




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 193-205.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0314
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
位春杰( ), 王海燕(
), 王海燕( ), 崔雪, 董齐琪, 张亦凡, 高子滢
), 崔雪, 董齐琪, 张亦凡, 高子滢
收稿日期:2024-04-18
接受日期:2024-07-12
出版日期:2025-10-15
发布日期:2025-10-15
通讯作者:
王海燕
作者简介:位春杰 E-mail: chunjie_wei@163.com;
基金资助:
Chunjie WEI( ), Haiyan WANG(
), Haiyan WANG( ), Xue CUI, Qiqi DONG, Yifan ZHANG, Ziying GAO
), Xue CUI, Qiqi DONG, Yifan ZHANG, Ziying GAO
Received:2024-04-18
Accepted:2024-07-12
Online:2025-10-15
Published:2025-10-15
Contact:
Haiyan WANG
摘要:
活性有机碳能反映土壤碳的动态特征,是土壤碳库的重要组成部分。为揭示森林土壤活性有机碳组分分布规律,以内蒙古旺业甸林场阔叶林、针阔混交林、针叶林和灌木林为研究对象,测定不同林分不同土层深度的易氧化有机碳(easily oxidizable organic carbon,EOC)、颗粒有机碳(particulate organic carbon,POC)和可溶性有机碳(dissolved organic carbon,DOC)含量,采用方差分析、相关性分析、冗余分析和灰色关联分析等方法分析土壤EOC、POC和DOC的分布特征及其与地形因子、林分因子和土壤理化性质之间的关系。结果表明,土壤EOC、POC和DOC含量均在0—10 cm土层中最大,且随着土壤深度的增加而逐渐减小。在0—10 cm土层,土壤EOC含量在针阔混交林与阔叶林之间无显著差异,在10—30和30—50 cm土层,针阔混交林土壤EOC含量均显著大于其他3种林分。各土层POC含量最高的均为阔叶林土壤,DOC含量在阔叶林和针阔混交林中相近且均高于针叶林和灌木林。在4种林分类型中,对土壤活性有机碳组分存在主要影响的理化性质有pH、全氮和速效钾,同时海拔和郁闭度也有较大影响。综上可知,土壤活性有机碳含量随土壤深度的增加而降低,不同土层中不同活性有机碳组分对林分变化的响应不同;土壤pH、全氮、速效钾、海拔和郁闭度是EOC、POC和DOC的主要影响因子。研究结果为旺业甸林场碳汇功能评价提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
位春杰, 王海燕, 崔雪, 董齐琪, 张亦凡, 高子滢. 旺业甸林场不同林型土壤活性有机碳分布特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(10): 193-205.
Chunjie WEI, Haiyan WANG, Xue CUI, Qiqi DONG, Yifan ZHANG, Ziying GAO. Distribution Characteristics of Soil Active Organic Carbon in Different Forest Types in Wangyedian Forest Farm[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(10): 193-205.
理化性质 Physicochemical property | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 灌木林 Shrubwood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 4.51±1.47 αa | 4.49±1.05 αa | 2.05±0.80 αb | 3.66±1.00 αa |
| 10—30 | 2.62±1.03 βa | 2.96±0.97 βa | 1.48±0.69 βb | 2.85±0.63 αβa | |
| 30—50 | 2.05±0.99 βa | 1.79±0.58 γa | 1.00±0.47 γb | 1.88±0.46 βa | |
有效磷 Available phosphorus/ (mg·kg-1) | 0—10 | 7.93±7.63 αa | 7.01±3.73 αa | 7.18±6.18 αa | 2.50±1.09 αa |
| 10—30 | 8.42±7.86 αa | 6.04±2.59 αβa | 7.50±7.78 αa | 4.27±2.12 αa | |
| 30—50 | 8.95±10.13 αa | 4.07±1.52 βa | 6.24±4.67 αa | 2.81±1.00 αa | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium/ (mg·kg-1) | 0—10 | 172.34±49.90 αa | 179.08±26.92 αa | 93.45±33.01 αb | 149.48±39.93 αa |
| 10—30 | 111.34±47.14 βa | 107.67±50.53 βa | 56.87±26.06 βb | 77.32±34.19 βab | |
| 30—50 | 90.21±44.98 βa | 80.18±34.88 βab | 47.89±16.95 βc | 51.55±20.62 βbc | |
土壤密度 Soil bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | 0—10 | 1.03±0.32 βb | 1.10±0.25 αab | 1.34±0.23 αa | 1.16±0.32 αab |
| 10—30 | 1.16±0.35 αβa | 1.16±0.18 αa | 1.35±0.20 αa | 1.21±0.21 αa | |
| 30—50 | 1.33±0.22 αab | 1.22±.021 αb | 1.44±0.23 αab | 1.49±0.30 αa | |
| pH | 0—10 | 5.94±0.33 βb | 5.96±0.34 αβb | 6.24±0.19 βa | 6.20±0.27 βab |
| 10—30 | 5.88±0.24 βab | 5.80±0.11 βb | 6.08±0.37 γab | 6.14±0.09 βa | |
| 30—50 | 6.16±0.26 αb | 6.17±0.20 αb | 6.38±0.24 αab | 6.60±0.15 αa |
表1 不同林分类型不同土层深度土壤的理化性质
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties of different stand types at varied soil depths
理化性质 Physicochemical property | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 灌木林 Shrubwood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 4.51±1.47 αa | 4.49±1.05 αa | 2.05±0.80 αb | 3.66±1.00 αa |
| 10—30 | 2.62±1.03 βa | 2.96±0.97 βa | 1.48±0.69 βb | 2.85±0.63 αβa | |
| 30—50 | 2.05±0.99 βa | 1.79±0.58 γa | 1.00±0.47 γb | 1.88±0.46 βa | |
有效磷 Available phosphorus/ (mg·kg-1) | 0—10 | 7.93±7.63 αa | 7.01±3.73 αa | 7.18±6.18 αa | 2.50±1.09 αa |
| 10—30 | 8.42±7.86 αa | 6.04±2.59 αβa | 7.50±7.78 αa | 4.27±2.12 αa | |
| 30—50 | 8.95±10.13 αa | 4.07±1.52 βa | 6.24±4.67 αa | 2.81±1.00 αa | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium/ (mg·kg-1) | 0—10 | 172.34±49.90 αa | 179.08±26.92 αa | 93.45±33.01 αb | 149.48±39.93 αa |
| 10—30 | 111.34±47.14 βa | 107.67±50.53 βa | 56.87±26.06 βb | 77.32±34.19 βab | |
| 30—50 | 90.21±44.98 βa | 80.18±34.88 βab | 47.89±16.95 βc | 51.55±20.62 βbc | |
土壤密度 Soil bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | 0—10 | 1.03±0.32 βb | 1.10±0.25 αab | 1.34±0.23 αa | 1.16±0.32 αab |
| 10—30 | 1.16±0.35 αβa | 1.16±0.18 αa | 1.35±0.20 αa | 1.21±0.21 αa | |
| 30—50 | 1.33±0.22 αab | 1.22±.021 αb | 1.44±0.23 αab | 1.49±0.30 αa | |
| pH | 0—10 | 5.94±0.33 βb | 5.96±0.34 αβb | 6.24±0.19 βa | 6.20±0.27 βab |
| 10—30 | 5.88±0.24 βab | 5.80±0.11 βb | 6.08±0.37 γab | 6.14±0.09 βa | |
| 30—50 | 6.16±0.26 αb | 6.17±0.20 αb | 6.38±0.24 αab | 6.60±0.15 αa |
活性有机碳组分 Active organic carbon component | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 灌木林 Shrubwood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易氧化有机碳EOC/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 4.15±1.32 αab | 4.87±0.91 αa | 3.01±1.35 αb | 3.38±0.87 αb |
| 10—30 | 2.42±1.06 βb | 3.96±1.03 αβa | 2.19±0.90 βb | 1.84±0.51 βb | |
| 30—50 | 2.27±1.28 βb | 3.21±1.06 βa | 1.70±0.72 βb | 1.46±0.19 βb | |
