




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 102-112.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0877
王子凡1( ), 李燕1, 张庆银1, 王丹丹1, 师建华1, 耿晓彬1, 田东良1, 钟增明2, 赵晓明1, 齐连芬1(
), 李燕1, 张庆银1, 王丹丹1, 师建华1, 耿晓彬1, 田东良1, 钟增明2, 赵晓明1, 齐连芬1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-14
接受日期:2022-12-19
出版日期:2024-06-15
发布日期:2024-06-12
通讯作者:
齐连芬
作者简介:王子凡 E-mail:wzfwan666@163.com;
基金资助:
Zifan WANG1( ), Yan LI1, Qingyin ZHANG1, Dandan WANG1, Jianhua SHI1, Xiaobin GENG1, Dongliang TIAN1, Zengming ZHONG2, Xiaoming ZHAO1, Lianfen QI1(
), Yan LI1, Qingyin ZHANG1, Dandan WANG1, Jianhua SHI1, Xiaobin GENG1, Dongliang TIAN1, Zengming ZHONG2, Xiaoming ZHAO1, Lianfen QI1( )
)
Received:2022-10-14
Accepted:2022-12-19
Online:2024-06-15
Published:2024-06-12
Contact:
Lianfen QI
摘要:
为探究微生物菌剂对番茄产量、病害发生率、土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构的影响,以不加微生物菌剂为对照(CK),设置在番茄定植后1~3个月分别施用1(T1)、2(T2)、3次(T3)枯草芽孢杆菌,分析不同施用次数处理下番茄植株的发病率、产量及土壤的理化性质和微生物群落结构。结果表明,与CK相比,T1、T2、T3处理的产量分别显著提高16.60%、39.58%、29.43%,且显著降低了设施番茄灰霉病、叶霉病、晚疫病的发病率。Alpha多样性指数显示,T1、T2和T3处理土壤细菌的Chao指数和Shannon指数显著增加,而土壤真菌的Chao指数和Shannon指数均显著降低,说明添加微生物菌剂提高了土壤细菌群落的多样性和丰富度,降低了真菌群落的多样性和丰富度。随着微生物菌剂使用次数的增加,提高了土壤细菌群落中放线菌门、拟杆菌门、芽单胞菌门、厚壁菌门、髌骨细菌门以及真菌群落中被孢菌门、担子菌门、壶菌门、油壶菌门和Calcarisporiellomycota的相对丰度,降低了土壤细菌群落中绿弯菌门、酸杆菌门以及真菌群落中子囊菌门的相对丰度。冗余分析(redundancy analysis,RDA)表明,土壤有机质、全氮、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾含量与细菌群落结构的相关性较大,而土壤pH、电导率及有机质、全钾、有效磷、速效钾含量与真菌群落结构的相关性较大。综上所述,施用微生物菌剂可显著降低番茄病害发生率,提高番茄产量,改善土壤中微生物群落结构,调节土壤微生物群落朝着健康的方向发展。
中图分类号:
王子凡, 李燕, 张庆银, 王丹丹, 师建华, 耿晓彬, 田东良, 钟增明, 赵晓明, 齐连芬. 微生物菌剂对设施番茄主要病害及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 102-112.
Zifan WANG, Yan LI, Qingyin ZHANG, Dandan WANG, Jianhua SHI, Xiaobin GENG, Dongliang TIAN, Zengming ZHONG, Xiaoming ZHAO, Lianfen QI. Effect of Microbicides on Main Diseases and Soil Microbial Communities of Tomatoes in Facilities[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 102-112.
