




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 173-181.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0496
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lu ZHANG1( ), Lei ZHENG2, Siru LIU3, Zejiang CAI1(
), Lei ZHENG2, Siru LIU3, Zejiang CAI1( ), Nan SUN1, Qiang ZHANG2(
), Nan SUN1, Qiang ZHANG2( ), Minggang XU1,3
), Minggang XU1,3
Received:2022-06-04
Accepted:2022-08-29
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Zejiang CAI,Qiang ZHANG
张璐1( ), 郑磊2, 刘思汝3, 蔡泽江1(
), 郑磊2, 刘思汝3, 蔡泽江1( ), 孙楠1, 张强2(
), 孙楠1, 张强2( ), 徐明岗1,3
), 徐明岗1,3
通讯作者:
蔡泽江,张强
作者简介:张璐E-mail:zhanglu01@caas.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lu ZHANG, Lei ZHENG, Siru LIU, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Minggang XU. Soil Initial Available Phosphorus and Exchangeable Magnesium Shaping the Response of Wheat Growth to pH[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 173-181.
张璐, 郑磊, 刘思汝, 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 张强, 徐明岗. 土壤初始有效磷和交换性镁含量改变了小麦生长对pH的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 173-181.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0496
土壤母质 Soil parent material | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 有效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium/(cmol+·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
板页岩 Plate shale | 5.93 | 23.3 | 120.1 | 30.4 | 81.3 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 1.35 | 6.80 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 4.60 | 16.1 | 76.7 | 5.7 | 87.5 | 0.72 | 4.61 | 0.26 | 1.52 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 5.39 | 17.8 | 105.9 | 15.4 | 50.0 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 3.73 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 4.45 | 30.6 | 175.4 | 9.7 | 68.8 | 0.24 | 7.76 | 0.23 | 0.72 |
花岗岩 Granite | 4.74 | 39.4 | 217.7 | 12.1 | 62.5 | 0.19 | 4.34 | 0.15 | 0.37 |
Table 1 Selected chemical properties of the soils as the initial conditions for the pot experiment in this study
土壤母质 Soil parent material | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 有效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium/(cmol+·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
板页岩 Plate shale | 5.93 | 23.3 | 120.1 | 30.4 | 81.3 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 1.35 | 6.80 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 4.60 | 16.1 | 76.7 | 5.7 | 87.5 | 0.72 | 4.61 | 0.26 | 1.52 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 5.39 | 17.8 | 105.9 | 15.4 | 50.0 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 3.73 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 4.45 | 30.6 | 175.4 | 9.7 | 68.8 | 0.24 | 7.76 | 0.23 | 0.72 |
花岗岩 Granite | 4.74 | 39.4 | 217.7 | 12.1 | 62.5 | 0.19 | 4.34 | 0.15 | 0.37 |

Fig. 1 pH buffering curve of soils derived from different parent materialsNote: >0 or <0 at y-axis represent acid or alkali addition rates, respectively;** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
