




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 187-196.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0244
夏秀波( ), 李涛(
), 李涛( ), 曹守军, 姚建刚, 王虹云, 张丽莉
), 曹守军, 姚建刚, 王虹云, 张丽莉
收稿日期:2021-03-23
接受日期:2021-06-01
出版日期:2022-07-15
发布日期:2022-08-15
通讯作者:
李涛
作者简介:夏秀波 E-mail:xiuboxia@163.com;
基金资助:
Xiubo XIA( ), Tao LI(
), Tao LI( ), Shoujun CAO, Jiangang YAO, Hongyun WANG, Lili ZHANG
), Shoujun CAO, Jiangang YAO, Hongyun WANG, Lili ZHANG
Received:2021-03-23
Accepted:2021-06-01
Online:2022-07-15
Published:2022-08-15
Contact:
Tao LI
摘要:
为研究液态有机肥部分替代化肥对设施番茄根区细菌群落的影响,以化学冲施肥为对照(T_CK),设置液态有机肥分别替代20%(T_R20)、30%(T_R30)和40%化学冲施肥(T_R40)3个处理,应用16S rRNA 高通量测序技术,分析番茄根区土壤样本中细菌的群落多样性、结构组成和差异。结果表明,在97%的相似水平下,共发现3 747个OTU,37个门,104个纲,268个目,441个科,730个属,1 401个种。3个处理和对照样品中共有OTU为1 338个,独有的OTU数值分别为140(T_R20)、129(T_R30)和263(T_R40)。T_R30处理的细菌丰富度和多样性最高,其优势菌门为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)、酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes);优势菌属为norank_c_subgroup_6、芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)、norank_f_A4b。通过聚类分析、主成分分析、非度量多维尺度分析和共现性网络分析发现, T_R30和对照处理细菌的菌落组成相似度较高,共性最大。利用PICRUSt软件对细菌群落功能组成进行预测,发现各处理土壤样本的主要COG功能组成较为相似,但各COG相对丰度有所差异。综上所述,液态有机肥不同比例替代化学冲施肥能增加外源细菌种类,改变丰富度、多样性和菌落组成,以替代30%比例时效果最佳,为液态有机肥与化学冲施肥配施提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
夏秀波, 李涛, 曹守军, 姚建刚, 王虹云, 张丽莉. 液态有机肥部分替代化肥对设施番茄根区细菌群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 187-196.
Xiubo XIA, Tao LI, Shoujun CAO, Jiangang YAO, Hongyun WANG, Lili ZHANG. Effect of Liquid Organic Fertilizer Partial Replacing Chemical Fertilizer on Bacterial Community in Greenhouse Tomato Root Zone[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 187-196.
处理 Treatment | 肥料类型 Fertilization type | 次数 Times | |
|---|---|---|---|
化学冲施肥 Chemical fertilizer /(kg·hm-2) | 液态有机肥 Liquid organic fertilizer /(kg·L-1) | ||
| T_CK | 90.0 | 0 | 5 |
| T_R20 | 72.0 | 15.0 | 5 |
| T_R30 | 63.0 | 22.5 | 5 |
| T_R40 | 54.0 | 30.0 | 5 |
表1 不同处理的施肥量
Table 1 Fertilization amount of different treatments
处理 Treatment | 肥料类型 Fertilization type | 次数 Times | |
|---|---|---|---|
化学冲施肥 Chemical fertilizer /(kg·hm-2) | 液态有机肥 Liquid organic fertilizer /(kg·L-1) | ||
