




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 238-249.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0292
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
方晶1( ), 刘春铄1, 刘蕊1, 徐哲丰1, 陈雨秋3, 齐伟辰2, 陈长宝1(
), 刘春铄1, 刘蕊1, 徐哲丰1, 陈雨秋3, 齐伟辰2, 陈长宝1( ), 张涛1,2(
), 张涛1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-12
接受日期:2024-07-19
出版日期:2025-10-15
发布日期:2025-10-15
通讯作者:
陈长宝,张涛
作者简介:方晶 E-mail:835506940@qq.com
基金资助:
Jing FANG1( ), Chunshuo LIU1, Rui LIU1, Zhefeng XU1, Yuqiu CHEN3, Weichen QI2, Changbao CHEN1(
), Chunshuo LIU1, Rui LIU1, Zhefeng XU1, Yuqiu CHEN3, Weichen QI2, Changbao CHEN1( ), Tao ZHANG1,2(
), Tao ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-04-12
Accepted:2024-07-19
Online:2025-10-15
Published:2025-10-15
Contact:
Changbao CHEN,Tao ZHANG
摘要:
为探究外源磷肥对改良参地土壤中人参质量的影响,以改良后的人参连作土壤为试验材料,分别施用磷肥0.00(CK)、0.44(P1)、0.62(P2)、0.80 g·kg-1(P3),共计4个处理,对不同处理下栽培人参的皂苷含量、根际土壤理化性质和土壤酶活性进行检测,结合相关性分析和主成分分析明确人参皂苷及土壤性质随生长时期变化的规律。结果表明,人参的鲜重和干重随磷肥施用量的增加而增加,P1和P2处理对土壤碱解氮、速效钾和有机质含量有正向促进作用。低水平磷处理对人参皂苷及总皂苷的积累有正向调控作用;土壤电导率、速效钾和土壤蛋白酶对人参皂苷积累有正向调控作用。主成分分析提取出2个主成分,累计贡献率达94.726%。综合分析表明,P1(0.44 g·kg-1)处理栽培人参的长势更好,人参皂苷有效成分积累更多,土壤环境更适宜人参生长。以上研究结果为改良后人参连作土壤合理施用磷肥提供了科学依据。
中图分类号:
方晶, 刘春铄, 刘蕊, 徐哲丰, 陈雨秋, 齐伟辰, 陈长宝, 张涛. 外源磷对栽培人参皂苷含量及根际土壤的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(10): 238-249.
Jing FANG, Chunshuo LIU, Rui LIU, Zhefeng XU, Yuqiu CHEN, Weichen QI, Changbao CHEN, Tao ZHANG. Effect of Exogenous Phosphorus Regulation on Saponins Content and Inter-root Soil of Cultivated Ginseng[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(10): 238-249.
时间 Time/min | 流动相A Fluid phase A/% | 流动相B Fluid phase B/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0—18 | 19→23 | 81→77 |
| 18—28 | 23→28 | 77→72 |
| 28—30 | 28→32 | 72→68 |
| 30—50 | 32→34 | 68→66 |
| 50—70 | 34→80 | 66→20 |
表1 梯度洗脱条件
Table 1 Gradient elution conditions
时间 Time/min | 流动相A Fluid phase A/% | 流动相B Fluid phase B/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0—18 | 19→23 | 81→77 |
| 18—28 | 23→28 | 77→72 |
| 28—30 | 28→32 | 72→68 |
| 30—50 | 32→34 | 68→66 |
| 50—70 | 34→80 | 66→20 |
人参皂苷 Ginsenoside | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数 R2 | 含量线性范围 Linear range of content/mg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ro | y=214 055x+26.759 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rg1 | y=223 076x+23.105 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Re | y=220 380x+10.868 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rf | y=306 357x+62.417 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rb1 | y=155 839x+1.099 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rc | y=181 626x-10.791 | 0.999 9 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
| Rb2 | y=217 709x-2.963 | 0.999 8 | 0.000 9~0.018 0 |
| Rb3 | y=203 643x-2.797 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rd | y=212 073x+1.318 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rh2 | y=152 219x+9.985 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 3~0.026 0 |
| Rg3 | y=509 071x+44.312 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
