




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 32-42.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2025.0123
• Special Forum for Green Aquaculture • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yunyun YAN1,2( ), Fubao WANG3, Junjian DONG2, Hetong ZHANG2, Fengying GAO2, Yuan ZHANG2, Xing YE2, Chengfei SUN2(
), Fubao WANG3, Junjian DONG2, Hetong ZHANG2, Fengying GAO2, Yuan ZHANG2, Xing YE2, Chengfei SUN2( ), Chengbin WU1(
), Chengbin WU1( )
)
Received:2025-02-26
Accepted:2025-05-07
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2025-11-17
Contact:
Chengfei SUN,Chengbin WU
闫芸芸1,2( ), 汪福保3, 董浚键2, 张赫桐2, 高风英2, 张媛2, 叶星2, 孙成飞2(
), 汪福保3, 董浚键2, 张赫桐2, 高风英2, 张媛2, 叶星2, 孙成飞2( ), 吴成宾1(
), 吴成宾1( )
)
通讯作者:
孙成飞,吴成宾
作者简介:闫芸芸 E-mail: 20222170546@pgs.hebau.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yunyun YAN, Fubao WANG, Junjian DONG, Hetong ZHANG, Fengying GAO, Yuan ZHANG, Xing YE, Chengfei SUN, Chengbin WU. Effect of Replacing Live Bait with Compound Feed on Growth Performance, Digestive Function and Antioxidant Capacity of Siniperca chuatsi[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 32-42.
闫芸芸, 汪福保, 董浚键, 张赫桐, 高风英, 张媛, 叶星, 孙成飞, 吴成宾. 配合饲料替代活饵对翘嘴鳜生长性能、消化功能及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(11): 32-42.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2025.0123
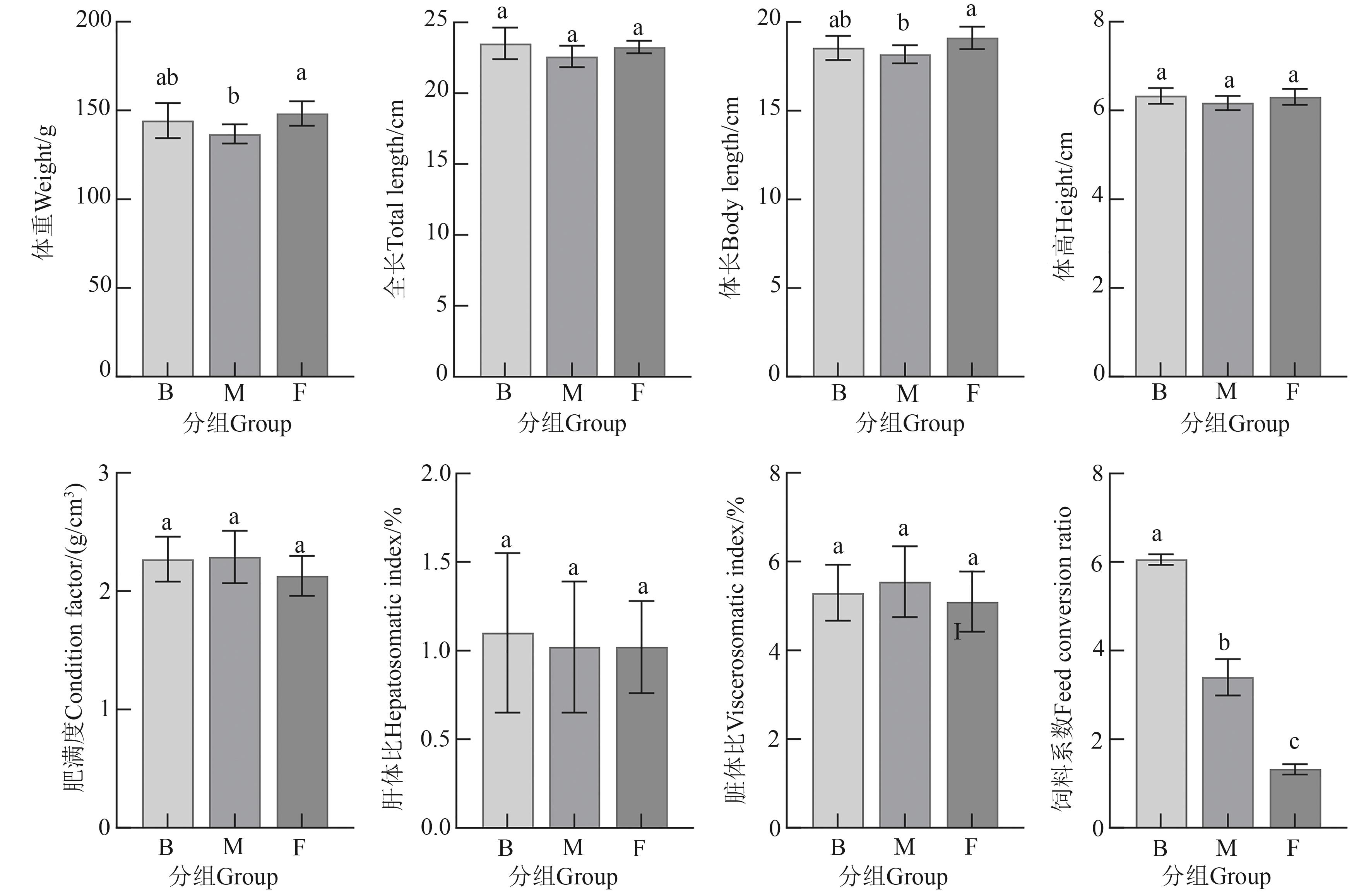
Fig. 1 Growth indexes of S. chuatsi under different feeding practicesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
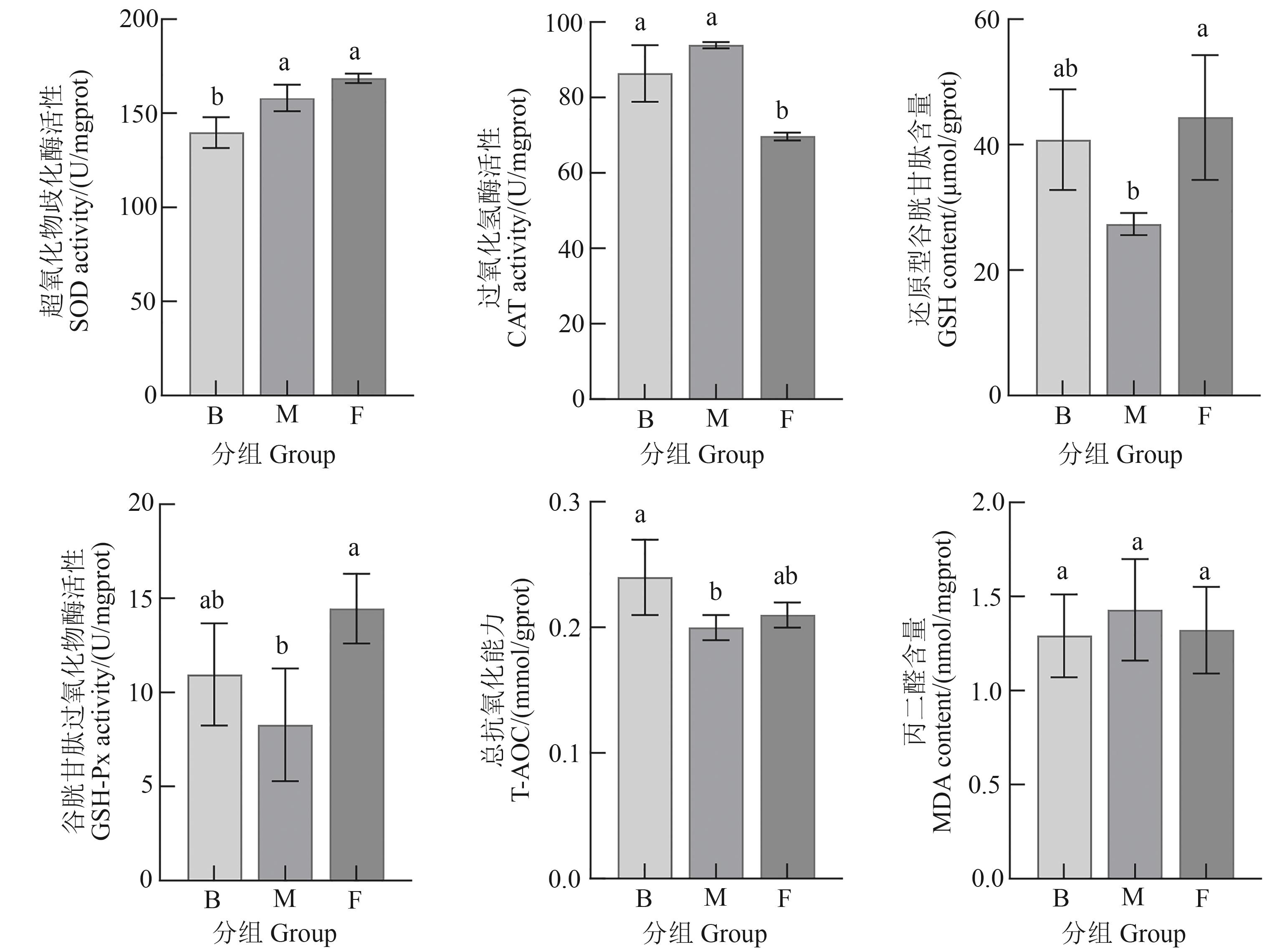
Fig. 2 Antioxidant enzyme activities in the liver tissue of S. chuatsi under different feeding practicesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
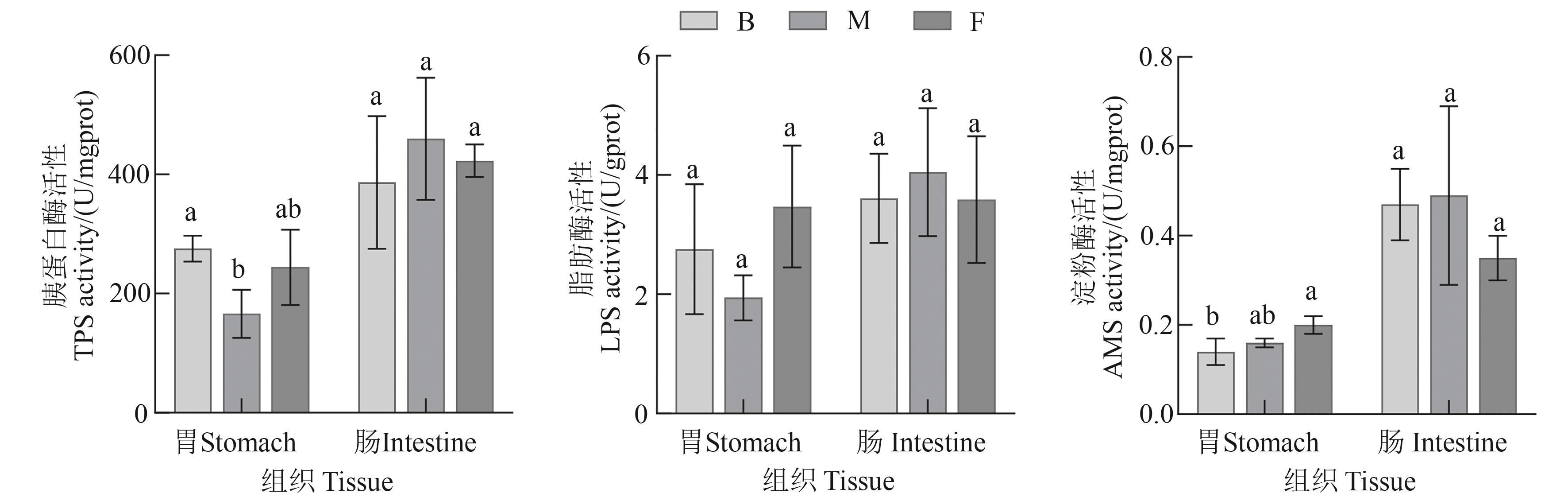
Fig. 3 Digestive enzyme activities in the stomach and intestine tissues of S. chuatsi under different feeding practicesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
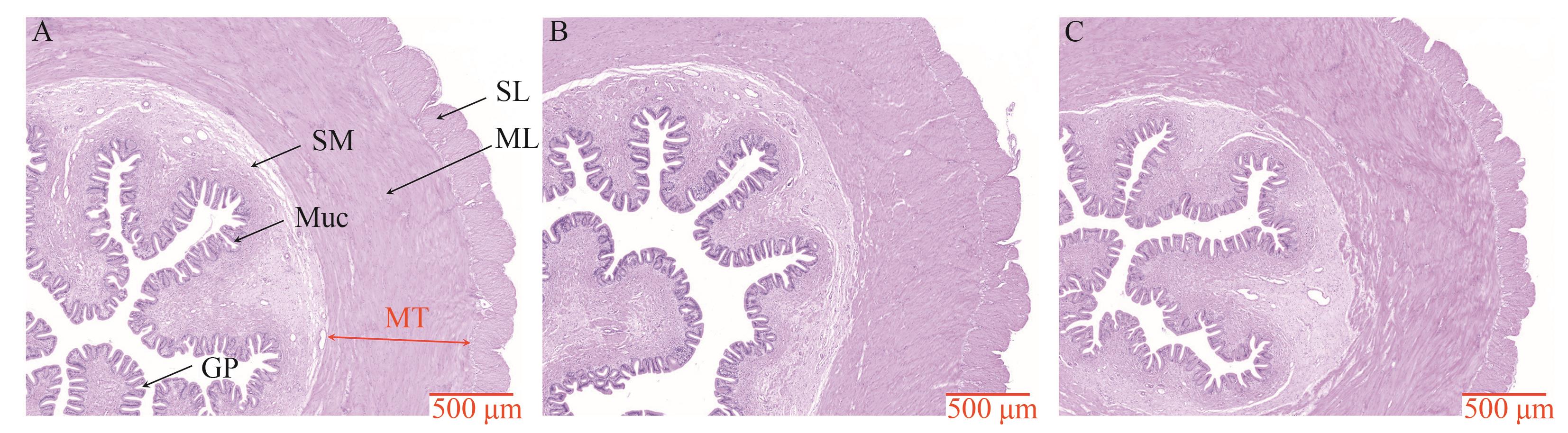
