




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 208-217.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0073
• INNOVATIVE METHODS AND TECHNOLOGIES • Previous Articles
Kaiqiang WANG1( ), Xue YANG1, Changfeng LI1, Xiao DUAN1, Qing PENG2, Yu QIAO2, Bo SHI2(
), Xue YANG1, Changfeng LI1, Xiao DUAN1, Qing PENG2, Yu QIAO2, Bo SHI2( )
)
Received:2022-01-28
Accepted:2022-06-02
Online:2022-10-15
Published:2022-10-25
Contact:
Bo SHI
王凯强1( ), 杨雪1, 李常风1, 段晓1, 彭晴2, 乔宇2, 石波2(
), 杨雪1, 李常风1, 段晓1, 彭晴2, 乔宇2, 石波2( )
)
通讯作者:
石波
作者简介:王凯强 E-mail:wangkaiqiang@czmc.edu.cn;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Kaiqiang WANG, Xue YANG, Changfeng LI, Xiao DUAN, Qing PENG, Yu QIAO, Bo SHI. Optimization of Glyceollins Synthesis Condition Induced by Xylooligosaccharides Based on Response Surface Methodology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(10): 208-217.
王凯强, 杨雪, 李常风, 段晓, 彭晴, 乔宇, 石波. 响应面法优化低聚木糖诱导大豆抗毒素合成条件[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 208-217.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0073
| 时间Time/min | 流速Rate/(mL·min-1) | A/% | B/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 17 | 1.0 | 55 | 45 |
| 27 | 1.0 | 10 | 90 |
| 33 | 1.0 | 10 | 90 |
| 34 | 1.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 49 | 1.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 50 | 1.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 65 | 1.0 | 100 | 0 |
Table 1 HPLC gradient elution procedure
| 时间Time/min | 流速Rate/(mL·min-1) | A/% | B/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 17 | 1.0 | 55 | 45 |
| 27 | 1.0 | 10 | 90 |
| 33 | 1.0 | 10 | 90 |
| 34 | 1.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 49 | 1.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 50 | 1.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 65 | 1.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 水平Level | 因素Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
X1:诱导时间 Induction time/d | X2:XOS诱导质量浓度 XOS concentration/(g·100 mL-1) | X3:培养温度 Temperature/℃ | |
| -1.682 | 2 | 2.0 | 17 |
| -1.000 | 3 | 3.0 | 21 |
| 0.000 | 4 | 4.0 | 25 |
| +1.000 | 5 | 5.0 | 29 |
| +1.682 | 6 | 6.0 | 33 |
