




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 238-249.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0292
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Jing FANG1( ), Chunshuo LIU1, Rui LIU1, Zhefeng XU1, Yuqiu CHEN3, Weichen QI2, Changbao CHEN1(
), Chunshuo LIU1, Rui LIU1, Zhefeng XU1, Yuqiu CHEN3, Weichen QI2, Changbao CHEN1( ), Tao ZHANG1,2(
), Tao ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-04-12
Accepted:2024-07-19
Online:2025-10-15
Published:2025-10-15
Contact:
Changbao CHEN,Tao ZHANG
方晶1( ), 刘春铄1, 刘蕊1, 徐哲丰1, 陈雨秋3, 齐伟辰2, 陈长宝1(
), 刘春铄1, 刘蕊1, 徐哲丰1, 陈雨秋3, 齐伟辰2, 陈长宝1( ), 张涛1,2(
), 张涛1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
陈长宝,张涛
作者简介:方晶 E-mail:835506940@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jing FANG, Chunshuo LIU, Rui LIU, Zhefeng XU, Yuqiu CHEN, Weichen QI, Changbao CHEN, Tao ZHANG. Effect of Exogenous Phosphorus Regulation on Saponins Content and Inter-root Soil of Cultivated Ginseng[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(10): 238-249.
方晶, 刘春铄, 刘蕊, 徐哲丰, 陈雨秋, 齐伟辰, 陈长宝, 张涛. 外源磷对栽培人参皂苷含量及根际土壤的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(10): 238-249.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0292
时间 Time/min | 流动相A Fluid phase A/% | 流动相B Fluid phase B/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0—18 | 19→23 | 81→77 |
| 18—28 | 23→28 | 77→72 |
| 28—30 | 28→32 | 72→68 |
| 30—50 | 32→34 | 68→66 |
| 50—70 | 34→80 | 66→20 |
Table 1 Gradient elution conditions
时间 Time/min | 流动相A Fluid phase A/% | 流动相B Fluid phase B/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0—18 | 19→23 | 81→77 |
| 18—28 | 23→28 | 77→72 |
| 28—30 | 28→32 | 72→68 |
| 30—50 | 32→34 | 68→66 |
| 50—70 | 34→80 | 66→20 |
人参皂苷 Ginsenoside | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数 R2 | 含量线性范围 Linear range of content/mg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ro | y=214 055x+26.759 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rg1 | y=223 076x+23.105 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Re | y=220 380x+10.868 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rf | y=306 357x+62.417 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rb1 | y=155 839x+1.099 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rc | y=181 626x-10.791 | 0.999 9 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
| Rb2 | y=217 709x-2.963 | 0.999 8 | 0.000 9~0.018 0 |
| Rb3 | y=203 643x-2.797 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rd | y=212 073x+1.318 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rh2 | y=152 219x+9.985 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 3~0.026 0 |
| Rg3 | y=509 071x+44.312 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
总皂苷 Total saponins | y=1.939 7x+0.144 | 0.999 7 | 0.100 0~1.000 4 |
Table 2 Regression equations of ginsenosides