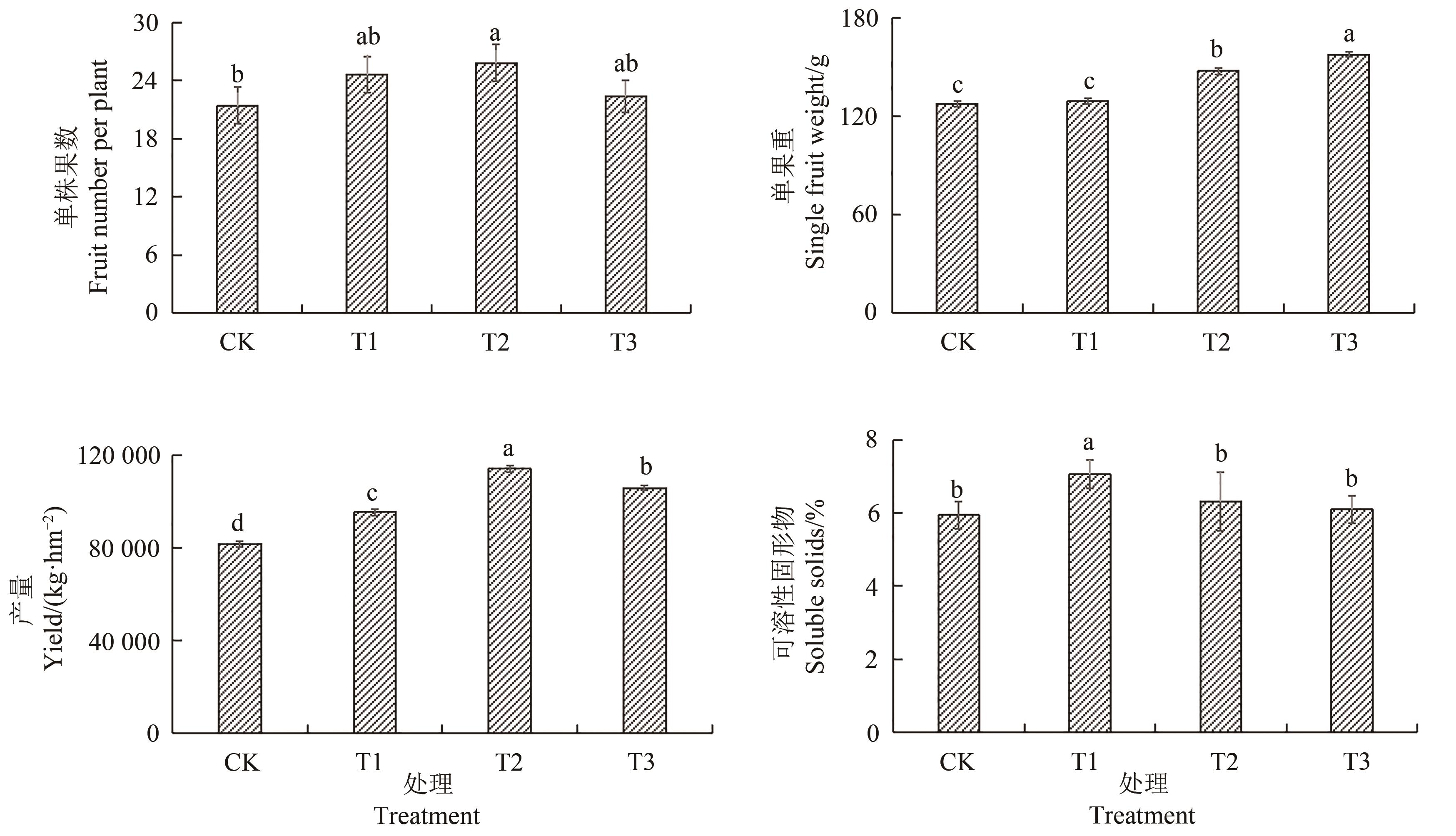
图1 施用不同量微生物菌剂下的番茄果实产量及可溶性固形物含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Fruit yield and fruit brix of tomatoes under different amounts of microbicides applicationNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 发病率 Incidence | ||
|---|---|---|---|
晚疫病 Late blight | 灰霉病 Botrytis cinerea | 叶霉病 Leaf mildew | |
| CK | 36.67±0.06 a | 33.33±0.15 a | 16.67±0.06 a |
| T1 | 10.00±0.01 b | 10.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 b |
| T2 | 3.33±0.06 b | 3.33±0.06 b | 0.00±0.00 b |
| T3 | 16.67±0.06 b | 16.67±0.06 b | 6.67±0.06 b |
表1 施用不同量微生物菌剂下的番茄病害发病率 (%)
Table 1 Incidence of tomato diseases with the application of different microbicides
| 处理Treatment | 发病率 Incidence | ||
|---|---|---|---|
晚疫病 Late blight | 灰霉病 Botrytis cinerea | 叶霉病 Leaf mildew | |
| CK | 36.67±0.06 a | 33.33±0.15 a | 16.67±0.06 a |
| T1 | 10.00±0.01 b | 10.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 b |
| T2 | 3.33±0.06 b | 3.33±0.06 b | 0.00±0.00 b |
| T3 | 16.67±0.06 b | 16.67±0.06 b | 6.67±0.06 b |
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus/(g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkali solution nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | pH | 电导率 EC/ (mS·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.67±0.87 b | 1.60±0.15 b | 0.88±0.09 a | 19.08±0.96 a | 166.42±1.10 a | 107.36±0.97 a | 353.60±3.21 a | 7.65±0.86 a | 3.50±0.25 b |
| T1 | 28.91±1.60 a | 1.36±0.04 b | 0.73±0.12 a | 18.51±0.95 a | 112.11±2.15 c | 57.87±1.35 c | 121.39±3.00 d | 8.23±1.10 a | 0.40±0.16 c |
| T2 | 28.85±1.51 a | 1.98±0.24 a | 0.90±0.20 a | 18.53±1.20 a | 148.77±2.23 b | 61.58±1.30 b | 319.53±6.85 b | 8.52±1.10 a | 4.99±0.53 a |
| T3 | 18.59±0.72 b | 1.34±0.12 b | 0.81±0.09 a | 18.48±0.35 a | 76.88±1.50 d | 42.41±0.80 d | 185.41±4.97 c | 7.81±1.09 a | 2.85±0.37 b |
表2 施用不同量微生物菌剂下的土壤理化性质
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of soils with different amounts of microbicides
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus/(g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkali solution nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | pH | 电导率 EC/ (mS·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.67±0.87 b | 1.60±0.15 b | 0.88±0.09 a | 19.08±0.96 a | 166.42±1.10 a | 107.36±0.97 a | 353.60±3.21 a | 7.65±0.86 a | 3.50±0.25 b |