Table 2 Factors and levels for central composite design
| 水平Level | 因素Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
X1:诱导时间 Induction time/d | X2:XOS诱导质量浓度 XOS concentration/(g·100 mL-1) | X3:培养温度 Temperature/℃ | |
| -1.682 | 2 | 2.0 | 17 |
| -1.000 | 3 | 3.0 | 21 |
| 0.000 | 4 | 4.0 | 25 |
| +1.000 | 5 | 5.0 | 29 |
| +1.682 | 6 | 6.0 | 33 |
运行 Run | X1:时间 Time/d | X2:质量浓度 Mass concentration/(g·100 mL-1) | X3:温度 Temperature/℃ | 大豆抗毒素含量 GLYs content/(mg·g-1 DW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
实际值 Actual value | 预测值 Predicted value | ||||
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 21 | 0.935 8 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 21 | 0.932 7 | 1.00 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 21 | 0.949 0 | 0.96 |
| 4 | 5 | 5 | 21 | 1.047 5 | 1.00 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 29 | 0.526 8 | 0.61 |
| 6 | 5 | 3 | 29 | 0.594 0 | 0.62 |
| 7 | 3 | 5 | 29 | 0.807 9 | 0.78 |
| 8 | 5 | 5 | 29 | 0.850 7 | 0.82 |
| 9 | 2 | 4 | 25 | 1.012 5 | 0.95 |
| 10 | 6 | 4 | 25 | 0.964 1 | 0.98 |
| 11 | 4 | 2 | 25 | 1.017 4 | 0.89 |
| 12 | 4 | 6 | 25 | 0.948 3 | 1.02 |
| 13 | 4 | 4 | 17 | 1.002 8 | 0.96 |
| 14 | 4 | 4 | 33 | 0.489 9 | 0.48 |
| 15 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.631 6 | 1.39 |
| 16 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.350 2 | 1.39 |
| 17 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.318 1 | 1.39 |
| 18 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.326 0 | 1.39 |
| 19 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.308 9 | 1.39 |
| 20 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.390 9 | 1.39 |
Table 3 CCD of induction time, XOS concentration and temperature and the GLYs content
运行 Run | X1:时间 Time/d | X2:质量浓度 Mass concentration/(g·100 mL-1) | X3:温度 Temperature/℃ | 大豆抗毒素含量 GLYs content/(mg·g-1 DW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
实际值 Actual value | 预测值 Predicted value | ||||
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 21 | 0.935 8 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 21 | 0.932 7 | 1.00 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 21 | 0.949 0 | 0.96 |