人参皂苷 Ginsenoside | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数 R2 | 含量线性范围 Linear range of content/mg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ro | y=214 055x+26.759 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rg1 | y=223 076x+23.105 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Re | y=220 380x+10.868 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rf | y=306 357x+62.417 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rb1 | y=155 839x+1.099 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rc | y=181 626x-10.791 | 0.999 9 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
| Rb2 | y=217 709x-2.963 | 0.999 8 | 0.000 9~0.018 0 |
| Rb3 | y=203 643x-2.797 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rd | y=212 073x+1.318 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rh2 | y=152 219x+9.985 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 3~0.026 0 |
| Rg3 | y=509 071x+44.312 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
总皂苷 Total saponins | y=1.939 7x+0.144 | 0.999 7 | 0.100 0~1.000 4 |

Fig. 2 Contents of ginsenoside under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
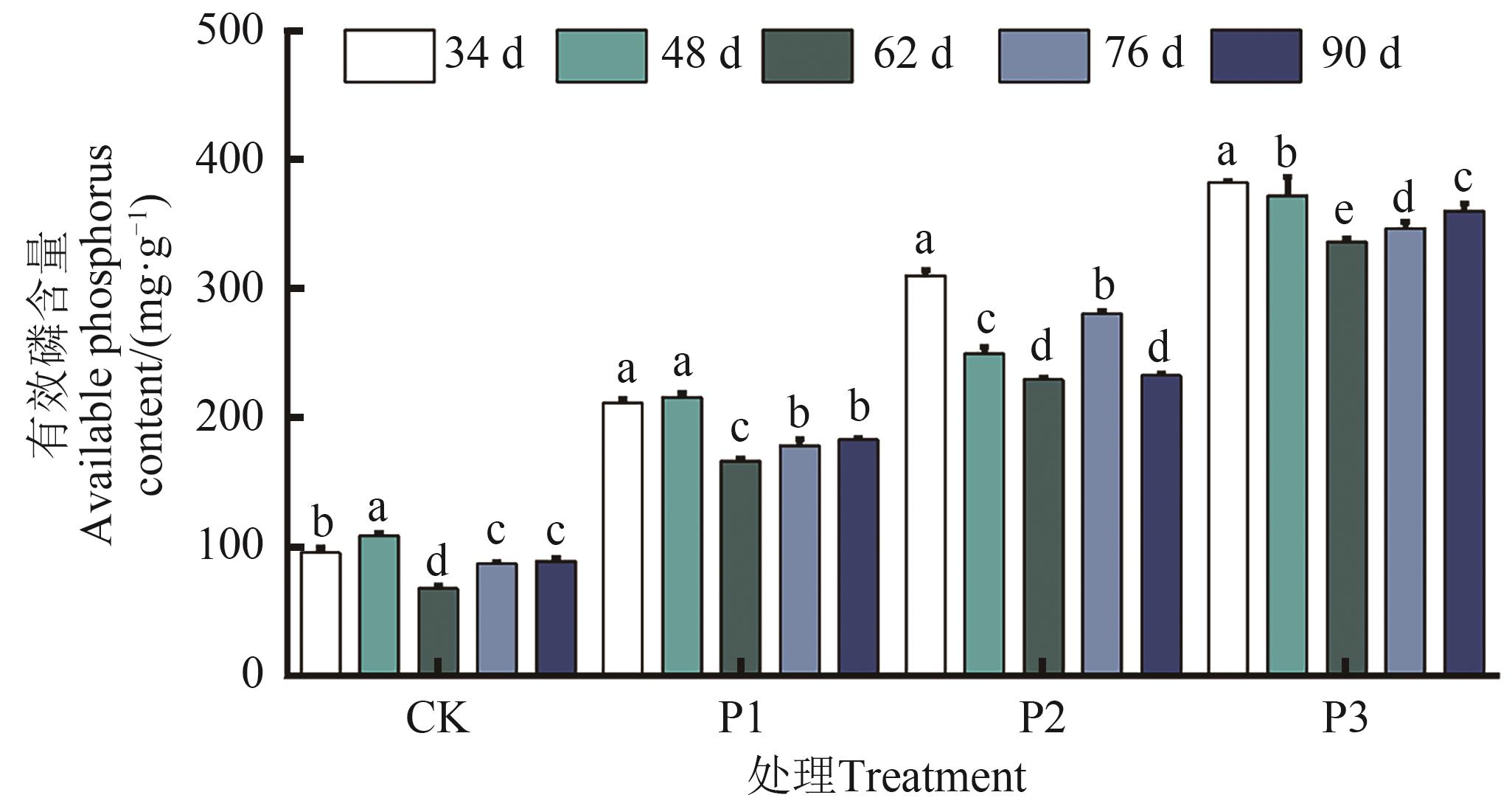
Fig. 3 Available phosphorus content in soil under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
移栽后时间 Time after planting/d | 处理 Treatment | pH | 电导率 Electric conductivity/(μS·cm-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | CK | 5.30±0.00 d | 37.53±9.04 d | 45.97±4.76 d | 167.42±0.08 d | 26.40±0.35 c |
| P1 | 5.55±0.01 c | 123.67±6.81 c | 79.57±5.30 c | 194.60±0.06 c | 25.34±0.39 c | |
| P2 | 5.69±0.00 b | 152.23±3.22 a | 92.63±4.28 b | 238.88±0.13 a | 30.09±0.23 b | |
| P3 | 5.95±0.01 a | 138.67±5.03 b | 103.13±3.86 a | 222.34±0.07 b | 47.21±1.84 a | |
| 48 | CK | 4.93±0.01 d | 44.33±8.33 d | 39.43±2.91 d | 167.84±0.1 d | 28.36±0.57 d |
| P1 | 5.48±0.00 b | 153.33±8.50 c | 85.40±0.70 c | 175.27±0.06 c | 30.85±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.53±0.00 a | 189.00±6.24 a | 96.37±1.46 b | 216.21±0.07 a | 35.37±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.28±0.01 c | 164.67±9.07 b | 107.57±2.14 a | 181.49±0.07 b | 39.82±0.78 a | |
| 62 | CK | 5.14±0.00 d | 59.67±15.95 d | 40.37±0.40 d | 176.19±0.07 c | 31.6±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.17±0.01 c | 196.33±17.79 b | 87.03±2.65 c | 217.82±0.08 b | 34.99±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.35±0.01 b | 344.67±20.21 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 237.08±0.07 a | 39.52±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.85±0.00 a | 175.67±9.24 c | 111.07±1.46 a | 216.95±0.33 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 76 | CK | 4.85±0.01 d | 45.33±9.29 d | 41.53±1.07 d | 179.04±0.04 d | 29.64±0.60 d |
