




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 188-197.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0748
刘云飞1( ), 韦凤杰2, 夏茂林1, 于兆锦1, 夏昊3, 衣春宇1, 常剑波4(
), 韦凤杰2, 夏茂林1, 于兆锦1, 夏昊3, 衣春宇1, 常剑波4( ), 姬小明1(
), 姬小明1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-27
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2023-03-15
发布日期:2023-05-22
通讯作者:
常剑波,姬小明
作者简介:刘云飞 E-mail:1448789042@qq.com
基金资助:
Yunfei LIU1( ), Fengjie WEI2, Maolin XIA1, Zhaojin YU1, Hao XIA3, Chunyu YI1, Jianbo CHANG4(
), Fengjie WEI2, Maolin XIA1, Zhaojin YU1, Hao XIA3, Chunyu YI1, Jianbo CHANG4( ), Xiaoming JI1(
), Xiaoming JI1( )
)
Received:2021-08-27
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-03-15
Published:2023-05-22
Contact:
Jianbo CHANG,Xiaoming JI
摘要:
为研究新型复合水凝胶对镉(Cd)胁迫烟草幼苗的缓解作用及其对Cd的吸附机理,以合成的新型生物炭复合水凝胶(PVA/AA/B)和改性生物炭复合水凝胶(PVA/AA/MB)为材料,开展Cd吸附试验和烟草盆栽试验。结果表明,2种复合水凝胶对Cd的吸附方式均以多分子层吸附为主,PVA/AA/B和PVA/AA/MB对Cd的最大吸附量分别为314.17和371.83 mg·g-1;与CK相比,PVA/AA/B和PVA/AA/MB处理的植株鲜重分别显著增加172.94%和231.32%,干重分别显著增加135.29%和188.24%,土壤有效态Cd含量分别显著降低36.27%和65.18%,植株Cd含量分别显著降低54.47%和63.23%,叶片的SPAD值及抗氧化酶活性显著提高。2种合成的新型材料均能有效缓解Cd胁迫对烟草幼苗的毒害,促进Cd胁迫下烟草幼苗的生长,减少烟草中Cd积累,其中PVA/AA/MB效果更好,可为缓解烟草Cd胁迫提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
刘云飞, 韦凤杰, 夏茂林, 于兆锦, 夏昊, 衣春宇, 常剑波, 姬小明. 新型复合水凝胶对镉胁迫烟草幼苗的缓解效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 188-197.
Yunfei LIU, Fengjie WEI, Maolin XIA, Zhaojin YU, Hao XIA, Chunyu YI, Jianbo CHANG, Xiaoming JI. Alleviative Effect of New Composite Hydrogels on Cadmium Stress Tobacco Seedlings[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 188-197.
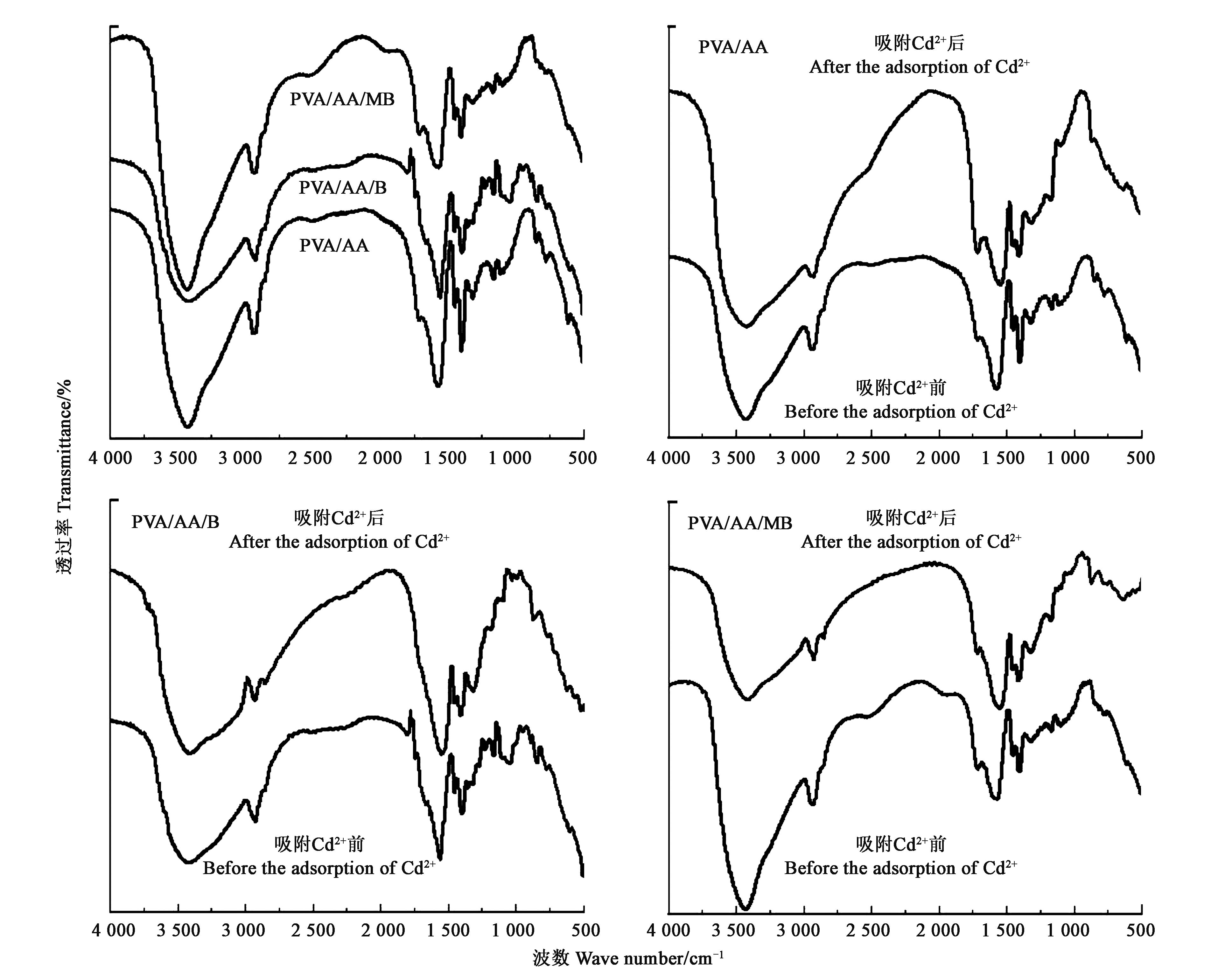
图1 PVA/AA、PVA/AA/B和PVA/AA/MB的红外光谱图及吸附Cd+前后的红外光谱对比
Fig.1 FTIR diagram of PVA/AA, PVA/AA/B and PVA/AA/MB and FTIR comparison diagram before and after adsorption of Cd+
指标 Idex | 材料Materials | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | MB | PVA/AA | PVA/AA/B | PVA/AA/MB | |
| Qe /(mg·g-1) | 38.67 e | 48.61 d | 60.27 c | 130.89 b | 187.45 a |
去除率 Removal rate/% | 19.34 e | 24.30 d | 30.14 c | 65.44 b | 93.72 a |
表1 不同材料对水溶液中Cd的平衡吸附量及去除率
Table 1 Equilibrium adsorption capacity and removal rate of Cd in aqueous solution by different materials
