




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 164-173.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2025.0529
• ANIMAL AND PLANT HEALTH • Previous Articles
Yuqian JIN1( ), Ziheng FU1, Xiaoyu GAO1, Weimin LI1,2(
), Ziheng FU1, Xiaoyu GAO1, Weimin LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-16
Accepted:2025-09-04
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2025-11-17
Contact:
Weimin LI
通讯作者:
李为民
作者简介:金玉倩 E-mail:1279609589@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuqian JIN, Ziheng FU, Xiaoyu GAO, Weimin LI. A Non-classical Secretory Protein ncSP35 of Candidatus Phytoplasma Ziziphi Inhibits Hypersensitive Response and Plant Growth and Development[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 164-173.
金玉倩, 傅子恒, 高小语, 李为民. 枣植原体分泌蛋白ncSP35抑制超敏反应及植物生长发育[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(11): 164-173.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2025.0529
| 基因/载体Gene/construct | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
ncSP35 ZjH2B pET-ncSP35-phoA pGR-ncSP35 pGR-SP35Δ2-11 pGR-SP35Δ90-107 pCam-ncSP35-GFP pNubG-H2B pCub-ncSP35 pCam-H2B-HA pCLuc-ncSP35 pNLuc-ZjH2B | 35-F 35-R H2B-F H2B-R phoA-35-F phoA-35-R PVX-35-F PVX-35-R PVX-35Δ2-11-F PVX-35-R PVX-35-F PVX-35Δ90-107-R 35-GFP-F 35-GFP-R RR3-H2B-F RR3-H2B-R BT3-35-F BT3-35-FR H2B-HA-F H2B-HA-R CLuc-35-F CLuc-35-R NLuc-H2B-F NLuc-H2B-R | ATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA TTAATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT ATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA ATTCGAGCTGGTCACCCTAGGC AAGGAGATATACATATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA CAAGCTTATCGGCGGTCGACATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT AGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA TTAAAAGAAACCAAAAGTTTTTTTC AGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATATGAGTCTTTTTAATTTATTTGTCA --- --- CAAGCTTATCGGCGGTCGAC TGGTTTGGATCAACAACATT GACGAGCTCGGGTACCATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA TGGTGTCGACTCTAGAATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT CAGAGTGGCCATTACGGCCATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA TCGAGAGGCCGAGGCGGCCCCTCAAGAGCTGGTAAATTTAGTCA TGTAATGGCCATTACGGCCATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA GCAGATGGCCGAGGCGGCCCCATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT GGACTCTTGACCATGGAT ATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA ATTCGAGCTGGTCACCCTAGGCATAATCCGGCACATCATAAGGGTAAGAGCT GGTAAATTTAGTCATCCCGGGGCGGTACCAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA CTGCAGGTCGACTTAATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT TCGGTACCCGGGATCC ATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA ACGAGATCTGGTCGAC AGAGCTGGTAAATTTAGTCA |
Table 1 Genes, recombinant constructs and primers involved in this study
| 基因/载体Gene/construct | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
ncSP35 ZjH2B pET-ncSP35-phoA pGR-ncSP35 pGR-SP35Δ2-11 pGR-SP35Δ90-107 pCam-ncSP35-GFP pNubG-H2B pCub-ncSP35 pCam-H2B-HA pCLuc-ncSP35 pNLuc-ZjH2B | 35-F 35-R H2B-F H2B-R phoA-35-F phoA-35-R PVX-35-F PVX-35-R PVX-35Δ2-11-F PVX-35-R PVX-35-F PVX-35Δ90-107-R 35-GFP-F 35-GFP-R RR3-H2B-F RR3-H2B-R BT3-35-F BT3-35-FR H2B-HA-F H2B-HA-R CLuc-35-F CLuc-35-R NLuc-H2B-F NLuc-H2B-R | ATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA TTAATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT ATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA ATTCGAGCTGGTCACCCTAGGC AAGGAGATATACATATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA CAAGCTTATCGGCGGTCGACATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT AGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA TTAAAAGAAACCAAAAGTTTTTTTC AGCACCAGCTAGCATCGATATGAGTCTTTTTAATTTATTTGTCA --- --- CAAGCTTATCGGCGGTCGAC TGGTTTGGATCAACAACATT GACGAGCTCGGGTACCATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA TGGTGTCGACTCTAGAATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT CAGAGTGGCCATTACGGCCATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA TCGAGAGGCCGAGGCGGCCCCTCAAGAGCTGGTAAATTTAGTCA TGTAATGGCCATTACGGCCATGAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA GCAGATGGCCGAGGCGGCCCCATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT GGACTCTTGACCATGGAT ATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA ATTCGAGCTGGTCACCCTAGGCATAATCCGGCACATCATAAGGGTAAGAGCT GGTAAATTTAGTCATCCCGGGGCGGTACCAATAATTTTGCTTTAGGTTTTA CTGCAGGTCGACTTAATATTCTTGTTGATTATGATGAAT TCGGTACCCGGGATCC ATGGCACCCAAGGCTGAGAA ACGAGATCTGGTCGAC AGAGCTGGTAAATTTAGTCA |
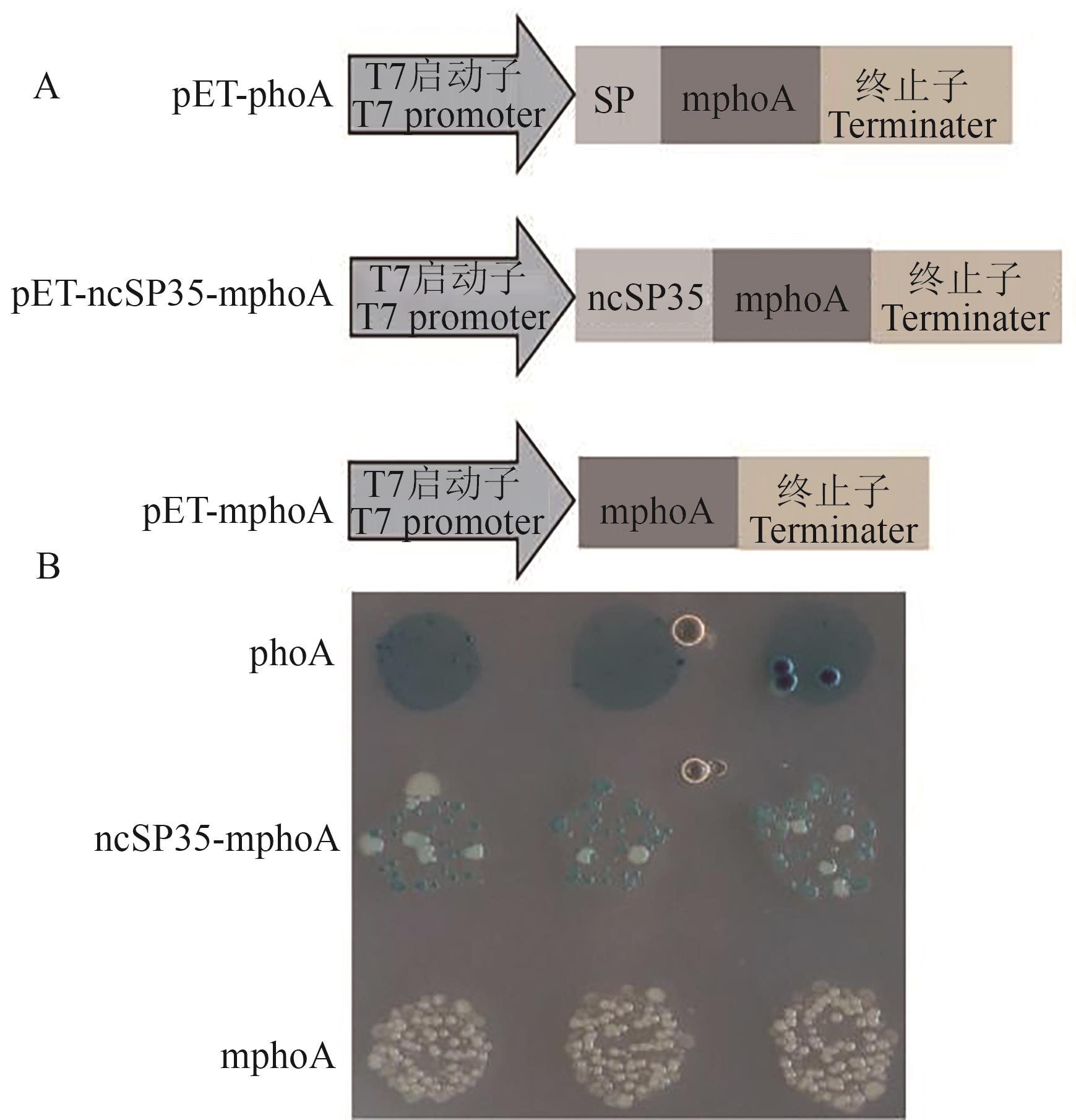
Fig. 1 Verification of ncSP35 extracellular secretionA: Schematic diagram of prokaryotic expression for phoA and ncSP35; B: Analysis of extracellular secretion of ncSP35-mphoA using the E. coli-based alkaline phosphatase reporter system
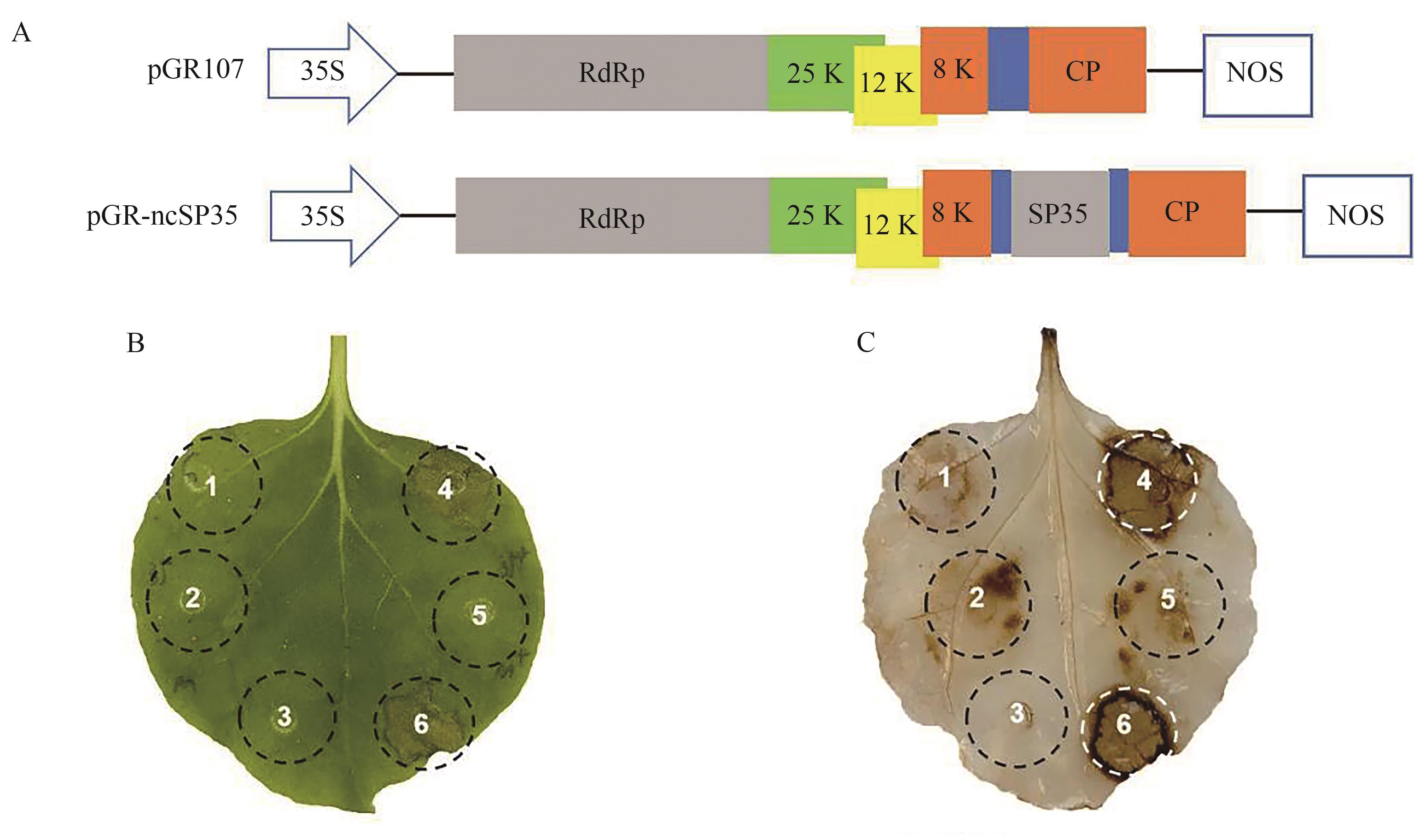
Fig. 2 ncSP35 suppressed Bax-triggered HR and H2O2 accumulation in N. benthamianaA: Schematic diagrams of the PVX recombinant plasmids; B: Phenotype of ncSP35 inhibiting Bax-triggered hypersensitive response; C: DAB staining.1—GFP;2—ncSP35;3—Buffer;4—GFP+Bax;5—ncSP35+Bax;6—Buffer+Bax
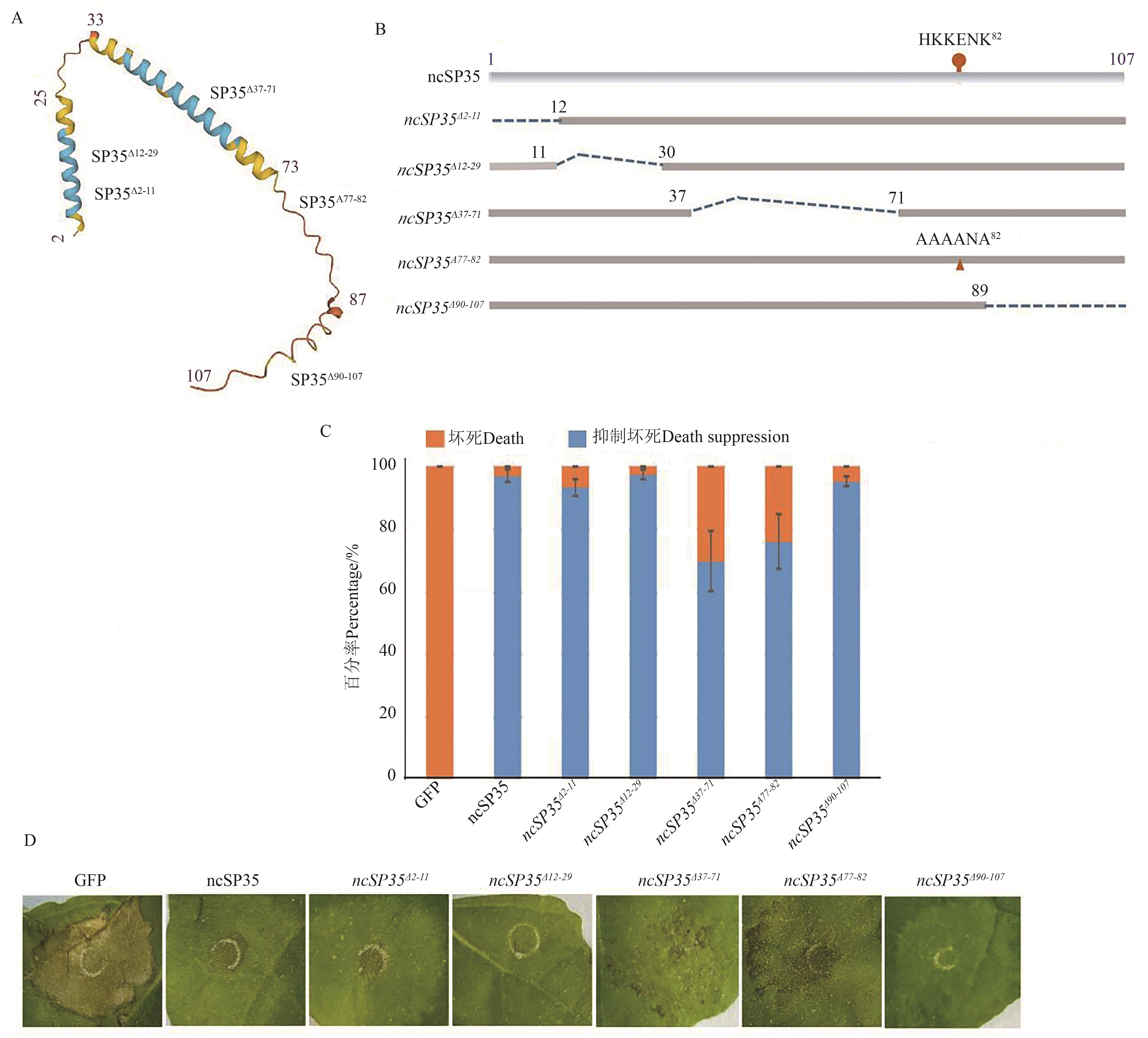
Fig. 3 Function analysis of the ncSP35 mutants in HR suppressionA: Three-dimensional structure of ncSP35 and spatial location of the corresponding mutants; B: Diagram of the ncSP35 mutants; C: Statistical analysis of the ncSP35 mutants in HR suppression; D: Typical HR suppression phenotypes of the ncSP35 mutants in N. benthamiana (after 5 d)
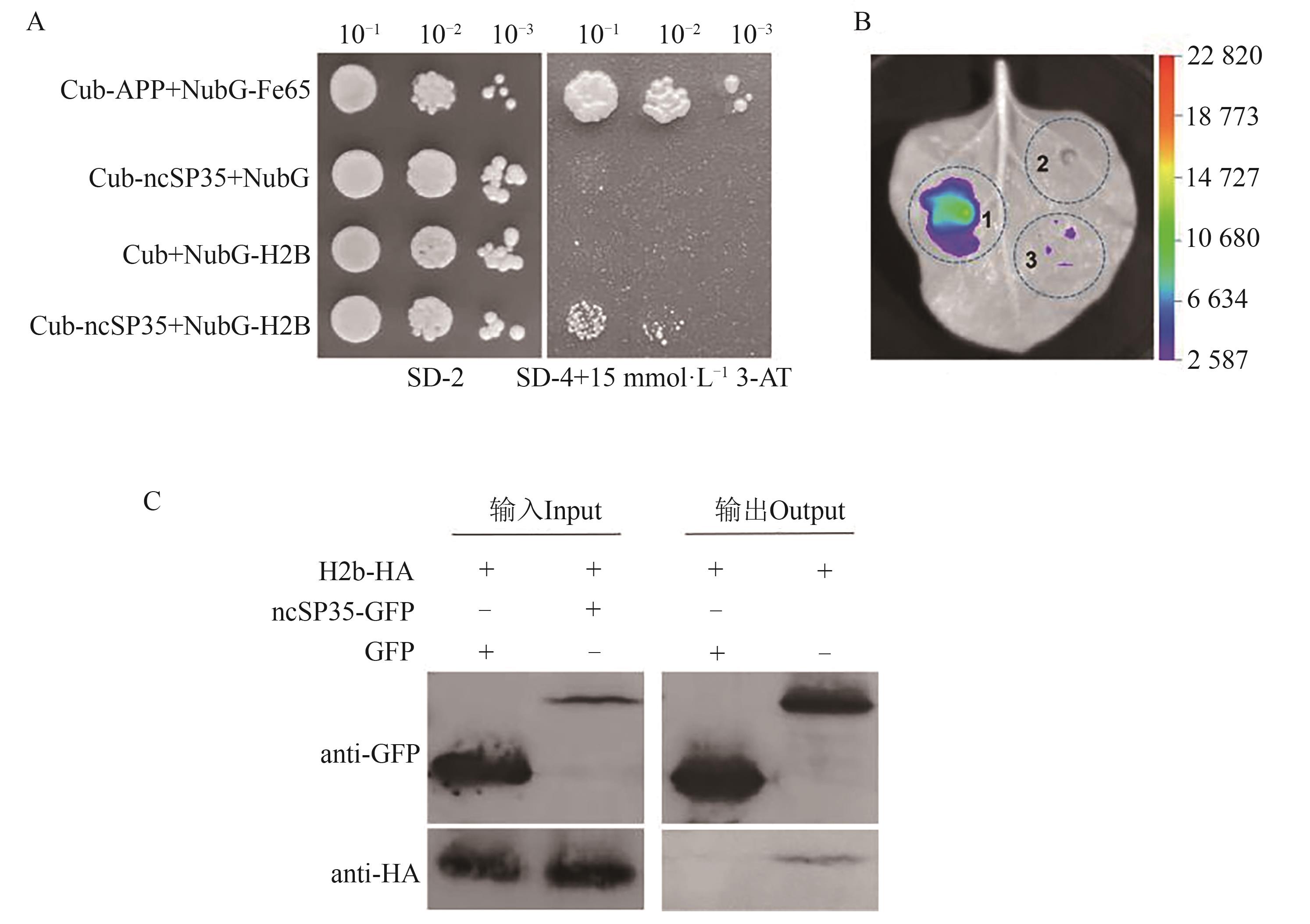
Fig. 6 ncSP35 protein interacted with ZjH2BA: Validation of the interaction between ncSP35 and ZjH2B via yeast two-hybrid; yeast cells co-transformed with Cub-APP/NubG-Fe65 was used as a positive control, and those co-transformed with Cub-ncSP35/NubG or Cub/NubG-H2B were as negative controls, SD-2 indicates the medium lacking leucine and tryptophan, while SD-4 represents the medium lacking leucine, tryptophan, histidine and adenine; B: Luciferase complementation imaging assay of the interaction between ncSP35 and ZjH2B,1—nLUC-H2B+ncSP35-cLUC,2—nLUC-H2B+cLUC,3—nLUC+ncSP35-cLUC; C: Co-IP analysis of the interaction between ncSP35 and ZjH2B
