




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 198-209.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0310
郭娟娟( ), 王珊, 栾好安, 李寒, 郭素萍, 齐国辉, 张雪梅(
), 王珊, 栾好安, 李寒, 郭素萍, 齐国辉, 张雪梅( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-17
接受日期:2022-06-08
出版日期:2023-10-15
发布日期:2023-10-27
通讯作者:
张雪梅
作者简介:郭娟娟 E-mail:G15200111060@136.com;
基金资助:
Juanjuan GUO( ), Shan WANG, Haoan LUAN, Han LI, Suping GUO, Guohui QI, Xuemei ZHANG(
), Shan WANG, Haoan LUAN, Han LI, Suping GUO, Guohui QI, Xuemei ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-04-17
Accepted:2022-06-08
Online:2023-10-15
Published:2023-10-27
Contact:
Xuemei ZHANG
摘要:
为探究微生物菌剂对红树莓生长及果实品质的提升效果,以3年生红树莓‘海尔特兹’为试验材料,分别于红树莓现蕾期(6月25日)至二次盛果期(T5)、初花期至二次盛果期(T4)、初果期至二次盛果期(T3)、一次盛果期至二次盛果期(T2)、二次盛果期(T1)施用微生物菌剂,以不施用微生物菌剂为对照(CK),探究其对株高、地径、生物量、可溶性固形物、叶片抗氧化酶活性、产投比以及活化土壤磷钾的影响,并通过主成分分析进行综合评价。结果表明,施用微生物菌剂可提高红树莓品质、产量及土壤的速效养分,以T5、T4处理效果较好。不同土层速效养分及有机质含量变化趋势大致相同,0—10 cm土层速效养分与有机质含量大于10—20 cm土层。T5处理土壤速效养分含量最高,其pH低于CK,改善了土壤碱性环境。T5处理结果数较CK高76.40%,产量较CK高25.75%;一次盛果期叶片超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶活性较CK分别高22.49%和25.02%,而过氧化物酶无显著差异。施用微生物菌剂对红树莓影响的综合评价表明,微生物菌剂可有效提高土壤速效养分,改善红树莓果实品质,以T5处理即微生物菌剂施用含量为20%、用量200 L·hm-2,于红树莓主要发育期施用5次效果最佳。研究结果为改良土壤及精确、高效施用微生物菌剂提供了理论基础。
中图分类号:
郭娟娟, 王珊, 栾好安, 李寒, 郭素萍, 齐国辉, 张雪梅. 微生物菌剂对红树莓生长、果实品质及土壤磷钾的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 198-209.