| T1 | 28.91±1.60 a | 1.36±0.04 b | 0.73±0.12 a | 18.51±0.95 a | 112.11±2.15 c | 57.87±1.35 c | 121.39±3.00 d | 8.23±1.10 a | 0.40±0.16 c |
| T2 | 28.85±1.51 a | 1.98±0.24 a | 0.90±0.20 a | 18.53±1.20 a | 148.77±2.23 b | 61.58±1.30 b | 319.53±6.85 b | 8.52±1.10 a | 4.99±0.53 a |
| T3 | 18.59±0.72 b | 1.34±0.12 b | 0.81±0.09 a | 18.48±0.35 a | 76.88±1.50 d | 42.41±0.80 d | 185.41±4.97 c | 7.81±1.09 a | 2.85±0.37 b |
处理 Treatment | 细菌Bacterium | 真菌 Fungus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | |
| CK | 312.51±23.56 c | 3.85±0.19 b | 0.77±0.04 b | 4 481.30±152.19 a | 11.12±0.04 a | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T1 | 456.78±40.59 b | 5.35±0.46 a | 0.90±0.04 a | 3 812.38±223.53 b | 10.37±0.27 c | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T2 | 485.15±66.63 b | 5.23±0.72 a | 0.88±0.07 ab | 3 935.45±416.59 b | 10.70±0.07 b | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T3 | 738.50±37.67 a | 6.02±0.83 a | 0.91±0.09 a | 3 318.33±104.99 c | 10.35±0.05 c | 1.00±0.00 a |
表3 不同量微生物菌剂下土壤中细菌和真菌α多样性
Table 3 Bacterial and fungal α diversity in soil under different amounts of microbicides application
处理 Treatment | 细菌Bacterium | 真菌 Fungus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | |
| CK | 312.51±23.56 c | 3.85±0.19 b | 0.77±0.04 b | 4 481.30±152.19 a | 11.12±0.04 a | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T1 | 456.78±40.59 b | 5.35±0.46 a | 0.90±0.04 a | 3 812.38±223.53 b | 10.37±0.27 c | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T2 | 485.15±66.63 b | 5.23±0.72 a | 0.88±0.07 ab | 3 935.45±416.59 b | 10.70±0.07 b | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T3 | 738.50±37.67 a | 6.02±0.83 a | 0.91±0.09 a | 3 318.33±104.99 c | 10.35±0.05 c | 1.00±0.00 a |
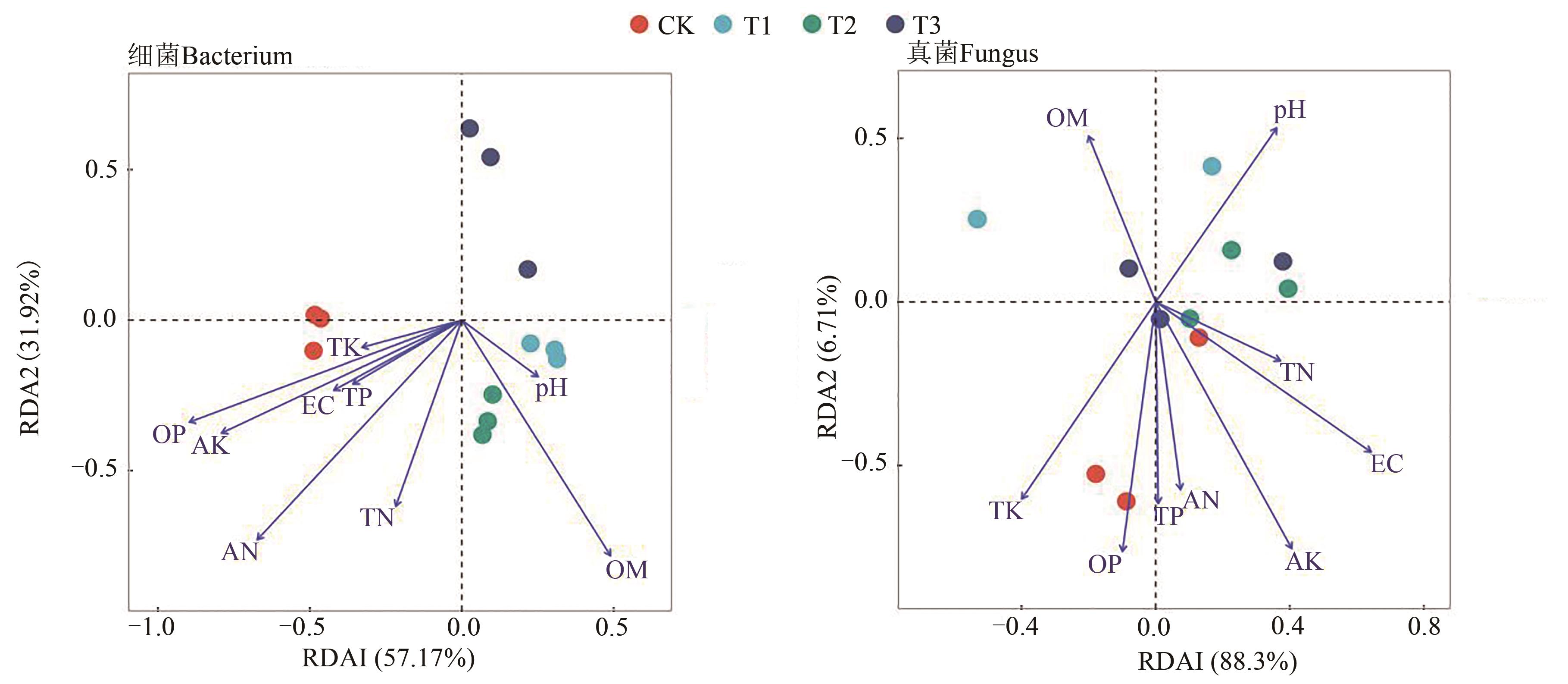
图7 土壤环境因子与微生物群落组成的RDA分析注:TN—全氮含量;TK—全钾含量;TP—全磷含量;AN—碱解氮;OP—有效磷;AK—速效钾;OM—有机质;EC—电导率。
Fig. 7 RDA analysis of soil environmental factors and microbial community compositionNote: TN—Total nitrogen content; TK—Total potassium content; TK—Total potassium content; TP—Total phosphorus content; AN—Alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen; OP—Available phosphorus; AK—Available potassium; OM—Organic matter; EC—Electric conductivity.