| [1] | KHAN M, SETO D, SUBRAMANIAM R, et al.. Oh, the places they’ll go! a survey of phytopathogen effectors and their host targets [J]. Plant J., 2018, 93(4): 651-663. |
| [2] | C-NMEISRIMLER, ALLAN C, ECCERSALL S, et al.. Interior design: how plant pathogens optimize their living conditions [J]. New Phytol., 2021, 229(5): 2514-2524. |
| [3] | 陈玉鑫, 张钰析, 刘锦春, 等. 枣疯病研究进展[J]. 延安大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 42(1): 90-95. |
| CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, LIU J, et al.. Research progress on jujube witches' broom [J]. J. Yan’an Univ.(Nat. Sci.), 2023, 42(1): 90-95. | |
| [4] | 杨帆, 虞国跃, 李姝, 等. 枣疯病媒介昆虫研究进展[J]. 落叶果树, 2024, 56(6): 47-52. |
| [5] | JUNG H Y, SAWAYANAGI T, KAKIZAWA S, et al.. ‘Candidatus phytoplasma ziziphi’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with jujube witches’-broom disease [J]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2003, 53(Pt 4): 1037-1041. |
| [6] | WANG J, SONG L, JIAO Q, et al.. Comparative genome analysis of jujube witches’-broom phytoplasma, an obligate pathogen that causes jujube witches’-broom disease [J/OL]. BMC Genom., 2018, 19(1): 689 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [7] | XUE C, ZHANG Y, LI H, et al.. The genome of Candidatus phytoplasma ziziphi provides insights into their biological characteristics [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2023, 23(1): 251 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [8] | ZHOU J, MA F, YAO Y, et al.. Jujube witches’ broom phytoplasma effectors SJP1 and SJP2 induce lateral bud outgrowth by repressing the ZjBRC1-controlled auxin efflux channel [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2021, 44(10): 3257-3272. |