| P1 | 5.34±0.01 c | 269.67±5.51 c | 91.47±2.14 c | 206.76±0.01 b | 32.73±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.70±0.02 b | 342.33±14.57 a | 102.67±2.46 b | 227.04±0.15 a | 37.26±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 6.09±0.01 a | 299.00±9.54 b | 113.63±1.46 a | 207.52±0.03 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 90 | CK | 4.82±0.03 d | 58.00±5.89 d | 42.47±1.46 c | 183.63±0.08 d | 28.58±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.27±0.00 c | 197.67±6.55 b | 92.87±1.07 b | 201.70±0.06 b | 37.26±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.92±0.00 b | 200.67±11.61 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 208.38±0.08 a | 42.53±0.00 b | |
| P3 | 6.21±0.01 a | 143.67±5.73 c | 115.73±1.07 a | 193.30±0.08 c | 45.17±0.65 a |
Table 3 Physicochemical parameter of rhizosphere soil under different treatments
移栽后时间 Time after planting/d | 处理 Treatment | pH | 电导率 Electric conductivity/(μS·cm-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | CK | 5.30±0.00 d | 37.53±9.04 d | 45.97±4.76 d | 167.42±0.08 d | 26.40±0.35 c |
| P1 | 5.55±0.01 c | 123.67±6.81 c | 79.57±5.30 c | 194.60±0.06 c | 25.34±0.39 c | |
| P2 | 5.69±0.00 b | 152.23±3.22 a | 92.63±4.28 b | 238.88±0.13 a | 30.09±0.23 b | |
| P3 | 5.95±0.01 a | 138.67±5.03 b | 103.13±3.86 a | 222.34±0.07 b | 47.21±1.84 a | |
| 48 | CK | 4.93±0.01 d | 44.33±8.33 d | 39.43±2.91 d | 167.84±0.1 d | 28.36±0.57 d |
| P1 | 5.48±0.00 b | 153.33±8.50 c | 85.40±0.70 c | 175.27±0.06 c | 30.85±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.53±0.00 a | 189.00±6.24 a | 96.37±1.46 b | 216.21±0.07 a | 35.37±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.28±0.01 c | 164.67±9.07 b | 107.57±2.14 a | 181.49±0.07 b | 39.82±0.78 a | |
| 62 | CK | 5.14±0.00 d | 59.67±15.95 d | 40.37±0.40 d | 176.19±0.07 c | 31.6±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.17±0.01 c | 196.33±17.79 b | 87.03±2.65 c | 217.82±0.08 b | 34.99±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.35±0.01 b | 344.67±20.21 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 237.08±0.07 a | 39.52±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.85±0.00 a | 175.67±9.24 c | 111.07±1.46 a | 216.95±0.33 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 76 | CK | 4.85±0.01 d | 45.33±9.29 d | 41.53±1.07 d | 179.04±0.04 d | 29.64±0.60 d |
| P1 | 5.34±0.01 c | 269.67±5.51 c | 91.47±2.14 c | 206.76±0.01 b | 32.73±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.70±0.02 b | 342.33±14.57 a | 102.67±2.46 b | 227.04±0.15 a | 37.26±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 6.09±0.01 a | 299.00±9.54 b | 113.63±1.46 a | 207.52±0.03 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 90 | CK | 4.82±0.03 d | 58.00±5.89 d | 42.47±1.46 c | 183.63±0.08 d | 28.58±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.27±0.00 c | 197.67±6.55 b | 92.87±1.07 b | 201.70±0.06 b | 37.26±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.92±0.00 b | 200.67±11.61 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 208.38±0.08 a | 42.53±0.00 b | |
| P3 | 6.21±0.01 a | 143.67±5.73 c | 115.73±1.07 a | 193.30±0.08 c | 45.17±0.65 a |

Fig. 4 Soil enzyme activity under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.