总皂苷 Total saponins | y=1.939 7x+0.144 | 0.999 7 | 0.100 0~1.000 4 |
表2 人参皂苷的回归方程
Table 2 Regression equations of ginsenosides
人参皂苷 Ginsenoside | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数 R2 | 含量线性范围 Linear range of content/mg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ro | y=214 055x+26.759 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rg1 | y=223 076x+23.105 | 0.999 0 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Re | y=220 380x+10.868 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rf | y=306 357x+62.417 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rb1 | y=155 839x+1.099 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rc | y=181 626x-10.791 | 0.999 9 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
| Rb2 | y=217 709x-2.963 | 0.999 8 | 0.000 9~0.018 0 |
| Rb3 | y=203 643x-2.797 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 1~0.022 0 |
| Rd | y=212 073x+1.318 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 2~0.024 0 |
| Rh2 | y=152 219x+9.985 | 0.999 7 | 0.001 3~0.026 0 |
| Rg3 | y=509 071x+44.312 | 0.999 8 | 0.001 0~0.020 0 |
总皂苷 Total saponins | y=1.939 7x+0.144 | 0.999 7 | 0.100 0~1.000 4 |

图2 不同处理的人参皂苷含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Contents of ginsenoside under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
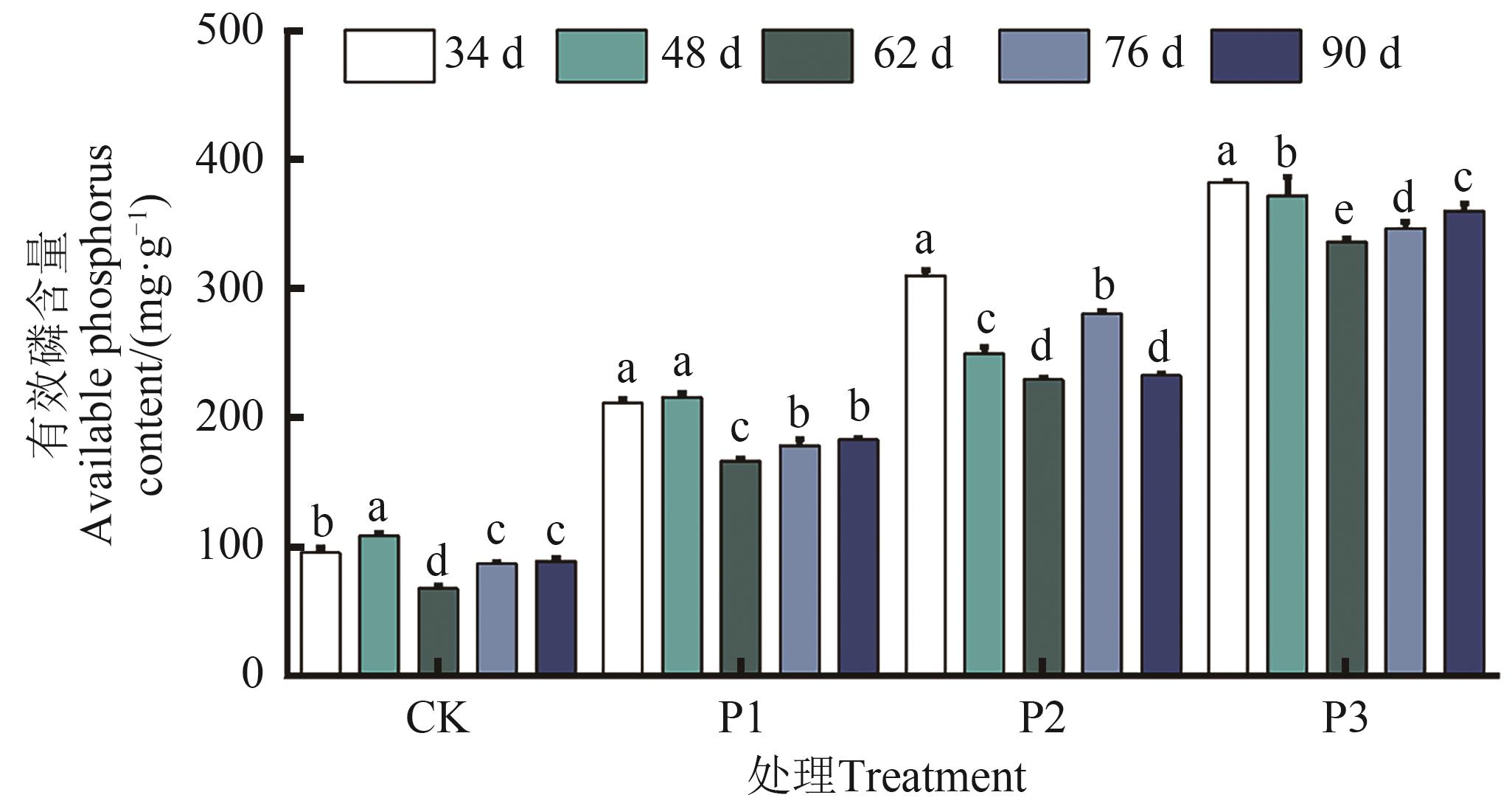
图3 不同处理的土壤有效磷含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Available phosphorus content in soil under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
移栽后时间 Time after planting/d | 处理 Treatment | pH | 电导率 Electric conductivity/(μS·cm-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | CK | 5.30±0.00 d | 37.53±9.04 d | 45.97±4.76 d | 167.42±0.08 d | 26.40±0.35 c |
| P1 | 5.55±0.01 c | 123.67±6.81 c | 79.57±5.30 c | 194.60±0.06 c | 25.34±0.39 c | |
| P2 | 5.69±0.00 b | 152.23±3.22 a | 92.63±4.28 b | 238.88±0.13 a | 30.09±0.23 b | |
| P3 | 5.95±0.01 a | 138.67±5.03 b | 103.13±3.86 a | 222.34±0.07 b | 47.21±1.84 a | |
| 48 | CK | 4.93±0.01 d | 44.33±8.33 d | 39.43±2.91 d | 167.84±0.1 d | 28.36±0.57 d |
| P1 | 5.48±0.00 b | 153.33±8.50 c | 85.40±0.70 c | 175.27±0.06 c | 30.85±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.53±0.00 a | 189.00±6.24 a | 96.37±1.46 b | 216.21±0.07 a | 35.37±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.28±0.01 c | 164.67±9.07 b | 107.57±2.14 a | 181.49±0.07 b | 39.82±0.78 a | |
| 62 | CK | 5.14±0.00 d | 59.67±15.95 d | 40.37±0.40 d | 176.19±0.07 c | 31.6±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.17±0.01 c | 196.33±17.79 b | 87.03±2.65 c | 217.82±0.08 b | 34.99±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.35±0.01 b | 344.67±20.21 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 237.08±0.07 a | 39.52±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.85±0.00 a | 175.67±9.24 c | 111.07±1.46 a | 216.95±0.33 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 76 | CK | 4.85±0.01 d | 45.33±9.29 d | 41.53±1.07 d | 179.04±0.04 d | 29.64±0.60 d |