指标 Idex | 材料Materials | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | MB | PVA/AA | PVA/AA/B | PVA/AA/MB | |
| Qe /(mg·g-1) | 38.67 e | 48.61 d | 60.27 c | 130.89 b | 187.45 a |
去除率 Removal rate/% | 19.34 e | 24.30 d | 30.14 c | 65.44 b | 93.72 a |
材料 Materials | Langmuir等温吸附模型 Langmuir isothermal adsorption model | Freundlich等温吸附模型 Freundlich isothermal adsorption model | 样本数 Sample number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | R12 | KF/(mg1-n·g-1·L-n) | 1/n | R22 | ||
| PVA/AA | 271.15 | 0.038 | 0.983 7** | 40.94 | 0.356 7 | 0.923 5** | 6 |
| PVA/AA/B | 314.17 | 0.046 | 0.955 2** | 47.79 | 0.372 4 | 0.991 5** | 6 |
| PVA/AA/MB | 371.83 | 0.178 | 0.938 7** | 101.91 | 0.310 5 | 0.994 7** | 6 |
表2 PVA/AA、PVA/AA/B、PVA/AA/MB吸附等温线拟合参数
Table 2 Fitting parameters of adsorption isotherms for PVA/AA, PVA/AA/B and PVA/AA/MB
材料 Materials | Langmuir等温吸附模型 Langmuir isothermal adsorption model | Freundlich等温吸附模型 Freundlich isothermal adsorption model | 样本数 Sample number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | R12 | KF/(mg1-n·g-1·L-n) | 1/n | R22 | ||
| PVA/AA | 271.15 | 0.038 | 0.983 7** | 40.94 | 0.356 7 | 0.923 5** | 6 |
| PVA/AA/B | 314.17 | 0.046 | 0.955 2** | 47.79 | 0.372 4 | 0.991 5** | 6 |
| PVA/AA/MB | 371.83 | 0.178 | 0.938 7** | 101.91 | 0.310 5 | 0.994 7** | 6 |
材料 Material | 准一级动力学模型 Pseudo-first-order plots | 准二级动力学模型 Pseudo-second-order plots | 样本数 Sample number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe/(mg·g-1) | k1/h-1 | R32 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | k2/(10-4·g·mg-1·h-1) | R42 | ||
| PVA/AA | 59.03 | 0.016 | 0.995 7** | 66.56 | 2.96 | 0.958 7** | 8 |
| PVA/AA/B | 134.81 | 0.006 | 0.996 1** | 169.46 | 3.43 | 0.987 9** | 8 |
| PVA/AA/MB | 197.63 | 0.005 | 0.993 4** | 255.98 | 1.78 | 0.989 8** | 8 |
表3 PVA/AA、PVA/AA/B、PVA/AA/MB的吸附动力学拟合参数
Table 3 Adsorption kinetics fitting parameters of PVA/AA, PVA/AA/B and PVA/AA/MB
材料 Material | 准一级动力学模型 Pseudo-first-order plots | 准二级动力学模型 Pseudo-second-order plots | 样本数 Sample number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe/(mg·g-1) | k1/h-1 | R32 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | k2/(10-4·g·mg-1·h-1) | R42 | ||
| PVA/AA | 59.03 | 0.016 | 0.995 7** | 66.56 | 2.96 | 0.958 7** | 8 |