| 1 | 史静,张乃明,包立.我国设施农业土壤质量退化特征与调控研究进展[J].中国生态农业学报,2013,21(7):787-794. |
| SHI J, ZHANG N M, BAO L. Research progress on soil degradation and regulation of facility agriculture in China [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2013, 21(7):787-794. | |
| 2 | 刘霓红,蒋先平,程俊峰,等.国外有机设施园艺现状及对中国设施农业可持续发展的启示[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(15):1-9. |
| LIU N H, JIANG X P, CHENG J F, et al.. Current status of organic horticulture and its enlightenment to sustainable development of organic agriculture in China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2018, 34(15):1-9. | |
| 3 | 田恬,田永强,高丽红.设施菜田土壤质量研究进展[J].中国蔬菜,2021(10):35-44. |
| TIAN T, TIAN Y Q, GAO L H. Research progress on soil quality of protected vegetable fields [J]. China Veget., 2021(10):35-44. | |
| 4 | HEIKO N, ANDREA T, ANTJE W, et al.. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of bacterial community structure along different management types in German forest and grassland soils [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2017, 6(2):e17000 [2022-09-20]. . |
| 5 | 田永强,王敬国,高丽红.设施菜田土壤微生物学障碍研究进展[J].中国蔬菜,2013(20):1-9. |
| TIAN Y Q, WANG J G, GAO L H. Research progress on vegetable soil microbial obstacles in protected cropping systems [J]. China Veget., 2013(20):1-9. | |
| 6 | 武兴友.微生物菌肥对农业生产的影响及研究趋势分析[J].中国果菜,2018,38(4):9-11, 15. |
| WU X Y. Analysis of the effect on microbial fertilizer on agricultural production and research trends [J]. China Fruit Veget., 2018, 38(4):9-11, 15. | |
| 7 | 王赫,李晓雪,王亚玲,等.化肥减量配施有机肥和菌剂对辣椒产量、品质和养分累积的影响[J].北方园艺,2021(16):1-7. |
| WANG H, LI X X, WANG Y L, et al.. Efects of reduced chemical fertilizer combined application of organic fertilizers and microbial inoculants on yield,quality and nutrient acumulation in chili pepper [J]. Northern Hortic., 2021(16):1-7. | |
| 8 | 邱敬萍,黄艳霞,王超,等.EG03菌剂对辣椒青枯病的防治效果及对根围土壤微生物群落的影响[J].应用生态学报,2014,25(5):1468-1474. |
| QIU J P, HUANG Y X, WANG C, et al.. Effects of bacterial consortium EG03 on control of pepper bacterial wilt and rhizosphere microbial community characteristics in fields [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2014, 25(5):1468-1474. | |