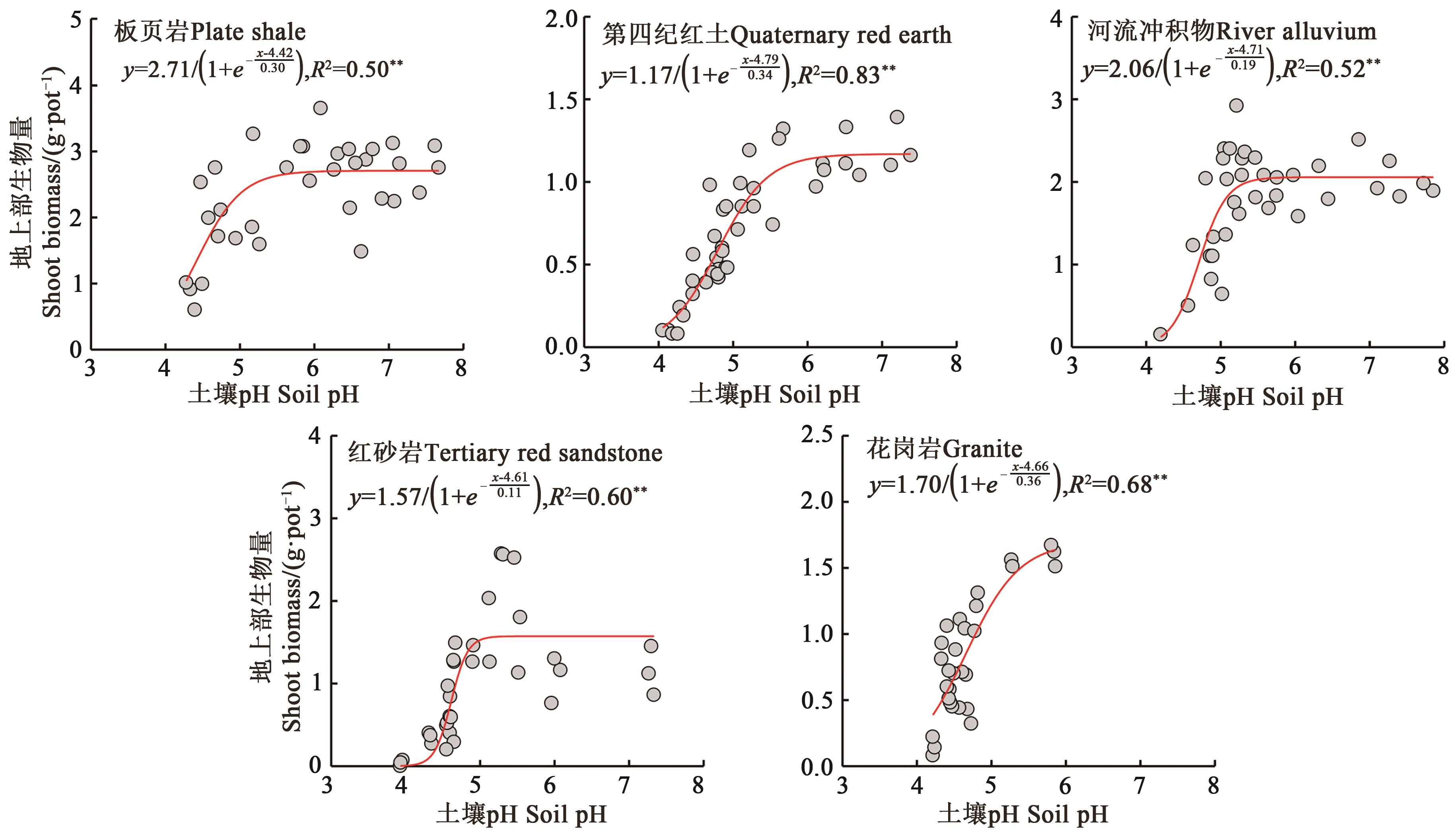
Fig. 2 Response of wheat shoot biomass to pH of soils derived from different parent materialsNote: ** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 2.71 | 5.31 | 4.42 | 3.53 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 1.17 | 5.79 | 4.79 | 3.80 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 2.06 | 5.25 | 4.71 | 4.16 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 1.57 | 4.94 | 4.61 | 4.29 |
花岗岩 Granite | 1.70 | 5.72 | 4.66 | 3.59 |
Table 2 Critical pH of wheat shoot biomass in soils derived from different parent materials
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 2.71 | 5.31 | 4.42 | 3.53 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 1.17 | 5.79 | 4.79 | 3.80 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 2.06 | 5.25 | 4.71 | 4.16 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 1.57 | 4.94 | 4.61 | 4.29 |
花岗岩 Granite | 1.70 | 5.72 | 4.66 | 3.59 |

Fig. 3 Response of wheat root biomass to pH of soils derived from different parent materialsNote: ** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 0.59 | 6.20 | 4.79 | 3.39 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 0.41 | 4.73 | 4.40 | 4.07 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 0.49 | 5.60 | 4.91 | 4.21 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 0.40 | 4.70 | 4.28 | 3.87 |
花岗岩 Granite | 0.48 | 4.38 | 4.27 | 4.16 |
Table 3 Critical pH of wheat root biomass in soils derived from different parent materials
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 0.59 | 6.20 | 4.79 | 3.39 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 0.41 | 4.73 | 4.40 | 4.07 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 0.49 | 5.60 | 4.91 | 4.21 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 0.40 | 4.70 | 4.28 | 3.87 |
花岗岩 Granite | 0.48 | 4.38 | 4.27 | 4.16 |
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/cm | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 51.34 | 4.67 | 4.02 | 3.37 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 34.76 | 5.17 | 4.36 | 3.56 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 53.40 | 5.09 | 4.32 | 3.55 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 42.43 | 5.01 | 4.31 | 3.61 |
花岗岩 Granite | 36.70 | 4.32 | 4.26 | 4.20 |
Table 4 Critical pH of wheat height in soils derived from different parent materials
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/cm | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 51.34 | 4.67 | 4.02 | 3.37 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 34.76 | 5.17 | 4.36 | 3.56 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 53.40 | 5.09 | 4.32 | 3.55 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 42.43 | 5.01 | 4.31 | 3.61 |
花岗岩 Granite | 36.70 | 4.32 | 4.26 | 4.20 |
小麦生长 Wheat growth | 阈值 Critical value | 有机质 Organic matter | pH | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 有效钾 Available potassium | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部生物量 Shoot biomass | pH95% | -0.02 | -0.15 | -0.12 | -0.27 | 0.33 | 0.53 | -0.12 | -0.23 | -0.22 |