| PVA/AA/B | 134.81 | 0.006 | 0.996 1** | 169.46 | 3.43 | 0.987 9** | 8 |
| PVA/AA/MB | 197.63 | 0.005 | 0.993 4** | 255.98 | 1.78 | 0.989 8** | 8 |
根系指标 Root index | 处理 Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | |
鲜重 Fresh weight/g | 0.728 d | 1.406 c | 1.584 c | 1.876 b | 1.987 b | 2.412 a |
干重 Dry weight/g | 0.085 d | 0.131 c | 0.155 bc | 0.187 b | 0.200 b | 0.245 a |
总根长 Total length of root/cm | 15.37 d | 28.14 c | 25.75 c | 34.47 b | 46.16 a | 49.34 a |
根表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 1.77 e | 3.45 d | 3.48 d | 5.92 c | 6.95 b | 8.89 a |
根体积 Root volume/(10-3·cm-3) | 18.88 d | 43.68 c | 42.82 cd | 59.02 c | 84.66 b | 118.49 a |
平均根直径 Average root diameter/mm | 0.477 c | 0.519 bc | 0.515 bc | 0.530 b | 0.543 ab | 0.576 a |
根尖数 Number of root tips | 29 f | 52 e | 94 d | 159 c | 179 b | 205 a |
表4 不同处理下生物量积累及根系指标
Table 4 Biomass accumulation and root indexes under different treatments
根系指标 Root index | 处理 Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | |
鲜重 Fresh weight/g | 0.728 d | 1.406 c | 1.584 c | 1.876 b | 1.987 b | 2.412 a |
干重 Dry weight/g | 0.085 d | 0.131 c | 0.155 bc | 0.187 b | 0.200 b | 0.245 a |
总根长 Total length of root/cm | 15.37 d | 28.14 c | 25.75 c | 34.47 b | 46.16 a | 49.34 a |
根表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 1.77 e | 3.45 d | 3.48 d | 5.92 c | 6.95 b | 8.89 a |
根体积 Root volume/(10-3·cm-3) | 18.88 d | 43.68 c | 42.82 cd | 59.02 c | 84.66 b | 118.49 a |
平均根直径 Average root diameter/mm | 0.477 c | 0.519 bc | 0.515 bc | 0.530 b | 0.543 ab | 0.576 a |
根尖数 Number of root tips | 29 f | 52 e | 94 d | 159 c | 179 b | 205 a |
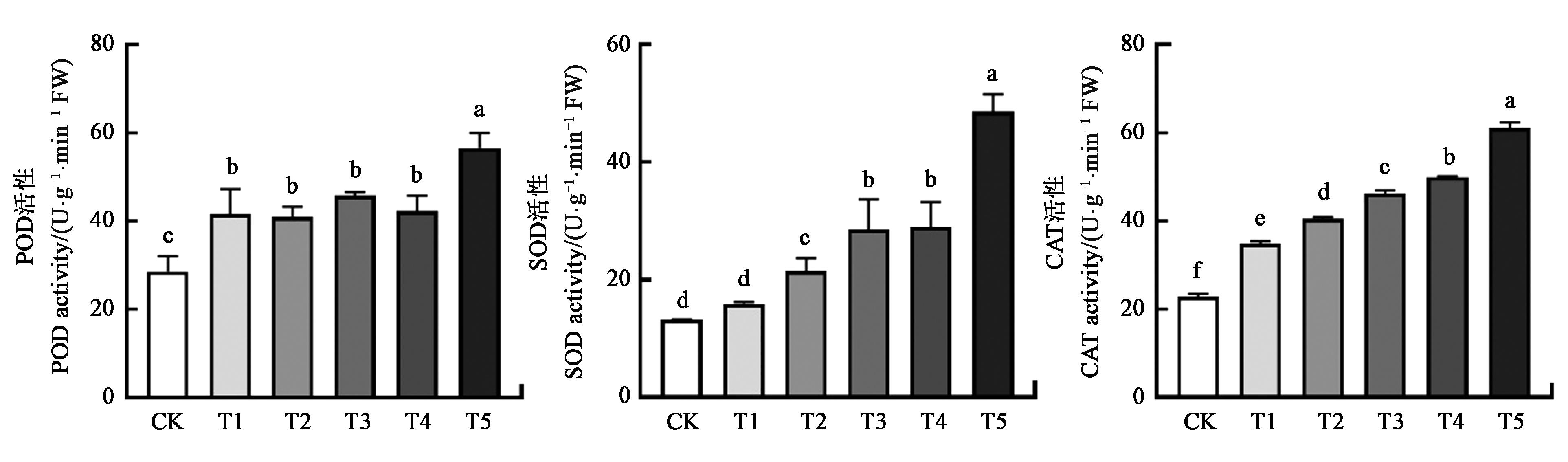
图5 不同处理下烟草幼苗抗氧化酶活性注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.5 Antioxidant enzyme activities of tobacco seedlings under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
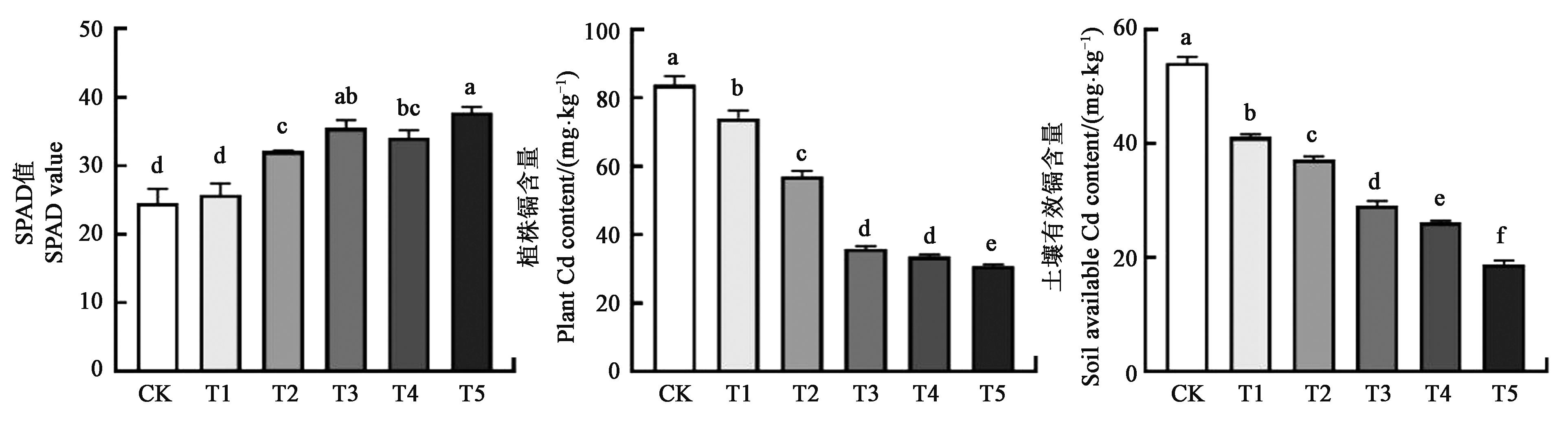
图6 不同处理下叶片SPAD值、土壤有效态镉和植株镉含量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.6 Leaf SPAD value, soil available Cd and plant Cd contents under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | ZHAO F J, MA Y, ZHU Y G, et al.. Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(2):750-759. |