颗粒有机碳 POC/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 19.83±3.71 αa | 16.50±1.41 αb | 10.56±2.41 αc | 10.06±2.77 αc |
| 10—30 | 10.99±2.46 βa | 7.93±1.20 βb | 6.28±2.11 βbc | 5.72±2.78 βc | |
| 30—50 | 5.77±1.86 γa | 5.07±0.92 γab | 4.27±1.32 γb | 1.97±0.11 γc | |
可溶性有机碳 DOC/(mg·kg-1) | 0—10 | 289.69±114.81 αa | 279.13±82.31 αa | 241.45±106.60 αa | 228.23±125.28 αa |
| 10—30 | 131.76±45.24 βa | 159.82±64.50 βa | 132.91±66.72 βa | 67.75±15.33 βb | |
| 30—50 | 92.56±53.73 βa | 93.76±31.16 γa | 75.23±38.35 γab | 45.78±9.93 βb |
表2 不同林分类型不同土层深度下土壤活性有机碳组分
Table 2 Soil active organic carbon component under different stand types at varied soil depths
活性有机碳组分 Active organic carbon component | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 灌木林 Shrubwood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易氧化有机碳EOC/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 4.15±1.32 αab | 4.87±0.91 αa | 3.01±1.35 αb | 3.38±0.87 αb |
| 10—30 | 2.42±1.06 βb | 3.96±1.03 αβa | 2.19±0.90 βb | 1.84±0.51 βb | |
| 30—50 | 2.27±1.28 βb | 3.21±1.06 βa | 1.70±0.72 βb | 1.46±0.19 βb | |
颗粒有机碳 POC/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 19.83±3.71 αa | 16.50±1.41 αb | 10.56±2.41 αc | 10.06±2.77 αc |
| 10—30 | 10.99±2.46 βa | 7.93±1.20 βb | 6.28±2.11 βbc | 5.72±2.78 βc | |
| 30—50 | 5.77±1.86 γa | 5.07±0.92 γab | 4.27±1.32 γb | 1.97±0.11 γc | |
可溶性有机碳 DOC/(mg·kg-1) | 0—10 | 289.69±114.81 αa | 279.13±82.31 αa | 241.45±106.60 αa | 228.23±125.28 αa |
| 10—30 | 131.76±45.24 βa | 159.82±64.50 βa | 132.91±66.72 βa | 67.75±15.33 βb | |
| 30—50 | 92.56±53.73 βa | 93.76±31.16 γa | 75.23±38.35 γab | 45.78±9.93 βb |
| 指标Index | 差异源Variance source | F 值F value | P 值P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 易氧化有机碳EOC | 土层深度 Soil depth | 24.236 | 0.000** |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 19.617 | 0.000** | |
| 土层深度×林分类型 Soil depth × stand type | 0.885 | 0.507 | |
| 颗粒有机碳POC | 土层深度 Soil depth | 188.400 | 0.000** |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 75.060 | 0.000** | |
| 土层深度×林分类型Soil depth × stand type | 13.839 | 0.000** | |
| 可溶性有机碳DOC | 土层深度 Soil depth | 58.322 | 0.000** |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 3.010 | 0.032* | |
| 土层深度×林分类型Soil depth × stand type | 0.558 | 0.763 |
表3 不同林分类型不同土层深度下的土壤活性有机碳组分双因素方差分析
Table 3 Two-way ANOVA of soil organic carbon under different stand types at varied soil depths
| 指标Index | 差异源Variance source | F 值F value | P 值P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 易氧化有机碳EOC | 土层深度 Soil depth | 24.236 | 0.000** |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 19.617 | 0.000** | |
| 土层深度×林分类型 Soil depth × stand type | 0.885 | 0.507 | |
| 颗粒有机碳POC | 土层深度 Soil depth | 188.400 | 0.000** |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 75.060 | 0.000** | |
| 土层深度×林分类型Soil depth × stand type | 13.839 | 0.000** | |
| 可溶性有机碳DOC | 土层深度 Soil depth | 58.322 | 0.000** |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 3.010 | 0.032* | |
| 土层深度×林分类型Soil depth × stand type | 0.558 | 0.763 |
林分类型 Stand type | 指标 Index | 易氧化有机碳 EOC | 颗粒有机碳 POC | 可溶性有机碳 DOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 海拔 Altitude | -0.255 | -0.188 | -0.298 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.260 | -0.224 | 0.218 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.063 | 0.123 | 0.426 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.168 | -0.245 | 0.160 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.124 | -0.527* | -0.314 | |
| pH | -0.333 | 0.184 | -0.253 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | -0.023 | -0.116 | -0.267 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.324 | -0.145 | -0.027 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | -0.167 | 0.187 | -0.347 | |
针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 海拔 Altitude | -0.396 | -0.491 | -0.826** |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.317 | -0.053 | 0.152 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | -0.260 | 0.269 | 0.589 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | -0.107 | 0.181 | 0.423 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.289 | -0.684* | -0.294 | |
| pH | -0.267 | 0.141 | 0.603 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.339 | 0.084 | 0.399 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.111 | 0.546 | 0.510 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | -0.392 | -0.487 | -0.477 | |
针叶林 Coniferous forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.435* | 0.417* | 0.447* |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.176 | 0.006 | 0.218 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | -0.081 | 0.230 | -0.247 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | -0.269 | -0.170 | 0.106 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | -0.397* | -0.369* | -0.590** | |
| pH | -0.101 | 0.055 | -0.500** | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.290 | 0.256 | 0.500** | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.175 | -0.053 | 0.093 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.175 | 0.255 | 0.348 | |