| 4 | 5 | 5 | 21 | 1.047 5 | 1.00 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 29 | 0.526 8 | 0.61 |
| 6 | 5 | 3 | 29 | 0.594 0 | 0.62 |
| 7 | 3 | 5 | 29 | 0.807 9 | 0.78 |
| 8 | 5 | 5 | 29 | 0.850 7 | 0.82 |
| 9 | 2 | 4 | 25 | 1.012 5 | 0.95 |
| 10 | 6 | 4 | 25 | 0.964 1 | 0.98 |
| 11 | 4 | 2 | 25 | 1.017 4 | 0.89 |
| 12 | 4 | 6 | 25 | 0.948 3 | 1.02 |
| 13 | 4 | 4 | 17 | 1.002 8 | 0.96 |
| 14 | 4 | 4 | 33 | 0.489 9 | 0.48 |
| 15 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.631 6 | 1.39 |
| 16 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.350 2 | 1.39 |
| 17 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.318 1 | 1.39 |
| 18 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.326 0 | 1.39 |
| 19 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.308 9 | 1.39 |
| 20 | 4 | 4 | 25 | 1.390 9 | 1.39 |
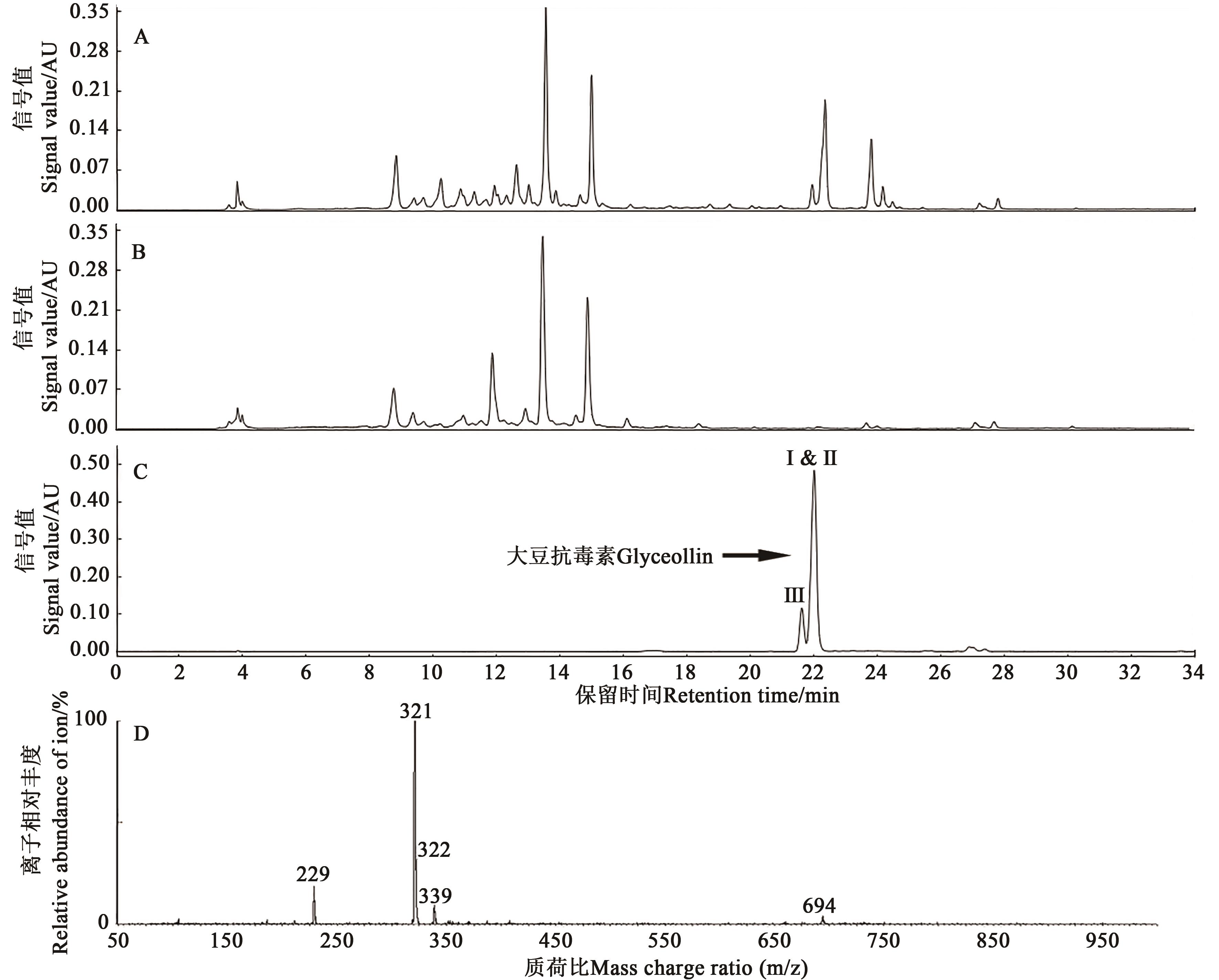
Fig. 1 Confirmation of the glyceollins synthesis from XOS-induced soybean cotyledon tissueA: HPLC chromatogram of XOS-treated cotyledon tissue; B: HPLC chromatogram of untreated cotyledon tissue; C and D: HPLC chromatogram and MS spectrum of separated and purified GLYs
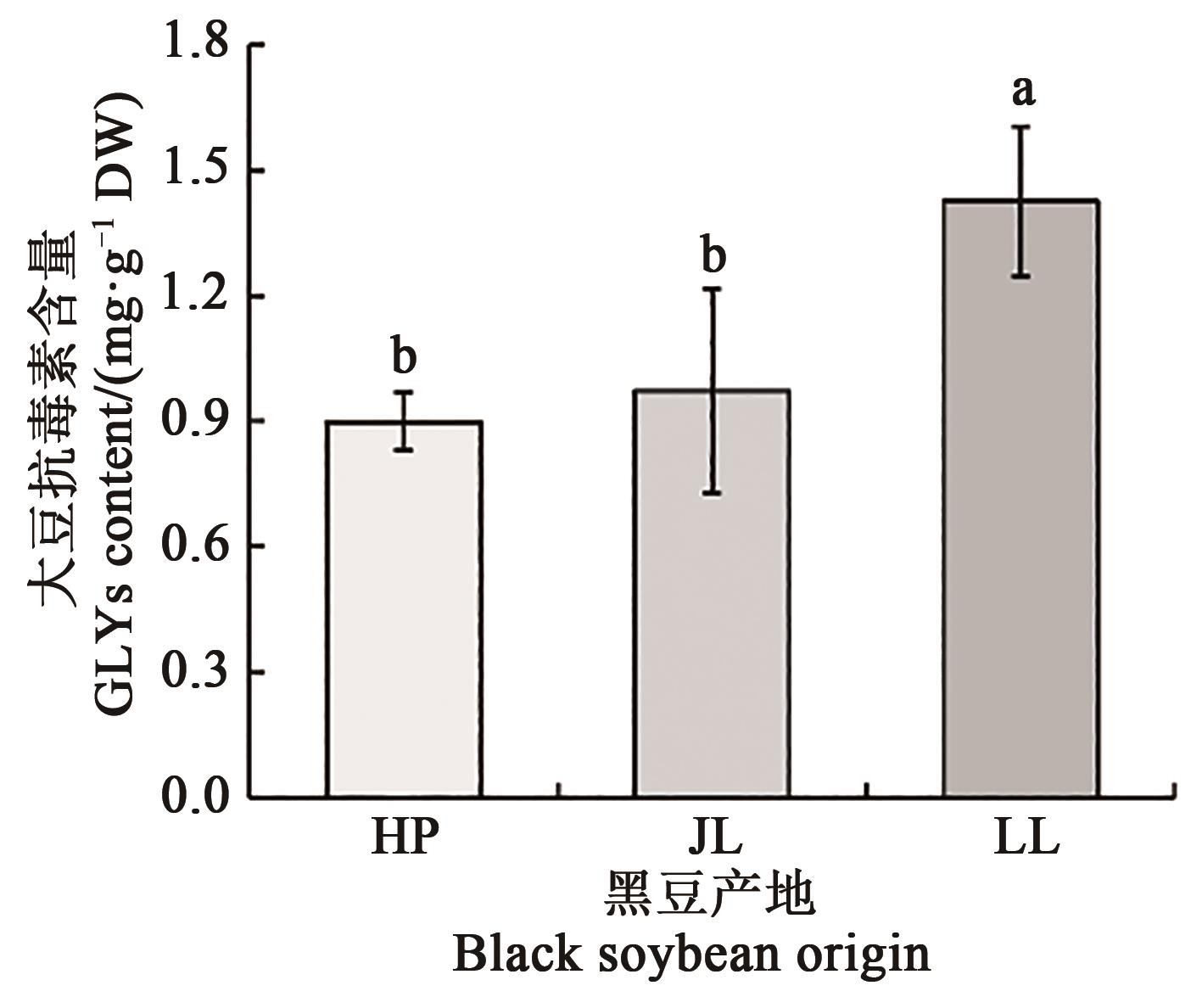
Fig. 2 Synthesized GLYs content from three origins of black soybean under inductionNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significantly differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
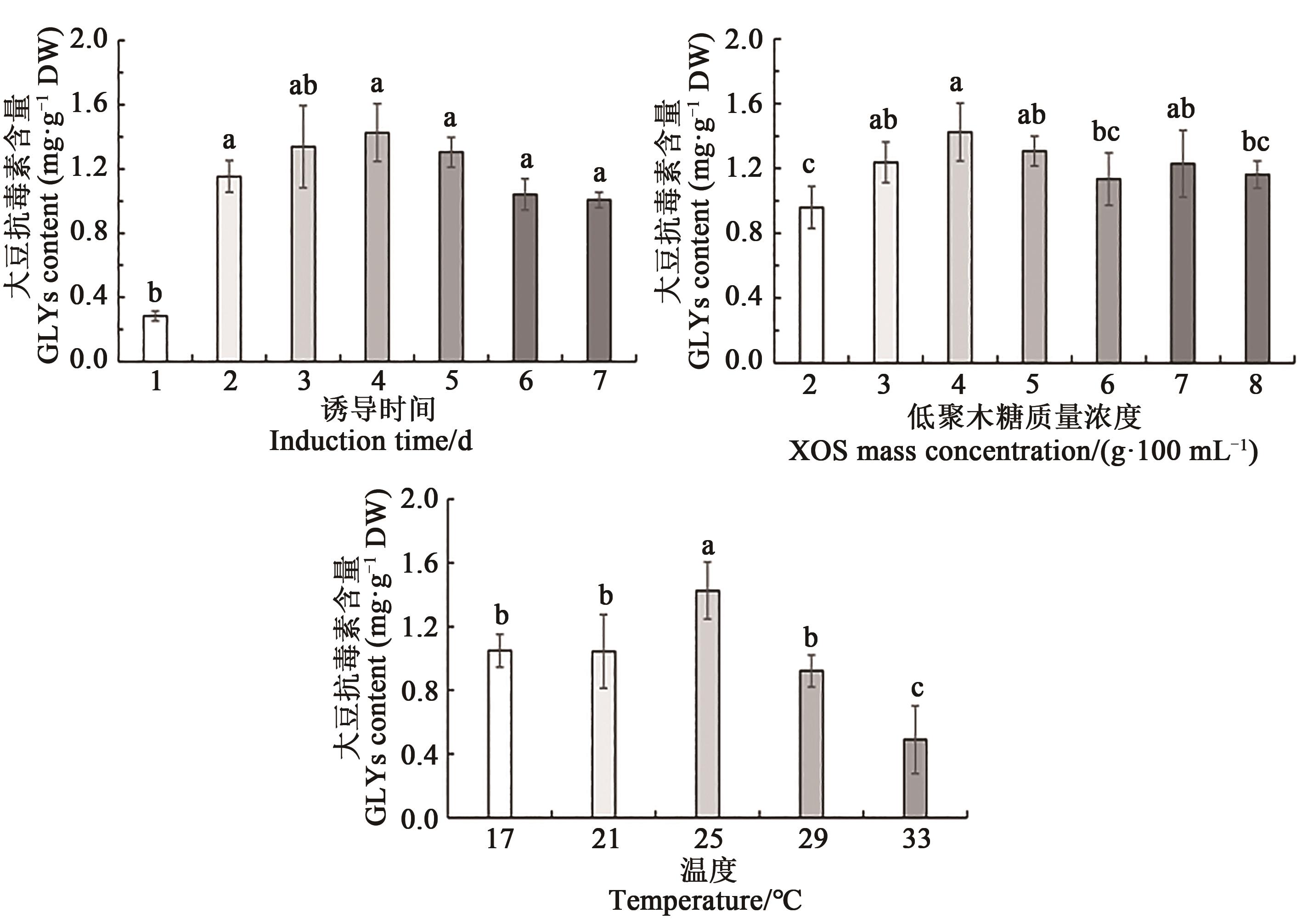
Fig. 3 Synthesized GLYs contents from LL under induction of different factorsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significantly differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型Model | 1.570 | 9 | 0.170 | 13.780 | 0.000 2 |
| X1 | 1.126×10-3 | 1 | 1.126×10-3 | 0.089 | 0.771 5 |
| X2 | 0.022 | 1 | 0.022 | 1.750 | 0.215 5 |
| X3 | 0.280 | 1 | 0.280 | 21.980 | 0.000 9 |
| X1X2 | 7.450×10-4 | 1 | 7.450×10-4 | 0.059 | 0.813 1 |
| X1X3 | 2.664×10-5 | 1 | 2.664×10-5 | 2.107×10-3 | 0.964 3 |
| X2X3 | 0.021 | 1 | 0.021 | 1.660 | 0.226 6 |
| X | 0.330 | 1 | 0.330 | 25.950 | 0.000 5 |
| X | 0.340 | 1 | 0.340 | 26.620 | 0.000 4 |
| X | 0.810 | 1 | 0.810 | 63.710 | <0.000 1 |
| 残差Residual | 0.130 | 10 | 0.013 | — | — |
| 失拟项Lack of fit | 0.051 | 5 | 0.010 | 0.670 | 0.665 0 |