| 9 | 仝倩倩,祝英,崔得领,等.我国微生物肥料发展现状及在蔬菜生产中的应用[J].中国土壤与肥料,2022(4):259-266. |
| TONG Q Q, ZHU Y, CUI D L, et al.. The development status of microbial fertilizer in China and its application in vegetable planting [J]. China Soil Fert., 2022(4):259-266. | |
| 10 | 杨志刚,叶英杰,常海文,等.微生物菌肥及土壤修复剂对干制辣椒生长、品质及产量的影响[J].北方园艺,2020(19):1-7. |
| YANG Z G, YE Y J, CHANG H W, et al.. Efects of microbial fertilizer and soil amendment on the growth, quality and yield of dry pepper [J]. Northern Hortic., 2020(19):1-7. | |
| 11 | 王继芳,张赢心,李祥云,等.微生物菌剂与玉米秸秆配比对番茄产量、品质及生产效益的影响[J].青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,38(3):218-223. |
| WANG J F, ZHANG Y X, LI X Y, et al.. Effects of microbial agent and corn stalk ratio on yield, quality and efficiency of tomato [J]. J. Qingdao Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 38(3):218-223. | |
| 12 | 王君正,张琪,高子星,等.两种微生物菌剂对有机基质袋培秋黄瓜产量、品质及根际环境的影响[J].中国农业科学,2021,54(14):3077-3087. |
| WANG J Z, ZHANG Q, GAO Z X, et al.. Effects of two microbial agents on yield, quality and rhizosphere environment of autumn cucumber cultured in organic substrate [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2021, 54(14):3077-3087. | |
| 13 | 马凤捷,蔡立群,刘垠霖,等.不同微生物菌剂处理对哈密瓜品质及土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2021(2):69-77. |
| MA F J, CAI L Q, LIU Y L, et al.. Effects of different microbial inoculants on the quality of cantaloupe and soil nutrients and enzyme activities [J]. China Soil Fert., 2021(2):69-77. | |
| 14 | 李凤霞,赵营.氮肥减量配施微生物菌剂对灌淤土花椰菜产量及土壤微生物的影响[J].水土保持研究,2017,24(2):94-100. |
| LI F X, ZHAO Y. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer reduction with microbial inoculants on brocoli production and the influence of the soil microbial characteristics [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 24(2):94-100. | |
| 15 | 马慧媛,黄媛媛,刘胜尧,等.微生物菌剂施用对设施茄子根际土壤养分和细菌群落多样性的影响[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(1):140-150. |
| MA H Y, HUANG Y Y, LIU S Y, et al.. Effects of microbial agents on nutrient and bacterial community diversity in rhizosphere soil of eggplant cultivated in facilities [J]. Microbiology, 2020, 47(1):140-150. | |
| 16 | 张绪美,曹亚茹,沈文忠,等.微生物肥对设施土壤次生盐渍化和番茄生产的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2019(5):119-126. |