| 2 | 陈能场,郑煜基,何晓峰,等. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(9):1689-1692. |
| CHEN N C, ZHENG Y J, HE X F, et al.. Analysis of the bulletin of national soilpollution survey [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2017, 36(9):1689-1692. | |
| 3 | RAI V, KHATOON S, BISHT S S, et al.. Effect of cadmium on growth, ultramorphology of leaf and secondary metabolites of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. and Thonn [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 61(11):1644-1650. |
| 4 | RIZWAN M, ALI S, REHMAN M, et al.. A critical review on the effects of zinc at toxic levels of cadmium in plants [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2019, 26(7):6279-6289. |
| 5 | ROSEN K, ERIKSSON J, VINICHUK M. Uptake and translocation of 109Cd and stable Cd within tobacco plants [J]. J. Environ. Radioactiv., 2012, 113:16-20. |
| 6 | 刘领,悦飞雪,李继伟,等. 镉胁迫下生物炭与锌/钾叶面肥促进烟草生长降低镉富集的协同效应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(6):982-990. |
| LIU L, YUE F X, LI J W, et al.. Interaction between biochar and Zn or K foliar fertilizer on the growth and Cd uptake of tobacco under cadmium stress [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2019, 25(6):982-990. | |
| 7 | MOHAN D, KUMAR H, SARSWAT A, et al.. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars [J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 236:513-528. |
| 8 | JARUP L, AKESSON A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem [J]. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm., 2009, 238(3):201-208. |
| 9 | SARMAH D, KARAK N. Double network hydrophobic starch based amphoteric hydrogel as an effective adsorbent for both cationic and anionic dyes [J/OL]. Carbohyd. Polym., 2020, 242:116320 [2021-08-26]. . |
| 10 | WANG H, DING J, CHI Q, et al.. The effect of biochar on soil-plant-earthworm-bacteria system in metal(loid) contaminated soil [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020, 263:114610 [2021-08-26]. . |
| 11 | WIBOWO N, SETYADHI L, WIBOWO D, et al.. Adsorption of benzene and toluene from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and its acid and heat treated forms: influence of surface chemistry on adsorption [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 146(1-2):237-242. |