| 纯误差Pure error | 0.076 | 5 | 0.015 | — | — |
| 总误差Total error | 1.700 | 19 | — | — | — |
Table 4 Credibility for CCD model of induction time, XOS concentration and temperature
变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型Model | 1.570 | 9 | 0.170 | 13.780 | 0.000 2 |
| X1 | 1.126×10-3 | 1 | 1.126×10-3 | 0.089 | 0.771 5 |
| X2 | 0.022 | 1 | 0.022 | 1.750 | 0.215 5 |
| X3 | 0.280 | 1 | 0.280 | 21.980 | 0.000 9 |
| X1X2 | 7.450×10-4 | 1 | 7.450×10-4 | 0.059 | 0.813 1 |
| X1X3 | 2.664×10-5 | 1 | 2.664×10-5 | 2.107×10-3 | 0.964 3 |
| X2X3 | 0.021 | 1 | 0.021 | 1.660 | 0.226 6 |
| X | 0.330 | 1 | 0.330 | 25.950 | 0.000 5 |
| X | 0.340 | 1 | 0.340 | 26.620 | 0.000 4 |
| X | 0.810 | 1 | 0.810 | 63.710 | <0.000 1 |
| 残差Residual | 0.130 | 10 | 0.013 | — | — |
| 失拟项Lack of fit | 0.051 | 5 | 0.010 | 0.670 | 0.665 0 |
| 纯误差Pure error | 0.076 | 5 | 0.015 | — | — |
| 总误差Total error | 1.700 | 19 | — | — | — |
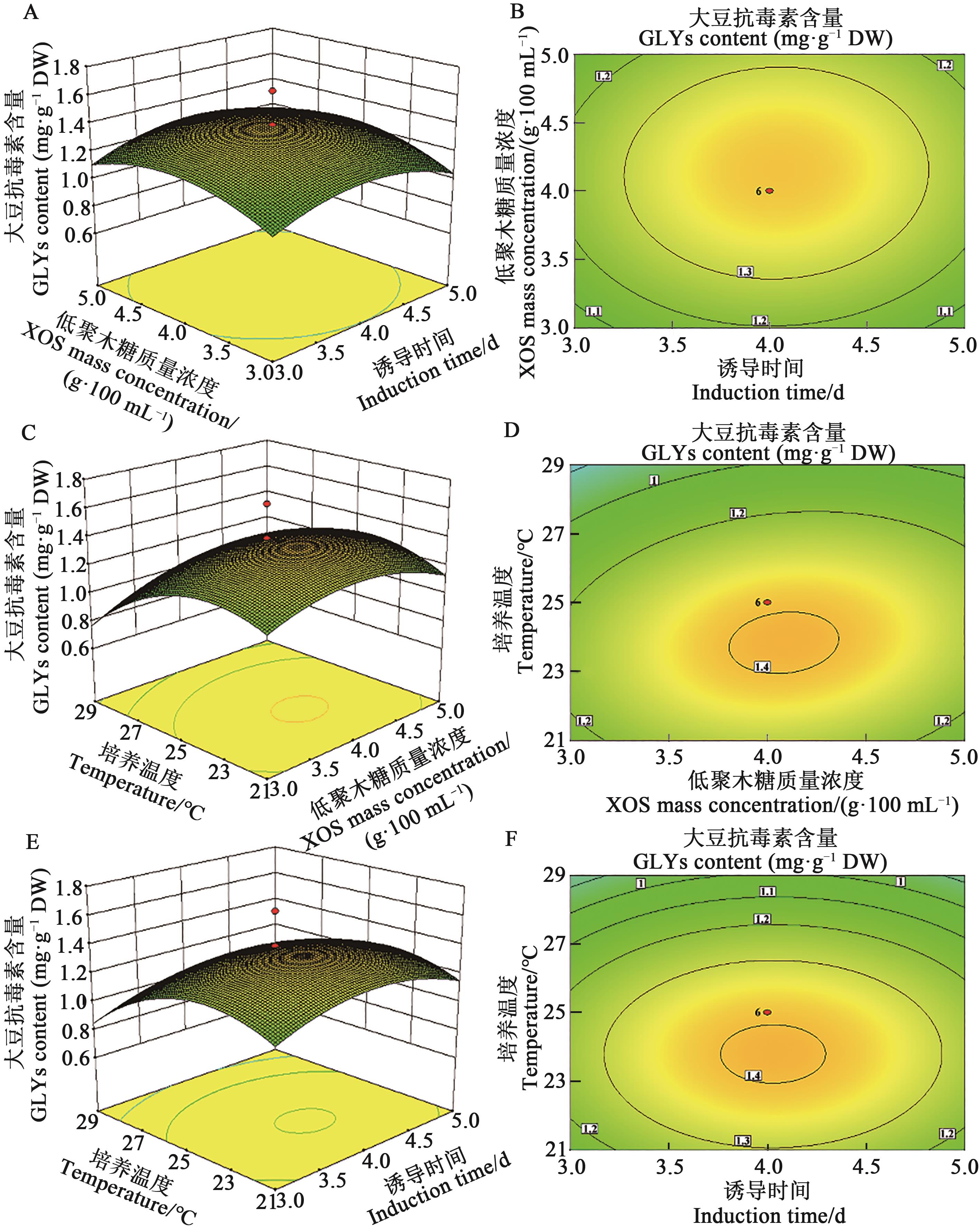
Fig. 5 Contour and response surface plots for the interactive effects of induction time, XOS mass concentrationA and B: Interactive effect of induction time and XOS concentration; C and D: Interactive effect of temperature and XOS mass concentration; E and F: Interactive effect of temperature and induction time.and temperature on GLYs content
| 1 | 龚凌霄,倪勤学,张英.植物抗毒素研究进展及其作为食品功能性成分的应用前景[J].天然产物研究与开发,2012,24(3):421-425, 377. |
| GONG L X, NI Q X, ZHANG Y. Research on phytoalexins and its application prospect as a food functional component [J]. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev., 2012, 24(3):421-425, 377. | |
| 2 | BAMJI S F, CORBITT C. Glyceollins: soybean phytoalexins that exhibit a wide range of health-promoting effects [J]. J. Funct. Foods, 2017, 34:98-105. |
| 3 | NWACHUKWU I D, LUCIANO F B, UDENIGWE C C. The inducible soybean glyceollin phytoalexins with multifunctional health-promoting properties [J]. Food Res. Int., 2013, 54(1):1208-1216. |
| 4 | KALLI S, ARAYA-CLOUTIER C, LIN Y R, et al.. Enhanced biosynthesis of the natural antimicrobial glyceollins in soybean seedlings by priming and elicitation [J/OL]. Food Chem., 2020, 317:126389 [2021-12-10]. . |