| ZHANG X M, CAO Y R, SHEN W Z, et al.. Effects of microbial fertilizer on soil secondary salinization and tomato production in protected cultivation [J]. China Soil Fert., 2019(5):119-126. | |
| 17 | 王亚文,史慧芳,张鹏,等.微生物菌肥在设施蔬菜生产中的研究进展[J].农学学报,2021,11(11):27-32. |
| WANG Y W, SHI H F, ZHANG P, et al.. Research progress of microbial fertilizer in facility vegetable production [J]. J. Agric., 2021, 11(11):27-32. | |
| 18 | 杨剑虹,王成林,代亨林.土壤农化分析与环境监测[M].北京:中国大地出版社,2008:27-90. |
| 19 | 黄绍文,唐继伟,李春花,等.我国蔬菜化肥减施潜力与科学施用对策[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(6):1480-1493. |
| HUANG S W, TANG J W, LI C H, et al.. Reducing potential of chemical fertilizers and scientific fertilization countermeasure in vegetable production in China [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2017, 23(6):1480-1493. | |
| 20 | 孙猛,徐媛,刘茂辉,等.天津市农田氮肥施用氨排放量估算及分布特征分析[J].中国生态农业学报,2016,24(10):1364-1370. |
| SUN M, XU Y, LIU M H, et al.. Emission and distribution characteristics of ammonia from nitrogen application in farmland of Tianjin [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2016, 24(10):1364-1370. | |
| 21 | 周丽平,赵秋,宁晓光,等.绿肥对设施青椒产量品质及土壤理化性状的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2022(2):65-71. |
| ZHOU L P, ZHAO Q, NING X G, et al.. Effects of green manure on yield and quality of green pepper and soil physical and chemical properties in greenhouse [J]. China Soil Fert., 2022(2):65-71. | |
| 22 | 黄文,郭竞,刘慧超,等.不同微生物菌剂对番茄产量及品质的影响[J].中国瓜菜,2022,35(8):75-78. |
| HUANG W, GUO J, LIU H C, et al.. Different microbial agents affect tomato yield and quality [J]. China Cucurbit Veget., 2022, 35(8):75-78. | |
| 23 | 郭成瑾,陈杭,王喜刚,等.育苗基质添加复配微生物菌剂对番茄生长及根腐病发生的影响[J].北方园艺,2022(16):52-57. |
| GOU C J, CHEN H, WANG X G, et al.. Effects of compound microbial agent added to seedling substrate on tomato growth and root rot occurrence [J]. Northern Hortic., 2022(16):52-57. | |
| 24 | 王剑,连瑛,王笑,等.有机肥配施微生物菌剂对草莓生长和土壤肥力的影响[J].浙江农业科学,2021,62(11):2197-2200. |
| WANG J, LIAN Y, WANG X, et al.. Effects of combination of organic fertilizer and microbial agent on strawberry growth and soil fertility [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2021, 62(11):2197-2200. | |