| 12 | 王瑞峰, 周亚男, 孟海波, 等. 不同改性生物炭对溶液中Cd的吸附研究[J].中国农业科技导报,2016,18(6):103-111. |
| WANG R F, ZHOU Y N, MENG H B, et al.. Adsorption of Cd in solution by different modified biochar [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2016, 18(6):103-111. | |
| 13 | 况帅,冯迪,宋科,等. 低钾胁迫对烟草幼苗活性氧及抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2018, 24(2):48-54. |
| KUANG S, FENG D, SONG K, et al.. Effect of potassium deficiency stress on active oxygen and antioxidant enzyme system in tobacco seedlings [J]. Acta Tab. Sin., 2018, 24(2):48-54. | |
| 14 | 刘宛宜,王天野,王铖熠,等. 聚(丙烯酸酸-co-丙烯酰胺)水凝胶对阳离子染料亚甲基蓝和孔雀石绿吸附性能的研究[J]. 分析化学, 2019, 47(11):1785-1793. |
| LIU W Y, WANG T Y, WANG C Y, et al.. Study of adsorption performance of cationic dyes methylene blue and malachite green by poly (acrylate-co-acrylamide) hydrogel [J]. Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 2019, 47(11):1785-1793. | |
| 15 | PAULINO A T, GUILHERME M R, REIS A V, et al.. Capacity of adsorption of Pb2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solutions by chitosan produced from silkworm chrysalides in different degrees of deacetylation [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 147(1-2):139-147. |
| 16 | 张立志,易平,方丹丹,等. 超顺磁性纳米Fe3O4@SiO2功能化材料对镉的吸附机制[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(6):2917-2927. |
| ZHANG L Z, YI P, FANG D D, et al.. Adsorption mechanism of cadmium by superparamangnetic nano-Fe3O4@SiO2 functionalized materials [J]. Environ. Sci., 2021, 42(6):2917-2927. | |
| 17 | 庞发虎,吴雪姣,孔雪菲,等. 重金属钝化剂阻控生菜Cd吸收的功能稳定性和适用性[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5):2502-2511. |
| PANG F H, WU X J, KONG X F, et al.. Functional stability and applicability of heavy metal passivators in reducing Cd uptake by lettuce [J]. Environ. Sci., 2021, 42(5):2502-2511. | |
| 18 | NOLAN A L, ZHANG H, MCLAUGHLIN M J. Prediction of zinc, cadmium, lead, and copper availability to wheat in contaminated soils using chemical speciation, diffusive gradients in thin films, extraction, and isotopic dilution techniques [J]. J. Environ. Qual., 2005, 34(2): 496-507. |
