




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 186-194.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0715
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
易丽霞1( ), 周勇2, 杨伟1, 姚涞1(
), 周勇2, 杨伟1, 姚涞1( ), 蒋梦蝶1, 聂江文1, 朱波1, 刘章勇1
), 蒋梦蝶1, 聂江文1, 朱波1, 刘章勇1
收稿日期:2024-09-02
接受日期:2025-05-07
出版日期:2025-11-15
发布日期:2025-11-17
通讯作者:
姚涞
作者简介:易丽霞 E-mail:yilixia525@163.com;
基金资助:
Lixia YI1( ), Yong ZHOU2, Wei YANG1, Lai YAO1(
), Yong ZHOU2, Wei YANG1, Lai YAO1( ), Mengdie JIANG1, Jiangwen NIE1, Bo ZHU1, Zhangyong LIU1
), Mengdie JIANG1, Jiangwen NIE1, Bo ZHU1, Zhangyong LIU1
Received:2024-09-02
Accepted:2025-05-07
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2025-11-17
Contact:
Lai YAO
摘要:
为探究黑麦草配施尿素对稻田土壤中氨挥发的影响,以南方水稻-绿肥(黑麦草)轮作模式为研究对象进行盆栽试验,设置5种配施比例:单施尿素(CF)、25%黑麦草+75%尿素(25%RG)、50%黑麦草+50%尿素(50%RG)、75%黑麦草+25%尿素(75%RG)和单施黑麦草(100%RG),所有处理施氮量均为100 mg N?kg-1风干土,监测不同处理下水稻季的氨挥发速率、水稻产量和土壤环境指标。结果表明,各处理氨挥发速率均在尿素施用后迅速增加,氨挥发排放峰值随黑麦草替代尿素比例的增加而降低。氨挥发累计量的大小依次为CF>25%RG>50%RG>75%RG>100%RG,其中最大值为30.53 mg·m-2,最小值为22.07 mg·m-2。与CF处理相比,黑麦草还田处理氨挥发累计量分别降低4.8%、17.2%、20.7%和27.7%,其中50%RG的排放因子(单位氮肥投入的氨排放强度)显著低于CF(P<0.05)。25%RG和50%RG处理的水稻产量与CF之间无显著差异,但50%RG处理的氨挥发排放强度最低,与其他处理差异显著(P<0.05)。土壤温度、pH、铵态氮和硝态氮含量均显著影响稻田氨挥发速率(P<0.05)。综上,50%RG处理在兼顾水稻产量的同时能够有效减缓稻田土壤氨挥发的损失,对减少稻田氮素损失和保护生态环境具有一定指导意义。
中图分类号:
易丽霞, 周勇, 杨伟, 姚涞, 蒋梦蝶, 聂江文, 朱波, 刘章勇. 黑麦草还田替代尿素对稻田土壤氨挥发的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(11): 186-194.
Lixia YI, Yong ZHOU, Wei YANG, Lai YAO, Mengdie JIANG, Jiangwen NIE, Bo ZHU, Zhangyong LIU. Effect of Ryegrass Return to Field as Substitute for Urea on Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 186-194.