| 25 | 马阳,郑卫红,张培,等.不同调控措施对甜瓜土壤性质、细菌多样性和产量的影响[J].河北农业大学学报,2022,45(1):48-54. |
| MA Y, ZHENG W H, ZHANG P, et al.. Effects of different control measures on soil properties, bacterial diversity and yield of muskmelon [J]. J. Hebei Agric. Univ., 2022, 45(1):48-54. | |
| 26 | 宋晓,陈莉,李建芬,等.增施微生物菌剂对设施土壤理化性质及微生物的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2021,49(21):169-171. |
| SONG X, CHEN L, LI J F, et al.. Effects of microbial agents on physical and chemical properties and microbial biomass of greenhouse soil [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2021, 49(21):169-171. | |
| 27 | 常芳娟,张贵云,张丽萍,等.生物熏蒸配施微生物菌剂对西瓜连作土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2022,30(2):248-257. |
| CHANG F J, ZHANG G Y, ZHANG L P, et al.. Effects of biological fumigation combined with microbial agents on fungi com-munity structure in continuous watermelon cropping soil [J]. China J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30(2):248-257. | |
| 28 | 丁新景,黄雅丽,敬如岩,等.基于高通量测序的黄河三角洲4种人工林土壤细菌结构及多样性研究[J].生态学报,2018,38(16):5857-5864. |
| DING X J, HUANG Y L, JING R Y, et al.. Bacterial structure and diversity of four plantations in the Yellow River Delta by high-throughput sequencing [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2018, 38(16):5857-5864. | |
| 29 | 李金花,高克祥,万利,等.微生物菌剂对楸树幼苗生长及根际土细菌群落结构的影响[J].生态学报,2020,40(21):7588-7601. |
| LI J H, GAO K X, WAN L, et al.. Effects of microbial agent on the growth of Catalpa bungei seedlings and the diversity of bacterial community in rhizosphere soil [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2020, 40(21):7588-7601. | |
| 30 | 魏艳丽,李红梅,扈进冬,等.臭氧水与生防菌剂组合应用对番茄根结线虫及根际微生物群落的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50(12):121-127. |
| WEI Y L, LI H M, HU J D, et al.. Impacts of combined application of ozonated water and microbial agents on tomato root-knot nematodes and rhizosphere microbial community [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2022, 50(12):121-127. | |
| 31 | 张艳敏.云南省部分观赏植物叶面病原真菌的多样性调查和系统学研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2012. |
| ZHANG Y M. Diversity survey and phylogenetic study on foliar pathogenic fungi of some ornamental plants of Yunnan [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2012. | |