灌木林 Shrubwood | 海拔 Altitude | -0.202 | -0.925 | 0.420 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.641 | 0.059 | -0.697 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | -0.519 | -0.046 | 0.837 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.403 | -0.128 | 0.989* | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.321 | 0.829 | -0.630 | |
| pH | -0.051 | 0.830 | 0.308 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.108 | -0.693 | 0.578 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.138 | -0.947 | -0.194 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.937 | 0.040 | -0.097 |
表4 不同林分类型土壤活性有机碳组分与理化性质及环境因子相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of soil organic carbon components with physicochemical properties and environmental factors in different stand types
林分类型 Stand type | 指标 Index | 易氧化有机碳 EOC | 颗粒有机碳 POC | 可溶性有机碳 DOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 海拔 Altitude | -0.255 | -0.188 | -0.298 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.260 | -0.224 | 0.218 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.063 | 0.123 | 0.426 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.168 | -0.245 | 0.160 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.124 | -0.527* | -0.314 | |
| pH | -0.333 | 0.184 | -0.253 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | -0.023 | -0.116 | -0.267 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.324 | -0.145 | -0.027 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | -0.167 | 0.187 | -0.347 | |
针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 海拔 Altitude | -0.396 | -0.491 | -0.826** |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.317 | -0.053 | 0.152 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | -0.260 | 0.269 | 0.589 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | -0.107 | 0.181 | 0.423 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.289 | -0.684* | -0.294 | |
| pH | -0.267 | 0.141 | 0.603 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.339 | 0.084 | 0.399 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.111 | 0.546 | 0.510 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | -0.392 | -0.487 | -0.477 | |
针叶林 Coniferous forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.435* | 0.417* | 0.447* |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.176 | 0.006 | 0.218 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | -0.081 | 0.230 | -0.247 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | -0.269 | -0.170 | 0.106 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | -0.397* | -0.369* | -0.590** | |
| pH | -0.101 | 0.055 | -0.500** | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.290 | 0.256 | 0.500** | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.175 | -0.053 | 0.093 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.175 | 0.255 | 0.348 | |
灌木林 Shrubwood | 海拔 Altitude | -0.202 | -0.925 | 0.420 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.641 | 0.059 | -0.697 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | -0.519 | -0.046 | 0.837 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.403 | -0.128 | 0.989* | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.321 | 0.829 | -0.630 | |
| pH | -0.051 | 0.830 | 0.308 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.108 | -0.693 | 0.578 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.138 | -0.947 | -0.194 | |
| 速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.937 | 0.040 | -0.097 |
林分类型 Stand type | 指标 Index | 易氧化有机碳 EOC | 颗粒有机碳 POC | 可溶性有机碳 DOC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | ||
阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.898 | 2 | 0.920 | 3 | 0.854 | 2 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.799 | 9 | 0.799 | 9 | 0.814 | 6 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.906 | 1 | 0.922 | 2 | 0.873 | 1 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.831 | 7 | 0.825 | 7 | 0.828 | 5 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.886 | 4 | 0.864 | 6 | 0.836 | 4 | |
| pH | 0.896 | 3 | 0.936 | 1 | 0.853 | 3 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.877 | 5 | 0.881 | 5 | 0.810 | 8 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.808 | 8 | 0.805 | 8 | 0.781 | 9 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.862 | 6 | 0.903 | 4 | 0.813 | 7 | |
针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.796 | 4 | 0.843 | 3 | 0.668 | 6 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.595 | 9 | 0.570 | 9 | 0.568 | 9 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.779 | 6 | 0.908 | 1 | 0.740 | 3 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.654 | 8 | 0.648 | 8 | 0.646 | 7 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.798 | 3 | 0.765 | 6 | 0.621 | 8 | |
| pH | 0.810 | 2 | 0.905 | 2 | 0.755 | 1 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.810 | 1 | 0.770 | 5 | 0.745 | 2 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.684 | 7 | 0.691 | 7 | 0.677 | 5 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.779 | 5 | 0.832 | 4 | 0.695 | 4 | |