处理 Treatment | 尿素总量 Total urea amount/(g·m-2) | 绿肥量 Green fertilizer amount/(g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| CF | 0.64 | 0.0 |
| 25%RG | 0.48 | 7.2 |
| 50%RG | 0.32 | 14.3 |
| 75%RG | 0.16 | 21.5 |
| 100%RG | 0.00 | 28.7 |
表 1 各处理施肥量
Table 1 Fertilizer application rate for each treatment
处理 Treatment | 尿素总量 Total urea amount/(g·m-2) | 绿肥量 Green fertilizer amount/(g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| CF | 0.64 | 0.0 |
| 25%RG | 0.48 | 7.2 |
| 50%RG | 0.32 | 14.3 |
| 75%RG | 0.16 | 21.5 |
| 100%RG | 0.00 | 28.7 |
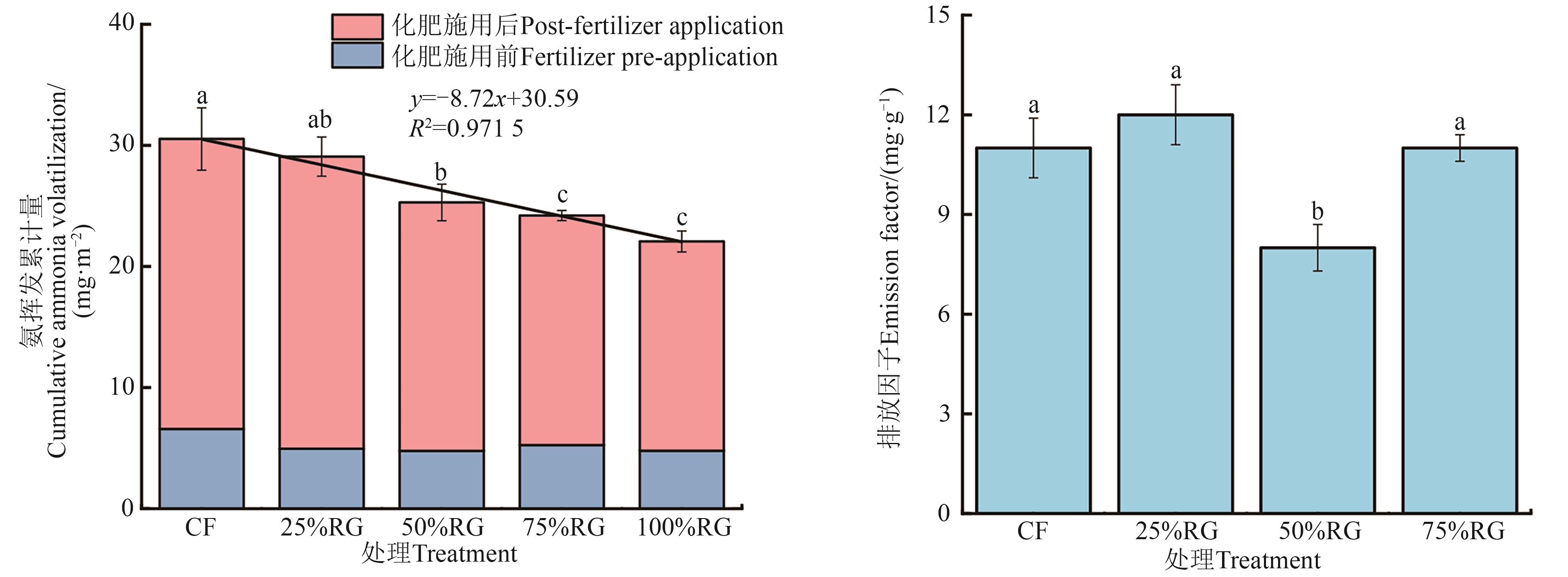
图2 不同施肥处理下的氨挥发累计量和氨排放因子注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Cumulative ammonia volatilization and ammonia emission factors under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 头季First season | 再生季Regeneration season | 总产量 Total output/(g·m-2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling/% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling /% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | ||
