




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 223-230.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0503
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Shuo ZHANG1( ), Yun FANG1, Zhishun LYU2, Luozhong TANG1(
), Yun FANG1, Zhishun LYU2, Luozhong TANG1( )
)
Received:2024-06-23
Accepted:2024-08-28
Online:2025-10-15
Published:2025-10-15
Contact:
Luozhong TANG
通讯作者:
唐罗忠
作者简介:张硕 E-mail:2574573069@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Shuo ZHANG, Yun FANG, Zhishun LYU, Luozhong TANG. Study on Microclimate Characteristics of Young-aged Poplar Agroforestry[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(10): 223-230.
张硕, 方云, 吕治顺, 唐罗忠. 杨树幼龄林复合经营系统小气候特征研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(10): 223-230.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0503
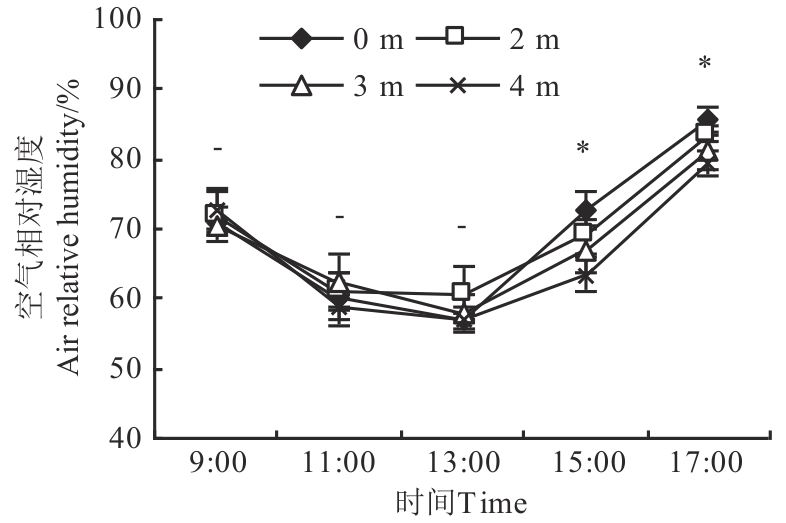
Fig. 4 Air relative humidity in different sites of plantationNote:- indicates no significant difference between different sites at P<0.05 level;* indicates significant difference between different sites at P<0.05 level.
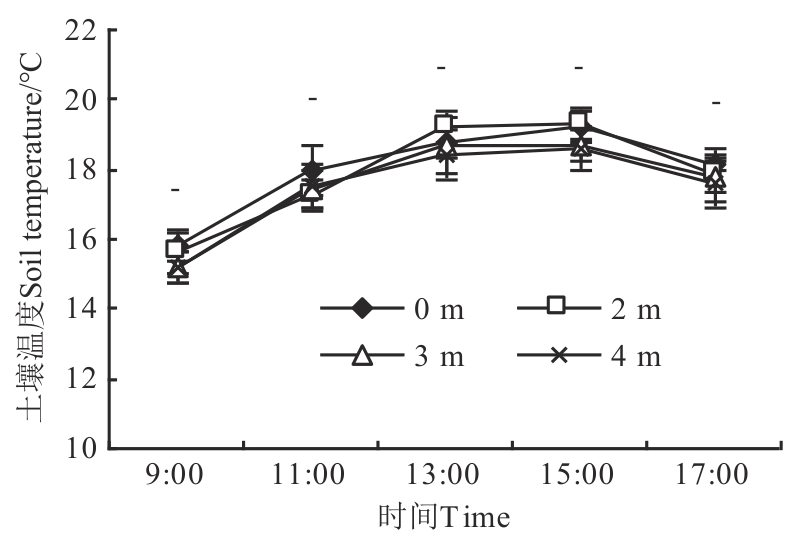
Fig. 6 Soil temperature at 5 cm depth in different sites of plantationNote:- indicates no significant difference between different sites at P<0.05 level.