Juanjuan GUO, Shan WANG, Haoan LUAN, Han LI, Suping GUO, Guohui QI, Xuemei ZHANG. Effects of Microbial Inoculum on Red Raspberry Growth, Fruit Quality and Activating Soil Phosphorus and Potassium[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 198-209.
处理 Treatment | 微生物菌剂施用时期及施用量 Fertilization program/(L·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6/25 | 7/15 | 8/11 | 9/15 | 10/10 | |
| CK | — | — | — | — | — |
| T5 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| T4 | — | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| T3 | — | — | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| T2 | — | — | — | 200 | 200 |
| T1 | — | — | — | — | 200 |
表1 不同处理施菌剂情况
Table 1 Fertilization of different treatments
处理 Treatment | 微生物菌剂施用时期及施用量 Fertilization program/(L·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6/25 | 7/15 | 8/11 | 9/15 | 10/10 | |
| CK | — | — | — | — | — |
| T5 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| T4 | — | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| T3 | — | — | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| T2 | — | — | — | 200 | 200 |
| T1 | — | — | — | — | 200 |
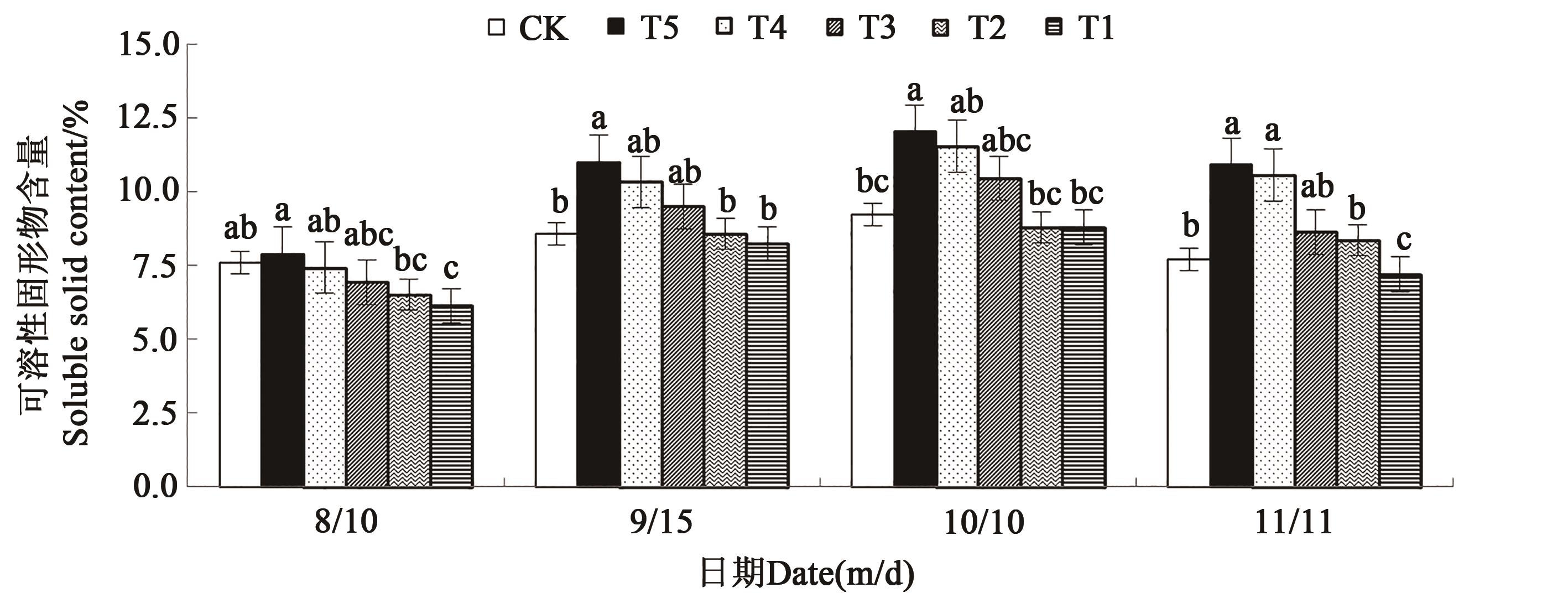
图2 在微生物菌剂下不同时期红树莓可溶性固形物含量注:同一时期中不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Soluble solids content of red raspberry in different periods under microbial inoculumNote: Different lowercase letters in same date indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
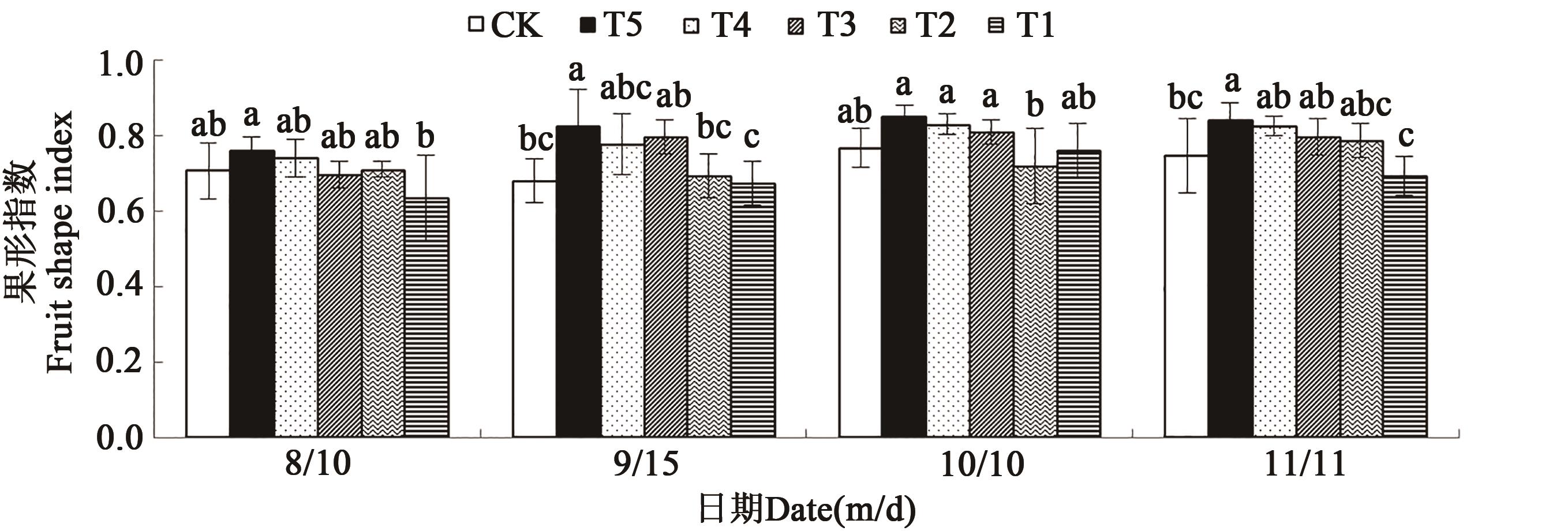