| CF | 9 a | 798 a | 91.5 a | 28.3 a | 719.6 a | 5 a | 92 a | 72.8 a | 26.2 a | 76.7 a | 796.3 a |
| 25%RG | 8 ab | 743 b | 92.2 a | 29.4 a | 695.8 a | 4 a | 93 a | 71.9 a | 26.3 a | 77.9 a | 773.7 a |
| 50%RG | 8 ab | 733 c | 85.6 ab | 28.6 a | 667.6 a | 4 a | 91 a | 67.9 b | 27.5 a | 79.6 a | 747.2 a |
| 75%RG | 6 c | 558 c | 87.0 a | 31.6 a | 560.0 b | 3 a | 89 a | 67.6 b | 27.6 a | 78.3 a | 639.2 b |
| 100%RG | 4 c | 536 c | 81.7 b | 30.1 a | 513.8 b | 5 a | 90 a | 72.4 a | 28.3 a | 81.1 a | 594.9 b |
表 2 各施肥配比下的水稻产量
Table 2 Rice yield under different fertilization ratios
| 处理Treatment | 头季First season | 再生季Regeneration season | 总产量 Total output/(g·m-2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling/% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling /% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | ||
| CF | 9 a | 798 a | 91.5 a | 28.3 a | 719.6 a | 5 a | 92 a | 72.8 a | 26.2 a | 76.7 a | 796.3 a |
| 25%RG | 8 ab | 743 b | 92.2 a | 29.4 a | 695.8 a | 4 a | 93 a | 71.9 a | 26.3 a | 77.9 a | 773.7 a |
| 50%RG | 8 ab | 733 c | 85.6 ab | 28.6 a | 667.6 a | 4 a | 91 a | 67.9 b | 27.5 a | 79.6 a | 747.2 a |
| 75%RG | 6 c | 558 c | 87.0 a | 31.6 a | 560.0 b | 3 a | 89 a | 67.6 b | 27.6 a | 78.3 a | 639.2 b |
| 100%RG | 4 c | 536 c | 81.7 b | 30.1 a | 513.8 b | 5 a | 90 a | 72.4 a | 28.3 a | 81.1 a | 594.9 b |
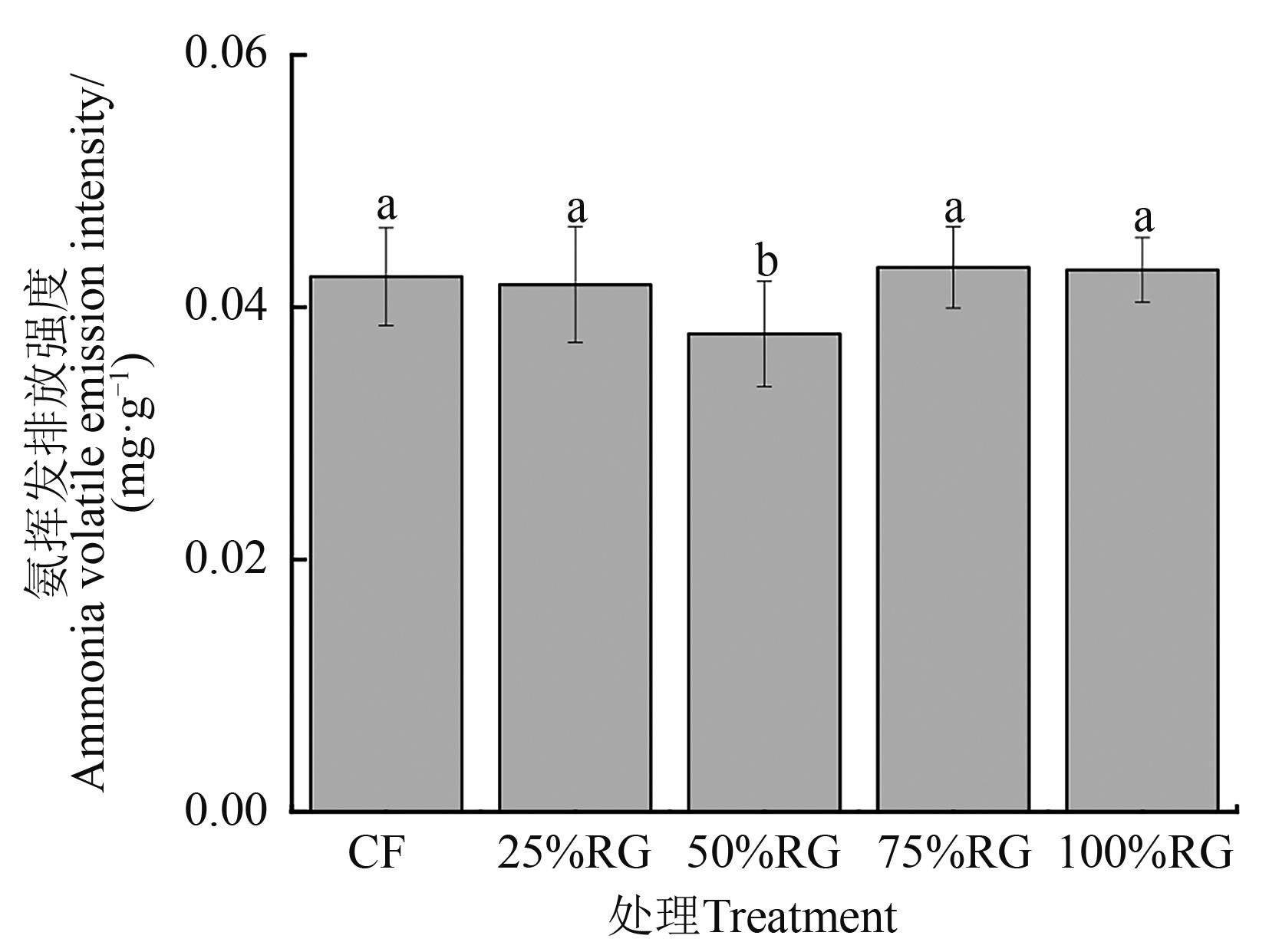
图3 不同施肥处理下氨挥发排放强度注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Emission intensity of ammon ia volatilization under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
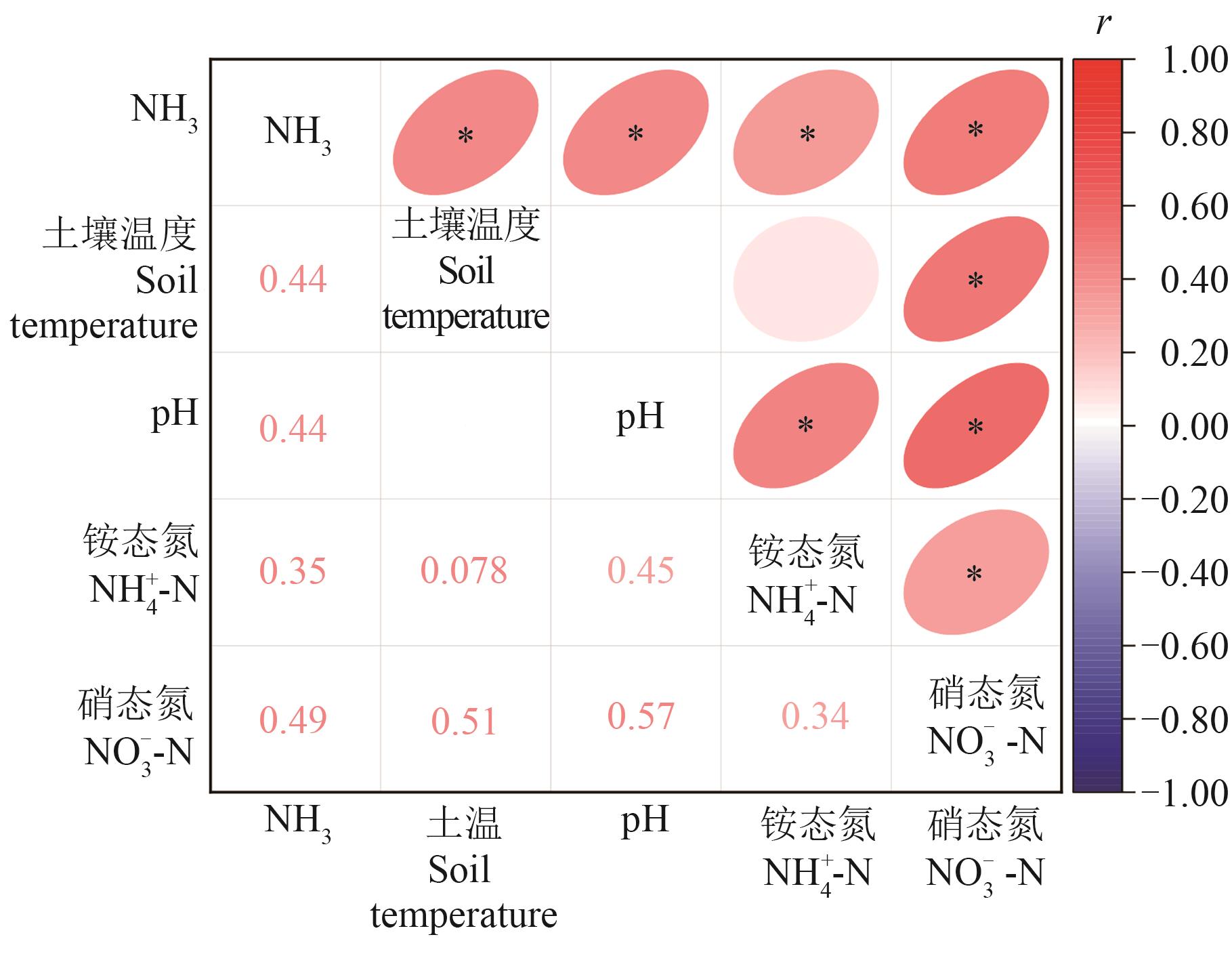
图5 土壤指标与稻田土壤氨挥发的相关性分析注:*表示在P<0.05水平显著相关。
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis of soil indexes and ammonia volatilization from paddy soilNote: * indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 level.