Fig. 4 Stomach tissue structure of S. chuatsi under different feeding practicesA:Stomach tissue section of the live bait group, SL—Serosa layer, ML—Muscularis layer, SM—Submucosa layer, Muc—Mucous layer, GP—Gastric pits, MT—muscle thickness; B:Stomach tissue section of the mixed diet group; C: Stomach tissue section of the compound feed group
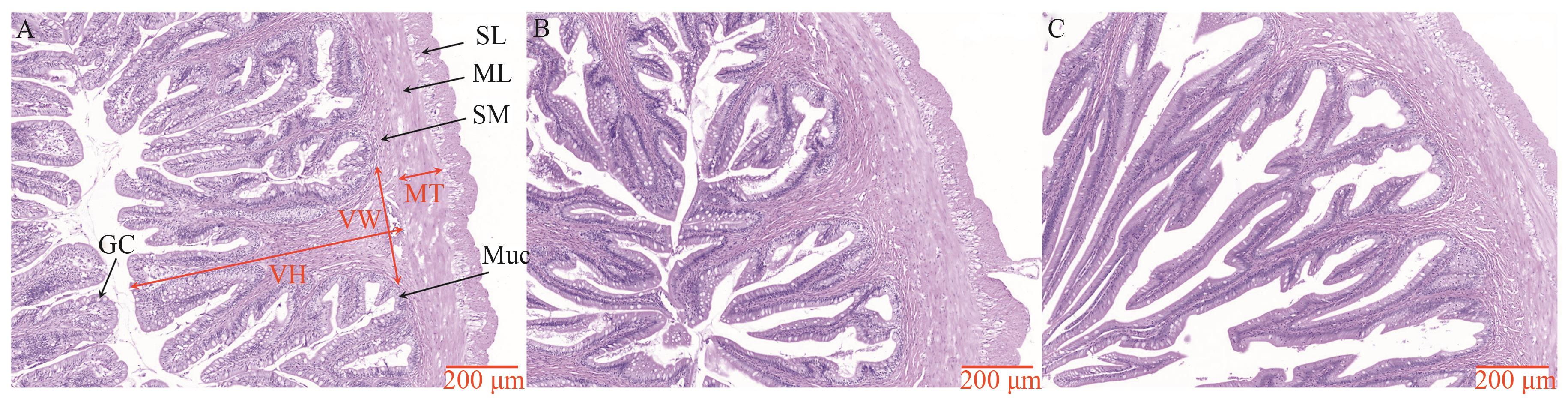
Fig. 5 Intestinal tissue structure of S. chuatsi under different feeding practicesA:Intestinal tissue section of the live bait group, SL—Serosa layer, ML—Muscularis layer, SM—Submucosa layer, Muc—Mucous layer, GC—Goblet cell, VH—Villus height, VW—Villus width, MT—Muscle thickness; B:Intestinal tissue section of the mixed diet group; C:Intestinal tissue section of the compound feed group
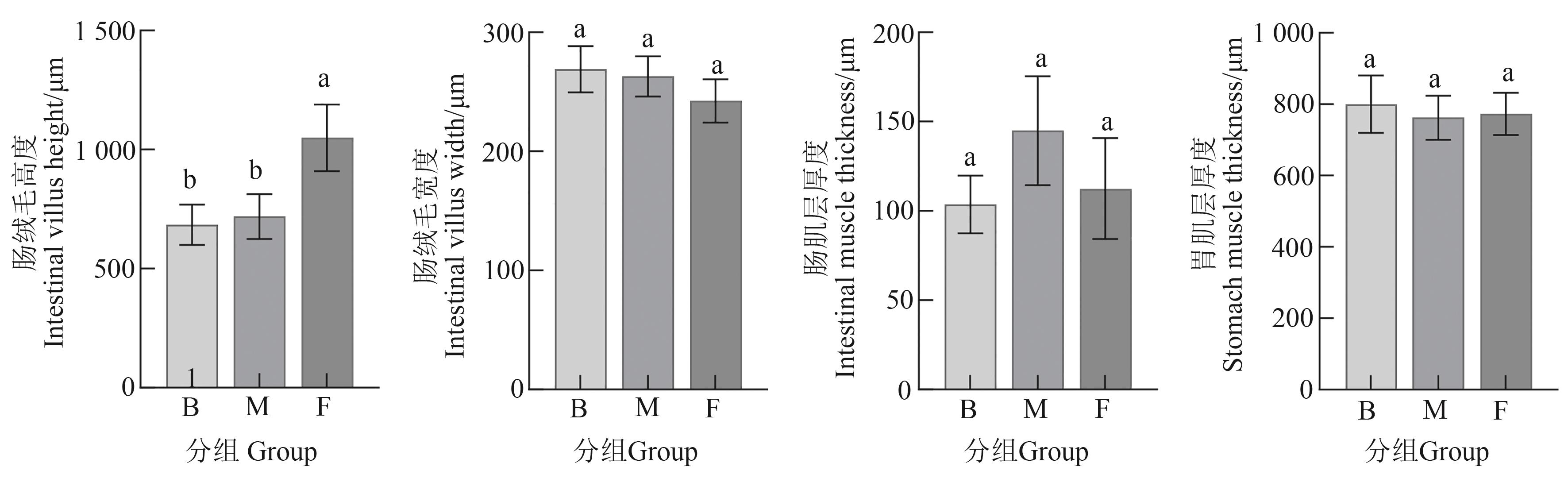
Fig. 6 Effect of different feeding practices on stomach and intestinal tissues structure of S. chuatsiNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
| [1] | 李松林, 韩志豪, 王小源, 等. 鳜养殖概况及摄食调控机制研究进展[J]. 水产学报, 2021, 45(10): 1787-1795. |
| LI S L, HAN Z H, WANG X Y, et al.. Research progress on aquaculture and feeding regulation mechanism of mandarin fish [J]. J. Fish. China, 2021, 45(10): 1787-1795. | |
| [2] | 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局,全国水产技术推广总站,中国水产学会.2024中国渔业统计年鉴[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2024:1-159. |
| [3] | 张梅,王洋.鳜鱼养殖现状及2024年养殖趋势[J].科学养鱼,2024(7):3-5. |
| [4] | 刘立维.700亿的鳜鱼产业风口已现,不能再被这些问题“卡脖子”了[J].当代水产,2023,48(6):74-75. |
| [5] | LIANG X F, KIU J K, HUANG B Y. The role of sense organs in the feeding behaviour of Chinese perch [J]. J. Fish Biol., 1998,52(5):1058-1067. |
| [6] | HE S, LI L, LYU L Y,et al.. Mandarin fish (Sinipercidae) genomes provide insights into innate predatory feeding [J/OL].Commun.Biol.,2020,3(1):361 [2025-01-16].. |
| [7] | LIANG X F, LIN X T, LI S Q, et al.. Impact of environmental and innate factors on the food habit of Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) (Percichthyidae) [J].Aquac.Res.,2008,39(2):150-157. |
| [8] | LIANG X F, OKU H, OGATA H Y, et al.. Weaning Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) onto artificial diets based upon its specific sensory modality in feeding [J]. Aquac. Res., 2001,32(S1):76-82. |