图3 在微生物菌剂下不同时期的果实果形指数注:同一时期中不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Fruit shape index in different periods under microbial inoculumNote: Different lowercase letters in same date indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
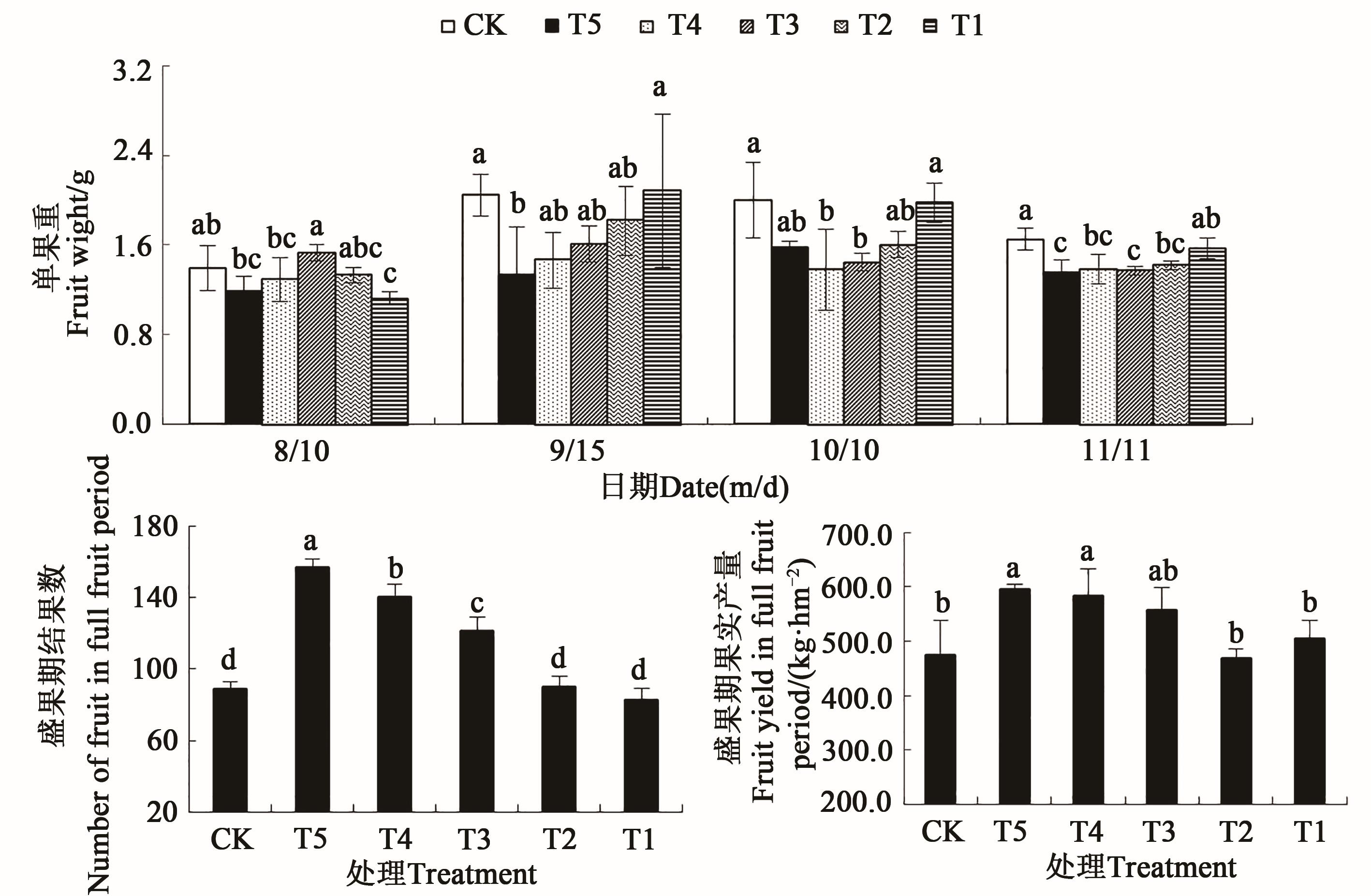
图4 在微生物菌剂下红树莓盛果期产量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在 P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 4 Yield of red raspberry in full bloom under microbial inoculumNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
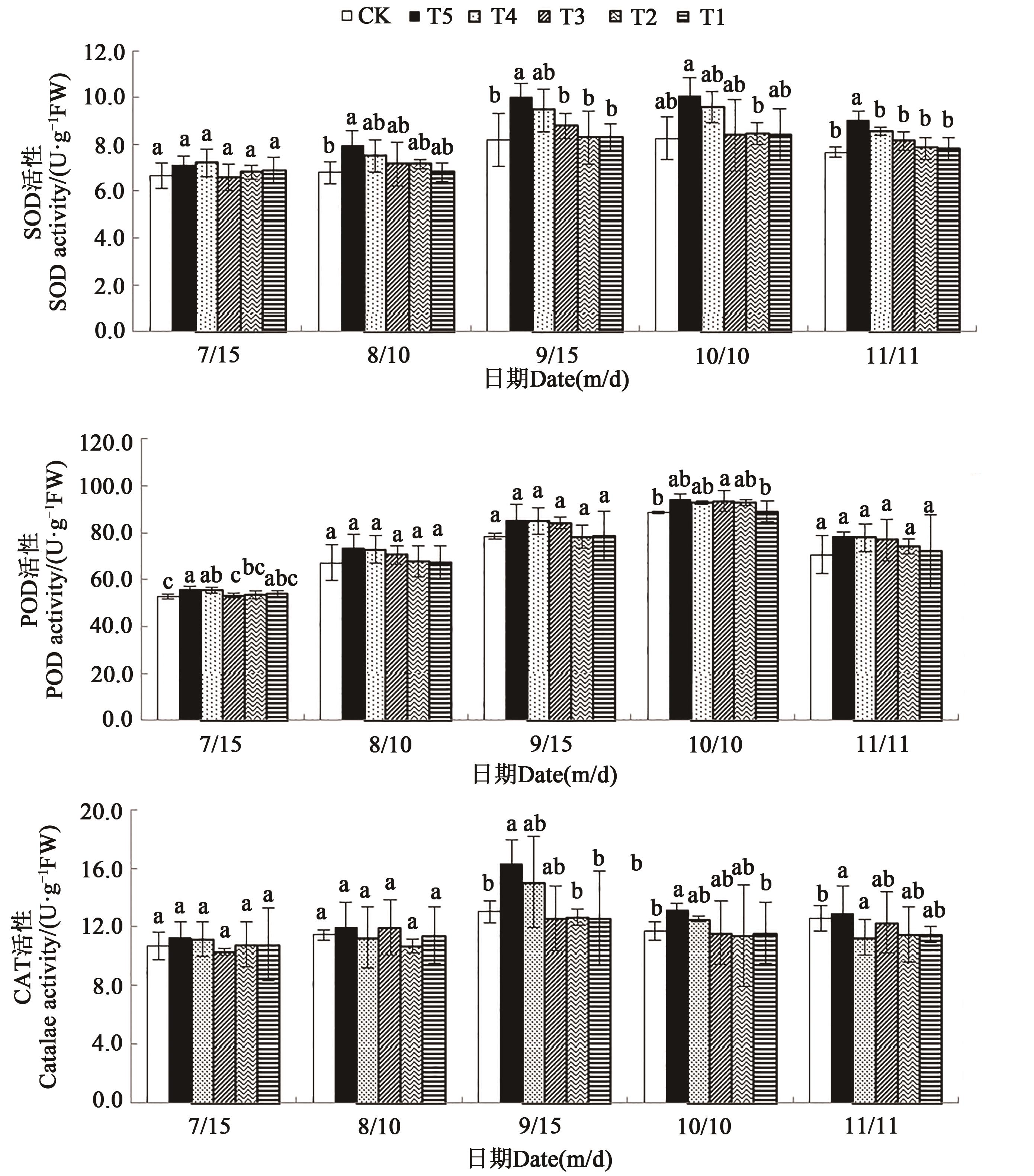
图5 在微生物菌剂下不同时期红树莓叶片抗氧化酶的活性注:同一时期中不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 5 Antioxidant enzymes activities of red raspberry leaves at different periods under microbial inoculumNote: Different lowercase letters in same date indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
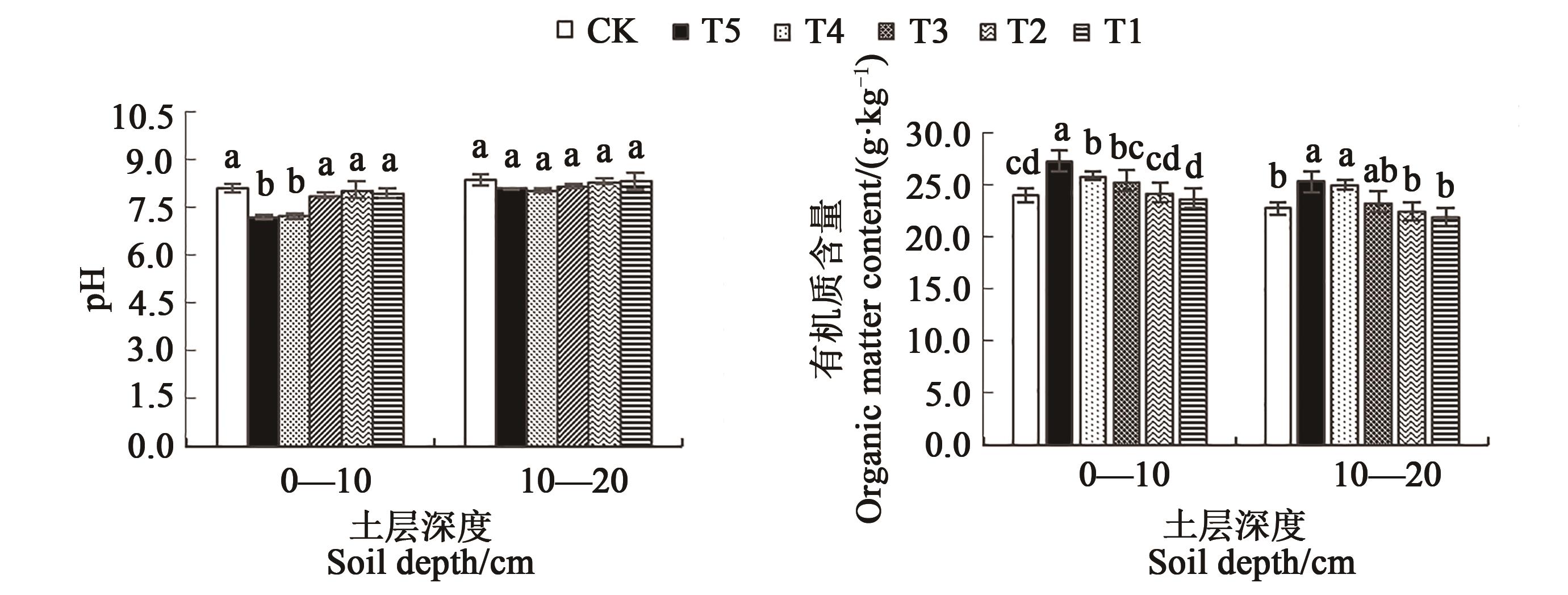
图6 在微生物菌剂下红树莓盛果期土壤pH和有机质含量注:同一土层中不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 6 Soil pH and organic matter content of red raspberry in fruiting season under microbial inoculumNote: Different lowercase letters in same soil indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
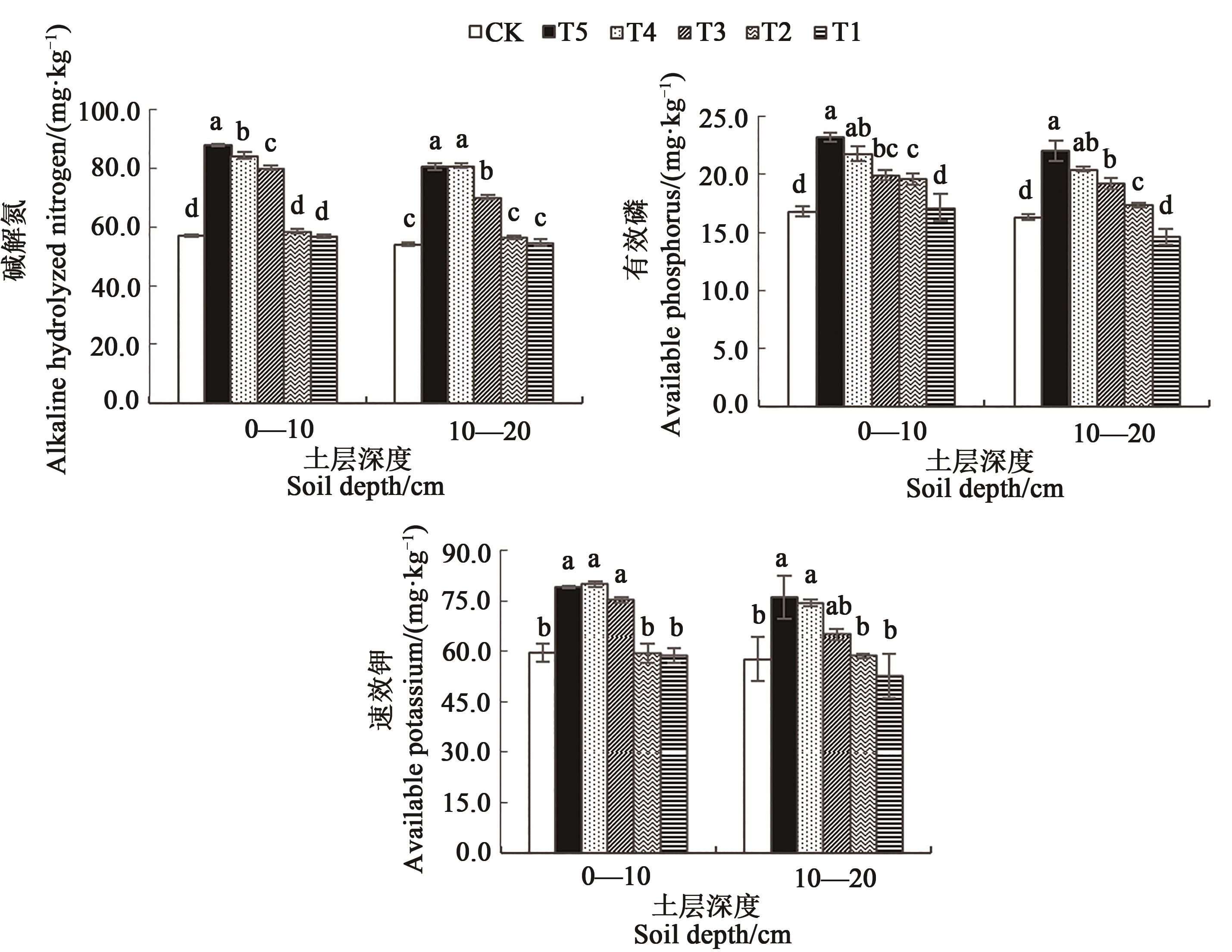
图7 在微生物菌剂下红树莓盛果期土壤速效养分含量注:同一土层中不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 7 Available nutrients content of red raspberry soils in fruiting season under microbial inoculumNote: Different lowercase letters in same soil indicate significa nt differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) | 较CK Compared to CK | 微生物菌剂用量 Amount of topdressing/(L·hm-2) | 微生物菌剂投入成本/(元·hm-2) Fertilizer input cost/(yuan·hm-2) | 增产效益/(元·hm-2) Increased benefits/ (yuan·hm-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