| [1] | PENG X L, MAHARJAN B, YU C L, et al.. A laboratory evaluation of ammonia volatilization and nitrate leaching following nitrogen fertilizer application on a coarse-textured soil [J]. Agron. J., 2015, 107(3): 871-879. |
| [2] | 曹玉博,邢晓旭,柏兆海,等.农牧系统氨挥发减排技术研究进展[J].中国农业科学, 2018, 51(3): 566-580. |
| CAO Y B, XING X X, BAI Z H, et al.. Review on ammonia emission mitigation techniques of crop-livestock production system [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2018, 51(3): 566-580. | |
| [3] | 刘学军,沙志鹏,宋宇,等.我国大气氨的排放特征、减排技术与政策建议[J].环境科学研究, 2021, 34(1): 149-157. |
| LIU X J, SHA Z P, SONG Y, et al.. China’s atmospheric ammonia emission characteristics, mitigation options and policy recommendations [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2021, 34(1):149-157. | |
| [4] | 龚苏宁,王业明,刘荣桂.我国将加强氨排放治理[J].生态经济, 2020(11): 9-12. |
| [5] | 谢梓豪,樊品镐,武华,等.基于氨挥发因子方法的中国农田氨排放量估算[J].环境科学学报, 2020, 40(11): 4180-4188. |
| XIE Z H, FAN P H, WU H, et al.. Deriving volatile factors and estimating direct ammonia emissions for crop cultivation in China [J]. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(11): 4180-4188. | |
| [6] | LIAO B, LIAO P, HU R G, et al.. Mitigating ammonia volatilization in rice cultivation:the impact of partial organic fertilizer substitution [J/OL].Chemosphere,2023,344:140326 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [7] | 万雪薇,丁紫娟,聂江文,等.不同施肥方式对再生稻田氨挥发及氮肥利用率的影响[J].南方农业学报,2023, 54(12):3550-3560. |
| WAN X W, DING Z J, NIE J W, et al.. Effects of different fertilizer application methods on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate in regenerating rice fields [J].J. South. Agric., 2023, 54(12): 3550-3560. | |
| [8] | SUN L Y, WU Z, MA Y C, et al.. Ammonia volatilization and atmospheric N deposition following straw and urea application from a rice-wheat rotation in southeastern China [J]. Atmos.Environ., 2018, 181: 97-105. |
| [9] | WANG B, LI R, WAN Y F, et al.. Air warming and CO2 enrichment cause more ammonia volatilization from rice paddies:an OTC field study [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021,752:142071 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [10] | 朱晓琦,胡正义,王惠惠,等.滇池柴河流域蔬菜地土壤施用控释尿素与普通尿素的氮损失比较[J].中国农业科技导报,2014,16(6):109-116. |
| ZHU X Q, HU Z Y, WANG H H, et al.. Comparison of nitrogen loss between controlled release urea and common urea in vegetable soils at Chaihe Catchment of Dianchi Lake [J]. J.Agric. Sci. Technol., 2014,16(6):109-116. | |
| [11] | 卢丽丽,吴根义.农田氨排放影响因素研究进展[J].中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24(1):149-162. |
| LU L L, WU G Y. Advances in affecting factors of ammonia emission in farmland [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2019,24(1):149-162. | |
| [12] | 常菲,红梅,武岩,等.灌溉方式和改良措施对河套灌区盐渍土氨挥发的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2019(2):38-45. |
| CHANG F, HONG M, WU Y, et al.. Effects of irrigation methods and improvement measures on ammonia volatilization of saline soil in Hetao Irrigation Area [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China,2019(2): 38-45. | |
| [13] | 许云翔,何莉莉,陈金媛,等.生物炭对农田土壤氨挥发的影响机制研究进展[J].应用生态学报, 2020, 31(12): 4312-4320. |
| XU Y X, HE L L, CHEN J Y, et al.. Effects of biochar on ammonia volatilization from farmland soil: a review [J]. Chin. J.Appl. Ecol., 2020, 31(12): 4312-4320. | |
| [14] | DENG X Z, XU T T, XUE L X, et al..Effects of warming and fertilization on paddy N2O emissions and ammonia volatilization [J/OL]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2023,347:108361 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [15] | 张靖,朱潇,沈健林,等.生物有机肥与化肥配施对稻田氨挥发的影响[J].中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(1):15-25. |