| pH50% | -0.25 | -0.65 | -0.22 | -0.89* | -0.16 | 0.79 | 0.35 | -0.80 | -0.67 | |
| pH5% | -0.20 | -0.40 | -0.07 | -0.46 | -0.46 | 0.12 | 0.42 | -0.42 | -0.33 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.03 | 0.93* | -0.02 | 0.98** | -0.14 | -0.80 | -0.77 | 0.90* | 0.88* | |
根系生物量 Root biomass | pH95% | -0.51 | 0.95* | -0.50 | 0.87 | 0.04 | -0.44 | -0.83 | 0.94* | 0.99** |
| pH50% | -0.62 | 0.87* | -0.57 | 0.66 | -0.26 | -0.30 | -0.90* | 0.71 | 0.85 | |
| pH5% | 0.05 | -0.58 | 0.11 | -0.78 | -0.55 | 0.45 | 0.27 | -0.84 | -0.70 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.02 | 0.94* | -0.06 | 0.95* | -0.02 | -0.67 | -0.85 | 0.88 | 0.86 | |
株高 Height | pH95% | -0.81 | -0.17 | -0.75 | -0.37 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 0.11 | -0.12 | 0.01 |
| pH50% | -0.12 | -0.79 | -0.07 | -0.95* | -0.27 | 0.68 | 0.57 | -0.90* | -0.79 | |
| pH5% | 0.80 | -0.48 | 0.78 | -0.40 | -0.36 | -0.09 | 0.35 | -0.63 | -0.69 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.34 | 0.81 | -0.27 | 0.73 | -0.42 | -0.62 | -0.71 | 0.70 | 0.79 |
Table 5 Coefficient of correlation between critical pH of wheat and soil initial chemical properties
小麦生长 Wheat growth | 阈值 Critical value | 有机质 Organic matter | pH | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 有效钾 Available potassium | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部生物量 Shoot biomass | pH95% | -0.02 | -0.15 | -0.12 | -0.27 | 0.33 | 0.53 | -0.12 | -0.23 | -0.22 |
| pH50% | -0.25 | -0.65 | -0.22 | -0.89* | -0.16 | 0.79 | 0.35 | -0.80 | -0.67 | |
| pH5% | -0.20 | -0.40 | -0.07 | -0.46 | -0.46 | 0.12 | 0.42 | -0.42 | -0.33 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.03 | 0.93* | -0.02 | 0.98** | -0.14 | -0.80 | -0.77 | 0.90* | 0.88* | |
根系生物量 Root biomass | pH95% | -0.51 | 0.95* | -0.50 | 0.87 | 0.04 | -0.44 | -0.83 | 0.94* | 0.99** |
| pH50% | -0.62 | 0.87* | -0.57 | 0.66 | -0.26 | -0.30 | -0.90* | 0.71 | 0.85 | |
| pH5% | 0.05 | -0.58 | 0.11 | -0.78 | -0.55 | 0.45 | 0.27 | -0.84 | -0.70 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.02 | 0.94* | -0.06 | 0.95* | -0.02 | -0.67 | -0.85 | 0.88 | 0.86 | |
株高 Height | pH95% | -0.81 | -0.17 | -0.75 | -0.37 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 0.11 | -0.12 | 0.01 |
| pH50% | -0.12 | -0.79 | -0.07 | -0.95* | -0.27 | 0.68 | 0.57 | -0.90* | -0.79 | |
| pH5% | 0.80 | -0.48 | 0.78 | -0.40 | -0.36 | -0.09 | 0.35 | -0.63 | -0.69 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.34 | 0.81 | -0.27 | 0.73 | -0.42 | -0.62 | -0.71 | 0.70 | 0.79 |
| 1 | 徐明岗, 文石林, 周世伟, 等. 南方地区红壤酸化及综合防治技术[J]. 科技创新与品牌, 2016 (7): 74-77. |
| XU M G, WEN S L, ZHOU S W, et al.. Acidification and integrated control techniques of red soil in southern China [J]. Sci. Technol. Innov., 2016(7): 74-77. | |
| 2 | GUO J H, LIU X J, ZHANG Y, et al.. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands [J]. Science, 2010, 327(5968): 1008-1010. |