针叶林 Coniferous forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.822 | 1 | 0.890 | 1 | 0.806 | 3 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.783 | 6 | 0.740 | 8 | 0.746 | 8 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.797 | 4 | 0.872 | 3 | 0.777 | 5 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.715 | 9 | 0.742 | 7 | 0.753 | 7 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.780 | 7 | 0.834 | 4 | 0.758 | 6 | |
| pH | 0.809 | 2 | 0.880 | 2 | 0.790 | 4 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.799 | 3 | 0.797 | 6 | 0.809 | 2 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.743 | 8 | 0.700 | 9 | 0.722 | 9 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.796 | 5 | 0.833 | 5 | 0.811 | 1 | |
灌木林 Shrubwood | 海拔 Altitude | 0.772 | 1 | 0.682 | 4 | 0.697 | 4 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.607 | 6 | 0.529 | 8 | 0.546 | 9 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.498 | 9 | 0.530 | 7 | 0.802 | 2 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.638 | 5 | 0.519 | 9 | 0.923 | 1 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.693 | 4 | 0.834 | 2 | 0.596 | 8 | |
| pH | 0.761 | 2 | 0.754 | 3 | 0.662 | 5 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.605 | 7 | 0.648 | 5 | 0.709 | 3 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.546 | 8 | 0.600 | 6 | 0.642 | 6 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.695 | 3 | 0.889 | 1 | 0.639 | 7 | |
表5 不同林分类型土壤活性有机碳与理化性质及环境因子关联程度 (续表Continued)
Table 5 Correlation degree of soil active organic carbon with physicochemical properties and environmental factors in different stand types
林分类型 Stand type | 指标 Index | 易氧化有机碳 EOC | 颗粒有机碳 POC | 可溶性有机碳 DOC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | ||
阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.898 | 2 | 0.920 | 3 | 0.854 | 2 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.799 | 9 | 0.799 | 9 | 0.814 | 6 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.906 | 1 | 0.922 | 2 | 0.873 | 1 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.831 | 7 | 0.825 | 7 | 0.828 | 5 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.886 | 4 | 0.864 | 6 | 0.836 | 4 | |
| pH | 0.896 | 3 | 0.936 | 1 | 0.853 | 3 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.877 | 5 | 0.881 | 5 | 0.810 | 8 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.808 | 8 | 0.805 | 8 | 0.781 | 9 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.862 | 6 | 0.903 | 4 | 0.813 | 7 | |
针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.796 | 4 | 0.843 | 3 | 0.668 | 6 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.595 | 9 | 0.570 | 9 | 0.568 | 9 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.779 | 6 | 0.908 | 1 | 0.740 | 3 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.654 | 8 | 0.648 | 8 | 0.646 | 7 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.798 | 3 | 0.765 | 6 | 0.621 | 8 | |
| pH | 0.810 | 2 | 0.905 | 2 | 0.755 | 1 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.810 | 1 | 0.770 | 5 | 0.745 | 2 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.684 | 7 | 0.691 | 7 | 0.677 | 5 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.779 | 5 | 0.832 | 4 | 0.695 | 4 | |
针叶林 Coniferous forest | 海拔 Altitude | 0.822 | 1 | 0.890 | 1 | 0.806 | 3 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.783 | 6 | 0.740 | 8 | 0.746 | 8 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.797 | 4 | 0.872 | 3 | 0.777 | 5 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.715 | 9 | 0.742 | 7 | 0.753 | 7 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.780 | 7 | 0.834 | 4 | 0.758 | 6 | |
| pH | 0.809 | 2 | 0.880 | 2 | 0.790 | 4 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.799 | 3 | 0.797 | 6 | 0.809 | 2 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.743 | 8 | 0.700 | 9 | 0.722 | 9 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.796 | 5 | 0.833 | 5 | 0.811 | 1 | |
灌木林 Shrubwood | 海拔 Altitude | 0.772 | 1 | 0.682 | 4 | 0.697 | 4 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.607 | 6 | 0.529 | 8 | 0.546 | 9 | |
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.498 | 9 | 0.530 | 7 | 0.802 | 2 | |
| 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness | 0.638 | 5 | 0.519 | 9 | 0.923 | 1 | |
| 土壤密度 Soil bulk density | 0.693 | 4 | 0.834 | 2 | 0.596 | 8 | |
| pH | 0.761 | 2 | 0.754 | 3 | 0.662 | 5 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.605 | 7 | 0.648 | 5 | 0.709 | 3 | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.546 | 8 | 0.600 | 6 | 0.642 | 6 | |
速效钾 Readily available potassium | 0.695 | 3 | 0.889 | 1 | 0.639 | 7 | |
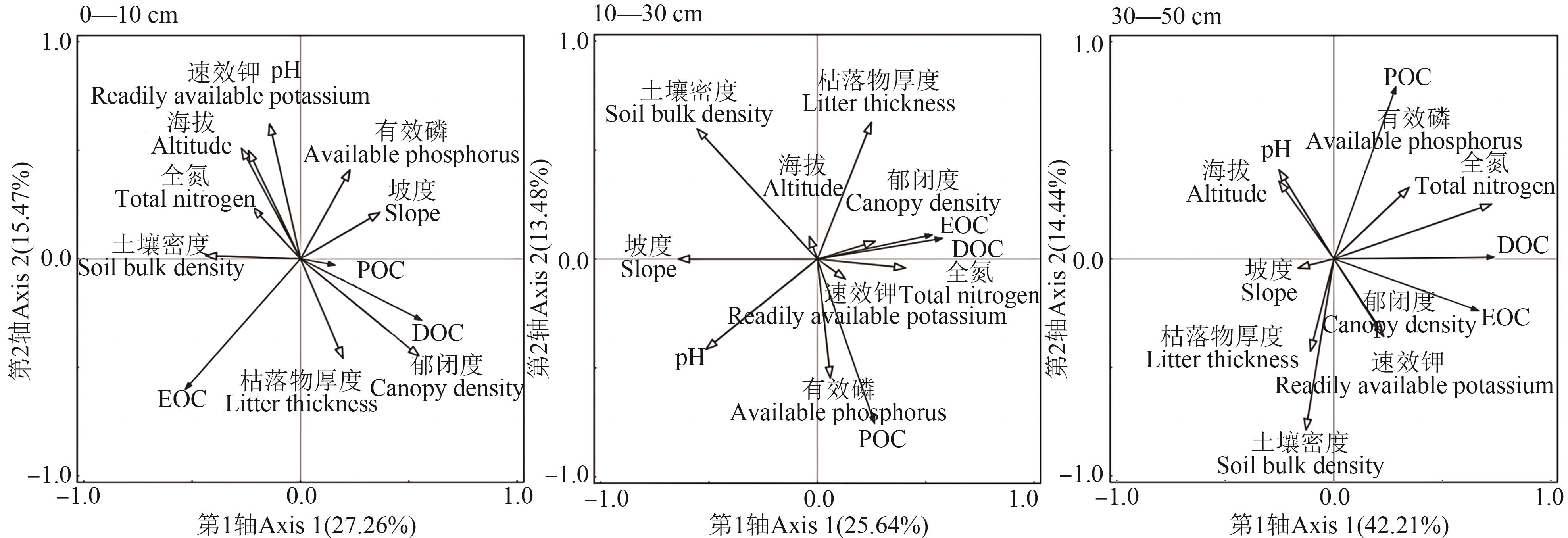
图1 阔叶林土壤活性有机碳组分与环境因子的冗余分析注: EOC—易氧化有机碳;POC—颗粒有机碳;DOC—可溶性有机碳。
Fig. 1 Redundancy analysis of soil active organic carbon components and environmental factors in broad-leaved forestsNote: EOC—Easily oxidizable organic carbon;POC—Particulate organic carbon organic carbon;DOC—Dissolved organic carbon.