| [9] | SHEN Y W, LI H Y, ZHAO J L, et al.. The digestive system of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) can adapt to domestication by feeding with artificial diet [J/OL].Aquaculture,2021,538:736546 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [10] | SHEN Y W, SONG L Y, CHEN T T, et al.. Identification of hub genes in digestive system of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) fed with artificial diet by weighted gene co-expression network analysis [J/OL].Comp.Biochem.Physiol.Part D Genomics Proteomics,2023,47:101112 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [11] | JIAO F, ZHANG L, LIMBU S M, et al.. A comparison of digestive strategies for fishes with different feeding habits:digestive enzyme activities,intestinal morphology,and gut microbiota [J/OL]. Ecol. Evol., 2023,13(9):e10499 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [12] | ZHANG Y P, FENG H X, LIANG X F, et al.. Dietary bile acids reduce liver lipid deposition via activating farnesoid X receptor,and improve gut health by regulating gut microbiota in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi) [J]. Fish Shellfish. Immunol., 2022,121:265-275. |
| [13] | MAI Q Y, JIN Y Q, CHEN Y F, et al.. Assessing the effects of dietary live prey versus an artificial compound feed on growth performance,immune response,and intestinal microflora of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides [J]. Aquac. Int., 2023,31(3):1213-1230. |
| [14] | MARTÍNEZ-ÁLVAREZ R M, MORALES A E, SANZ A. Antioxidant defenses in fish:biotic and abiotic factors [J]. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish., 2005,15(1):75-88. |
| [15] | 樊玉文, 张木子, 黎明, 等. 饲料中添加雨生红球藻对黄颡鱼生长、抗氧化酶活性、免疫应答及氨氮耐受的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2022, 46(11): 2168-2176. |
| FAN Y W, ZHANG M Z, LI M, et al.. Effects of dietary Haematococcus pluvialis on growth, antioxidant enzyme activity, immune response and ammonia tolerance in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco [J]. J. Fish. China, 2022, 46(11): 2168-2176. | |