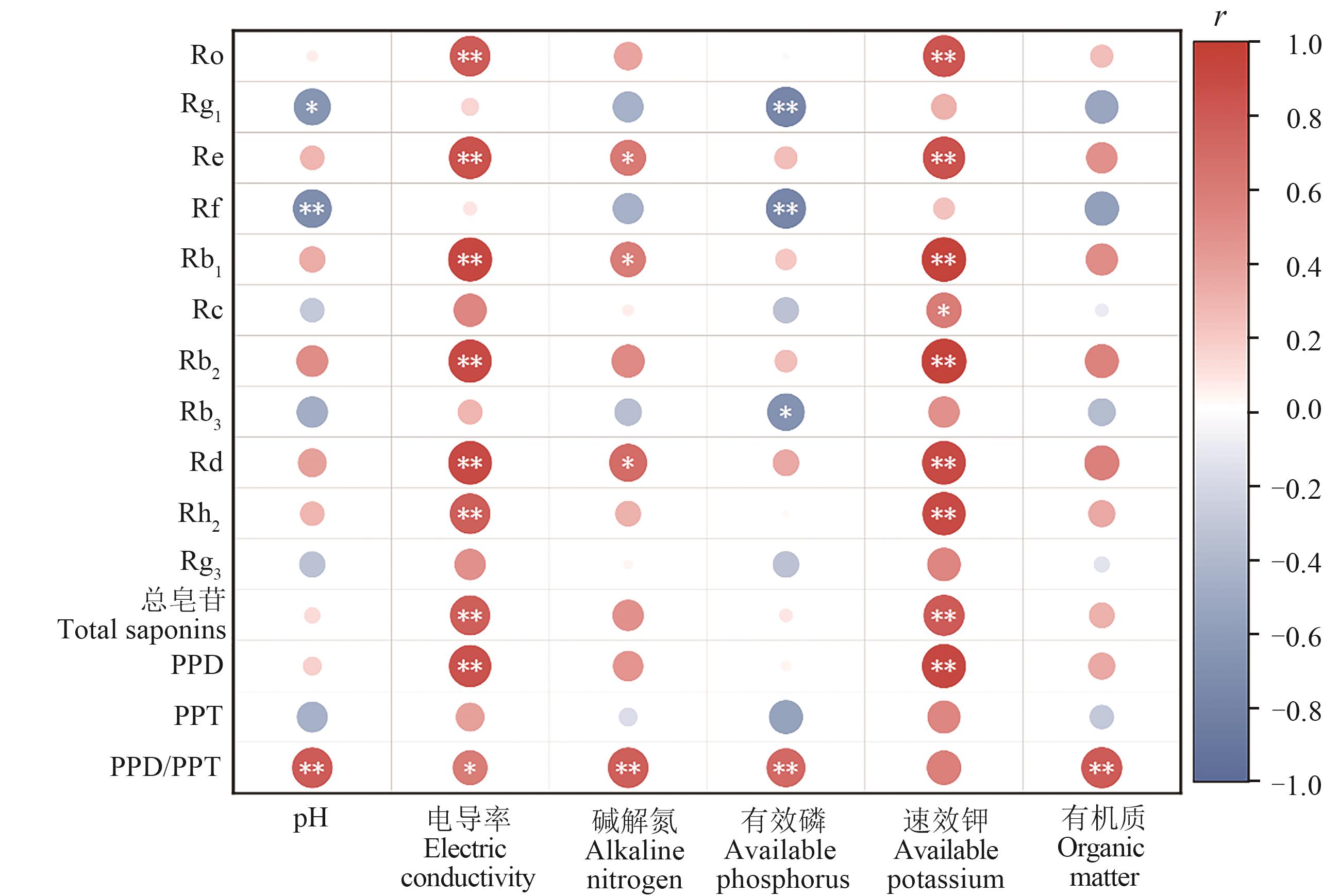
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis between ginsenoside content and soil physicochemical parameterNote:* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
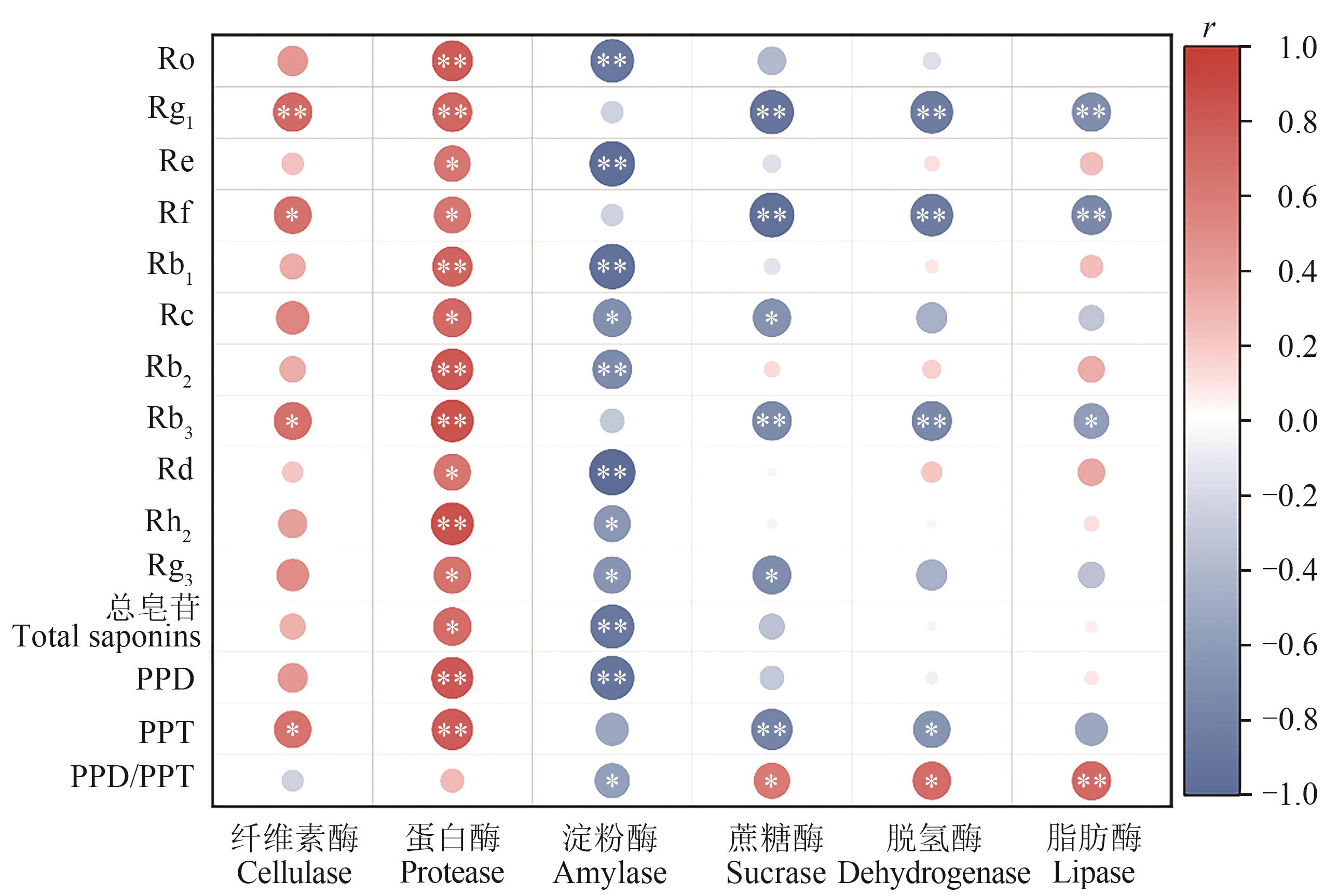
Fig. 6 Correlation analysis between ginsenoside content and soil enzymeNote:* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
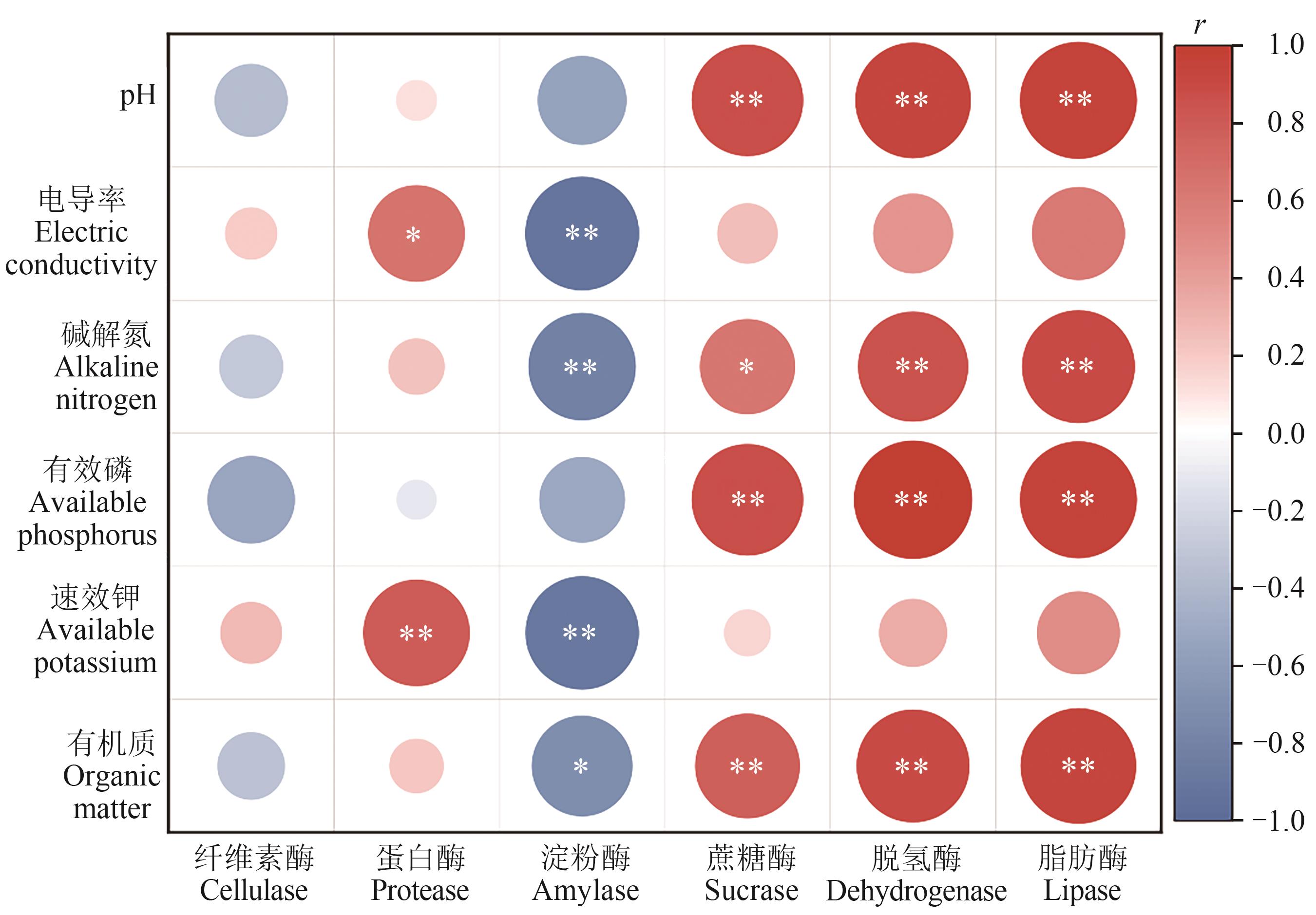
Fig. 7 Correlation analysis between soil physicochemical parameter and soil enzymeNote:* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
指标 Index | 载荷值Loading value | 得分Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | |
| x1:Rb1 | 0.988 | -0.143 | 0.155 | -0.011 |
| x2:Rg1 | 0.574 | 0.814 | -0.205 | 0.477 |
| x3:Re | 0.950 | -0.173 | 0.160 | -0.030 |
| x4:PPD | 0.998 | 0.022 | 0.101 | 0.079 |
| x5:PPT | 0.780 | 0.613 | -0.117 | 0.382 |
x6:总皂苷 Total saponins | 0.949 | -0.001 | 0.104 | 0.063 |
x7:电导率 Electric conductivity | 0.865 | -0.433 | 0.237 | -0.176 |
x8:速效钾 Available potassium | 0.920 | -0.266 | 0.188 | -0.082 |
x9:蛋白酶 Protease | 0.825 | 0.337 | -0.021 | 0.237 |
x10:淀粉酶 Amaylase | -0.917 | 0.349 | -0.215 | 0.127 |
特征值 Eigenvalue | 7.924 | 1.548 | — | — |
贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 15.482 | — | — |
累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 94.726 | — | — |
Table 4 Loadings matrix and score coefficient matrix for each principal component
指标 Index | 载荷值Loading value | 得分Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | |
| x1:Rb1 | 0.988 | -0.143 | 0.155 | -0.011 |
| x2:Rg1 | 0.574 | 0.814 | -0.205 | 0.477 |
| x3:Re | 0.950 | -0.173 | 0.160 | -0.030 |
| x4:PPD | 0.998 | 0.022 | 0.101 | 0.079 |
| x5:PPT | 0.780 | 0.613 | -0.117 | 0.382 |
x6:总皂苷 Total saponins | 0.949 | -0.001 | 0.104 | 0.063 |
x7:电导率 Electric conductivity | 0.865 | -0.433 | 0.237 | -0.176 |
x8:速效钾 Available potassium | 0.920 | -0.266 | 0.188 | -0.082 |
x9:蛋白酶 Protease | 0.825 | 0.337 | -0.021 | 0.237 |
x10:淀粉酶 Amaylase | -0.917 | 0.349 | -0.215 | 0.127 |
特征值 Eigenvalue | 7.924 | 1.548 | — | — |
贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 15.482 | — | — |
累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 94.726 | — | — |
| 处理Treatment | FPC1 | FPC2 | F | 排序Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 31.65 | 10.91 | 28.26 | 4 |
| P1 | 79.46 | -12.32 | 64.46 | 1 |
| P2 | 78.61 | -13.61 | 63.54 | 2 |
| P3 | 59.49 | -9.04 | 48.29 | 3 |
Table 5 Principal component scores of different treatments
| 处理Treatment | FPC1 | FPC2 | F | 排序Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 31.65 | 10.91 | 28.26 | 4 |