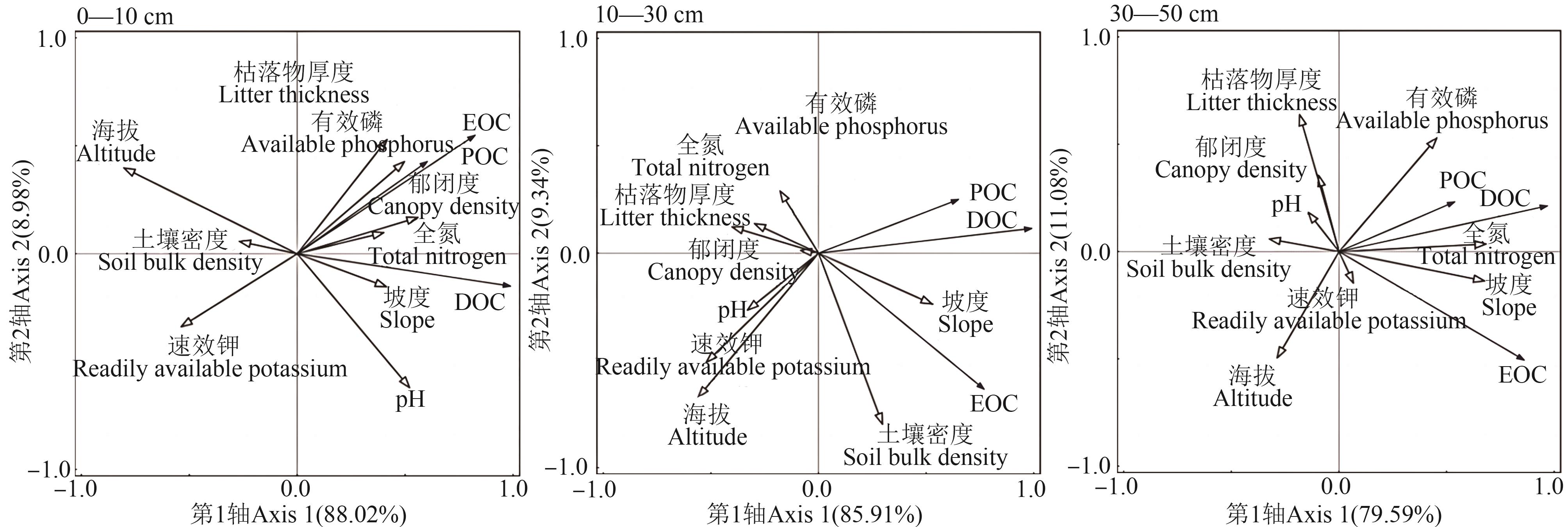
图2 针阔混交林土壤活性有机碳组分与环境因子的冗余分析注: EOC—易氧化有机碳;POC—颗粒有机碳;DOC—可溶性有机碳。
Fig. 2 Redundancy analysis of soil active organic carbon components and environmental factors in coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forestsNote: EOC—Easily oxidizable organic carbon;POC—Particulate organic carbon organic carbon;DOC—Dissolved organic carbon.
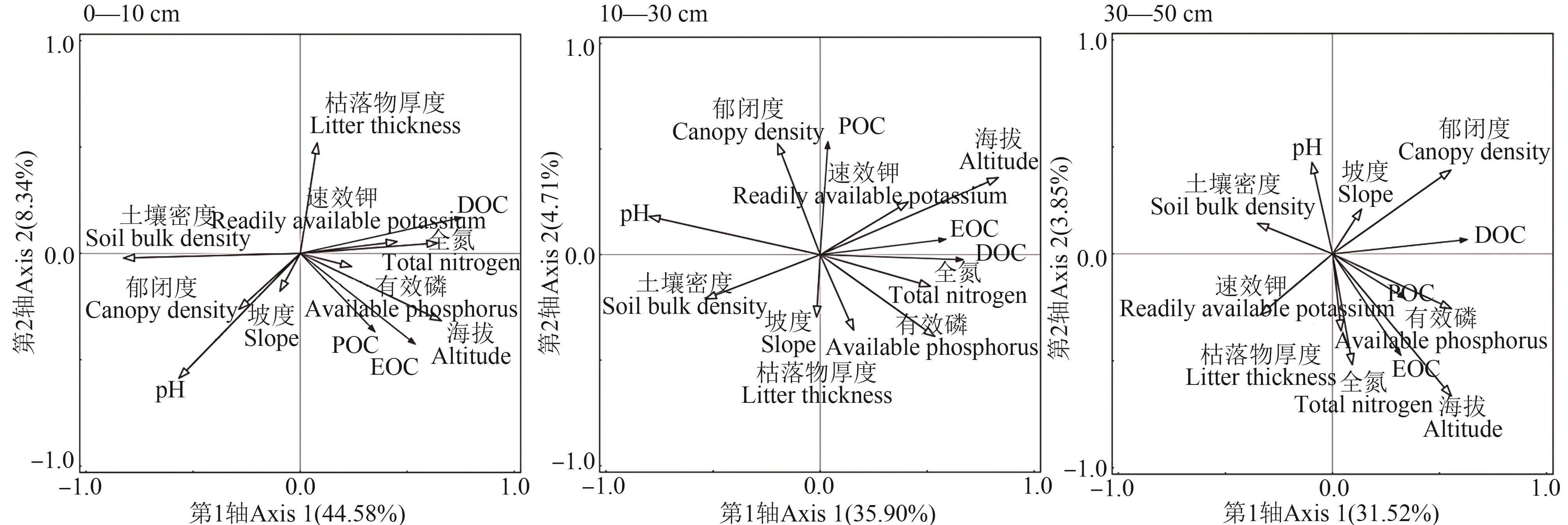
图3 针叶林土壤活性有机碳组分与环境因子的冗余分析注: EOC—易氧化有机碳;POC—颗粒有机碳;DOC—可溶性有机碳。
Fig.3 Redundancy analysis of soil active organic carbon components and environmental factors in coniferous forestsNote: EOC—Easily oxidizable organic carbon;POC—Particulate organic carbon organic carbon;DOC—Dissolved organic carbon.