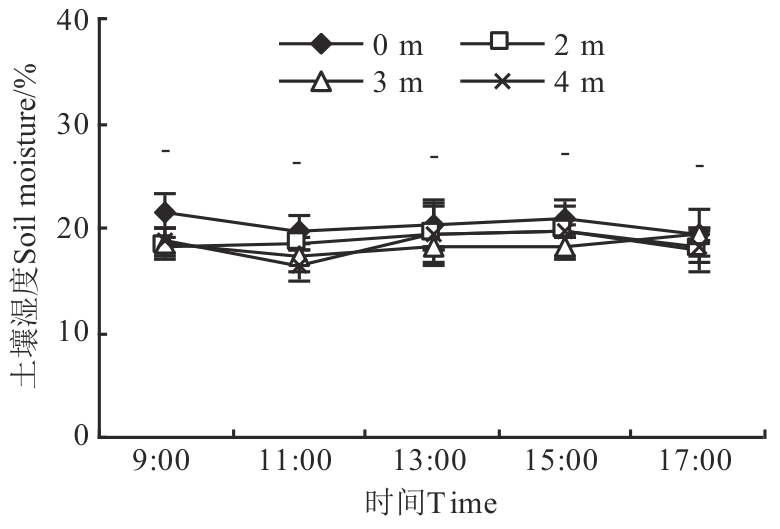
Fig. 7 Soil moisture at 5 cm depth in different sites of plantationNote:- indicates no significant difference between different sites at P<0.05 level.
因子 Factor | 光照强度 Light intensity | 气温 Air temperature | 空气相对湿度 Air relative humidity | 地表温度 Ground temperature | 5 cm深土壤温度 Soil temperature at 5 cm depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
气温 Air temperature | 0.666* | ||||
空气相对湿度 Air relative humidity | -0.869** | -0.838** | |||
地表温度 Ground temperature | 0.772** | 0.962** | -0.900** | ||
5 cm深土壤温度 Soil temperature at 5 cm depth | 0.035 | 0.657* | -0.240 | 0.485* | |
5 cm深土壤湿度 Soil moisture at 5 cm depth | -0.239 | 0.062 | 0.078 | 0.054 | 0.163 |
Table 1 Linear correlation analysis of different microclimate factors