| 19 | 程启明,黄青,刘英杰,等. 花生壳与花生壳生物炭对镉离子吸附性能研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(10):2022-2029. |
| CHENG Q M, HUANG Q, LIU Y J, et al.. Adsorption of cadmium (Ⅱ) on peanut shell and its biochar [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2014, 33(10):2022-2029. | |
| 20 | WAN S, HE F, WU J, et al.. Rapid and highly selective removal of lead from water using graphene oxide-hydrated manganese oxide nanocomposites [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2016, 314:32-40. |
| 21 | 邢瑶,马兴华. 氮素形态对植物生长影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(2):109-117. |
| XING Y, MA X H. Research progress on effect of nitrogen form on plant growth [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2015, 17(2):109-117. | |
| 22 | GUO T R, ZHANG G P, ZHOU M X, et al.. Influence of aluminum and cadmium stresses on mineral nutrition and root exudates in two barley cultivars [J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(4): 505-512. |
| 23 | 刘庆,董元杰,刘双,等. 外源水杨酸(SA)对NaCl胁迫下棉花幼苗生理生化特性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(2):165-168, 174. |
| LIU Q, DONG Y J, LIU S, et al.. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of contton seedlings under salt stress [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2014, 28(2):165-168, 174. | |
| 24 | 杨彪,杜荣宇,杨玉,等. 便携式植物叶片叶绿素含量无损检测仪设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(12):180-186. |
| YANG B, DU R Y, YANG Y, et al.. Design of portable nondestructive detector for chlorophyll content of plant leaves [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2019, 50(12):180-186. | |
| 25 | CHOPPALA G, SAIFULLAH, BOLAN N, et al.. Cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance to cadmium toxicity [J]. Crit. Rev. Plant. Sci., 2014, 33(5):374-391. |
| 26 | 悦飞雪,李继伟,王艳芳,等. 施用秸秆生物炭和鸡粪对镉胁迫下玉米生长及镉吸收的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(10):2118-2126. |
| YUE F X, LI J W, WANG Y F, et al.. Effects of soil amendments with stalk-derived biochar and chicken manure on the growth and Cd uptake of maize under Cd stress [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2018, 37(10):2118-2126. | |
| 27 | 刘彩凤,史刚荣,余如刚,等. 硅缓解植物镉毒害的生理生态机制[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(23):7799-7810. |