| 3 | 徐仁扣. 土壤酸化及其调控研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(2): 238-244. |
| XU R K. Research progresses in soil acidification and its control [J]. Soils, 2015, 47(2): 238-244. | |
| 4 | CAI Z J, WANG B R, XU M G, et al.. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China [J]. J. Soil Sediment., 2015, 15(2): 260-270. |
| 5 | MULLEN C L, SCOTT B J, EVANS C M, et al.. Effect of soil acidity and liming on lucerne and following crops in central-western New South Wales [J]. Anim. Prod. Sci., 2006, 46(10): 1291-1300. |
| 6 | 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 王伯仁, 等. 长期施肥对红壤 pH、作物产量及氮、磷、钾养分吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1): 71-78. |
| CAI Z J, SUN N, WANG B R, et al.. Effects of long-term fertilization on pH of red soil crop yields and uptakes of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2011, 17(1): 71-78. | |
| 7 | ZHU Q C, LIU X J, HAO T X, et al.. Cropland acidification increases risk of yield losses and food insecurity in China [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020, 256: 113145 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 8 | BAQUY M A, LI J Y, JIANG J, et al.. Critical pH and exchangeable Al of four acidic soils derived from different parent materials for maize crops [J]. J. Soil Sediment., 2018, 18:1490-1499. |
| 9 | 梁文君, 蔡泽江, 宋芳芳, 等. 不同母质发育红壤上玉米生长与土壤pH、交换性铝、交换性钙的关系[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(8): 1544-1550. |
| LIANG W J, CAI Z J, SONG F F, et al.. Relationships between maize growth and the pH, exchangeable aluminum and calcium of red soils derived from different parent materials [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2017, 36(8): 1544-1550. | |
| 10 | BACHE B W, CROOKE W M. Interactions between aluminum, phosphorus and pH in the response of barley to soil acidity [J]. Plant Soil, 1981, 61(3): 365-375. |
| 11 | 成杰民, 胡光鲁, 潘根兴, 等. 用酸碱滴定曲线拟合参数表征土壤对酸缓冲能力的新方法[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23 (3): 569-573. |
| CHENG J M, HU G L, PAN G X, et al.. New method for evaluating buffering capacity and equilibrium pH of paddy soil with simulation parameter [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2004, 23(3): 569-573. | |
| 12 | 汪吉东, 冯冰, 李传哲, 等. 中国几种典型土壤酸碱缓冲容量测定方法的比较[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2020, 36(6): 1452-1458. |
| WANG J D, FENG B, LI C Z, et al.. Comparative study on determination methods for acid buffering capacity of several typical soils in China [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2020, 36(6): 1452-1458. | |
| 13 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000:1-495. |
| 14 | 王如月, 袁世力, 文武武, 等. 磷对铝胁迫紫花苜蓿幼苗根系生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 53-62. |
| WANG R Y, YUAN S L, WEN W W, et al.. Effects of phosphorus on root growth and photosynthetic physiology of alfalfa seedlings under aluminum stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2021, 30(10): 53-62. | |