因子 Factor | 光照强度 Light intensity | 气温 Air temperature | 空气相对湿度 Air relative humidity | 地表温度 Ground temperature | 5 cm深土壤温度 Soil temperature at 5 cm depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
气温 Air temperature | 0.666* | ||||
空气相对湿度 Air relative humidity | -0.869** | -0.838** | |||
地表温度 Ground temperature | 0.772** | 0.962** | -0.900** | ||
5 cm深土壤温度 Soil temperature at 5 cm depth | 0.035 | 0.657* | -0.240 | 0.485* | |
5 cm深土壤湿度 Soil moisture at 5 cm depth | -0.239 | 0.062 | 0.078 | 0.054 | 0.163 |
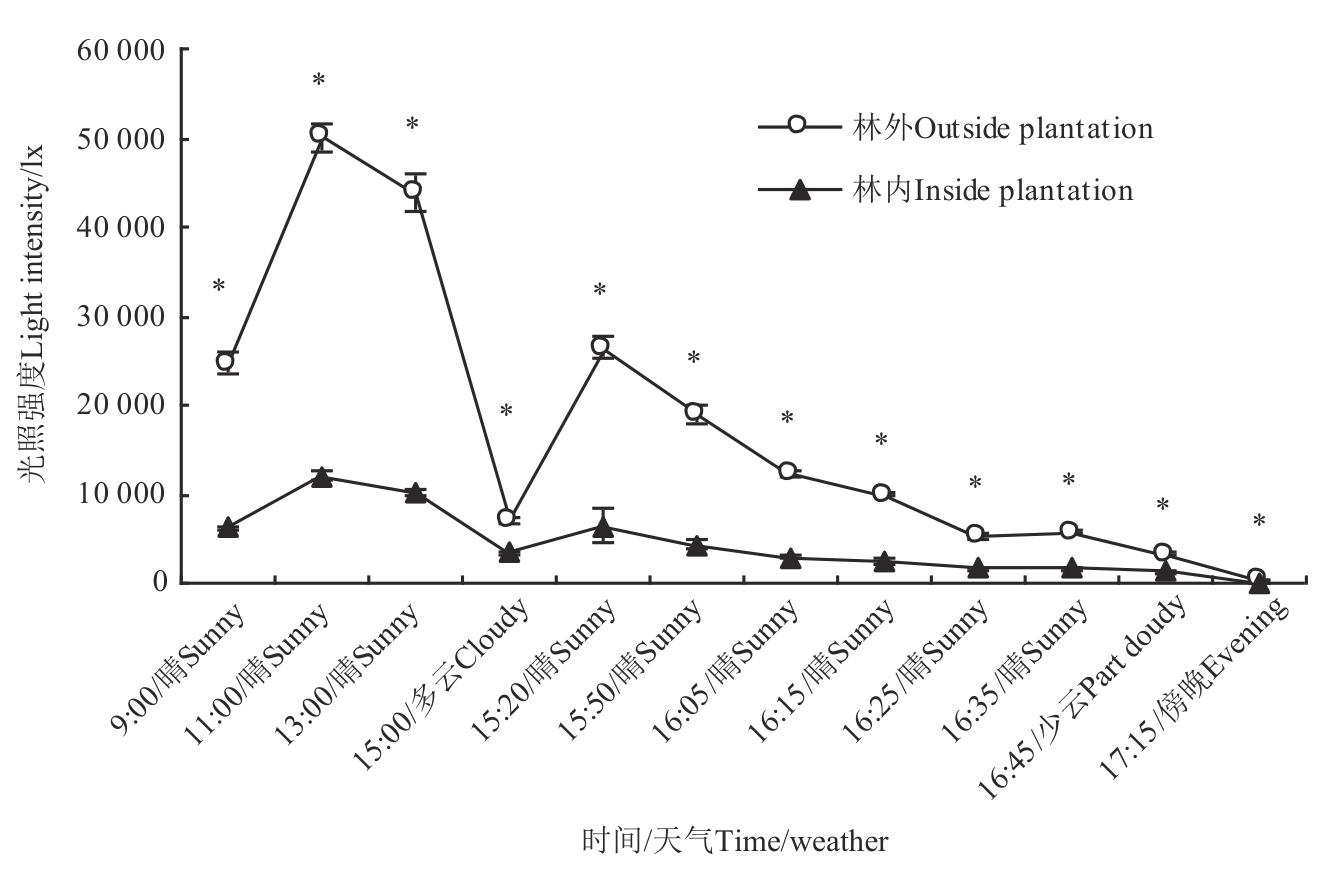
Fig. 8 Light intensity at outside plantation and inside plantationNote:* indicates significant difference between outside plantation and inside plantation at P<0.05 level.