| P1 | 5.34±0.01 c | 269.67±5.51 c | 91.47±2.14 c | 206.76±0.01 b | 32.73±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.70±0.02 b | 342.33±14.57 a | 102.67±2.46 b | 227.04±0.15 a | 37.26±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 6.09±0.01 a | 299.00±9.54 b | 113.63±1.46 a | 207.52±0.03 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 90 | CK | 4.82±0.03 d | 58.00±5.89 d | 42.47±1.46 c | 183.63±0.08 d | 28.58±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.27±0.00 c | 197.67±6.55 b | 92.87±1.07 b | 201.70±0.06 b | 37.26±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.92±0.00 b | 200.67±11.61 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 208.38±0.08 a | 42.53±0.00 b | |
| P3 | 6.21±0.01 a | 143.67±5.73 c | 115.73±1.07 a | 193.30±0.08 c | 45.17±0.65 a |
表3 不同处理的根际土壤的理化性质
Table 3 Physicochemical parameter of rhizosphere soil under different treatments
移栽后时间 Time after planting/d | 处理 Treatment | pH | 电导率 Electric conductivity/(μS·cm-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | CK | 5.30±0.00 d | 37.53±9.04 d | 45.97±4.76 d | 167.42±0.08 d | 26.40±0.35 c |
| P1 | 5.55±0.01 c | 123.67±6.81 c | 79.57±5.30 c | 194.60±0.06 c | 25.34±0.39 c | |
| P2 | 5.69±0.00 b | 152.23±3.22 a | 92.63±4.28 b | 238.88±0.13 a | 30.09±0.23 b | |
| P3 | 5.95±0.01 a | 138.67±5.03 b | 103.13±3.86 a | 222.34±0.07 b | 47.21±1.84 a | |
| 48 | CK | 4.93±0.01 d | 44.33±8.33 d | 39.43±2.91 d | 167.84±0.1 d | 28.36±0.57 d |
| P1 | 5.48±0.00 b | 153.33±8.50 c | 85.40±0.70 c | 175.27±0.06 c | 30.85±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.53±0.00 a | 189.00±6.24 a | 96.37±1.46 b | 216.21±0.07 a | 35.37±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.28±0.01 c | 164.67±9.07 b | 107.57±2.14 a | 181.49±0.07 b | 39.82±0.78 a | |
| 62 | CK | 5.14±0.00 d | 59.67±15.95 d | 40.37±0.40 d | 176.19±0.07 c | 31.6±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.17±0.01 c | 196.33±17.79 b | 87.03±2.65 c | 217.82±0.08 b | 34.99±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.35±0.01 b | 344.67±20.21 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 237.08±0.07 a | 39.52±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 5.85±0.00 a | 175.67±9.24 c | 111.07±1.46 a | 216.95±0.33 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 76 | CK | 4.85±0.01 d | 45.33±9.29 d | 41.53±1.07 d | 179.04±0.04 d | 29.64±0.60 d |
| P1 | 5.34±0.01 c | 269.67±5.51 c | 91.47±2.14 c | 206.76±0.01 b | 32.73±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.70±0.02 b | 342.33±14.57 a | 102.67±2.46 b | 227.04±0.15 a | 37.26±0.65 b | |
| P3 | 6.09±0.01 a | 299.00±9.54 b | 113.63±1.46 a | 207.52±0.03 b | 44.04±0.65 a | |
| 90 | CK | 4.82±0.03 d | 58.00±5.89 d | 42.47±1.46 c | 183.63±0.08 d | 28.58±0.65 d |
| P1 | 5.27±0.00 c | 197.67±6.55 b | 92.87±1.07 b | 201.70±0.06 b | 37.26±0.65 c | |
| P2 | 5.92±0.00 b | 200.67±11.61 a | 99.63±1.07 b | 208.38±0.08 a | 42.53±0.00 b | |
| P3 | 6.21±0.01 a | 143.67±5.73 c | 115.73±1.07 a | 193.30±0.08 c | 45.17±0.65 a |

图4 不同处理的土壤酶活性注:不同小写字母表示同一时间不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Soil enzyme activity under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.
