| 17 | 范丙全.我国生物肥料研究与应用进展[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(6):1602-1613. |
| FAN B Q. Advances in biofertilizer research and development in China [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2017, 23(6):1602-1613. | |
| 18 | LIU B, TU C, HU S, et al.. Effect of organic, sustainable, and conventional management strategies in grower fields on soil physical, chemical, and biological factors and the incidence of southern blight [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2007, 37(3):202-214. |
| 19 | WEI S, TETSUO T, LIU S K. Isolation and characterization of an alkaliphilic and halotolerant Nesterenkonia. sp from an extreme soda saline-alkali soil in the northeastern of China [J]. Mol. Soil Biol., 2011, 64(11):914-920. |
| 20 | CUI C, MA L, SHI J, et al.. Metabolic pathway for degradation of nthracene by halophilic Martelella sp. AD-3 [J]. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2014, 89(2):67-73. |
| 21 | 李凤霞,郭永忠,许兴.盐碱地土壤微生物生态特征研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2011,39(23):14065-14067, 14174. |
| LI F X, GUO Y Z, XU X. Research progress of the microbial characteristics of saline-alkali soil [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2011, 39(23):14065-14067, 14174. | |
| 22 | 李瀚,杨吉顺,张冠初,等.花生品种萌发期耐盐性比较鉴定[J].花生学报,2015,44(4):48-52. |
| LI H, YANG J S, ZHANG G C, et al.. Identification of salt tolerancein germination period of peanut varieties [J]. J. Peant Sci., 2015, 44(4):48-52. | |
| 23 | 慈敦伟,戴良香,宋文武,等.花生萌发至苗期耐盐胁迫的基因型差异[J].植物生态学报,2013, 37(11):1018-1027. |
| CI D W, DAI L X, SONG W W, et al.. Genotypic differences in salt tolerance from germination to seedling stage in peanut [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2013, 37(11):1018-1027. | |
| 24 | 温赛群.苗期花生品种耐盐性鉴定及生理生化评价[D].河北保定:河北农业大学,2019. |
| WEN S Q. Identification of salt tolerance of peanut germplasm and physiological evaluation [D]. Hebei Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 25 | 田家明,张智猛,戴良香,等.外源钙对盐碱土与非盐碱土花生生长发育与光合特性的影响[J].华北农学报,2018,33(6):130-136. |
| TIAN J M, ZHANG Z M, DAI L X, et al.. Effects of exogenous calcium on the development and photosynthetic characteristics of peanut in saline-alkali soil and normal soil [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2018, 33(6):130 -136. | |
| 26 | 张冠初,史晓龙,慈敦伟,等.干旱和盐胁迫对花生干物质积累及光合特性的影响[J].核农学报,2019,33(5):999-1005. |
| ZHANG G C, SHI X L, CI D W, et al.. Effect of drought and salt stress on accumulation of plant dry weight and photosynthetic characteristics [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2019, 33(5):999-1005. | |
| 27 | 张冠初,张智猛,慈敦伟,等.干旱和盐胁迫对花生渗透调节和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].华北农学报,2018,33(3):176-181. |
| ZHANG G C, ZHANG Z M, CI D W, et al.. Effects of drought and salt stress on osmotic regulator and antioxidase activities [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2018, 33(3):176-181. | |
| 28 | 史晓龙,张智猛,戴良香,等.外源施钙对盐胁迫下花生营养元素吸收与分配的影响[J].应用生态报,2018,29(10):3302-3310. |
| SHI X L, ZHANG Z M, DAI L X, et al.. Effects of calcium fertilizer application on absorption and distribution of nutrients in peanut under salt stress [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2018, 29(10):3302-3310. | |
| 29 | DAI L X, ZHANG G C, YU Z P, et al.. Effect of drought stress and developmental stages on microbial community structure and diversity in peanut rhizosphere soil [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20(9):2265 [2020-12-20]. . |
| 30 | 孙波,赵其国,张桃林,等.土壤质量与持续环境 Ⅲ:土壤质量评价的生物学指标[J].土壤,1997,29(5):225-234. |
| SUN B, ZHAO Q G, ZANG T L, et al.. Soil quality and sustainable environment Ⅲ: biological indicators of soil quality evaluation [J]. Soils, 1997, 29(5):225-234. | |