增产量 Increased yield/(kg·hm-2) | 增产率 Percentage/% | |||||
| CK | 24 930±2.03 b | — | — | — | — | — |
| T5 | 31 590±8.45 a | 6 660 | 26.71 | 5 000.25 | 16 875 | 49 725 |
| T4 | 31 395±7.66 a | 6 465 | 25.93 | 4 000.20 | 13 500 | 51 150 |
| T3 | 27 765±8.09 ab | 2 835 | 11.37 | 3 000.15 | 10 125 | 18 225 |
| T2 | 26 055±9.95 b | 1 125 | 4.51 | 2 000.10 | 6 750 | 4 500 |
| T1 | 25 035±8.77 b | 105 | 0.42 | 1 000.05 | 3 375 | -2 325 |
表2 不同处理的经济效益
Table 2 Economic benefits of different treatments
处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) | 较CK Compared to CK | 微生物菌剂用量 Amount of topdressing/(L·hm-2) | 微生物菌剂投入成本/(元·hm-2) Fertilizer input cost/(yuan·hm-2) | 增产效益/(元·hm-2) Increased benefits/ (yuan·hm-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
增产量 Increased yield/(kg·hm-2) | 增产率 Percentage/% | |||||
| CK | 24 930±2.03 b | — | — | — | — | — |
| T5 | 31 590±8.45 a | 6 660 | 26.71 | 5 000.25 | 16 875 | 49 725 |
| T4 | 31 395±7.66 a | 6 465 | 25.93 | 4 000.20 | 13 500 | 51 150 |
| T3 | 27 765±8.09 ab | 2 835 | 11.37 | 3 000.15 | 10 125 | 18 225 |
| T2 | 26 055±9.95 b | 1 125 | 4.51 | 2 000.10 | 6 750 | 4 500 |
| T1 | 25 035±8.77 b | 105 | 0.42 | 1 000.05 | 3 375 | -2 325 |