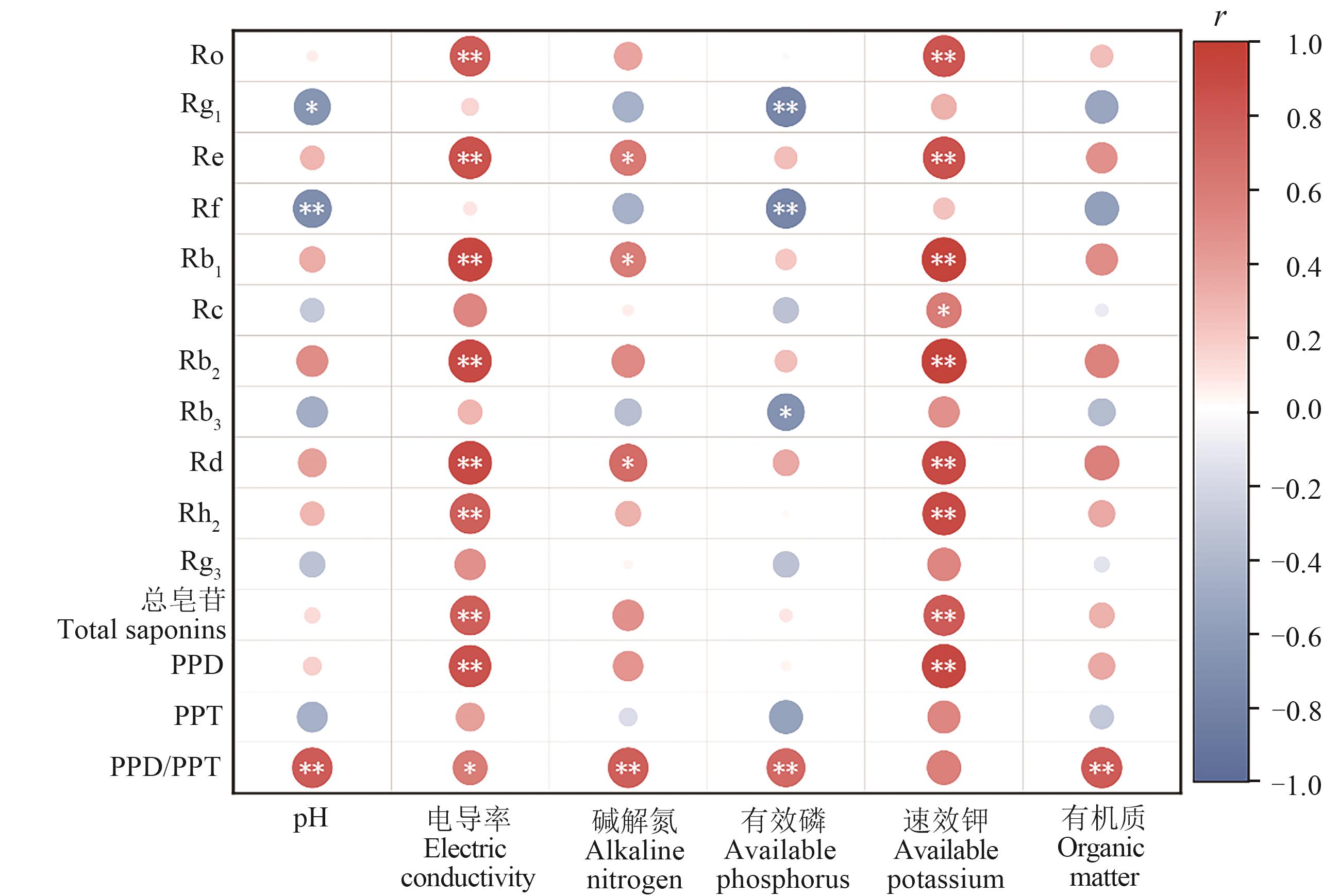
图5 人参皂苷含量与土壤理化性质的相关性分析注:*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis between ginsenoside content and soil physicochemical parameterNote:* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
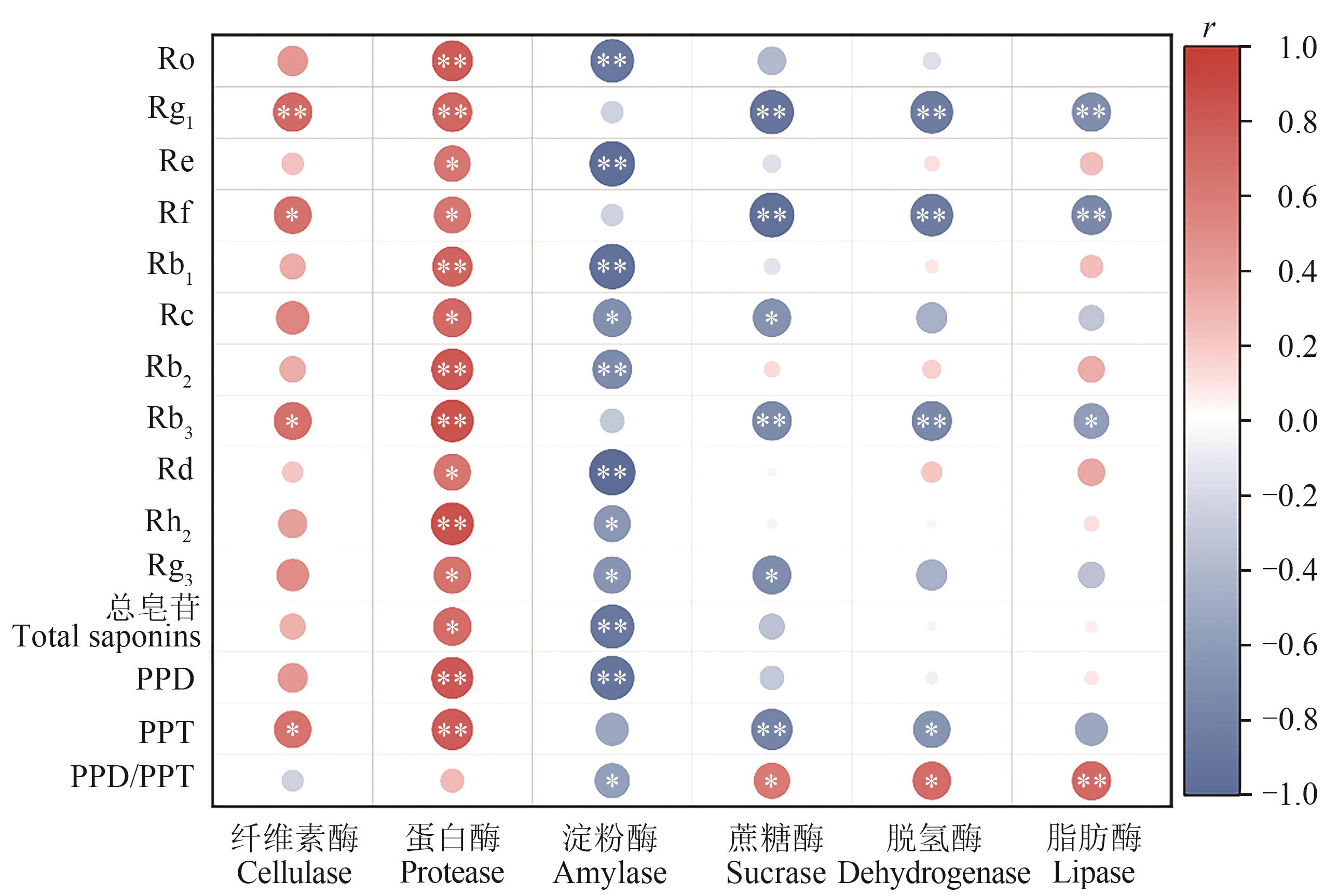
图6 人参皂苷含量与土壤酶的相关性分析注:*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 6 Correlation analysis between ginsenoside content and soil enzymeNote:* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
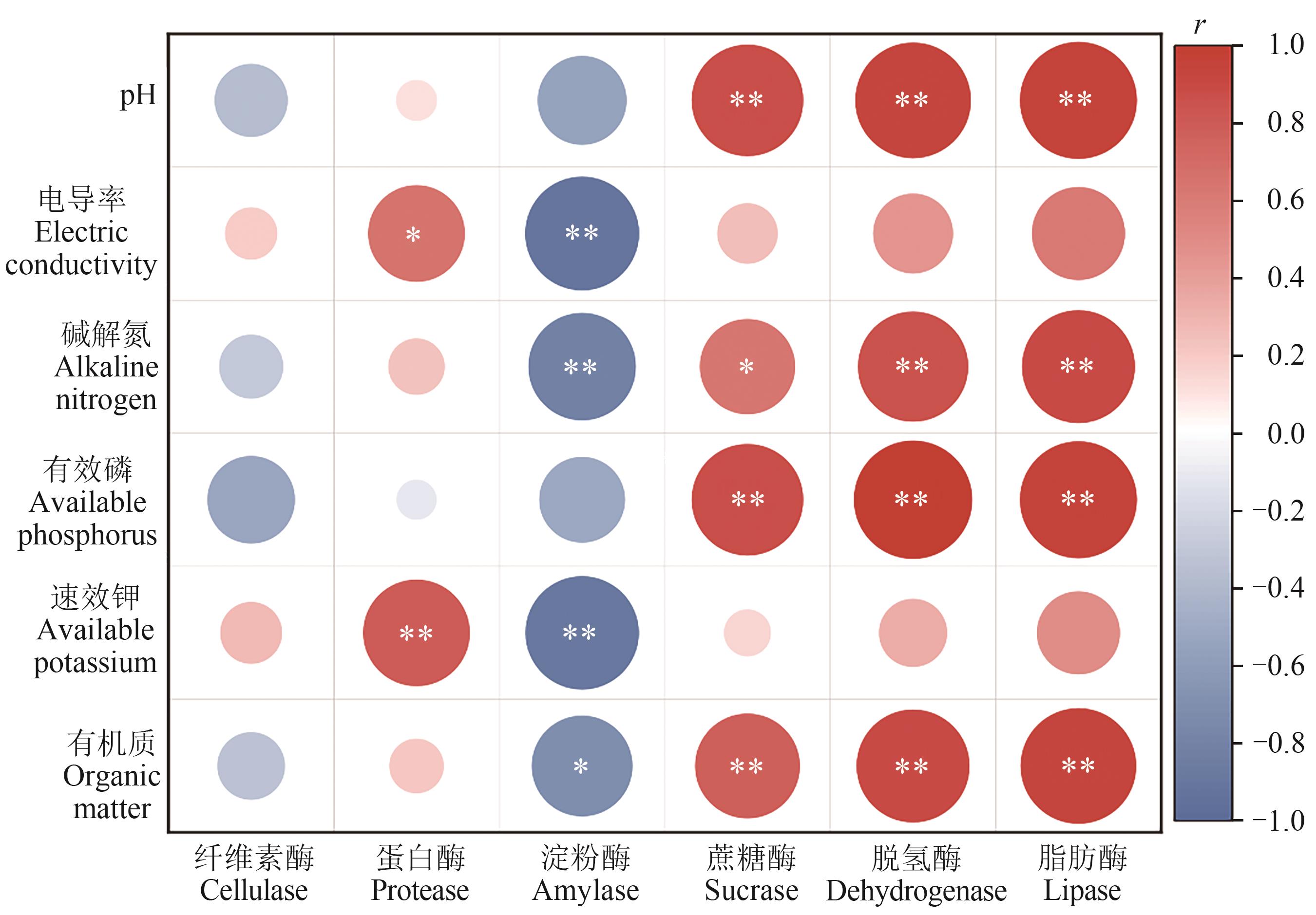
图7 土壤理化性质与土壤酶相关性注:*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 7 Correlation analysis between soil physicochemical parameter and soil enzymeNote:* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
指标 Index | 载荷值Loading value | 得分Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | |
| x1:Rb1 | 0.988 | -0.143 | 0.155 | -0.011 |
| x2:Rg1 | 0.574 | 0.814 | -0.205 | 0.477 |
| x3:Re | 0.950 | -0.173 | 0.160 | -0.030 |
| x4:PPD | 0.998 | 0.022 | 0.101 | 0.079 |
| x5:PPT | 0.780 | 0.613 | -0.117 | 0.382 |
x6:总皂苷 Total saponins | 0.949 | -0.001 | 0.104 | 0.063 |
x7:电导率 Electric conductivity | 0.865 | -0.433 | 0.237 | -0.176 |
x8:速效钾 Available potassium | 0.920 | -0.266 | 0.188 | -0.082 |
x9:蛋白酶 Protease | 0.825 | 0.337 | -0.021 | 0.237 |
x10:淀粉酶 Amaylase | -0.917 | 0.349 | -0.215 | 0.127 |
特征值 Eigenvalue | 7.924 | 1.548 | — | — |
贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 15.482 | — | — |
累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 94.726 | — | — |
表4 各主成分载荷矩阵和得分系数矩阵
Table 4 Loadings matrix and score coefficient matrix for each principal component
指标 Index | 载荷值Loading value | 得分Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | 第1主成分PC1 | 第2主成分PC2 | |
| x1:Rb1 | 0.988 | -0.143 | 0.155 | -0.011 |
| x2:Rg1 | 0.574 | 0.814 | -0.205 | 0.477 |
| x3:Re | 0.950 | -0.173 | 0.160 | -0.030 |
| x4:PPD | 0.998 | 0.022 | 0.101 | 0.079 |
| x5:PPT | 0.780 | 0.613 | -0.117 | 0.382 |
x6:总皂苷 Total saponins | 0.949 | -0.001 | 0.104 | 0.063 |
x7:电导率 Electric conductivity | 0.865 | -0.433 | 0.237 | -0.176 |
x8:速效钾 Available potassium | 0.920 | -0.266 | 0.188 | -0.082 |
x9:蛋白酶 Protease | 0.825 | 0.337 | -0.021 | 0.237 |
x10:淀粉酶 Amaylase | -0.917 | 0.349 | -0.215 | 0.127 |