| [1] | ATANGANA A, CHANG S, KHASA D, et al.. Tropical Agroforestry [M]. New York: Springer, 2014:151-172. |
| [2] | VRAHNAKIS M, NASIAKOU S, KAZOGLOU Y,et al..A conceptual business model for an agroforestry consulting company [J]. Agrofor. Syst., 2016, 90(2):219-236. |
| [3] | 李岩泉,何春霞.我国农林复合系统自然资源利用率研究进展[J].林业科学,2014,50(8):141-145. |
| LI Y Q, HE C X. Research progress of natural resource utilization in agroforestry system in China [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin.,2014, 50(8): 141-145. | |
| [4] | SÁNCHEZ I A, LASSALETTA L, MCCOLLIN D, et al.. The effect of hedgerow loss on microclimate in the Mediterranean Region:an investigation in central Spain [J]. Agrofor. Syst., 2010, 78(1):13-25. |
| [5] | 李亚男,许雪飞,许中旗,等.抚育间伐对燕山北部山地林内小气候的影响[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2015,35(11):121-127. |
| LI Y N, XU X F, XU Z Q, et al.. Effects of thinning on forest microclimate in northern region of Yanshan mountain [J]. J.Cent. South Univ. For. Technol., 2015, 35(11):121-127. | |
| [6] | 毛东雷, 蔡富艳, 赵枫, 等. 新疆和田吉亚乡新开垦地防护林小气候空间差异[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(4): 821-829. |
| MAO D L, CAI F Y, ZHAO F, et al.. Spatial difference of microclimate in shelterbelts in newly reclaimed land in Jiya town, Hotan city, Xinjiang [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2018, 35(4): 821-829. | |
| [7] | SILVA-PANDO F J, GONZÁLEZ-HERNÁNDEZ M P, ROZADOS-LORENZO M J.Pasture production in a silvopastoral system in relation with microclimate variables in the Atlantic coast of Spain [J]. Agrofor. Syst., 2002, 56(3):203-211. |
| [8] | PENG X, THEVATHASAN N V, GORDON A M, et al.. Photosynthetic response of soybean to microclimate in 26-year-old tree-based intercropping systems in southern Ontario,Canada [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6):e0129467 [2024-05-22]. . |
| [9] | 吴发启,刘秉正.黄土高原流域农林复合配置[M].郑州:黄河水利出版社,2003:73-81. |
| [10] | 王来, 高鹏翔, 刘滨, 等. 农林复合对近地面微气候环境的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(5): 21-25. |
| WANG L, GAO P X, LIU B, et al.. Effect of agroforestry on microclimate environment (near land surface) [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2017, 35(5):21-25. | |
| [11] | 张劲松,孟平,宋兆民,等.我国平原农区复合农林业小气候效应研究概述[J].中国农业气象,2004,25(3):52-55, 62. |
| ZHANG J S, MENG P, SONG Z M, et al.. An overview on micro-climatic effects of agro-forestry systems in plain agricultural areas in China [J]. Chin. J. Agrometeorol., 2004, 25(3):52-55, 62. | |
| [12] | YANG T, OUYANG X Y, WANG B, et al.. Understanding the effects of tree-crop intercropping systems on crop production in China by combining field experiments with a meta-analysis [J/OL]. Agric. Syst., 2023,210:103705 [2024-05-22]. . |
| [13] | 江苏省白马湖农场志编纂委员会. 白马湖农场志(1959—2009)[R]. 2009: 10-15. |
| [14] | 王颖, 袁玉欣, 魏红侠, 等. 杨粮间作系统小气候研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2001, 9(3): 40-42. |
| WANG Y, YUAN Y X, WEI H X, et al.. A study on microclimate under poplar-crop intercropping systems [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2001, 9(3):40-42. | |
| [15] | 袁玉欣,贾渝彬,邵吉祥,等.杨粮间作系统小气候水平分布特征研究[J].中国生态农业学报,2002,10(3):21-23. |
| YUAN Y X, JIA Y B, SHAO J X, et al.. A study on distribution law of microclimate factors in poplar-crop intercropping system [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2002, 10(3):21-23. | |
| [16] | 袁玉欣,王颖,裴保华,等.杨粮间作系统中林木遮荫作用研究[J].林业科学,2002,38(1):36-43. |
| YUAN Y X, WANG Y, PEI B H, et al.. The study on shading effect under poplar-crop intercropping system [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin., 2002, 38(1): 36-43. | |