指标 Indicator | 有机质 Organic matter | pH | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 株高 Plant heigh | 地径 Ground diameter | POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 可溶性固形物 Soluble solids | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | -0.72** | ||||||||||
碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen | -0.72** | -0.84** | |||||||||
有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.81** | -0.75** | 0.91** | ||||||||
速效钾 Available potassium | 0.746** | -0.74** | 0.90** | 0.88** | |||||||
株高 Plant height | 0.57* | -0.51* | 0.49* | 0.55* | 0.52* | ||||||
地径 Ground diameter | 0.73** | -0.51* | 0.70** | 0.69** | 0.69** | 0.408 | |||||
POD | 0.31 | -0.48* | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.436 | 0.174 | 0.035 | ||||
过氧化氢酶 CAT | 0.50* | -0.50* | 0.63** | 0.64** | 0.54* | 0.18 | 0.58* | 0.076 | |||
可溶性固形物 Soluble solids | 0.79** | -0.64** | 0.74** | 0.82** | 0.72** | 0.52* | 0.73** | 0.223 | 0.76** | ||
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.77** | -0.71** | 0.79** | 0.80** | 0.75** | 0.364 | 0.71** | 0.128 | 0.51* | 0.63** | |
果形指数 Fruit shape index | 0.59* | -0.71** | 0.67** | 0.70** | 0.55* | 0.47* | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.56* | 0.51* |
表3 在微生物菌剂下红树莓性状及土壤指标相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of raspberry characters and soil indexes under microbial inoculum
指标 Indicator | 有机质 Organic matter | pH | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 株高 Plant heigh | 地径 Ground diameter | POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 可溶性固形物 Soluble solids | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | -0.72** | ||||||||||
碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen | -0.72** | -0.84** | |||||||||
有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.81** | -0.75** | 0.91** | ||||||||
速效钾 Available potassium | 0.746** | -0.74** | 0.90** | 0.88** | |||||||
株高 Plant height | 0.57* | -0.51* | 0.49* | 0.55* | 0.52* | ||||||
地径 Ground diameter | 0.73** | -0.51* | 0.70** | 0.69** | 0.69** | 0.408 | |||||
POD | 0.31 | -0.48* | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.436 | 0.174 | 0.035 | ||||
过氧化氢酶 CAT | 0.50* | -0.50* | 0.63** | 0.64** | 0.54* | 0.18 | 0.58* | 0.076 | |||
可溶性固形物 Soluble solids | 0.79** | -0.64** | 0.74** | 0.82** | 0.72** | 0.52* | 0.73** | 0.223 | 0.76** | ||
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 0.77** | -0.71** | 0.79** | 0.80** | 0.75** | 0.364 | 0.71** | 0.128 | 0.51* | 0.63** | |
果形指数 Fruit shape index | 0.59* | -0.71** | 0.67** | 0.70** | 0.55* | 0.47* | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.56* | 0.51* |
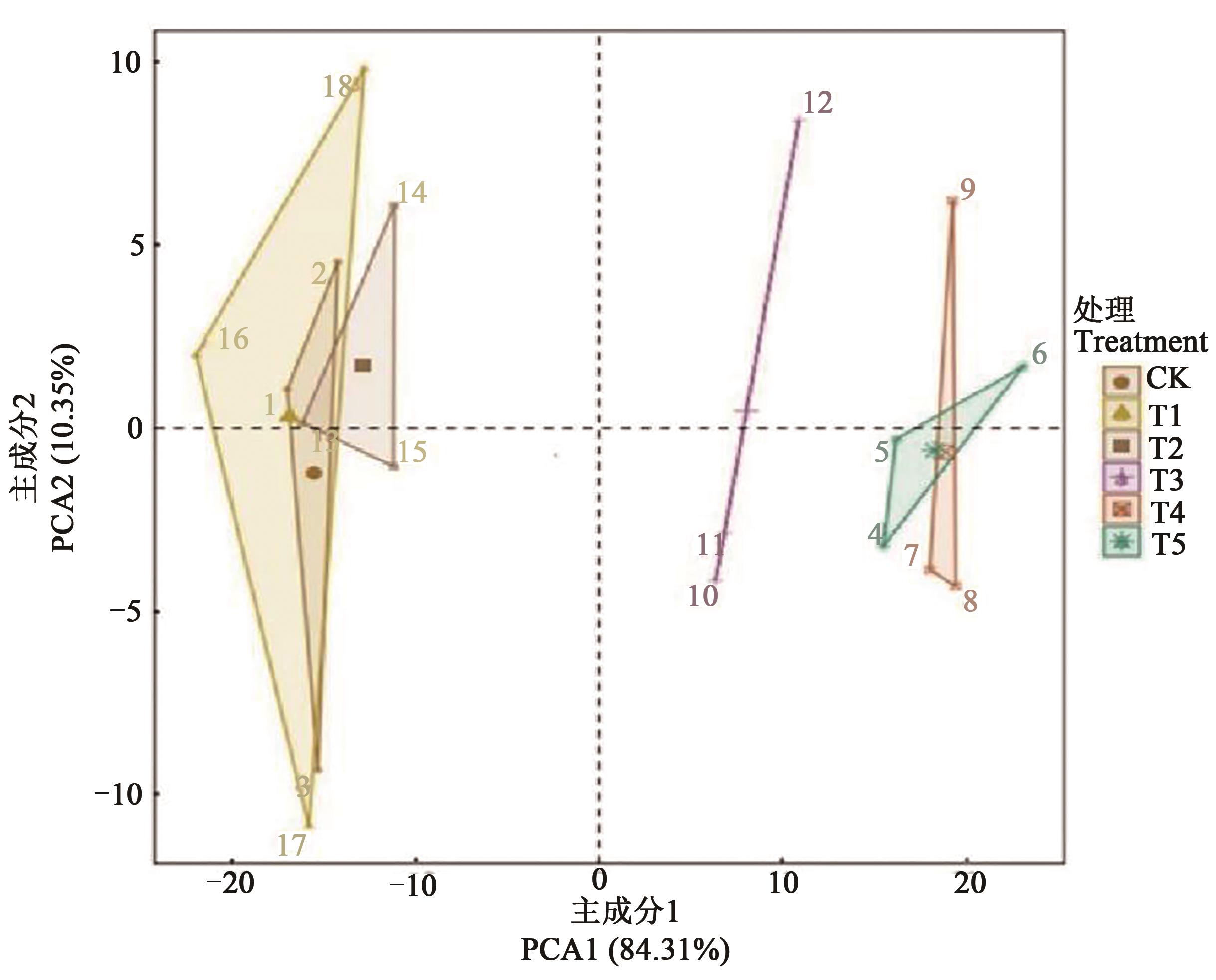
图8 在微生物菌剂下不同处理红树莓性状及土壤指标PCoA分析注:1~3代表CK的3个重复;4~6代表T5的3个重复;以此类推,16~18代表T1的3个重复。
Fig. 8 PCoA analysis Compared to CK of red raspberry traits and soil indicators in different treatments under microbial inoculumNote: 1~3 represent three repeats of CK; 4~6 represent three repeats of T5; and so on, 16~18 represent three repeats of T1.