特征值 Eigenvalue | 7.924 | 1.548 | — | — |
贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 15.482 | — | — |
累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate/% | 79.244 | 94.726 | — | — |
| 处理Treatment | FPC1 | FPC2 | F | 排序Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 31.65 | 10.91 | 28.26 | 4 |
| P1 | 79.46 | -12.32 | 64.46 | 1 |
| P2 | 78.61 | -13.61 | 63.54 | 2 |
| P3 | 59.49 | -9.04 | 48.29 | 3 |
表5 不同处理的主成分得分
Table 5 Principal component scores of different treatments
| 处理Treatment | FPC1 | FPC2 | F | 排序Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 31.65 | 10.91 | 28.26 | 4 |
| P1 | 79.46 | -12.32 | 64.46 | 1 |
| P2 | 78.61 | -13.61 | 63.54 | 2 |
| P3 | 59.49 | -9.04 | 48.29 | 3 |
| [1] | YANG L, CHEN J J, SHENG-XIAN TEO B, et al.. Research progress on the antitumor molecular mechanism of ginsenoside Rh2 [J]. Am. J. Chin. Med., 2024, 52(1): 217-230. |
| [2] | IM D S. Pro-resolving effect of ginsenosides as an anti-inflammatory mechanism of Panax ginseng [J/OL].Biomolecules, 2020, 10(3): E444 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [3] | TIAN T T, KO C N, LUO W Y, et al.. The anti-aging mechanism of ginsenosides with medicine and food homology [J]. Food Funct., 2023, 14(20): 9123-9136. |
| [4] | 谢丽娟,苑冰冰,李健豪,等.人参皂苷结构修饰的研究进展[J].人参研究,2019,31:57-60. |
| XIE L J, YUAN B B, LI J H, et al.. Research progress of structural modification ginsenosides [J] Ginseng Res., 2019, 31:57-60. | |
| [5] | KIM D, KIM M, RAÑA G S, et al.. Seasonal variation and possible biosynthetic pathway of ginsenosides in Korean ginseng Panax ginseng Meyer [J/OL]. Molecules, 2018, 23(7): E1824 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [6] | 刘静婉,李琼,王恩鹏,等.人参栽培研究进展[J].应用化学,2022,39:1641-1651. |
| LIU J W, LI Q, WANG E P, et al.. Research progress on cultivation of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Chem., 2022, 39: 1641-1651. | |
| [7] | 闫宁,战宇,谢昊臻,等.不同改土方式对连作人参生长发育的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50(6):120-125. |
| [8] | 战宇,苗馨月,王二刚,等.灭菌方式对人参连作土壤养分及真菌群落结构的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(2):235-244. |
| [9] | LIU D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. |