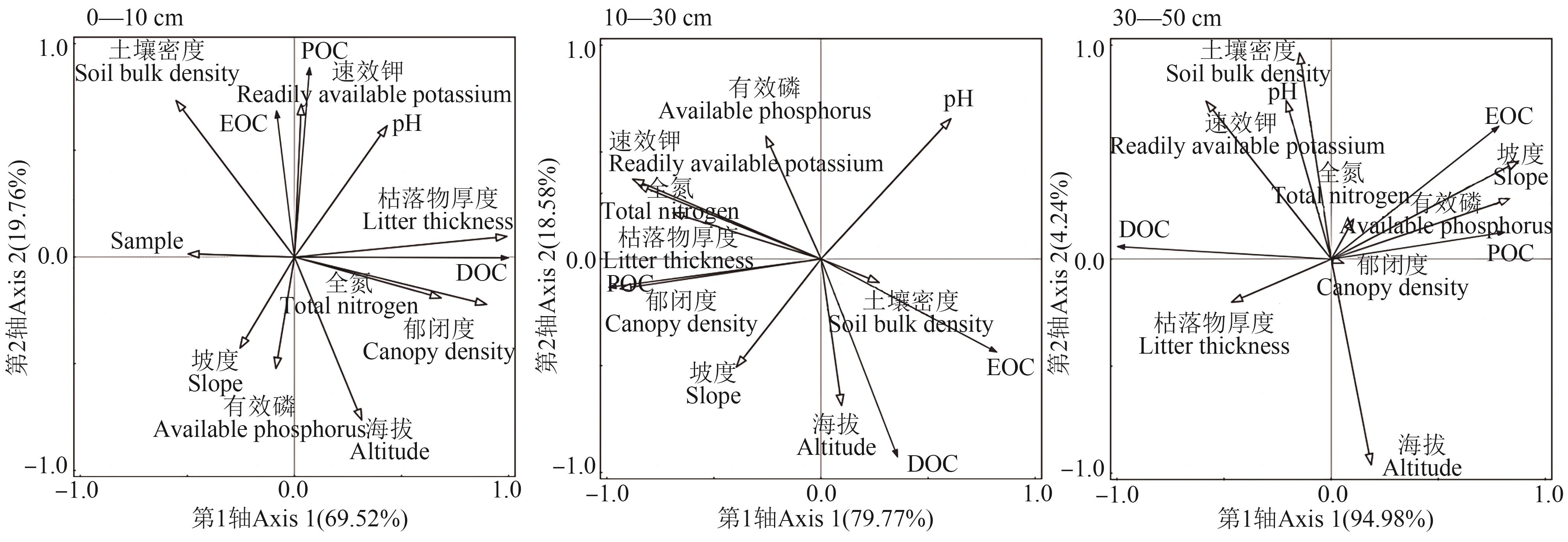
图4 灌木林土壤活性有机碳组分与环境因子的冗余分析注: EOC—易氧化有机碳;POC—颗粒有机碳;DOC—可溶性有机碳。
Fig. 4 Redundancy analysis of soil active organic carbon components and environmental factors in the shrubwoodNote: EOC—Easily oxidizable organic carbon;POC—Particulate organic carbon organic carbon;DOC—Dissolved organic carbon.