| 31 | STENBERG B. Monitoring soil quality of arable land: microbiological indicators [J]. Acta Agric. Scandinavica, 1999, 49(1):1-24. |
| 32 | WINDING A, HUND-RINKE K, RUTGERS M. The use of microorganisms in ecological soil classification and assessment concepts [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 2005, 62(2):230-248. |
| 33 | 张瑜斌,林鹏,魏小勇,等.盐度对稀释平板法研究红树林区土壤微生物数量的影响[J].生态学报,2008,28:1288-1296. |
| ZHANG Y B, LIN P, WEI X Y, et al.. Effect of salinity on microbial densities of soil in the dilution plate technique applied in mangrove areas [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2008, 28:1288-1296. | |
| 34 | KHAN K S, GATTINGER A, BUEGGER F, et al.. Microbial use of organic amendments in saline soils monitored by changes in the 13C/12C ratio [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2008, 40(5):1217-1224. |
| 35 | 乔正良,来航线,强郁荣,等.陕西主要盐碱土中微生物生态初步研究[J].西北农业学报,2006,15(3):60-64. |
| QIAO Z L, LAI H X, QIANG Y R, et al.. Primary study on microorganism ecology in saline-alkali soil of Shaanxi Province [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2006, 15(3):60-64. | |
| 36 | 李新,焦燕,杨铭德.用磷脂脂肪酸(PLFA)谱图技术分析内蒙古河套灌区不同盐碱程度土壤微生物群落多样性[J].生态科学,2014,33(3):488-494. |
| LI X, JIAO Y, YANG M D. Microbial diversity of different saline-alkaline soil analyzing by PLFA in the Hetao area of Inner Mongolia [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2014, 33(3):488-494. | |
| 37 | 牛世全,景彩虹,廖世齐,等.河西走廊盐碱土细菌种群结构多样性的研究[J].西北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2013,49(2):90-95. |
| NIU S Q, JING C H, LIAO S Q, et al.. Bacterial population structure diversity in saline-alkali soil in Hexi Corridor [J]. J. Northwest Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2013, 49(2):90-95. | |
| 38 | 黄明勇,杨剑芳,王怀锋,等.天津滨海盐碱土地区城市绿地土壤微生物特性研究[J].土壤通报,2007,38(6):1131-1135. |
| HUANG M Y, YANG J F, WANG H F, et al.. Microbial properties in urban soils in coastal alkali-saline area of Tianjin [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2007, 38(6):1131-1135. | |
| 39 | 朱泓,王小敏,黄涛,等.NaCl 胁迫对滨梅根际细菌群落多样性及优势菌群的影响[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,40(4):49-54. |
| ZHU H, WANG X M, HUANG T, et al.. Effect of NaCl stress on bacterial community diversity and core microbiome in rhizosphere and bulk soil of beach plum (Prunus maritima Marshall) [J]. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2017, 40(4):49-54. | |
| 40 | YANG Y, SHAO T Y, LONG X H, et al.. Microbiome structure and function in rhizosphere of Jerusalem artichoke grown in saline land [J/OL].Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 724(168):138259 [2020-12-20]. . |
| 41 | 吉丽.盐碱胁迫下大豆根际微生物多样性分析[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2017. |
| JI L. Diversity analysis of rhizosphere microorganisms in soybean under saline alkali stress [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 42 | XIA J B, REN J Y, ZHANG S Y, et al.. Forest and grass composite patterns improve the soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta, China [J]. Geoderma, 2019, 349:25-35. |
| 43 | SHI W, TAKANO T, LIU S K. Isolation and characterization of novel bacterial taxa from extreme alkali-saline soil [J].World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, 28 (5):2147-2157. |
| 44 | VALENZUELA-ENCINAS C, NERIA-GONZ LEZ I, NTARA-HERN NDEZ R J, et al.. Changes in the bacterial populations of the highly alkaline saline soil of the former lake Texcoco (Mexico) following flooding [J]. Extremophiles, 2009, 13(4):609-621. |
| 45 | VALENZUELA-ENCINAS C, NERIA-GONZ LEZ I, NTARA-HERN NDEZ R J, et al.. Phylogenetic analysis of the archaeal community in an alkaline-saline soil of the former lake Texcoco (Mexico) [J]. Extremophiles, 2008, 12(2):247-254. |