| P1 | 79.46 | -12.32 | 64.46 | 1 |
| P2 | 78.61 | -13.61 | 63.54 | 2 |
| P3 | 59.49 | -9.04 | 48.29 | 3 |
| [1] | YANG L, CHEN J J, SHENG-XIAN TEO B, et al.. Research progress on the antitumor molecular mechanism of ginsenoside Rh2 [J]. Am. J. Chin. Med., 2024, 52(1): 217-230. |
| [2] | IM D S. Pro-resolving effect of ginsenosides as an anti-inflammatory mechanism of Panax ginseng [J/OL].Biomolecules, 2020, 10(3): E444 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [3] | TIAN T T, KO C N, LUO W Y, et al.. The anti-aging mechanism of ginsenosides with medicine and food homology [J]. Food Funct., 2023, 14(20): 9123-9136. |
| [4] | 谢丽娟,苑冰冰,李健豪,等.人参皂苷结构修饰的研究进展[J].人参研究,2019,31:57-60. |
| XIE L J, YUAN B B, LI J H, et al.. Research progress of structural modification ginsenosides [J] Ginseng Res., 2019, 31:57-60. | |
| [5] | KIM D, KIM M, RAÑA G S, et al.. Seasonal variation and possible biosynthetic pathway of ginsenosides in Korean ginseng Panax ginseng Meyer [J/OL]. Molecules, 2018, 23(7): E1824 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [6] | 刘静婉,李琼,王恩鹏,等.人参栽培研究进展[J].应用化学,2022,39:1641-1651. |
| LIU J W, LI Q, WANG E P, et al.. Research progress on cultivation of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Chem., 2022, 39: 1641-1651. | |
| [7] | 闫宁,战宇,谢昊臻,等.不同改土方式对连作人参生长发育的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50(6):120-125. |
| [8] | 战宇,苗馨月,王二刚,等.灭菌方式对人参连作土壤养分及真菌群落结构的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(2):235-244. |
| [9] | LIU D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. |
| [10] | FENG G, GAI J, FENG X, et al.. Strategies for improving fertilizer phosphorus use efficiency in Chinese cropping systems [J]. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng., 2019, 6(4): 341-347. |
| [11] | 吕林,张亚玉.磷素营养对人参等植物生长及其品质影响的研究进展[J].特产研究, 2019, 41(1):115-119. |
| LYU L, ZHANG Y Y. Effects of phosphorus nutrition on yield and quality of Panax ginseng and other plants [J]. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res., 2019, 41(1): 115-119. | |
| [12] | 郜玉钢,郝建勋,臧埔,等.高效液相色谱法测定农田人参中9种人参皂苷单体含量[J].食品科学,2012,33(2):189-193. |
| GAO Y G, HAO J X, ZANG P, et al.. Content determination of 9 ginsenoside monomers in farmland ginseng by HPLC [J]. Food Sci., 2012, 33(2): 189-193. | |
| [13] | 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典一部:2020年版[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020:1-328. |
| [14] | 冯家,曹志强,仲伟同,等. 地理标志产品 吉林长白山人参: [S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2009. |
| [15] | 张涛.人参及其皂苷生物合成对低温的生理生态响应机制研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2019. |