| ZHANG J, ZHU X, SHEN J L, et al.. Effects of combined application of microbial organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer on ammonia volatilization in a paddy field with double rice cropping [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30(1):15-25. | |
| [16] | 梁琴,周泽弘,马雪清,等.绿肥翻压与氮肥减施对水稻产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(10):124-130. |
| LIANG Q, ZHOU Z H, MA X Q, et al.. Effects of green manure turning over and nitrogen reducing on rice yield,quality and soil fertility [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(10):124-130. | |
| [17] | 赵炯平,邓小华,江智敏,等.不同绿肥翻压还土后植烟土壤主要养分动态变化[J].作物研究, 2015, 29(2):161-165. |
| ZHAO J P, DENG X H, JIANG Z M, et al.. Dynamic changes of main nutrients in tobacco-planting soil under different green manure application [J]. Crop Res., 2015, 29(2):161-165. | |
| [18] | ZHANG X X, ZHANG R J, GAO J S, et al.. Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017, 104: 208-217. |
| [19] | 乔伟艳,顾洪如,沈益新.稻茬种植多花黑麦草对土壤肥力和微生物组成的影响[J].草业科学,2017,34(2): 240-245. |
| QIAO W Y, GU H R, SHEN Y X. Effects of planting Italian ryegrass in winter fallow fields on soil fertility and microorganisms [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2017, 34(2):240-245. | |
| [20] | CAO M Y, XIANG Y, HE H B, et al.. Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.)-rice (Oryza sativaL.) rotation promotes the nitrogen cycle in the rice rhizosphere through dominant ammonia-oxidizing bacteria [J/OL].Appl.Soil Ecol.,2024,193: 105121 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [21] | 龙莉,杨旭初,熊斌,等.冬作物秸秆还田对双季稻产量和土壤肥力的影响[J].作物研究,2019,33(2):104-109. |
| LONG L, YANG X C, XIONG B, et al.. Effect of winter crops straw returning on yield and soil fertility in a double cropping rice paddy [J]. Crop Res., 2019, 33(2):104-109. | |
| [22] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版. 北京:中国农业出版社,2000: 1-495. |
| [23] | 沈仕洲,杨艳,王瑞琦,等.施肥对云南洱海流域蒜田土壤氨挥发和大蒜产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(3): 470-479. |
| SHEN S Z, YANG Y, WANG R Q, et al.. Effects of fertilization on ammonia volatilization and garlic yield in Erhai Lake Basin of Yunnan province [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2021,27(3):470-479. | |
| [24] | ZHANG T, LIU H B, LUO J F, et al.. Long-term manure application increased greenhouse gas emissions but had no effect on ammonia volatilization in a Northern China upland field [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 633: 230-239. |
| [25] | 李诗豪,刘天奇,马玉华,等.耕作方式与氮肥类型对稻田氨挥发、氮肥利用率和水稻产量的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2018, 35(5): 447-454. |
| LI S H, LIU T Q, MA Y H, et al.. Effects of tillage practices and nitrogen sources on NH3 volatilization,nitrogen use efficiency and yield in paddy fields in Central China [J]. J.Agric. Resour. Environ., 2018, 35(5): 447-454. | |
| [26] | 唐良梁,李艳,李恋卿,等.不同施氮量对稻田氨挥发的影响及阈值探究[J].土壤通报, 2015, 46(5):1232-1239. |
| TANG L L, LI Y, LI L Q, et al.. Effect of different nitrogen application rate on paddy ammonia volatilization and nitrogen threshold [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2015, 46(5): 1232-1239. | |
| [27] | 易宗建,靳拓,袁沛,等.有机肥氮替代比例对双季稻氮肥利用率及氨挥发特征的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2024(10):172-181. |
| YI Z J, JIN T, YUAN P, et al.. Effects of organic fertilizer nitrogen replacement ratio on nitrogen use efficiency and ammonia volatilization of double-crop rice [J]. Soil Fert. Sci.China, 2024(10): 172-181. | |