| [16] | 汪福保,孙成飞,董浚键,等.投喂配合饲料和活饵对翘嘴鳜形体和肌肉品质的影响[J].淡水渔业,2022,52(6):102-111. |
| WANG F B, SUN C F, DONG J J, et al.. Effects of compound feed and live bait on the nutrient composition and meat quality of Siniperca chuatisi [J]. Freshwater Fish., 2022,52(6):102-111. | |
| [17] | 陈晓虹,洪越群,谭永基,等.鳜鱼配合饲料对翘嘴鳜生长的影响和驯化养殖技术[J].当代水产,2022,47(7):76-78, 81. |
| [18] | 窦亚琪,梁旭方,易提林,等.翘嘴鳜不同月龄性状的主成分与判别分析[J].中国水产科学,2014,21(6):1116-1124. |
| DOU Y Q, LIANG X F, YI T L, et al.. Principal component and discriminant analyses of traits of Siniperca chuatsi at different ages [J]. J. Fish. Sci. China, 2014,21(6):1116-1124. | |
| [19] | 刘慧军,杨海明,胥蕾,等.畜禽肠道组织H.E.染色石蜡切片制作要点及关键技术[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2018(15):206-210. |
| LIU H J, YANG H M, XU L, et al.. Key points and techniques of H.E.staining and paraffin sectionin livestock and poultry intestines [J].Heilongjiang Anim.Sci.Vet.Med., 2018(15):206-210. | |
| [20] | WANG C, XIE S, ZHENG K, et al.. Effects of live food and formulated diets on survival, growth and protein content of first-feeding larvae of Plelteobagrus fulvidraco [J]. J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2005,21(3):210-214. |
| [21] | 陈剑斌,于俊琦,徐杭忠,等.配合饲料和饵料鱼对鳜生长、胃肠结构功能及肉质的影响[J].水产学报,2023,47(10):84-98. |
| CHEN J B, YU J Q, XU H Z, et al.. Effects of compound feed and bait fish on growth,gastrointestinal structure and function and meat quality of Siniperca chuatsi [J]. J. Fish. China, 2023,47(10):84-98. | |
| [22] | 班赛男, 朱传忠, 杨新冬, 等. 摄食不同饵料对翘嘴鳜生长、体成分和消化酶活性的影响[J]. 淡水渔业, 2020, 50(1): 93-100. |
| BAN S N, ZHU C Z, YANG X D, et al.. Effect of different diet on the growth performance, body composition and digestive enzymes active of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatisi) [J]. Freshwater Fish., 2020, 50(1): 93-100. | |
| [23] | 马林,李明泽,毕相东,等.摄食不同饵料对翘嘴鳜生长性能、肌肉营养成分及消化酶活性的影响[J].饲料研究,2023,46(6):44-49. |
| MA L, LI M Z, BI X D, et al.. Effect of different diets on growth performance,muscle nutrient composition and digestive enzyme activity of Siniperca chuatsi [J]. Feed. Res., 2023,46(6):44-49. | |
| [24] | 曾萌冬,徐俊,宋银都,等.配合饲料替代活饵对鳜生长性能、消化功能及小肽转运载体基因表达的影响[J].南方农业学报,2021,52(1):228-237. |