| 15 | 艾佐佐, 袁军, 黄丽媛, 等. 磷对铝胁迫下油茶幼苗根冠比及根系形态的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(12): 106-108. |
| AI Z Z, YUAN J, HUANG L Y, et al.. Effects of phosphorus on root-shoot ratio and root morphology of camellia oleifera seedlings under aluminum stress [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2017, 45(12): 106-108. | |
| 16 | 朱美红, 蔡妙珍, 吴韶辉, 等. 磷对铝胁迫下荞麦元素吸收与运输的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2009, 23(2): 183-187. |
| ZHU M H, CAI M Z, WU S H, et al.. Effect of phosphorus on element uptake and transportation in buckwheat under aluminum stress [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2009, 23(2): 183-187. | |
| 17 | 王宁, 郑怡, 王芳妹, 等. 铝毒胁迫下磷对荞麦根系铝形态和分布的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(5): 168-171. |
| WANG N, ZHENG Y, WANG F M, et al.. Effect of phosphorus on speciation and distribution of aluminum in the roots of buckwheat under aluminum toxicity [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2011, 25(5): 168-171. | |
| 18 | 吴良泉. 科学施镁, 让土地“美”起来! [J]. 中国农资, 2018 (46): 24. |
| WU L Q. Let the land “beautiful” up by scientific applying magnesium [J]. China Agri-product. News, 2018(46): 24. | |
| 19 | 赵越, 杨金玲, 许哲, 等. 模拟酸雨淋溶下不同母质发育雏形土矿物风化中的盐基离子与硅计量关系[J/OL]. 土壤学报, 2022 [2022-05-12]. . |
| ZHAO Y, YANG J L, XU Z, et al.. Stoichiometry of base cations and silicon of cambosols derived from different parent materials as leached by simulated acid rain [J/OL]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2022 [2022-05-12]. . | |
| 20 | BOSSOLANI J W, CRUSCIOL C A C, MORETTI L G, et al.. Improving soil fertility with lime and phosphogypsum enhances soybean yield and physiological characteristics [J/OL]. Agron. Sustain. Dev., 2022, 42: 26 [2022-05-12].. |
| 21 | LAURICELLA D, BUTTERLY C R, CLARK G J, et al.. Effectiveness of innovative organic amendments in acid soils depends on their ability to supply P and alleviate Al and Mn toxicity in plants [J]. J. Soil Sediment., 2020, 20(11): 3951-3962. |
| [1] | Yanxin HUANG, Xiang WU, Yan CAO, Xuyu YAN, Ling LI. Research Progress on Effect and Mechanism of Exogenous Calcium Induced Plant Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 165-171. |
| [2] | Wen HU, Pengpeng ZHANG, Liping ZHUANG, Pengli WANG, Yangjun ZOU. Effects of Clover Mulch on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Leaf Physiological Characteristics in Dryland Apple Orchards [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 193-203. |
| [3] | Junyu ZHOU, Yu GU, Haiyong WU, Mingde LI, Qiongfeng LIU, Xuan ZHOU, Chunhua DONG. Effects of Citric Acid on Enhance the Remediation of Cd-contaminated Soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 215-223. |
| [4] | Haili LI, Fan YANG, Jianhao CHEN, Kang YANG, Yiping YANG, Jingang DUAN, Bin LI, Wanqi ZHANG, Chunjiang MA. Analysis of Bacteriostasis Activity of Paenibacillus sp. Against Super Drug-resistant Escherichia coli Carrying NDM Genes [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 119-131. |