| [10] | FENG G, GAI J, FENG X, et al.. Strategies for improving fertilizer phosphorus use efficiency in Chinese cropping systems [J]. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng., 2019, 6(4): 341-347. |
| [11] | 吕林,张亚玉.磷素营养对人参等植物生长及其品质影响的研究进展[J].特产研究, 2019, 41(1):115-119. |
| LYU L, ZHANG Y Y. Effects of phosphorus nutrition on yield and quality of Panax ginseng and other plants [J]. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res., 2019, 41(1): 115-119. | |
| [12] | 郜玉钢,郝建勋,臧埔,等.高效液相色谱法测定农田人参中9种人参皂苷单体含量[J].食品科学,2012,33(2):189-193. |
| GAO Y G, HAO J X, ZANG P, et al.. Content determination of 9 ginsenoside monomers in farmland ginseng by HPLC [J]. Food Sci., 2012, 33(2): 189-193. | |
| [13] | 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典一部:2020年版[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020:1-328. |
| [14] | 冯家,曹志强,仲伟同,等. 地理标志产品 吉林长白山人参: [S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2009. |
| [15] | 张涛.人参及其皂苷生物合成对低温的生理生态响应机制研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2019. |
| ZHANG T. Physiological and ecological response mechanism of Panax ginseng and its saponins biosynthesis to low temperature [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [16] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| [17] | 曹婷婷,刘春,范又维,等.不同氮素供应水平对微型盆栽月季生长发育的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2024,26(2):67-79. |
| CAO T T, LIU C, FAN Y W, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen supply level on plant growth and development in miniature potted rose [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2024, 26(2): 67-79. | |
| [18] | 王学民.应用多元分析[M].2版.上海:上海财经大学出版社,2004:1-410. |
| [19] | 张亚玉.不同生长环境下人参根区土壤肥力特性研究[D].沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2016. |
| ZHANG Y Y. Studies on root-zone fertility characteristics in different growth environments of Ginseng [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| [20] | DONG L, LI Y, XU J, et al..Biofertilizers regulate the soil microbial community and enhance Panax ginseng yields [J/OL]. Chin. Med., 2019, 14:20 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [21] | TONG Y L, SONG X P, ZHANG Y X, et al.. Insight on structural modification,biological activity,structure-activity relationship of PPD-type ginsenoside derivatives [J/OL].Fitoterapia, 2022, 158: 105135 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [22] | ZHANG T, HAN M, YANG L, et al.. The effects of environmental factors on ginsenoside biosynthetic enzyme gene expression and saponin abundance [J/OL]. Mol. (Basel Switz.), 2018, 24(1): E14 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [23] | ZHAO X, LYU Y, JIN K, et al.. Leaf phosphorus concentration regulates the development of cluster roots and exudation of carboxylates in Macadamia integrifolia [J/OL].Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11: 610591 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [24] | 赵雪淞,王力恒,骆世洪,等.人参根际土壤微生物群落结构与土壤环境因子的关系[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2023, 54(1):27-35. |
| ZHAO X S, WANG L H, LUO S H, et al.. Relationship between microbial community structure and environmental factors in ginseng rhizosphere soil [J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2023, 54(1):27-35. | |
| [25] | 杜欣,谢阿贵,方新月,等.不同参龄、坡向及根际土壤微生物对林下园参皂苷积累的影响[J].中国食品添加剂,2024,35(2):88-97. |
| DU X, XIE A G, FANG X Y, et al.. Effects of different ginseng ages, slope directions and rhizosphere soil microorganisms on the accumulation of ginsenosides in understory garden ginseng [J]. China Food Addit., 2024, 35(2): 88-97. | |
| [26] | 吴艾轩,王鑫,吕云,等.农田栽参土壤养分研究进展[J].北方园艺,2018(22):177-186. |
| WU A X, WANG X, LYU Y, et al.. Progress of soil nutrients of cultivation of Panax ginseng in farmland [J]. North. Hortic., 2018(22): 177-186. | |
| [27] | KALENDAR O V, KOSTIKOVA V A, KUKUSHKINA T A, et al.. Seasonal development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and their contents of biologically active and reserve substances in the forest-steppe zone of Western Siberia [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2023, 9(1):102 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [28] | LAN Y, ZHANG M, HAN M, et al.. Differences in the quality, yield, and soil microecology of ginseng in different planting environments [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2023, 9(4): 520 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [29] | 吕柏辰,孙海,钱佳奇,等.药用植物根系分泌物与根际微生物相互作用及其在中药材生态种植中的应用[J].中国中药杂志,2024,49(8):2128-2137. |