| 5 | KALLI S, ARAYA-CLOUTIER C, DE BRUIJN W J C, et al.. Induction of promising antibacterial prenylated isoflavonoids from different subclasses by sequential elicitation of soybean [J/OL]. Phytochemistry, 2020, 179:112496 [2021-12-10]. . |
| 6 | JAHAN M A, KOVINICH N. Acidity stress for the systemic elicitation of glyceollin phytoalexins in soybean plants [J/OL]. Plant Signal. Behav., 2019, 14(7):1604018 [2021-12-10]. . |
| 7 | ANGELOVA Z, GEORGIEV S, ROOS W. Elicitation of plants [J]. Biotechnol. Biotec. Eq., 2006, 20:72-83. |
| 8 | 滕超,查沛娜,曲玲玉,等.功能性寡糖研究及其在食品中的应用进展[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2014,5(1):123-130. |
| TENG C, ZHA P N, QU L Y, et al.. Progress of research and application in food industry of functional oilgosaccharides [J]. J. Food Saf. Qual., 2014, 5(1):123-130. | |
| 9 | 黄强,张丽华,陶健,等.低聚木糖对植物乳杆菌发酵红枣汁品质的影响[J].食品科技,2021,46(10):7-12. |
| HUANG Q, ZHANG L H, TAO J, et al.. Effect of xylo-oligosaccharide on quality characteristics of jujube juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum [J]. Food Sci. Technol., 2021, 46(10):7-12. | |
| 10 | 宁俊,杨海军.功能食品配料——低聚木糖的功能及其应用研究[J].食品安全导刊,2018(10):46-48. |
| NING J, YANG H J. Functional food ingredients—low polysaccharide function and its application research [J]. China Food Saf. Mag., 2018(10):46-48. | |
| 11 | MANISSERI C, GUDIPATI M. Prebiotic activity of purified xylobiose obtained from ragi (Eleusine coracana, Indaf-15) bran [J]. Indian J. Microbiol., 2012, 52(2):251-257. |
| 12 | SAMANTA A K, JAYAPAL N, JAYARAM C, et al.. Xylooligosaccharides as prebiotics from agricultural by-products: production and applications [J]. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre, 2015, 5(1):62-71. |
| 13 | 鲁军.营养功能性食品发展趋势及产品创新[J].轻工标准与质量,2019(5):19. |
| LU J. Development trend and products innovation of nutritional functional food [J]. Stand. Qual. Light Ind., 2019(5):19. | |
| 14 | 田秀红,闫峰,刘鑫峰,等.大豆功能性食品及其开发应用前景[J].中国食物与营养,2008(4):50-53. |
| TIAN X H, YAN F, LIU X F, et al.. Functional soybean food and its prospect of development and application [J]. Food Nutr. China, 2008(4):50-53. | |
| 15 | 罗素亚,郑豆豆,何广正,等.响应面法优化脯氨酸羟化酶转化反应工艺条件[J].生物技术通报,2020,36(6): 157-164. |