| ZENG M D, XU J, SONG Y D, et al.. Effects of replacing live bait with compound feed on growth,digestion and expression of small peptide transporter (PepT1) gene of Siniperca chuatsi [J].J. South. Agric., 2021,52(1):228-237. | |
| [25] | LI X M, ZHU Y J, RINGØ E, et al.. Intestinal microbiome and its potential functions in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) under different feeding strategies [J/OL]. Peer J, 2018, 6:e6000 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [26] | PANG X, TAN G, SUN H, et al.. Effect of feeding different diets on postprandial metabolic response,digestive capacity and growth performance in juvenile southern catfish (Silurus meridionalis) [J/OL].Aquac. Rep., 2022,27:101413 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [27] | XUE S Y, DING J K, LI J Q, et al.. Effects of live,artificial and mixed feeds on the growth and energy budget of Penaeus vannamei [J/OL]. Aquac. Rep., 2021,19:100634 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [28] | LIU S C, LIU S J, SUN Z Q, et al.. Effects of dietary lipid and protein levels on growth,body composition,antioxidant capacity,and flesh quality of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) [J/OL].Aquac. Int., 2024,33(1):78 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [29] | ZELKO I N, MARIANI T J, FOLZ R J. Superoxide dismutase multigene family:a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1),Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,evolution,and expression [J]. Free. Radic. Biol. Med., 2002,33(3):337-349. |
| [30] | TAN P, DONG X J, XU H L, et al.. Dietary vegetable oil suppressed non-specific immunity and liver antioxidant capacity but induced inflammatory response in Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) [J]. Fish Shellfish. Immunol., 2017,63:139-146. |
| [31] | ALUTA U P, ADEROLU A Z, LAWAL M O, et al.. Inclusion effect of onion peel powder in the diet of African catfish,Clarias gariepinus:growth,blood chemistry,hepatic antioxidant enzymes activities and SOD mRNA responses [J/OL]. Sci. Afr., 2021,12:e00780 [2025-01-16].. |