| 1 | R.Workers PETCHESKY, hazardsreproductive, and the politics of protection : an introduction [J]. Feminist Studies, 1980, 5(2): 233-245. |
| 2 | CHEN J Y, DU J, LI M L, et al.. Degradation kinetics and pathways of red raspberry anthocyanins in model and juice systems and their correlation with color and antioxidant changes during storage [J/OL]. LWT Food Sci. Technol., 2020,128: 109448 [2022-03-16]. . |
| 3 | 张海军, 王彦辉, 张清华, 等. 国内外树莓产业发展现状研究 [J]. 林业实用技术, 2010 (10): 54- 56. |
| ZHANG H J, WANG Y H, ZHANG Q H, et al.. Study on the development status of raspberry industry at home and abroad [J]. Practical For. Technol., 2010 (10): 54-56. | |
| 4 | 张婉欣. 尚志市树莓产业发展研究 [D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG W X. Research on the development of raspberry industry in Shangzhi city [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 5 | 汪生新. 浅谈化肥过量施用的危害及防治措施 [J]. 青海农林科技, 2018(2): 34-35, 67. |
| WANG S X. Harm of excessive application of chemical fertilizer and its control measures [J]. Sci. Technol. Qinghai Agric. For., 2018(2): 34-35, 67. | |
| 6 | 邹湘, 易博, 张奇春, 等. 长期施肥对稻田土壤微生物群落结构及氮循环功能微生物数量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12): 2158-2167. |
| ZOU X, YI B, ZHANG Q C, et al.. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial community structure and nitrogen cycle function and microbial quantity in paddy field [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2020, 26(12): 2158-2167. | |
| 7 | MASSAHI S, NADERI D, PESSARAKLI M. Studying the effect of two biological fertilizers on salt tolerance of tall fescue (Festuca arundinaceae schreb.) [J]. J. Plant Nutr., 2018,41(17):2210-2221. |
| 8 | 李宁, 王珊珊, 马丽丽, 等. 两株高效溶磷菌的溶磷能力及其对玉米生长和红壤磷素形态的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(2): 275-283. |
| LI N, WANG S S, MA L L, et al.. Phosphorus solubilizing ability of two highly effective phosphorus solubilizing bacteria and their effects on maize growth and phosphorus form in red soil [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2021, 27 (2): 275-283. | |
| 9 | 程鸿燕, 张大琪, 黄斌, 等. 微生物菌肥对熏蒸剂处理后土壤微生态的影响研究进展 [J].农药学学报, 2020, 22(5): 734-741. |
| CHENG H Y, ZHANG D Q, HUANG B, et al.. Research progress of microbial fertilizer on soil microecology after fumigant treatment [J]. J. Pest. Sci., 2020, 22(5): 734-741. | |
| 10 | 李俊, 姜昕, 马鸣超. 新形势下微生物肥料产业运行状况及发展方向 [J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12): 2108-2114. |
| LI J, JIANG X, MA M C. Operation status and development direction of microbial fertilizer industry under the new situation [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2020, 26 (12): 2108-2114. | |
| 11 | 张博琦, 金锡九. 生物菌肥对饲料玉米生长及营养成分的影响 [J]. 饲料研究, 2020, 43(11): 88-91. |
| ZHANG B Q, JIN X J. Effects of microbial fertilizer on growth and nutritional components of feed corn [J]. Feed Res., 2020, 43 (11): 88-91. | |
| 12 | 李玉奇, 辛世杰, 奥岩松. 微生物菌肥对温室黄瓜生长、产量及品质的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(1): 259-263. |
| LI Y Q, XIN S J, AO Y S. Effects of microbial fertilizer on growth, yield and quality of cucumber in greenhouse [J]. China Agron. Bull., 2012, 28 (1): 259-263. | |
| 13 | DASCI M, GULLAP M K, ERKOVAN H I, et al.. Effects of phosphorus fertilizer and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria applications on clover dominant meadow: Ⅱ. chemical composition [J]. Turk. J. Field Crops, 2010, 15(1): 18-24. |
| 14 | HU X, CHEN J, GUO J. Two phosphate- and potassium-solubilizing bacteria isolated from Tianmu mountain, Zhejiang, China [J]. World J. Microb. Biot., 2006, 22(9): 983-990. |
| 15 | DIJIANA S, TOMO M, PAVLE M, et al.. Influence of organic, organo-mineral and mineral fertilisers on cane traits, productivity and berry quality of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2019, 252: 370-378. |
| 16 | 张敏硕, 赵英男, 杨威, 等. 微生物菌剂对张北冷凉坝上地区马铃薯产量, 品质及活化土壤磷钾的效果 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(3): 235-239. |
| ZHANG M S, ZHAO Y N, YANG W, et al.. Effects of microbial inoculants on potato yield, quality and activation of soil phosphorus and potassium in the Lengliang area of Zhangbei [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 33(3): 235-239. | |
| 17 | 王迎. 红树莓叶片矿质元素变化规律及施肥对果实功能性成分的影响[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2018. |
| WANG Y. Changes of mineral elements in red raspberry leaves and effects of fertilization on functional components of fruits [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 18 | 李冬梅, 魏珉, 张海森, 等. 氮、磷、钾用量和配比对温室黄瓜叶片相关代谢酶活性的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2006, 12(3): 382-387. |
| LI D M, WEI M, ZHANG H S, et al.. Effects of N,P,K rates and ratios on activities of metabolism enzymes in leaves of cucumber in greenhouse [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2006, 12(3): 382-387. | |
| 19 | 郭熙盛, 叶舒娅, 王文军, 等. 钾肥品种与用量对黄瓜产量和品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2004, 10(3): 292-297. |
| GUO X S, YE S Y, WANG W J, et al.. Effect of different K sources and rates on the yield and quality of cucumber [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2004, 10(3): 292-297. | |
| 20 | 武杞蔓, 田诗涵, 李昀烨, 等. 微生物菌肥对设施黄瓜生长、产量及品质的影响 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(1): 125-131. |
| WU Q M, TIAN S H, LI Y Y, et al.. Effects of microbial fertilizer on growth, yield and quality of greenhouse cucumber [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2022, 38(1): 125-131. | |
| 21 | 李青梅, 陆秀君, 张敏硕, 等. 微生物菌剂和生根粉对甜瓜产量和土壤生态效应的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2020(7): 100-105. |
| LI Q M, LU X J, ZHANG M S, et al.. Effects of microbial agents and rooting powder on melon yield and soil ecological effects [J]. Northern Hortic., 2020 (7): 100-105. | |