| LUO S Y, ZHENG D D, HE G Z, et al.. Optimization of catalytic reaction conditions for L-proline 4-hydroxylase using response surface methodology [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2020, 36(6):157-164. | |
| 16 | CHELLADURAI S J S, MURUGAN K, RAY A P, et al.. Optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology: a review [J]. Mater. Today: Proc., 2021, 37:1301-1304. |
| 17 | SHEN J J, ZHU A S, GAO T T, et al.. Optimization of extraction technology of sterols from discarded soybean pod by response surface methodology [J/OL]. Environ. Chall., 2021, 5:100272. [2021-12-10]. . |
| 18 | KUMAR M, DAHUJA A, SACHDEV A, et al.. Evaluation of enzyme and microwave-assisted conditions on extraction of anthocyanins and total phenolics from black soybean (Glycine max L.) seed coat [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, 135:1070-1081. |
| 19 | 胡佳,石波, EROMOSELE O,等.褐藻酸寡糖诱导下大豆中大豆抗毒素的累积变化[J].中国农业科学,2012,45 (8):1576-1586. |
| HU J, SHI B, EROMOSELE O, et al.. Effects of alginate oilgosaccharides on the accumulation of glyceollins in soybean [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2012, 45(8):1576-1586. | |
| 20 | OJOKOH E, SHI B, LIANG P. Induction of phytochemical glyceollins accumulation in soybean following treatment with biotic elicitor (Aspergillus oryzae) [J]. J. Funct. Foods, 2013, 5(3):1039-1048. |
| 21 | KOHNO Y, KOSO M, KUSE M, et al.. Formal synthesis of soybean phytoalexin glyceollin I [J]. Tetrahedron Lett., 2014, 55(10):1826-1828. |
| 22 | MALIK N, ZHANG Z Q, ERHARDT P. Total synthesis of (±)-glyceollin II and a dihydro derivative [J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2015, 78(12):2940-2947. |
| 23 | 董向艳,李静梅,石波,等.甘薯淀粉加工废渣制备复合寡糖的条件优化及其活性评价[J].中国农业科学, 2014,47(15):3044-3057. |
| DONG X Y, LI J M, SHI B, et al.. Optimization and functional assessment of oligosaccharides compound prepared by sweet potato residue [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2014, 47(15):3044-3057. | |
| 24 | 张迷敏,李静梅,乔宇,等.褐藻酸寡糖诱导下大豆营养成分的变化[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(16): 3239-3248. |
| ZHANG M M, LI J M, QIAO Y, et al.. Changes in nutritional properties of soybeans induced by alginate oligosaccharides [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2015, 48(16):3239-3248. | |