| 32 | 杨永,张学军,李寐华,等.微生物肥料对设施长期连作哈密瓜根际土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J].应用与环境生物学报,2018,24(1):68-74. |
| YANG Y, ZHANG X J, LI M H, et al.. Effects of microbiological fertilizer on rhizosphere soil fungus communities under long-term continuous cropping of protected Hami melon [J]. China J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2018, 24(1):68-74. |
| [1] | 谭施北, MKAPA Dietram Samson, 李升林, 习金根, 吴伟怀, 陈河龙, 黄兴, 梁艳琼, 易克贤, 郑金龙. 添加菌剂和石灰对剑麻渣腐解及养分含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 204-214. |
| [2] | 寇威, 刘佳月, 户可欣, 高铱遥, 许世奇, 何彦臻, 王旭东. 有机肥与鼠李糖脂和氯化胆碱配施对盐渍土性质和番茄耐盐性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 202-214. |
| [3] | 肖淑婷, 颜安. 天山典型天然林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 227-238. |
| [4] | 姜明君, 范燕敏, 武红旗, 张浩, 刘卓, 王德俊. 基于机器学习的加工番茄叶绿素相对含量遥感反演研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 89-99. |
| [5] | 王亚鑫, 吕洋成, 王文琦, 刘琦, 杨杰, 任桂鸿, 张吴平, 李富忠. 番茄植株生长过程中茎叶表型的无损分割与提取[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 90-100. |
| [6] | 王会来, 李帅, 王寅, 吴东涛, 马嘉伟, 叶正钱, 池永清, 王美. 长期施肥对葡萄土壤细菌群落多样性及ARGs分布的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 229-239. |
| [7] | 蓝江林, 肖荣凤, 王阶平, 张海峰, 刘波. 整合微生物组菌剂对番茄植株生长及根际细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 173-181. |
| [8] | 罗金城, 朱晓林, 魏小红, 王贤, 王宝强, 杜雪芬. 番茄黄化曲叶病毒胁迫下外源NO对番茄抗氧化物酶基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 125-135. |
| [9] | 米春娇, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 张砚迪. 我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标和推荐施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [10] | 熊橙梁, 张庆富, 姚未远, 夏滔, 许庆平, 周喜新, 张毅, 陈丽鹃, 杨柳. 添加不同类型水稻秸秆对植烟连作土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 233-240. |
| [11] | 李贤国, 戴麒, 王泽鹏, 陈兆龙, 闫会转, 李宁. 番茄CCCH类锌指蛋白家族的鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [12] | 王吉平, 卢铁东, 梁芷姮, 张野, 苏天明, 何铁光. 不同来源微生物对葡萄枝条猪粪共堆肥过程的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 224-233. |
| [13] | 张俊蕾, 盖晓彤, 赵正婷, 刘弟, 王金凤, 姜宁, 刘雅婷. 烟草番茄斑萎病毒RT-LAMP检测体系的建立及优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [14] | 张继东, 张亚雄, 程伟, 蒲莉, 柳路行, 王亚明. 生物质炭和有机肥配施对苹果重茬育苗地土壤理化性质和微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 213-222. |
| [15] | 张福林, 奚瑞, 刘宇翔, 陈兆龙, 余庆辉, 李宁. 番茄BURP结构域基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||