| [9] | MA F, ZHENG Y, ZHANG N, et al.. The ‘Candidatus phytoplasma ziziphi’ effectors SJP1/2 negatively control leaf size by stabilizing the transcription factor ZjTCP2 in jujube [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2024, 75(10): 3054-3069. |
| [10] | CHEN P, CHEN L, YE X, et al.. Phytoplasma effector Zaofeng6 induces shoot proliferation by decreasing the expression of ZjTCP7 in Ziziphus jujuba [J/OL]. Hortic. Res., 2022, 9: uhab032 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [11] | CHEN P, ZHANG Y, LI Y, et al.. Jujube witches’ broom phytoplasma effector Zaofeng3, a homologous effector of SAP54, induces abnormal floral organ development and shoot proliferation [J]. Phytopathology, 2024, 114(1): 200-210. |
| [12] | BENDTSEN J D, KIEMER L, FAUSBØLL A, et al.. Non-classical protein secretion in bacteria [J/OL]. BMC Microbiol., 2005, 5: 58 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [13] | WANG G, XIA Y, SONG X, et al.. Common non-classically secreted bacterial proteins with experimental evidence [J]. Curr. Microbiol., 2016, 72(1): 102-111. |
| [14] | GAO X, REN Z, ZHAO W, et al.. Candidatus phytoplasma ziziphi encodes non-classically secreted proteins that suppress hypersensitive cell death response in Nicotiana benthamiana [J/OL]. Phytopathol. Res., 2023, 5(1): 11 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [15] | LIU X, FAN Y, ZHANG C, et al.. Nuclear import of a secreted “Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus” protein is temperature dependent and contributes to pathogenicity in Nicotiana benthamiana [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10: 1684 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [16] | JONES L, HAMILTON A J, VOINNET O, et al.. RNA-DNA interactions and DNA methylation in post-transcriptional gene silencing [J]. Plant Cell, 1999, 11(12): 2291-2301. |
| [17] | LIN J S, LAI E M. Protein-protein interactions: co-immunoprecipitation [J]. Methods Mol. Biol., 2017, 1615: 211-219. |