| 25 | PENG Q, ZHANG M M, GAO L, et al.. Effects of alginate oligosaccharides with different molecular weights and guluronic to mannuronic acid ratios on glyceollin induction and accumulation in soybeans [J]. J. Food Sci. Technol., 2018, 55(5):1850-1858. |
| 26 | VADIVEL A K A, SUKUMARAN A, LI X Y, et al.. Soybean isoflavonoids: role of GmMYB176 interactome and 14-3-3 proteins [J]. Phytochem. Rev., 2016, 15(3):391-403. |
| [1] | Changlong FENG, Chenyang NING, Yixin ZHU, Shuping LI, Chunguang HUANG. Research on Design and Optimization of Ring Winding Mechanism for Trunk Bandages [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 122-132. |
| [2] | Ruyan ZHANG, Shenhao LI, Qipeng ZHU, Taigang FENG, Hongbo LI, Zebing XING, Yu XIAN. Effect of Biochar Content on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Garden Greening Waste/polylactic Acid Composites [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 192-200. |
| [3] | Changlong FENG, Chunguang HUANG, Chenyang NING, Shuping LI, Kejin CHEN. Optimization of Performance and Characteristics of Spiral Drill Bit Excavation Mechanism for Planting Machine [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 89-98. |
| [4] | Jingyi XI, Shuangqing WANG, Yitong BAI, Xiuli YAO, Bixuan HUANG, Qingyi LI, Liqing FAN, Shichen HUANG, Mingguo SUN. Study on Optimization of Processing Parameters Using Hermetia illucens Larva to Treat Food Waste by Response Surface Methodology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 241-249. |
| [5] | Lijun FU, Xiaoyu LIN, Jianhua LIN, Huinan SHEN, Yongzhen WU. Research on Processing Technology and Shelf Life of Red Matsutake Beef Sauce [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 148-158. |
| [6] | Dongling LIU, Hao SI, Baojiang ZHENG, Yuhong ZHANG. Optimization of Enzyme Assisted-ultrasonic Extraction of Sinigrin in Thlaspi arvense Seeds by Response Surface Methodology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 225-233. |