| [28] | 卢丽兰,甘炳春,许明会,等.不同施肥与灌水量对槟榔土壤氨挥发的影响[J].生态学报, 2011, 31(15): 4477-4484. |
| LU L L, GAN B C, XU M H, et al.. Effect of different fertilization and irrigation practices on soil ammonia volatilization of Arecanut (Areca catechu L.) [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin.,2011, 31(15): 4477-4484. | |
| [29] | 赵淼,田玉华,张敏,等.改善农学管理措施减少太湖稻麦轮作NH3和NO排放[J].土壤, 2015, 47(5): 836-841. |
| ZHAO M, TIAN Y H, ZHANG M, et al.. Improving agronomic practices to reduce ammonia and nitric oxide emissions from rice-wheat rotation field in Tai Lake Region, China [J]. Soils,2015, 47(5): 836-841. | |
| [30] | WANG S W, SHAN J, XIA Y Q, et al.. Different effects of biochar and a nitrification inhibitor application on paddy soil denitrification:a field experiment over two consecutive rice-growing seasons [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2017, 593: 347-356. |
| [31] | 彭玉净,田玉华,尹斌.添加脲酶抑制剂NBPT对麦秆还田稻田氨挥发的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2012,20(1):19-23. |
| PENG Y J, TIAN Y H, YIN B. Effects of NBPT urease inhibitor on ammonia volatilization in paddy fields with wheat straw application [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2012,20(1):19-23. | |
| [32] | 山楠,毕晓庆,杜连凤,等.基施氮肥对麦田冬前氨挥发损失的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2013(6): 47-51. |
| SHAN N, BI X Q, DU L F, et al.. Effect of basal nitrogen fertilization on cornfield ammonia volatilization loss ahead of winter in-site conditions [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2013(6):47-51. | |
| [33] | 山楠,杜连凤,毕晓庆,等.用15N肥料标记法研究潮土中玉米氮肥的利用率与去向[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2016,22(4):930-936. |
| SHAN N, DU L F, BI X Q, et al.. Nitrogen use efficiency and behavior studied with 15N labeled fertilizer in maize in fluvo-aquic soils [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2016, 22(4): 930-936. | |
| [34] | 黄思怡,田昌,谢桂先,等.控释尿素减少双季稻田氨挥发的主要机理和适宜用量[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(12):2102-2112. |
| HUANG S Y, TIAN C, XIE G X, et al.. Mechanism and suitable application dosage of controlled-release urea effectively reducing ammonia volatilization in double-cropping paddy fields [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2019, 25(12): 2102-2112. | |
| [35] | ZHANG Y S, LUAN S J, CHEN L L, et al.. Estimating the volatilization of ammonia from synthetic nitrogenous fertilizers used in China [J]. J. Environ. Manage., 2011,92(3):480-493. |
| [36] | NDEGWA P M, HRISTOV A N, AROGO J, et al.. A review of ammonia emission mitigation techniques for concentrated animal feeding operations [J]. Biosyst. Eng., 2008,100(4):453-469. |
| [37] | 万伟帆,李斐,红梅,等.氮肥用量和脲酶抑制剂对滴灌马铃薯田氧化亚氮排放和氨挥发的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(3):693-702. |
| WAN W F, LI F, HONG M, et al.. Effects of nitrogen rate and urease inhibitor on N2O emission and NH3 volatilization in drip irrigated potato fields [J].J. Plant Nutr.Fert.,2018,24(3):693-702. | |
| [38] | 宋涛,尹俊慧,胡兆平,等.脲酶/硝化抑制剂减少农田土壤氮素损失的作用特征[J].农业资源与环境学报,2021,38(4):585-597. |
| SONG T, YIN J H, HU Z P, et al.. Characteristics of urease/nitrification inhibitors in reducing nitrogen losses in farmland soils [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2021, 38(4): 585-597. | |
| [39] | 黄立华,杨易,刘伯顺,等.苏打盐碱化稻田土壤反硝化和氨挥发特征及主要影响因子[J].农业环境科学学报,2023:42(8): 1748-1757. |