| T_CK | 90.0 | 0 | 5 |
| T_R20 | 72.0 | 15.0 | 5 |
| T_R30 | 63.0 | 22.5 | 5 |
| T_R40 | 54.0 | 30.0 | 5 |
样本 Sample | 序列数 Sequence No. | 碱基数 Base No. | 平均序列长度 Mean sequence length/bp | 最短序列长度 Min sequence length/bp | 最长序列长度 Max sequence length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T_CK | 67 708 | 28 279 629 | 417.67 | 244 | 535 |
| T_R20 | 57 661 | 23 977 066 | 415.83 | 258 | 519 |
| T_R30 | 54 144 | 22 647 083 | 418.28 | 283 | 506 |
| T_R40 | 72 046 | 30 248 429 | 419.85 | 336 | 461 |
表2 样本信息统计表
Table 2 Sample information statistics chart
样本 Sample | 序列数 Sequence No. | 碱基数 Base No. | 平均序列长度 Mean sequence length/bp | 最短序列长度 Min sequence length/bp | 最长序列长度 Max sequence length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T_CK | 67 708 | 28 279 629 | 417.67 | 244 | 535 |
| T_R20 | 57 661 | 23 977 066 | 415.83 | 258 | 519 |
| T_R30 | 54 144 | 22 647 083 | 418.28 | 283 | 506 |
| T_R40 | 72 046 | 30 248 429 | 419.85 | 336 | 461 |
| 样品Sample | 覆盖度 Coverage | Ace指数 Ace index | Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Sobs指数 Sobs index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T_CK | 0.991 6 a | 3 002.15 b | 3 003.27 b | 6.52 a | 0.005 7 c | 2 694 a |
| T_R20 | 0.990 5 a | 2 745.79 d | 2 739.96 d | 6.41 a | 0.004 8 c | 2 441 c |
| T_R30 | 0.989 5 a | 3 081.20 a | 3 064.07 a | 6.46 a | 0.006 8 b | 2 721 a |
| T_R40 | 0.992 0 a | 2 886.29 c | 2 911.51 c | 6.15 b | 0.011 2 a | 2 544 b |
表3 样本细菌多样性指数
Table 3 Diversity index of Bacteria in samples
| 样品Sample | 覆盖度 Coverage | Ace指数 Ace index | Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Sobs指数 Sobs index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T_CK | 0.991 6 a | 3 002.15 b | 3 003.27 b | 6.52 a | 0.005 7 c | 2 694 a |
| T_R20 | 0.990 5 a | 2 745.79 d | 2 739.96 d | 6.41 a | 0.004 8 c | 2 441 c |
| T_R30 | 0.989 5 a | 3 081.20 a | 3 064.07 a | 6.46 a | 0.006 8 b | 2 721 a |
| T_R40 | 0.992 0 a | 2 886.29 c | 2 911.51 c | 6.15 b | 0.011 2 a | 2 544 b |
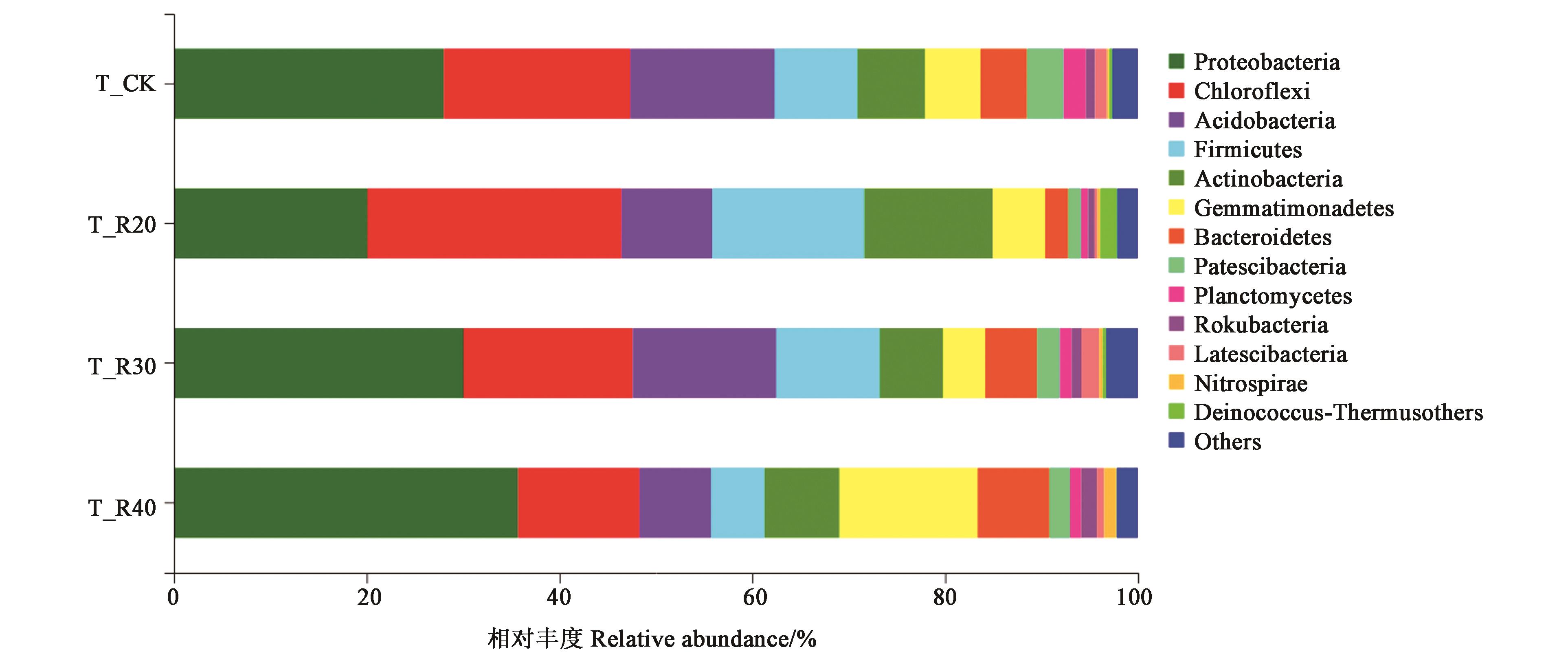
图3 门水平各样本中细菌群落组成注:Others为样本中丰度占比均小于1%的进行合并。
Fig. 3 Composition of bacterial community on Phylum levelNote: Others are the samples with abundance ratio less than 1%.