| [7] | Xiuying ZHAO, Qingwen HUANG, Haojie CAO, Jie WANG, Ruijiao LI, Dongxia NIE, Zheng HAN, Zhihui ZHAO. Optimization of Liquid Culture Conditions for the Production of Deoxynivalenol and Its Derivatives by Fusarium graminearum Using Response Surface Methodology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 222-233. |
| [8] | Yue WU, Yun’an WANG, Ha’nan SONG, Weijun GUAN, Nan LI. Primary Culture and Differentiation Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Gushi Chicken Umbilical Cord [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 79-87. |
| [9] | Wanwan ZHANG, Meisheng YI. Application and Development Prospect of Fish Stem Cell in Breeding [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 26-32. |
| [10] | JIA Mingliang, FANG Hefang, LI Tongjian, WEN Feng, HAN Xingjie, JIN Hongguang, XU Lingling, LIAO Liang*. Study on in vitro Cultivation of Lilium orential ‘Sorbonne’ [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 51-57. |
| [11] | GUO Huihui, LIN Congfa, JIANG Yuanbin, LI Zhigang. Optimization of Protocorm Proliferation Medium of Dendrobium huoshanense by Response Surface Methodology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(3): 173-180. |
| [12] |
JIA Mingliang, FANG Hefang, LI Tongjian, WEN Feng, HAN Xingjie,JIN Hongguang,XU Lingling, LIAO Liang*.
Callus Induction and Differentiation of Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) Koidz.
[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(3): 181-187.
|
| [13] | LI Wenjie, LI Meiyang*, GONG Hui. Research on Induction and Suspension Culture of Adventitious Root of Valeriana officinalis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(1): 179-186. |
| [14] | LIANG Zhaochao, GUO Xianwei, SONG Yanjuan, MA Tianfu, WANG Feng, WANG Liyan, JING Ruiyong*. Extraction Process of Polysaccharide in Agaricus bisporus Optimized by Response Surface Method and Its Antioxidant Activity in vitro [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(8): 161-168. |
| [15] | WU Qi1,2,3§, ZHANG Yuhui1,2§, SU Rongrong1,2, SUN Bo1,3, WU Qiuyun1,2, XIA Zhilan1,2*. Optimization of Submerged Fermentation Medium of Agaricus blazei Murrill for Mycelial Biomass Accumulation Using Response Surface Methodology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(3): 152-160. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号