| [32] | MONIRUZZAMAN M, GHOSAL I, DAS D, et al.. Melatonin ameliorates H2O2-induced oxidative stress through modulation of Erk/Akt/NFkB pathway [J/OL]. Biol. Res., 2018,51(1):17 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [33] | ZHOU C P, HUANG Z, LIN H Z, et al.. Rhizoma curcumae Longae ameliorates high dietary carbohydrate-induced hepatic oxidative stress,inflammation in golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus [J]. Fish Shellfish. Immunol., 2022,130:31-42. |
| [34] | 马兴宇, 唐忠林, 陈树桥, 等. 转食饲料对大口黑鲈幼鱼的存活率、抗氧化酶和消化酶活性及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 2024, 31(4): 403-415. |
| MA X Y, TANG Z L, CHEN S Q, et al.. Impacts of early weaning on survival rate, antioxidant and digestive enzyme activities, and intestinal microbiota of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) [J]. J. Fish. Sci. China, 2024, 31(4): 403-415. | |
| [35] | MUÑOZ-PEÑUELA M, NOSTRO F LLO, DAL’OLIO GOMES A, et al.. Diclofenac and caffeine inhibit hepatic antioxidant enzymes in the freshwater fish Astyanax altiparanae (Teleostei:Characiformes) [J/OL]. Comp.Biochem.Physiol.Part C Toxicol.Pharmacol., 2021,240:108910 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [36] | CAO L, HUANG W, SHAN X J, et al.. Tissue-specific accumulation of cadmium and its effects on antioxidative responses in Japanese flounder juveniles [J]. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2012,33(1):16-25. |
| [37] | 李良. 饥饿复投喂对翘嘴鳜酶活性、血液生化及基因表达的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2021. |
| LI L. Effects of starvation and refeeding on enzyme activity, blood biochemistry and gene expression of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [38] | ALI S S, AHSAN H, ZIA M K, et al.. Understanding oxidants and antioxidants:classical team with new players [J/OL].J.Food Biochem.,2020,44(3):e13145 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [39] | PIZZIMENTI S, CIAMPORCERO E, DAGA M, et al.. Interaction of aldehydes derived from lipid peroxidation and membrane proteins [J/OL]. Front. Physiol., 