| 46 | 徐扬,张冠初,丁红,等.干旱与盐胁迫对花生根际土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]].应用生态学报,2020,31(4):1305-1313. |
| XU Y, ZHANG G C, DING H, et al.. Effects of salt and drought stresses on rhizosphere soil bacterial community structure and peanut yield [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, 31(4):1305-1313. | |
| 47 | 戴良香,康涛,慈敦伟,等.黄河三角洲盐碱地花生根层土壤菌群结构多样性研究[J].生态学报,2019,39(19):7169-7178. |
| DAI L X, KANG T, CI D W, et al.. Comparison of the microbial community in the rhizosphere of peanuts between saline-alkali and non-saline soil at different soil depths and intercropping cultivation in the yellow river delta [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(19):7169-7178. | |
| 48 | 田平雅,沈聪,赵辉,等.银北盐碱区植物根际土壤酶活性及微生物群落特征[J].土壤学报,2020,57(1):217-226. |
| TIAN P Y, SHEN C, ZHAO H, et al.. Enzyme activities and microbial communities in rhizospheres of plants in salinized soil in north Yinchuan, China [J]. Acta Pedolog. Sin., 2020, 57(1):217-226. | |
| 49 | 张美娟,王冰,黄升财,等.糠醛渣改良土壤增强苕子对盐碱土的适应性[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(6):115-121. |
| ZHANG M J, WANG B, HUANG S C, et al.. Enhancing the adaptation of Vicia villosa Roth to salinity-alkalinity soils improved using furfural residues [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2020, 36(6):115-121. | |
| 50 | 许来鹏,万鲜花,孙向丽,等.畜禽粪肥和秸秆还田对玉米根际微生物群落结构的影响[J].生物技术通报,2020,36(9):137-146. |
| XU L P, WAN X H, SUN X L, et al.. Effects of livestock manure and straw returning to field on microbial community structure around maize rhizosphere [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2020, 36(9):137-146. | |
| 51 | BAI Y C, MEI L J, ZUO W G, et al.. Response of bacterial communities in coastal mudflat saline soil to sewage sludge amendment [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2019, 144:107-111. |
| 52 | 俞冰倩.我国不同盐碱土生态系统土壤微生物群落多样性研究[D].江苏镇江:江苏大学,2019. |
| YU B Q. Research on the diversity of microbial community in different saline-alkaline soil ecosystems in China [D]. Jiangsu Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2019. |
| [1] | 寇威, 刘佳月, 户可欣, 高铱遥, 许世奇, 何彦臻, 王旭东. 有机肥与鼠李糖脂和氯化胆碱配施对盐渍土性质和番茄耐盐性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 202-214. |
| [2] | 周琦, 刘强, 张靖, 邓超超, 王振龙, 柳洋, 吴芳, 常浩, 周彦芳, 宿翠翠, 施志国, 高正睿, 马凤捷. 有机肥替代化肥对土壤生物学特性及南瓜产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 190-203. |
| [3] | 张曦瑜, 沈幸, 李伟, 谢文歌, 李杰, 杨昌浩, 柴仲平. 氮肥减量配施有机肥对库尔勒香梨园土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 217-228. |
| [4] | 许静, 李晗, 陈平录, 罗江旎, 唐承露, 刘木华. 油茶茶枯离散元模型参数标定与试验[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 112-121. |
| [5] | 李大荣, 李小玲, 周武先, 张美德, 蒋小刚, 由金文, 王华. 有机肥替代部分化肥对湖北贝母生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 216-226. |
| [6] | 王兴松, 王娜, 杜宇, 周鹏, 王戈, 贾孟, 徐照丽, 白羽祥. 有机肥对玉溪植烟土壤有机质组分和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 201-212. |
| [7] | 韩秀丽, 李嘉伟, 张杰, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥替代化肥对葡萄生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 195-205. |
| [8] | 梁永进, 朱睿璇, 韦贝蕾, 袁小迈, 成武洋, 彭博, 王梓廷, 韦建玉. 有机肥配施对我国烟叶品质影响的整合分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(12): 164-175. |
| [9] | 张伟健, 冯景翊, 李悦, 何婉莹, 车延静, 王紫颖, 白雪燕, 谷思玉. 内-外源有机质对黑土磷素吸附及有效性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 180-190. |
| [10] | 高静娟, 朱晨宇, 柯玉琴, 郑朝元, 李春英, 李文卿. 烟稻轮作条件下有机肥施用时期对烤烟碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [11] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [12] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [13] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [14] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [15] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||