| [18] | CHEN H, ZOU Y, SHANG Y, et al.. Firefly luciferase complementation imaging assay for protein-protein interactions in plants [J]. Plant Physiol., 2008, 146(2): 368-376. |
| [19] | RAPISARDA C, FRONZES R. Secretion systems used by bacteria to subvert host functions [J]. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol., 2018, 25: 1-42. |
| [20] | KAKIZAWA S, OSHIMA K, NISHIGAWA H, et al.. Secretion of immunodominant membrane protein from onion yellows phytoplasma through the Sec protein-translocation system in Escherichia coli [J]. Microbiology, 2004, 150(Pt 1): 135-142. |
| [21] | 牟海青, 朱水芳, 徐霞, 等. 植原体病害研究概况[J]. 植物保护, 2011, 37(3): 17-22. |
| MOU H Q, ZHU S F, XU X, et al.. An overview of research on phytoplasma-induced diseases [J]. Plant Protect., 2011, 37(3): 17-22. | |
| [22] | DU P, ZHANG C, ZOU X, et al.. “Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus” secretes nonclassically secreted proteins that suppress host hypersensitive cell death and induce expression of plant pathogenesis-related proteins [J/OL]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2021, 87(8): e00019- 21 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [23] | HARTH G, HORWITZ M A. Expression and efficient export of enzymatically active Mycobacterium tuberculosis glutamine synthetase in Mycobacterium smegmatis and evidence that the information for export is contained within the protein [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 1997, 272(36): 22728-22735. |
| [24] | LIN Y H, XU M Y, HSU C C, et al.. Ustilago maydis PR-1-like protein has evolved two distinct domains for dual virulence activities [J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1): 5755 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [25] | SHEN Y, WEI W, ZHOU D X. Histone acetylation enzymes coordinate metabolism and gene expression [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2015, 20(10): 614-621. |
| [26] | KUMAR V, THAKUR J K, PRASAD M. Histone acetylation dynamics regulating plant development and stress responses [J]. Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2021, 78(10): 4467-4486. |