| ZHANG T. Physiological and ecological response mechanism of Panax ginseng and its saponins biosynthesis to low temperature [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [16] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| [17] | 曹婷婷,刘春,范又维,等.不同氮素供应水平对微型盆栽月季生长发育的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2024,26(2):67-79. |
| CAO T T, LIU C, FAN Y W, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen supply level on plant growth and development in miniature potted rose [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2024, 26(2): 67-79. | |
| [18] | 王学民.应用多元分析[M].2版.上海:上海财经大学出版社,2004:1-410. |
| [19] | 张亚玉.不同生长环境下人参根区土壤肥力特性研究[D].沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2016. |
| ZHANG Y Y. Studies on root-zone fertility characteristics in different growth environments of Ginseng [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| [20] | DONG L, LI Y, XU J, et al..Biofertilizers regulate the soil microbial community and enhance Panax ginseng yields [J/OL]. Chin. Med., 2019, 14:20 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [21] | TONG Y L, SONG X P, ZHANG Y X, et al.. Insight on structural modification,biological activity,structure-activity relationship of PPD-type ginsenoside derivatives [J/OL].Fitoterapia, 2022, 158: 105135 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [22] | ZHANG T, HAN M, YANG L, et al.. The effects of environmental factors on ginsenoside biosynthetic enzyme gene expression and saponin abundance [J/OL]. Mol. (Basel Switz.), 2018, 24(1): E14 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [23] | ZHAO X, LYU Y, JIN K, et al.. Leaf phosphorus concentration regulates the development of cluster roots and exudation of carboxylates in Macadamia integrifolia [J/OL].Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11: 610591 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [24] | 赵雪淞,王力恒,骆世洪,等.人参根际土壤微生物群落结构与土壤环境因子的关系[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2023, 54(1):27-35. |
| ZHAO X S, WANG L H, LUO S H, et al.. Relationship between microbial community structure and environmental factors in ginseng rhizosphere soil [J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2023, 54(1):27-35. | |
| [25] | 杜欣,谢阿贵,方新月,等.不同参龄、坡向及根际土壤微生物对林下园参皂苷积累的影响[J].中国食品添加剂,2024,35(2):88-97. |
| DU X, XIE A G, FANG X Y, et al.. Effects of different ginseng ages, slope directions and rhizosphere soil microorganisms on the accumulation of ginsenosides in understory garden ginseng [J]. China Food Addit., 2024, 35(2): 88-97. | |
| [26] | 吴艾轩,王鑫,吕云,等.农田栽参土壤养分研究进展[J].北方园艺,2018(22):177-186. |