| [1] | 郝江勃, 乔枫, 蔡子良. 亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤活性有机碳组分季节动态特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(2): 245-251. |
| HAO J B, QIAO F, CAI Z L.Seasonal dynamics of soil labile organic carbon and its fractions in subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2019, 28(2):245-251. | |
| [2] | ZHAO S X, TA N, LI Z H, et al.. Varying pyrolysis temperature impacts application effects of biochar on soil labile organic carbon and humic fractions [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2018, 123:484-493. |
| [3] | LI Y C, LI Y F, CHANG S X,et al.. Linking soil fungal community structure and function to soil organic carbon chemical composition in intensively managed subtropical bamboo forests [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017, 107: 19-31. |
| [4] | 安申群, 贡璐, 李杨梅, 等. 塔里木盆地北缘绿洲4种土地利用方式土壤有机碳组分分布特征及其与土壤环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(7): 3382-3390. |
| AN S Q, GONG L, LI Y M,et al.. Soil organic carbon components and their correlation with soil physicochemical factors in four different land use types of the northern Tarim Basin [J]. Environ. Sci., 2018, 39(7): 3382-3390. | |
| [5] | 孙金兵, 高菲, 宋金凤, 等. 长白山两种森林类型土壤颗粒有机碳和黑碳分布特征[J]. 林业科学研究, 2017, 30(2):222-231. |
| SUN J B, GAO F, SONG J F, et al.. Distributions of soil particulate organic carbon and black carbon of two forest types in Changbai Mountain [J]. For. Res., 2017, 30(2): 222-231. | |
| [6] | 李龙, 秦富仓, 姜丽娜, 等. 半干旱区土壤有机碳时空变异特征研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3):100-107. |
| LI L, QIN F C, JIANG L N, et al.. Spatio-temporal variability of soil organic carbon in semi-arid area [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020, 22(3): 100-107. | |
| [7] | 刘明慧, 孙雪, 于文杰, 等. 长白山不同海拔原始红松林土壤活性有机碳含量的生长季动态[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(2): 67-74. |
| LIU M H, SUN X, YU W J, et al.. Seasonal dynamics of soil active organic carbon content in the original Pinus koraiensis forest in Changbai Mountains, China [J]. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2018, 42(2): 67-74. | |
| [8] | 刘兆华, 林辉, 龙江平, 等. 基于高分二号的旺业甸林场蓄积量估测模型研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(3): 79-84, 118. |
| LIU Z H, LIN H, LONG J P, et al.. Study on volume estimation model of Wangyedian forest farm based on GF-2 [J]. J. Central South Univ. For. Technol., 2020, 40(3): 79-84, 118. | |
| [9] | 李文臣, 马成功, 金玉栋, 等. 喀喇沁旗旺业甸实验林场森林可持续经营模式[J]. 内蒙古林业调查设计, 2016, 39(6): 47-49, 55. |
| [10] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 14-97 . |
| [11] | CULMAN S W, SCHIPANSKI M E, ALl J B R, et al.. Permanganate oxidizable carbon reflects a processed soil fraction that is sensitive to management [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2012, 76(2): 494-504 |
| [12] | 李超, 王俊, 温萌萌, 等. 绿肥填闲种植对旱作冬小麦农田土壤团聚体有机碳含量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2023, 41(3): 210-217. |
| LI C, WANG J, WEN M M, et al.. Effect of green manure cover cropping on soil aggregate-associated organic carbon in a dryland winter wheat field [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2023, 41(3): 210-217. | |
| [13] | 张苗苗, 陈伟, 林丽, 等. 青海省不同高寒草地土壤主要养分及可溶性有机碳特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 20-28. |
| ZHANG M M, CHEN W, LIN L, et al.. A study of soil nutrient characteristics and soil soluble organic carbon levels in different types of alpine grassland in Qinghai province [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2019, 28(3): 20-28. | |
| [14] | 习丹, 余泽平, 熊勇, 等. 江西官山常绿阔叶林土壤有机碳组分沿海拔的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020,31(10): 3349-3356. |
| XI D, YU Z P, XIONG Y, et al..Altitudinal changes of soil organic carbon fractions of evergreen broadleaved forests in Guanshan Mountain, Jiangxi, China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, 31(10): 3349-3356. | |
| [15] | 王军广, 赵志忠, 王鹏, 等. 海南岛东南部热带雨林土壤易氧化有机碳特征及影响因素[J]. 西部林业科学, 2023, 52(2): 106-112, 131. |
| WANG G J, ZHAO Z Z, WANG P, et al.. Characteristics and influencing factors of easily oxidized organic carbon in tropical rain forest soil in southeast Hainan Island [J]. J. West China For. Sci., 2023, 52(2): 106-112, 131. | |
| [16] | 张义凡, 陈林, 张蚌蚌, 等. 荒漠草原表层土壤有机碳粒径组分及碳库管理指数特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(5): 283-290. |
| ZHANG Y F, CHEN L, ZHANG B B, et al.. Characteristics of organic carbon particle size composition and carbon pool management index in surface soil of desert grassland [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2023, 37(5): 283-290. | |
| [17] | 张青青, 张桂莲,伍海兵, 等. 上海市林地土壤有机碳分布特征及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(6): 1087-1095. |
| ZHANG Q Q, ZHANG G L, WU H B, et al.. Soil organic carbon distribution and its relationship with soil physicochemical properties in different forest types of Shanghai city [J]. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ., 2019, 36(6): 1087-1095. | |
| [18] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 等. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| MA H Y, LI X Z, MA X Y, et al.. Characteristics and driving factors of soil organic carbon fractions under different vegetation types of the mid-Northern piedmont of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. | |
| [19] | 王清奎, 汪思龙, 高洪, 等. 杉木人工林土壤活性有机质变化特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(7): 1270-1274. |
| WANG Q K, WANG S L, GAO H, et al.. Dynamics of soil active organic matter in Chinese fir plantations [J]. Chin.J. Appl. Ecol., 2005, 16(7): 1270-1274. | |
| [20] | 张剑, 汪思龙, 王清奎, 等. 不同森林植被下土壤活性有机碳含量及其季节变化[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(1): 41-47. |
| ZHANG J, WANG S L, WANG Q K, et al.. Content and seasonal change in soil labile organic carbon under different forest covers [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2009, 17(1): 41-47. | |
| [21] | 刘秉儒, 杨阳, 陈林. 宁夏荒漠草原4种典型植物群落土壤活性有机碳垂直分布特征[J]. 草地学报, 2014, 22(5): 986-990. |
| LIU B R, YANG Y, CHEN L. Distribution characteristics of soil labile organic carbon of four typical plant communities in desert steppe of Ningxia [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2014, 22(5): 986-990. | |
| [22] | LUO Z, FENG W, LUO Y, et al.. Soil organic carbon dynamics jointly controlled by climate, carbon inputs, soil properties and soil carbon fractions [J]. Glob. Change Biol., 2017, 23(10): 4430-4439. |