2013,4:242 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [40] | AYALA A, MUÑOZ M F, ARGÜELLES S. Lipid peroxidation:production,metabolism,and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal [J/OL]. Oxid. Med.Cell. Longev., 2014,2014(1):360438 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [41] | ZHAO J, LIU Y, JIANG J, et al.. Effects of dietary isoleucine on growth,the digestion and absorption capacity and gene expression in hepatopancreas and intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. jian) [J].Aquaculture, 2012, 368: 117-128. |
| [42] | TANG L, WANG G X, JIANG J, et al.. Effect of methionine on intestinal enzymes activities,microflora and humoral immune of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. jian) [J]. Aquac. Nutr., 2009,15(5):477-483. |
| [43] | BUDDINGTON R K, KROGDAHL A, BAKKE-MCKELLEP A M. The intestines of carnivorous fish: structure and functions and the relations with diet [J]. Acta Physiol.Scand. , 1997, 638:67-80. |
| [44] | ZHAO L L, LUO J, LIU Q, et al.. Different diets can affect the digestion and immunity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) according to enzyme activity assay and transcriptome sequencing [J/OL]. Aquaculture,2020,523:735176 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [45] | YAN Y Y, WANG F B, CHEN X, et al.. Comparative analysis of the intestinal flora of Siniperca chuatsi at different growth stages under three feeding practices [J/OL]. Aquac. Rep., 2025,40:102582 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [46] | DING L Y, ZHANG Y P, CHEN J C, et al.. Growth,muscle nutrition composition,and digestive enzyme activities of the juvenile and adult siniperca chuatsi fed on live baits and a formulated diet [J/OL]. Fishes, 2022,7(6):379 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [47] | 赵月月,赵健蓉,胡佐灿,等.不同饵料对稀有鮈鲫仔稚鱼生长、消化道及消化酶的影响[J].水生生物学报,2018,42(1):114-122. |
| ZHAO Y Y, ZHAO J R, HU Z C, et al.. The effects of different baits on the growth and activities of the digestive tract and enzyme of the larvae and juvenile Gobiocypris rarus [J]. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin., 2018,42(1):114-122. | |