| WU A X, WANG X, LYU Y, et al.. Progress of soil nutrients of cultivation of Panax ginseng in farmland [J]. North. Hortic., 2018(22): 177-186. | |
| [27] | KALENDAR O V, KOSTIKOVA V A, KUKUSHKINA T A, et al.. Seasonal development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and their contents of biologically active and reserve substances in the forest-steppe zone of Western Siberia [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2023, 9(1):102 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [28] | LAN Y, ZHANG M, HAN M, et al.. Differences in the quality, yield, and soil microecology of ginseng in different planting environments [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2023, 9(4): 520 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [29] | 吕柏辰,孙海,钱佳奇,等.药用植物根系分泌物与根际微生物相互作用及其在中药材生态种植中的应用[J].中国中药杂志,2024,49(8):2128-2137. |
| LYU B C, SUN H, QIAN J Q, et al.. Interaction between root exudates of medicinal plants and rhizosphere microorganisms and its application in ecological planting of Chinese medicinal materials [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2024, 49(8):2128-2137. | |
| [30] | 吴怡,董炜华,李晓强,等.土壤酶活性对土壤环境变化的响应研究进展[J].南方农业,2023,17(15): 42-46, 52. |
| WU Y, DONG W H, LI X Q, et al.. Research progress on the response of soil enzyme activity to changes in soil environment [J]. South China Agric., 2023, 17(15): 42-46, 52. |
| [1] | Yi HU, Jie GONG, Wei ZHAO, Rong CHENG, Zhongyu LIU, Shiqing GAO, Yazhen YANG. Identification of PHY Gene Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)and Their Expression Analysis Under Heat Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 30-43. |
| [2] | Pengyang SHAO, Yuzhu SHA, Xiu LIU, Guoshun CHEN, Caiye ZHU, Jiqing WANG, Fanxiong WANG, Xiaowei CHEN, Wenxin YANG. Effects of Astragalus Feed Additive on Growth Performance, Serum Ig, Rumen Fermentation and Microbiota of Lambs [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 83-94. |
| [3] | Chunjiao MI, Hongren SUN, Jiping ZHANG, Yucai LYU, Yandi ZHANG. Abundance-deficiency Index of Soil Available Phosphorus and Recommended Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rates for Tomato in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [4] | Shifang WANG, Haiyan SONG. Study on Characteristics of Visible and Near Infrared Reflectance Spectra of Soil Organic Matter [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(7): 183-188. |
| [5] | Xiaoyu SHI, Lianqing JIAO, Min YU, Yixin TIAN, Anni JIAO, Yilin LUAN. Multidimensional Evaluation and Optimization of High Temperature Short Time Process of Astragalus membranaceus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(7): 223-233. |