| [27] | C-HPARK, CHEN S, SHIRSEKAR G, et al.. The Magnaporthe oryzae effector AvrPiz-t targets the RING E3 ubiquitin ligase APIP6 to suppress pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in rice [J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(11): 4748-4762. |
| [28] | CHEN X, DUAN Y, QIAO F, et al.. A secreted fungal effector suppresses rice immunity through host histone hypoacetylation [J]. New Phytol., 2022, 235(5): 1977-1994. |
| [29] | SUAREZ-FERNANDEZ M, ÁLVAREZ-ARAGÓN R, PASTOR-MEDIAVILLA A, et al.. Sas3-mediated histone acetylation regulates effector gene activation in a fungal plant pathogen [J/OL]. mBio, 2023, 14(5): e0138623 [2025-06-20]. . |
| [30] | VIJAYAPALANI P, HEWEZI T, PONTVIANNE F, et al.. An effector from the cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii derepresses host rRNA genes by altering histone acetylation [J]. Plant Cell, 2018, 30(11): 2795-2812. |
| [31] | WANG L, CHEN H, LI J, et al.. Effector gene silencing mediated by histone methylation underpins host adaptation in an oomycete plant pathogen [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2020, 48(4): 1790-1799. |
| [1] | XIE Zheng-wen1, WANG Lian-jun2, CHEN Jin-yang1, WANG Jiao1, SU Yi-jun1, . Studies on WRKY Transcription Factors and Their Biological Functions in Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(3): 46-54. |
| [2] | LI Zao-xia|ZHAO Jun. Regulation of Nitric Oxide in Plant Drought Tolerance and Disease Resistance [J]. , 2008, 10(S1): 7-11. |
| [3] | YAO Qin-Tao, ZHANG Wen-wei| LIU Li| HAN Rong| JIAN Gui-liang| QI Fang-jun . Negative Regulation of Rice Whirly Transcription Factor for the Hypersensitive Response Induced by Non-host Pathogen Bacterium [J]. , 2008, 10(5): 53-58. |
| [4] | ZHAO Zhong-lin1, MA Xin2, LI Yan3, LI Shu-ying4, YUAN Chao1. Intein-based Biosensor [J]. , 1, 1(1): 56-60. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号