| [48] | 申亚伟. 鳜消化系统枢纽基因鉴定及Lect2的表达和功能分析[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2022. |
| SHEN Y W. Identification of hub genes in the digestive system of Siniperca chuatsi and expression and functional analysis of Lect2 [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2022. | |
| [49] | 欧红霞,王广军,李志斐,等.不同饲料对大口黑鲈肠道组织结构的影响[J].水产科学,2020,39(6):902-907. |
| OU H X, WANG G J, LI Z F, et al.. Influence of different diets on intestinal histological morphologic structure of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides [J]. Fish. Sci., 2020,39(6):902-907. | |
| [50] | 赖铭勇.投喂不同饵料对斑鳜生长及消化性能的影响[J].南方农业学报,2024,55(8):2523-2534. |
| LAI M Y. Effects of feeding different diets on growth and digestive performance of spotted mandarin fish (Siniperca scherzeri) [J]. J. South. Agric., 2024,55(8):2523-2534. | |
| [51] | CAO K L, WANG Y Y, LI M L, et al.. Supplementation of a multienzyme complex,an organic acid-essential oil complex,and prebiotic alone or in combination affects growth,nutrient utilization,and immune function of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [J/OL]. Aquac. Nutr., 2022,2022(1):1068537 [2025-01-16]. . |
| [1] | Wenhao ZHOU, Yuhan ZHANG, Delong MENG, Hui LIANG, Yuanpei ZHANG, Yalin YANG, Zhen ZHANG, Yuanyuan YAO, Chao RAN, Zhigang ZHOU. Research Progress on Application of Bacillus velezensis in Animal Husbandry [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 1-7. |
| [2] | Mi OU, Jian ZHAO, Qing LUO, Haiyang LIU, Rong HUANG, Yaping WANG, Kunci CHEN. Research Progress on the Breeding and Application of Sex Control in Snakehead [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 11-25. |
| [3] | HUANG Jun, DING Hong-biao, ZHAO Guo-qi. Effect of Trehalose on the Growth and Carcass Performance of AA Broilers [J]. , 2009, 11(4): 58-63. |
| [4] | ZHAN Yu-ming|ZHAO Ming-xiao|ZHU Liang-zhi|LIU Hua-yang|LI Bin. Determination of Clomiphene in Compound Feed Using HPLC [J]. , 2008, 10(S2): 48-52. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号