| HUANG L H, YANG Y, LIU B S, et al.. Characteristics and main influencing factors of denitrification and ammonia volatilization in saline-sodic paddy soils [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2023, 42(8): 1748-1757. | |
| [40] | 王吕,吴玉红,秦宇航,等.紫云英稻秆联合还田与氮肥减量对水稻产量及氨挥发的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2024,43(2): 462-472. |
| WANG L, WU Y H, QIN Y H, et al.. Effects of rice stalk mulching combined with green manure retention and nitrogen reduction on rice yield and ammonia emission [J]. J. Agro- Environ. Sci., 2024,43(2): 462-472. | |
| [41] | 王昱杭,唐旭,姜振辉,等.不同比例有机无机氮配施对长期稻麦轮作体系中水稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J].土壤通报, 2024, 55(2): 401-411. |
| WANG Y H, TANG X, JIANG Z H, et al.. Effects of long-term combined application of organic-inorganic fertilizers on rice yield,nitrogen uptake and utilization in a rice-wheat rotation system [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2024, 55(2): 401-411. | |
| [42] | 刘汝亮,张爱平,李友宏,等.长期配施有机肥对宁夏引黄灌区水稻产量和稻田氮素淋失及平衡特征的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5): 947-954. |
| LIU R L, ZHANG A P, LI Y H, et al.. Rice yield,nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and nitrogen leaching losses as affected by long-term combined applications of manure and chemical fertilizers in Yellow River irrigated region of Ningxia,China [J].J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(5): 947-954. | |
| [43] | 文春燕,熊运华,王萍,等.减施化肥配施不同有机肥对优质籼稻产量和品质的影响[J].土壤,2023,55(2):280-287. |
| WEN C Y, XIONG Y H, WANG P, et al.. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application on yield and quality of high-quality indica rice [J]. Soils, 2023, 55(2):280-287. |
| [1] | 吴艳, 邹乐萍, 宋惠洁, 胡丹丹, 柳开楼, 梁万里. 控释氮肥和尿素配施对田面水铵态氮和早稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 192-200. |
| [2] | 石纹碹, 谭金芳, 张倩, 李岚涛, 王宜伦. 一次性施肥对不同生态区夏玉米产量和氮肥效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 193-202. |
| [3] | 黄巧义, 吴永沛, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 张木, 逄玉万, 曾招兵, 唐拴虎. 控释尿素与尿素配施对甜玉米产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 163-173. |
| [4] | 党翼, 张建军, 赵刚, 樊廷录, 王磊, 李尚中, 周刚. 控释尿素和普通尿素配施对旱地玉米产量和水氮利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 156-165. |
| [5] | 易媛, 张会云, 刘立伟, 王静, 朱雪成, 赵娜, 冯国华. 活性腐殖酸缓释肥替代尿素对徐麦新品种产量和群体质量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 144-153. |
| [6] | 周旋, 康兴蓉, 彭建伟, 杨相东, 钟雪梅, 胡文峰, 龙俊佑. 聚氨酯包膜氮肥减施对双季早稻生长、产量及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 153-161. |
| [7] | 张茂,徐彦红,席溢*,裴应杰,黄本用,杨克超,李金孟. 铅、锌、镉胁迫对多年生黑麦草生长及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 41-50. |
| [8] | 吴天琦1,刘浪1,卞传飞1,谭景艾2,石绪根2*,李保同1*. 栽培方式与氮肥运筹对江西双季晚粳稻稻曲病及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 159-169. |
| [9] | 尹焕丽1,岳艳军2,常凤1,王海标1,苗玉红1,王宜伦1*. 新型尿素对冬小麦产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 145-152. |
| [10] | 徐彦红,左意才,席溢*,许钟丹,李斌. 不同钙磷配比及浓度对多花黑麦草生长特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 174-180. |
| [11] | 张运红1,姚健1*,宝德俊1,和爱玲1,骆晓声1,杜君1,杨占平1,杜保池2. 尿素硝酸铵溶液对玉米产量、品质及养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(9): 113-121. |
| [12] | 王海标,张博,常凤,陶静静,刘培,王宜伦*. 包膜尿素与普通尿素配施减氮对夏玉米产量及氮肥效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(7): 98-105. |
| [13] | 国世佳1,段玉2*,张君2,张润生1,史有国3. 不同类型尿素配施对加工番茄产量、品质及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(6): 96-103. |
| [14] | 汪武静1,王明利2*. 我国西南地区黑麦草种植技术效率及科技进步贡献分析——以四川省为例[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(6): 21-28. |
| [15] | 薛海龙1,2,许文年1,2,3,刘大翔2,3*,夏振尧2,3. 几种聚合材料包膜尿素的研制及评价方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(4): 92-99. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||