| [17] | 盛海燕,李伟成.延胡索光合与生长可塑性对光照的响应[J].生态科学,2018,37(6):168-174. |
| SHENG H Y, LI W C. Responses of photosynthesis and growth plasticity of Corydalis yanhusuo to light [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2018, 37(6):168-174. | |
| [18] | 黄天忠, 曹国璠, 赵明书, 等. 不同种植模式对油茶林地小气候和土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(11): 2512-2518. |
| HUANG T Z, CAO G F, ZHAO M S, et al.. Effects of different planting patterns on microclimate indicators and soil nutrient contents in Camellia oleifera forest [J]. J. South Agric., 2019, 50(11): 2512-2518. | |
| [19] | 许华森,毕华兴,高路博,等.晋西黄土区苹果+大豆间作系统小气候及其对作物生产力的影响[J].中国水土保持科学,2014,12(2):9-15. |
| XU H S, BI H X, GAO L B, et al.. Microclimate and its effects on crop productivity in the Malus pumila and Glycine max intercropping systems on the Loess Plateau of West Shanxi province [J]. Sci. Soil Water Conserv., 2014,12(2):9-15. | |
| [20] | 蔡智才,毕华兴,许华森,等.晋西黄土区苹果花生间作系统小气候效应[J].干旱地区农业研究,2018,36(2):234-241. |
| CAI Z C, BI H X, XU H S, et al.. The microclimate effect of Malus pumila and Arachis hypogaea intercropping system in the Loess Plateau of West Shanxi province [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2018,36(2):234-241. | |
| [21] | 姜会飞.农业气象学[M].北京:科学出版社,2008:41-44. |
| [22] | 王倩,刘美伶,宗桦.夏季林盘对周围环境微气象的影响研究[J].生态科学,2021,40(4):139-148. |
| WANG Q, LIU M L, ZONG H. Micrometeorology influence of Linpan on its adjacent environment in summer [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2021, 40(4):139-148. | |
| [23] | BOUTTIER L, PAQUETTE A, MESSIER C, et al.. Vertical root separation and light interception in a temperate tree-based intercropping system of Eastern Canada [J]. Agrofor. Syst., 2014, 88(4): 693-706. |
| [24] | LEROY C, SABATIER S, WAHYUNI N S, et al.. Virtual trees and light capture:a method for optimizing agroforestry stand design [J]. Agrofor. Syst., 2009, 77(1):37-47. |
| [25] | 廖文超,毕华兴,高路博,等.苹果-大豆间作系统光照分布及其对作物的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2014,29(1):25-29. |
| LIAO W C, BI H X, GAO L B, et al.. Light distribution in apple-soybean intercropping and its impact on the crops [J]. J.Northwest For. Univ., 2014, 29(1):25-29. | |
| [26] | 米方秋,徐锡增,方升佐,等.杨稻复合系统的胁地因子分析[J].林业科技开发,2008,22(4):56-58. |
| MI F Q, XU X Z, FANG S Z, et al.. Analysis on factors influencing rice yield in poplar-crop systems [J]. J. For. Eng., 2008, 22(4):56-58. | |
| [27] | 袁玉欣, 魏宏侠, 马荣泽, 等. 杨粮间作系统农作物产量研究[J]. 河北林果研究, 2001, 16(1):7-13. |
| YUAN Y X, WEI H X, MA R Z, et al.. The study on crop yield under poplar-crop intercropping system [J]. Hebei J. For. Orchard Res., 2001, 16(1):7-13. | |
| [28] | 王颖, 崔建州, 袁玉欣, 等. 农林间作系统林木遮荫及其对产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2003, 11(2):107-110. |
| WANG Y, CUI J Z, YUAN Y X, et al.. The shading and its effect on crop yield under poplar-crop intercropping system [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2003, 11(2):107-110. | |
| [29] | 王蒙.林农复合系统生态经济效益分析:以石首市为例[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2013. |
| WANG M. Analysis of ecological and economic benefits of agroforestry system-illustrated by the example of Shishou [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| [30] | 赵忠宝.徐淮平原农林复合系统小气候效益研究[D].南京:南京林业大学,2006. |
| ZHAO Z B. The microclimate effects of agroforestry system in Xuhuai plain areas [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2006. | |
| [31] | 吕爱霞.夏津县黄泛沙地复合经营型杨树人工林生态经济效益研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2006. |