| LIU C F, SHI G R, YU R G, et al.. Eco-physiological mechanisms of silicon-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in plants: a review [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(23):7799-7810. |
| [1] | 庆福, 梁洪月, 孙静, 鲁新蕊, 梁运江. 生物炭-氮肥配施对东北黑土团聚体及有机碳含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 195-204. |
| [2] | 侯赛赛, 仝姗姗, 王鹏企, 谢冰雪, 张瑞芳, 王鑫鑫. 生物炭和秸秆对不同作物生长性状和养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 179-191. |
| [3] | 张如艳, 李绅昊, 朱奇鹏, 冯太纲, 李红波, 邢泽炳, 羡瑜. 生物炭含量对园林绿化废弃物/聚乳酸复合材料物理力学性能影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 192-200. |
| [4] | 吕志伟, 李冬梅, 金梅娟, 张燕辉, 陶玥玥, 周新伟, 王海候. 热解温度及时间对生物炭理化性质及吸附性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 211-217. |
| [5] | 邢卓冉, 丁松爽, 张凯, 马明, 郭文龙, 刘旭东, 时向东. 计算机视觉与深度学习技术在烟叶生产上的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 96-106. |
| [6] | 史丹一, 邱禹, 黄成真, 王娟. 酸改性生物炭对滨海盐渍土壤水分入渗特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 183-192. |
| [7] | 周喜新, 袁世林, 杨柳, 夏滔, 张毅, 范伟. 连作烟草根系分泌物鉴定及潜在化感物质的筛选研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 136-146. |
| [8] | 蒲子天, 王红, 赵斌, 王鑫鑫. 不同土壤改良物料对连作黄芩生长及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 189-198. |
| [9] | 付彦博, 冷冰冰, 扁青永, 董志多, 刘国宏, 李海峰, 温云梦, 郭文博, 张万旭. 生物炭和油菜幼苗对土壤重金属镉污染的钝化效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 183-190. |
| [10] | 赵娅红, 胡骞予, 夏融, 王志江, 谢永辉, 叶贤文, 余磊, 齐颖, 羊绍武, 薛至勤, 吴治兴, 黄飞燕, 韩天华. 生物炭肥对易感根结线虫病烤烟根际菌群和理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 206-214. |
| [11] | 刘化冰, 党伟, 李奇, 张晓兵, 徐志强, 钟永健, 任志广, 张勇刚, 袁凯龙, 杨浩, 王辉, 孙聚涛. 烟草品种间氮素吸收和同化差异研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 66-78. |
| [12] | 常峻嘉, 盖佳鑫, 陶刚, 莫转龙海. 哈茨木霉菌对烟草的促生及其黑胫病的诱导抗性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 168-176. |
| [13] | 徐皖菁, 彭芳, 赵豆豆, 罗姣姣, 陶珊, 廖海浪, 毛常清, 吴宇, 朱秀, 徐正君, 张超. 基于转录组和代谢组解析川芎对镉胁迫的响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 98-109. |
| [14] | 唐天君, 陈洋, 胡军, 江浩田. 基于无人机影像数据的烟草精准识别方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 145-157. |
| [15] | 高静, 徐明岗, 李然, 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 张强, 郑磊. 整合分析生物炭施用对土壤pH的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 186-196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||