| [23] | 曹智, 文仕知, 何功秀, 等. 南方红壤丘陵区水土保持林对枯落物和土壤养分的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2024, 39(1): 154-161. |
| CAO Z, WEN S Z, HE G X, et al.. Effects of soil and water conservation forest on litter and soil nutrients in red hilly region of southern China [J]. J. Northwest For. Univ., 2024, 39(1): 154-161. | |
| [24] | NARESH R K, PURSHOTTAM S K, MALIK M, et al.. Effects of tillage, residue and nutrient management on top soil carbon stocks and soil labile organic carbon fractions in the Indo-gangetic plains of north west India: a review [J]. J. Pharmac. Phytochem., 2018, 7(3): 1818-1842. |
| [25] | 张智勇, 王瑜, 艾宁, 等. 陕北黄土区不同植被类型土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(11): 56-63. |
| ZHANG Z Y, WANG Y, AI N, et al.. Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors in different vegetation types in loess region of northern Shaanxi province, northwestern China [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2020, 42(11): 56-63. | |
| [26] | 刘聪, 李守中, 王从容, 等. 凋落物添加对亚热带水土流失区人工林土壤氮矿化的影响[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 34(4): 103-110. |
| LIU C, LI S Z, WANG C R,et al.. Effects of litter addition on soil nitrogen mineralization of soft erosion plantations in the subtropical zone [J]. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2018, 34(4): 103-110. | |
| [27] | GHANI A, SARATHCHANDRA U, LEDGARD S, et al.. Microbial decomposition of leached or extracted dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen from pasture soils [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2013, 49(6): 747-755. |
| [28] | 杨万勤, 邓仁菊, 张健. 森林凋落物分解及其对全球气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(12): 2889-2895. |
| YANG W Q, DENG R J, ZHANG J. Forest litter decomposition and its responses to global climate change [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2007, 18(12): 2889-2895. | |
| [29] | 岳天, 李永夫, 肖永恒, 等. 天然常绿阔叶林改造为板栗林对土壤有机碳库的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(7): 2181-2188. |
| YUE T, LI Y F, XIAO Y H, et al.. Effects of conversion of evergreen broad-leaved forest to Chinese chestnut plantation on soil organic carbon pools [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2016, 27(7): 2181-2188. | |
| [30] | JIA J, YU D P, ZHOU W M, et al.. Variations of soil aggregates and soil organic carbon mineralization across forest types on the northern slope of Changbai Mountain [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2015, 35(2): 1-7. |
| [31] | 王军, 满秀玲. 去除凋落物和草毡层对寒温带典型森林土壤活性有机碳的短期影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2024, 31(1): 168-177. |
| WANG J, MAN X L. Short term effects of litter and sod layer removal on soil active organic carbon in typical forests in cold temperate zone [J]. Res. Soil. Water Conserv., 2024, 31(1): 168-177. | |
| [32] | 张金硕, 李素艳, 孙向阳, 等. 山东省不同植被类型土壤有机碳及其组分分布特征[J]. 土壤, 2024, 56(2): 350-357. |
| ZHANG J S, LI S Y, SUN X Y, et al.. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and its components under different vegetation types in Shandong province [J]. Soils, 2024, 56(2): 350-357. | |
| [33] | LEI T Z, SI G C, WANG J, et al.. Microbial communities and associated enzyme activities in alpine wetlands with increasing altitude on the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Wetlands, 2017, 37(3): 401-412. |
| [34] | 陈曦, 张彦军, 邹俊亮, 等. 秦岭太白山森林表层土壤有机碳分布特征[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2022, 42(3): 244-252. |
| CHEN X, ZHANG Y J, ZOU J L, et al.. Distribution characteristics of forest surface soil organic carbon in Taibai Mountains of Qinling [J]. J. For. Environ., 2022, 42(3): 244-252. | |
| [35] | 刘雅洁, 王亮, 樊伟, 等. 海拔对杉木人工林土壤活性有机碳组分的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(8): 59-69. |
| LIU Y J, WANG L, FAN W, et al.. Effects of altitude on soil active organic carbon components in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ.(Nat. Sci.), 2021, 49(8): 59-69. | |
| [36] | 毋程琳, 卫星. 郁闭度对樟子松林下人工更新阔叶树种生长的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2023, 45(8): 65-73. |
| WU C L, WEI X. Effects of canopy density on the growth of broadleaved tree species under artificial regeneration of Pinus sylvestris forest [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2023, 45(8): 65-73. | |
| [37] | CHENG X, YU M, WANG G G, et al.. Growth, morphology and biomass allocation in response to light gradient in five subtropical evergreen broadleaved tree seedlings [J]. J. Trop. For. Sci., 2013, 25(4): 537-546. |
| [38] | 张东来, 张玲, 葛文志. 不同光环境对胡桃楸幼苗生物量及光合生理的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2017, 33(5): 8-11. |
| ZHANG D L, ZHANG L, GE W Z.Effect of different light environment on biomass and photosynthetic physiology of Juglan mandshurica seedling [J]. For. Eng., 2017, 33(5): 8-11. |
| [1] | 肖淑婷, 颜安. 天山典型天然林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 227-238. |
| [2] | 张继东, 张亚雄, 程伟, 蒲莉, 柳路行, 王亚明. 生物质炭和有机肥配施对苹果重茬育苗地土壤理化性质和微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 213-222. |
| [3] | 杨娅琳, 吴峰婧琳, 陈健鑫, 武自强, 刘丽, 张东华, 马焕成, 伍建榕. 油茶根腐病根际土壤、根系内真菌群落结构和多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 121-135. |
| [4] | 王子凡, 李燕, 张庆银, 王丹丹, 师建华, 耿晓彬, 田东良, 钟增明, 赵晓明, 齐连芬. 微生物菌剂对设施番茄主要病害及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [5] | 陈小双, 徐兴倩, 赵熹, 屈新, 王海军, 彭光灿. 镉污染红黏土电阻率特性及其评价模型研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 164-173. |
| [6] | 张绥林, 李洋, 李琰, 张赟齐, 齐建勋, 侯智霞. 核桃晚霜危害特性及影响机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 18-26. |
| [7] | 高丽敏, 顾泽辰, 贡雪菲, 崔联明, 郭东森, 周影, 王琳, 魏启舜. 果园生草对中国果树-土壤系统生产性能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 184-194. |
| [8] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [9] | 周旭东, 韩天华, 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 贺彪, 杨明英, 裴卫华, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 4种轮作模式下长期连作烟田土壤微生态的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 174-187. |
| [10] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [11] | 马铭泽, 张帆, 王田, 李文芳, 毛娟, 陈佰鸿, 马宗桓. 不同肥料配施对樱桃园土壤及幼树生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 191-203. |
| [12] | 郭靖捷, 任晓萌, 蒙仲举, 王涛, 祁帅, 宋佳佳, 宝孟克那顺, 韩胜利. 半干旱风沙草原区盐湖植物防护体系土壤理化性状特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 182-192. |
| [13] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [14] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [15] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 沈钦瑞. 黄淮海平原农田土壤温室气体排放对长期施加生物炭的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||