| LYU A X. Study on ecological and economic benefit of poplar plantation in sandy area of Yellow River in Xiajin [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2006. | |
| [32] | 蔡智才.晋西黄土区苹果花生间作系统小气候效应研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学,2017. |
| CAI Z C. The microclimate effect of apple-peanut intercropping system in the Loess Plateau of West Shanxi province [D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2017. | |
| [33] | LATIF ZABD, BLACKBURN G A.The effects of gap size on some microclimate variables during late summer and autumn in a temperate broadleaved deciduous forest [J].Int.J.Biometeorol., 2010, 54(2):119-129. |
| [34] | 张康,黄开栋,赵小军,等.修枝对杨树人工林林内小气候及林下植被的短期效应[J].生态环境学报,2019,28(8):1548-1556. |
| ZHANG K, HUANG K D, ZHAO X J, et al.. Effects of pruning on microclimate and understory vegetation in a poplar plantation [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2019, 28(8):1548-1556. |
| [1] | Xin JIN, Lu ZHANG, Peng WU, Ping LI, Wei TAN, Mingying GUI. Effects of Shading Treatment on Growth and Enzyme Activity of Bonsai Ganoderma lucidum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 147-156. |
| [2] | Jun CHEN, Qi ZHANG, Mengyu YANG, Zhenyang YUAN. Effects of Growing Grass on Microclimate Environment and Apple Leaves in Apple Orchard [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 158-167. |
| [3] | Jiayuan LIU, Yubin ZHANG, Wenke LIU. Effects of Preharvest Red and Blue Continuous Light Intensity on Growth, Quality and AsA Metabolism of Hydroponics Lettuce [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 76-84. |
| [4] | ZHAO Songchao1, ZHAO Zhe1, LI Yifan1, RAO Dongming2, QIN Yanmin2, FENG Xiaohu2, ZHANG Youwu2, ZHAO Mingqin1*. Influence of Planting Density on the Phenomenon of “High Temperature Induced Maturity” in Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(7): 145-154. |
| [5] | HUANG Qiaoyi1,2, ZHANG Mu1, LI Ping1, FU Hongting1, HUANG Xu1,TANG Shuanhu1*. Rice Canopy Image Segmentation Using Support Vector Machine and Otsus Method [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(4): 52-60. |
| [6] | DONG Xue1,2, ZHAO Yingming1,2,3*, HUANG Yaru1,2, LIU Yuting1,2, Ma Yingbin1,2,4, WANG Zhigang1,2, HAO Yuguang1,2, LIU Fang1,2. Growth Adaptability Evaluation of Insect Resistant Poplar Varieties of Middle Age in Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(7): 123-129. |
| [7] | ZHAO Yingming1,2,3, GAO Junliang1,2,3, YANG Wenbin2*, HUANG Yaru1,3, MA Yingbin1,3, . Comparison of 16 Agronomic Characters of Different Insect Species in Poplar Stand Replanting [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(3): 72-81. |
| [8] | ZHAO Zhe1, ZHAO Dongjie1, ZHANG Rui2, MAO Yabo1, NIU Lulu1, ZHOU Guowang2, ZHANG Zhigao2, LI Yan1, ZHAO Mingqin1*. Effects of Light Intensity on Senescence Physiological Characteristics of Flue-cured Tobacco at Mature Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(3): 90-97. |
| [9] | SHAO Hui-fang1, ZHAO Rong-rong1, FAN Lei2, ZHANG Man-man3, WANG Shan-shan1, XU Zi-cheng1. Effects of Recirculated Air Temperature in Ordering Cylinder on Chemical Components and Neutral Aroma Substances of Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(6): 138-145. |
| [10] | TANG Chun-Xiao1, WANG ZHAO-Rui1, LI En-bang1,2*. Study on the Distribution Characteristics of Scattered Light around Peach Pit [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(4): 79-86. |
| [11] | SI Wen-cai, LIU Jun-ming. Studies on Remote Sensing Monitoring Method for Spatial Distribution of Winter Wheat Critical Phenology [J]. , 2011, 13(6): 82-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号