| LYU B C, SUN H, QIAN J Q, et al.. Interaction between root exudates of medicinal plants and rhizosphere microorganisms and its application in ecological planting of Chinese medicinal materials [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2024, 49(8):2128-2137. | |
| [30] | 吴怡,董炜华,李晓强,等.土壤酶活性对土壤环境变化的响应研究进展[J].南方农业,2023,17(15): 42-46, 52. |
| WU Y, DONG W H, LI X Q, et al.. Research progress on the response of soil enzyme activity to changes in soil environment [J]. South China Agric., 2023, 17(15): 42-46, 52. |
| [1] | 王二刚, 吕朋元, 周一, 战宇, 何贵祥, 王丽翔, 苗馨月, 陈长宝, 李琼. 生防细菌对人参连作土壤性质及细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 140-148. |
| [2] | 邵鹏阳, 沙玉柱, 刘秀, 陈国顺, 朱才业, 王继卿, 王翻兄, 陈小伟, 杨文鑫. 黄芪饲料添加剂对羔羊生长性能、血清Ig和瘤胃发酵功能及微生物菌群特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 83-94. |
| [3] | 邓奕龙, 王建安, 顾少龙, 张小全, 苗晓辉, 施守杰, 段卫东. 变黄期变温烘烤对上部叶颜色参数与色素含量协同关系的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 238-249. |
| [4] | 米春娇, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 张砚迪. 我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标和推荐施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [5] | 徐哲丰, 刘春铄, 廖旭东, 隋佳宏, 陈雨秋, 陈长宝, 张涛, 魏丽娜. 生态因子对林地参和农田参质量差异的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 213-223. |
| [6] | 谢勇俊, 潘小卓, 陈福慧, 尹凯波, 金嘉悦, 王一兵. 人参酚酸类自毒物质降解菌的筛选鉴定及生防研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 147-155. |
| [7] | 时晓宇, 焦连庆, 于敏, 田义新, 焦安妮, 栾依琳. 多维度评价及优化黄芪瞬时高温灭菌工艺[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 223-233. |
| [8] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [9] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [10] | 张伟健, 冯景翊, 李悦, 何婉莹, 车延静, 王紫颖, 白雪燕, 谷思玉. 内-外源有机质对黑土磷素吸附及有效性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 180-190. |
| [11] | 路宁宁, 陈凌云, 杨太新, 杨树林, 刘国库. 珊瑚菜果实形成与内源激素含量的相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 63-69. |
| [12] | 贾滢暄, 张树林, 张达娟, 戴伟, 毕相东. 磷恢复对磷饥饿铜绿微囊藻光合色素和部分抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 70-77. |
| [13] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [14] | 刘鹏飞, 陆小双, 迪力木拉提·热合曼, 唐努尔·斯拉依, 曲延英, 陈全家, 邓晓娟. 陆地棉棉籽主要品质性状与农艺性状的遗传变异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 22-32. |
| [15] | 吴雨露, 扈嘉鑫, 陈宇熙, 郑炳松, 闫道良. 外施α-酮戊二酸对盐胁迫下海滨锦葵生长、碳氮磷养分积累及其计量关系的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||