| [6] | Erhao ZHANG, Panpan LIU, Ping HE, Yue JIAN, Yuting XU, Chengxin CHEN, Yazhou LU, Xiaozhong LAN, Sangmu SUOLANG. Physiochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Rhizosphere Soil of Dracocephalum tanguticum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [7] | Weijian ZHANG, Jingyi FENG, Yue LI, Wanying HE, Yanjing CHE, Ziying WANG, Xueyan BAI, Siyu GU. Effect of Endogenous and Exogenous Organic Matter on Phosphorus Adsorption and Availability in Black Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(11): 180-190. |
| [8] | Weiwei PEI, Zhe YANG, Yunying WANG, Xin WANG, Yangong DU. Carbon Sink Characteristics and Regulatory Factors of Qinghai Spruce Forests in the Qilian Mountains [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 226-233. |
| [9] | Ningning LU, Linyun CHEN, Taixin YANG, Shulin YANG, Guoku LIU. Correlation AnalysisBetweenFruit Formation and Endogenous Hormone Contents in Glehnia littoralis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 63-69. |
| [10] | Yingxuan JIA, Shulin ZHANG, Dajuan ZHANG, Wei DAI, Xiangdong BI. Effects of Phosphorus Recovery on Photosynthetic Pigments and Some Antioxidant Enzymes Activities of Phosphorus Starved Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 70-77. |
| [11] | Pengfei LIU, Xiaoshuang LU, Dilimurat Reheman, Tangnur Slay, Yanying QU, Quanjia CHEN, Xiaojuan DENG. Genetic Variation Analysis of Main Quality Traits and Agronomic Traits in Upland Cotton Seed [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 22-32. |
| [12] | Yulu WU, Jiaxin HU, Yuxi CHEN, Bingsong ZHENG, DaoLiang YAN. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [13] | Denglong CHEN, Yuxiang ZHANG, Jiajia SONG, Pengyu CHEN, Xiangzhen WEN, Yaling LI. Study of Volcanic Rock Deposition on the Running of Aquaponics [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 207-214. |
| [14] | Zhonghua MA, Juan CHEN, Na WU, Benju MAN, Xiaogang WANG, Yongqing ZHE, Jili LIU. Effects of Salt Stress and Phosphorus Supply on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Total Biomass of Switchgrass at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [15] | Zhixiong HOU, Changqing JING, Gongxin WANG, Wenzhang GUO, Weikang ZHAO. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Natural Grassland Vegetation Coverage and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors in Northern Xinjiang from 1998 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 140-151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号