| [5] | Hang CAO, Xinbing YANG, Yanlin LIU, Na HUO, Xiaokuan LIU, Xinyue LI. Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities of Reconstituted Soils from Limestone Mines [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 168-178. |
| [6] | Shuting XIAO, An YAN. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon in Typical Natural Forests in Tianshan Mountains [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 227-238. |
| [7] | Yanqin MA, Yujie ZHOU, Haicheng LONG, Ju LI, Haie WANG, Wei CHANG, Zhi LI, Jian ZHONG, Mingjun MIAO, Liang YANG. Construction of TRV-mediated VIGS System in Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis and Brassica juncea [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 239-249. |
| [8] | Xueqing LIU, Jing WANG, Yi YANG, Huiqin WU, Yanhong WANG, Luyao WANG, Jiawei LU, Kaixuan ZHANG, Yuan ZHAI, Yan CHENG. Effect of Exogenous Ethephon on Defoliation and Yield of Pigmented Pepper [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 36-46. |
| [9] | Xiaowei CHEN, Yuzhu SHA, Xiu LIU, Pengyang SHAO, Fanxiong WANG, Zhuanhui XIE, Wenxin YANG, Qianling CHEN, Min GAO, Wei HUANG. Analysis of Gene Expression Characteristics Associated with Quality, Nutrient Composition, and Meat Quality of Tibetan Sheep Meat During Different Phenological Stages [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 161-171. |
| [10] | Yi HU, Jie GONG, Wei ZHAO, Rong CHENG, Zhongyu LIU, Shiqing GAO, Yazhen YANG. Identification of PHY Gene Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)and Their Expression Analysis Under Heat Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 30-43. |
| [11] | Yanfang ZHU, Qiang CHANG, Yan HAO, Hailong CHEN. Effects of Reflective Film on Fruit Quality and Volatile Components of ‘Shine Muscat’ Grape [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 72-82. |
| [12] | Yaxin WANG, Yangcheng LYU, Wenqi WANG, Qi LIU, Jie YANG, Guihong REN, Wuping ZHANG, Fuzhong LI. Nondestructive Segmentation and Extraction of Stem and Leaf Phenotypes During Tomato Plant Growth [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 90-100. |
| [13] | Xiaoyan XIONG, Dandan TIAN, Yuxin GONG, Yu QIAO, Xiaoqing XU, Mengxin HE, Bo SHI, Qing PENG. Preparation of Quercetin from Sophora japonica and Its Effect Together with Colistin on Salmonella spp. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 136-147. |
| [14] | Wei WANG, Linnan DU, Yuanyuan XU, Hongwei YU. Three-level Mid-infrared Spectroscopy Study of Tubers Starch Crystal/amorphous Structure and Thermostability [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 148-157. |
| [15] | Sile HU, Yulong BAO, Tubuxinbayaer, Jifeng TAO, Enliang GUO. Chlorophyll Content Inversion of Spring Wheat Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral and Integrated Learning [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 93-103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号