| 22 | YANG W L, GONG T, WANG J W, et al.. Effects of compound microbial fertilizer on soil characteristics and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2020, 20(4): 740-748. |
| 23 | 王赫, 李晓雪, 王亚玲, 等. 化肥减量配施有机肥和菌剂对辣椒产量、品质和养分累积的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2021(16): 1-7. |
| WANG H, LI X X, WANG Y L, et al.. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer and bacterial agent on yield, quality and nutrient accumulation of pepper [J]. Northern Hortic., 2021(16): 1-7. | |
| 24 | AKKOPRU A, AKAT Ş, OZAKTAN H, et al.. The long-term colonization dynamics of endophytic bacteria in cucumber plants, and their effects on yield, fruit quality and angular leaf spot disease [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2021, 282: 110005 [2022-03-16]. . |
| 25 | TANGOLAR S, TANGOLAR S, TORUN A A, et al.. The effect of microbial fertilizer applications on grape yield, quality and mineral nutrition of some early table grape varieties [J]. Selcuk J. Agric. Food Sci., 2019, 33(2), 62-66. |
| 26 | KAFI S A, ARABHOSSEINI S, KARIMI E, et al.. Pseudomonas putida P 3- 57 induces cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) defense responses and improves fruit quality characteristics under commercial greenhouse conditions [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2021, 280:109942 [2022-03-16]. . |
| 27 | MI S, ZHANGX, WANG Y, et al.. Effect of different fertilizers on the physicochemical properties, chemical element and volatile composition of cucumbers [J/OL]. Food Chem., 2022, 367: 130667[2022-03-16]. . |
| 28 | 刘东阳, 江连强, 陈树鸿, 等. 微生物菌剂与不同有机肥协同作用对烟草根结线虫病的防控效果研究 [J]. 植物医生, 2021, 34(2): 23-28. |
| LIU D Y, JIANG L Q, CHEN S H, et al.. Study on the synergistic effect of microbial agents and different organic fertilizers on tobacco root knot nematode disease [J]. Plant Doctor, 2021, 34 (2): 23-28. | |
| 29 | 张恩平, 张淑红, 李天来, 等. 蔬菜钾素营养的研究现状与展望 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(8): 265-268. |
| ZHANG E P, ZHANG S H, LI T L, et al.. Advance of research on potassium nutrition [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2005, 21(8): 265-268. | |
| 30 | 彭福田, 姜远茂, 顾曼如, 等. 不同负荷水平下氮素对苹果果实生长发育的影响 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(6): 690-694. |
| PENG F T, JIANG Y M, GU M R, et al.. Effect of nitrogen on apple fruit development in different load [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2002, 35(6): 690-694. | |
| 31 | 姜永雷, 肖雨, 邓小鹏, 等. 微生物菌剂对烟草连作土壤理化性质及土壤胞外酶酶活性的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2022, 28(4): 59-66. |
| JIANG Y L, XIAO Y, DENG X P, et al.. Effects of microbial agents on soil physical and chemical properties and soil extracellular enzyme activities of continuous cropping tobacco [J]. Acta Tob. Sin., 2022, 28(4): 59-66. | |
| 32 | 王国丽, 张晓丽, 张晓霞,等. 施用功能微生物菌剂对重度盐碱地向日葵生长及土壤微生物的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2021(5):133-139. |
| WANG G L, ZHANG X L, ZHANG X X, et al.. Effects of applying functional microbial agents on sunflower growth and soil microorganism in severe saline alkali soil [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2021(5):133-139. | |
| 33 | 李星星. 复合微生物菌剂对土壤特性及马铃薯生长与产量的影响 [D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2020. |
| LI X X. Effects of compound microbial agents on soil characteristics and potato growth and yield [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 34 | WANG Z, CHEN Z, XU Z, et al.. Effects of phosphate- solubilizing bacteria and N2- fixing bacteria on nutrient uptake, growthplant, and bioactive compound accumulation in Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) iljinskaja [J/OL]. Forests, 2019, 10(9): 772 [2022-03-16]. . |
| 35 | YU X, LIU X, ZHU T H, et al.. Co-inoculation with phosphate- solubilzing and nitrogen- fixing bacteria on solubilization of rock phosphate and their effect on growth promotion and nutrient uptake by walnut`[J]. Eur. J. Soil Biol., 2012, 50: 112-117. |
| [1] | 谭施北, MKAPA Dietram Samson, 李升林, 习金根, 吴伟怀, 陈河龙, 黄兴, 梁艳琼, 易克贤, 郑金龙. 添加菌剂和石灰对剑麻渣腐解及养分含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 204-214. |
| [2] | 宋光永, 郭雅文, 薛婧, 杨克箐, 苏学德, 周龙. 不同肥水处理对7个设施鲜食葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 229-240. |
| [3] | 朱燕芳, 常强, 郝燕, 陈海龙. 反光膜对‘阳光玫瑰’果实品质及挥发性物质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 72-82. |
| [4] | 黄娟娟, 张志强, 毛娟, 马宗桓, 陈佰鸿. 不同叶面肥对‘黑比诺’葡萄生长发育和果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 205-217. |
| [5] | 王如月, 虎海防, 罗莎莎, 甄紫怡, 徐业勇, 胡晓静. 杏李不同采收成熟度果实品质分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 158-169. |
| [6] | 曾宝珍, 成永娟, 杨娟博, 车莉莉, 梁靖, 卢世雄, 梁国平, 马宗桓, 毛娟. 甘肃民勤地区‘慕合怀特’葡萄最佳采收期的确定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 70-79. |
| [7] | 王吉平, 卢铁东, 梁芷姮, 张野, 苏天明, 何铁光. 不同来源微生物对葡萄枝条猪粪共堆肥过程的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 224-233. |
| [8] | 白世践, 户金鸽, 李超, 蔡军社. 3种架式对‘新郁’葡萄栽培性状及果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 63-73. |
| [9] | 王子凡, 李燕, 张庆银, 王丹丹, 师建华, 耿晓彬, 田东良, 钟增明, 赵晓明, 齐连芬. 微生物菌剂对设施番茄主要病害及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [10] | 卢登洋, 童盼盼, 闫敏, 鲍荆凯, 刘鸣哲, 夏怡蕾, 吴翠云. 库尔勒香梨大果芽变的鉴定与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [11] | 陈芙蓉, 熊伟仡, 尹娇, 张小卓, 韩宇, 邓毅书. 微生物菌剂对叶菜废弃物堆肥过程的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 146-154. |
| [12] | 张海军, 张娟, 贾毅男, 王江龙, 冯丽. 不同架式对‘南太湖特早’葡萄果实香气成分及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 201-213. |
| [13] | 杜彩艳, 鲁海燕, 熊艳竹, 孙曦, 孙秀梅, 普继雄, 张乃明. 连续两年沼液与化肥配施对桃生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| [14] | 白世践, 户金鸽, 吴久赟, 张雯, 谢辉, 赵荣华, 陈光, 蔡军社. 不同砧木对吐鲁番地区‘克瑞森无核’葡萄生长特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 76-87. |
| [15] | 朱士江, 李虎, 徐文, 冯雅婷. 三峡库区土壤含水量对柑橘园果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 201-207. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||