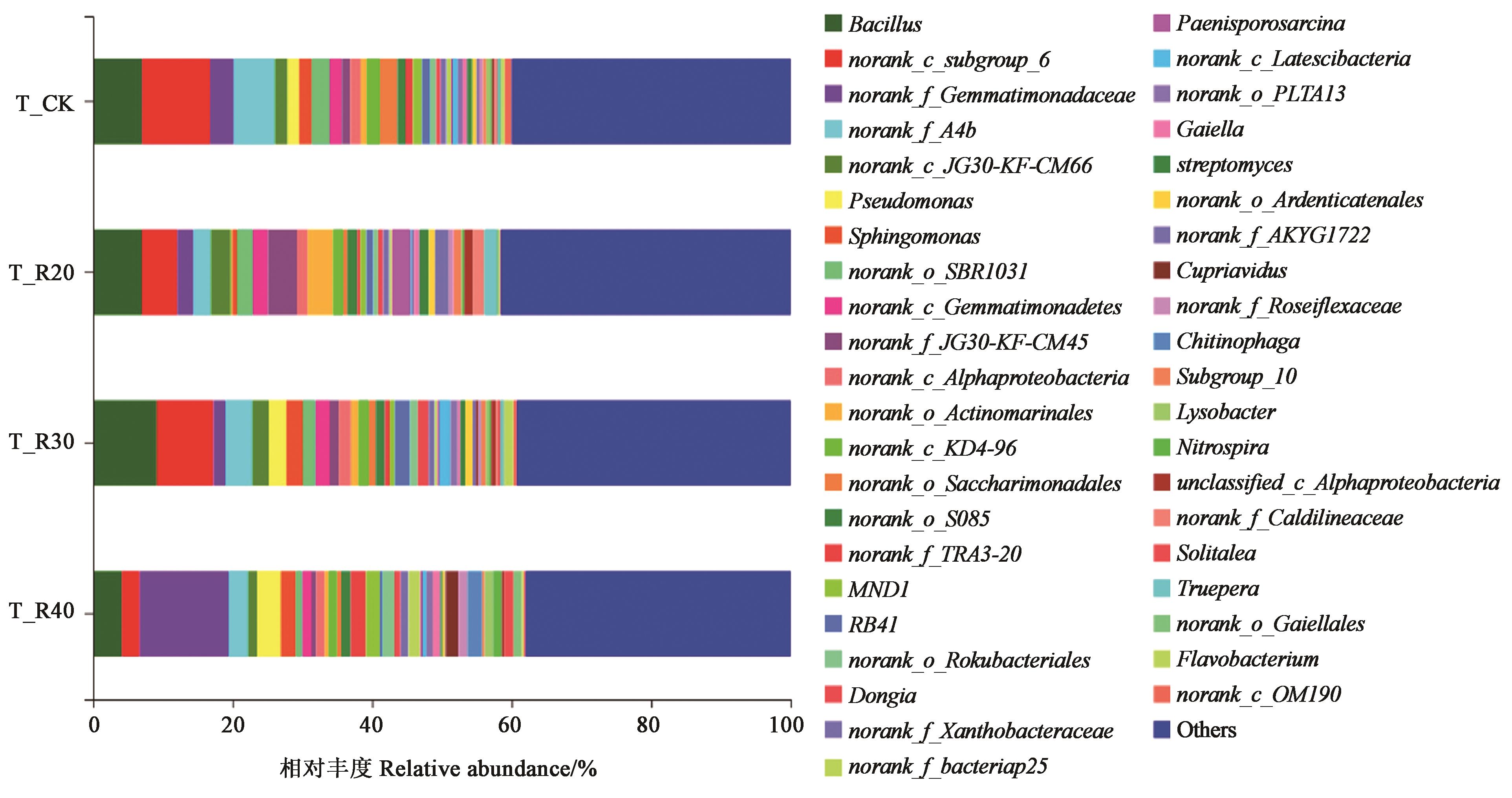
图4 属水平各样品中细菌群落组成注:Others为样本中丰度占比均小于1%的进行合并。
Fig. 4 Composition of bacterial community on Genus levelNote: Others are the samples with abundance ratio less than 1%.
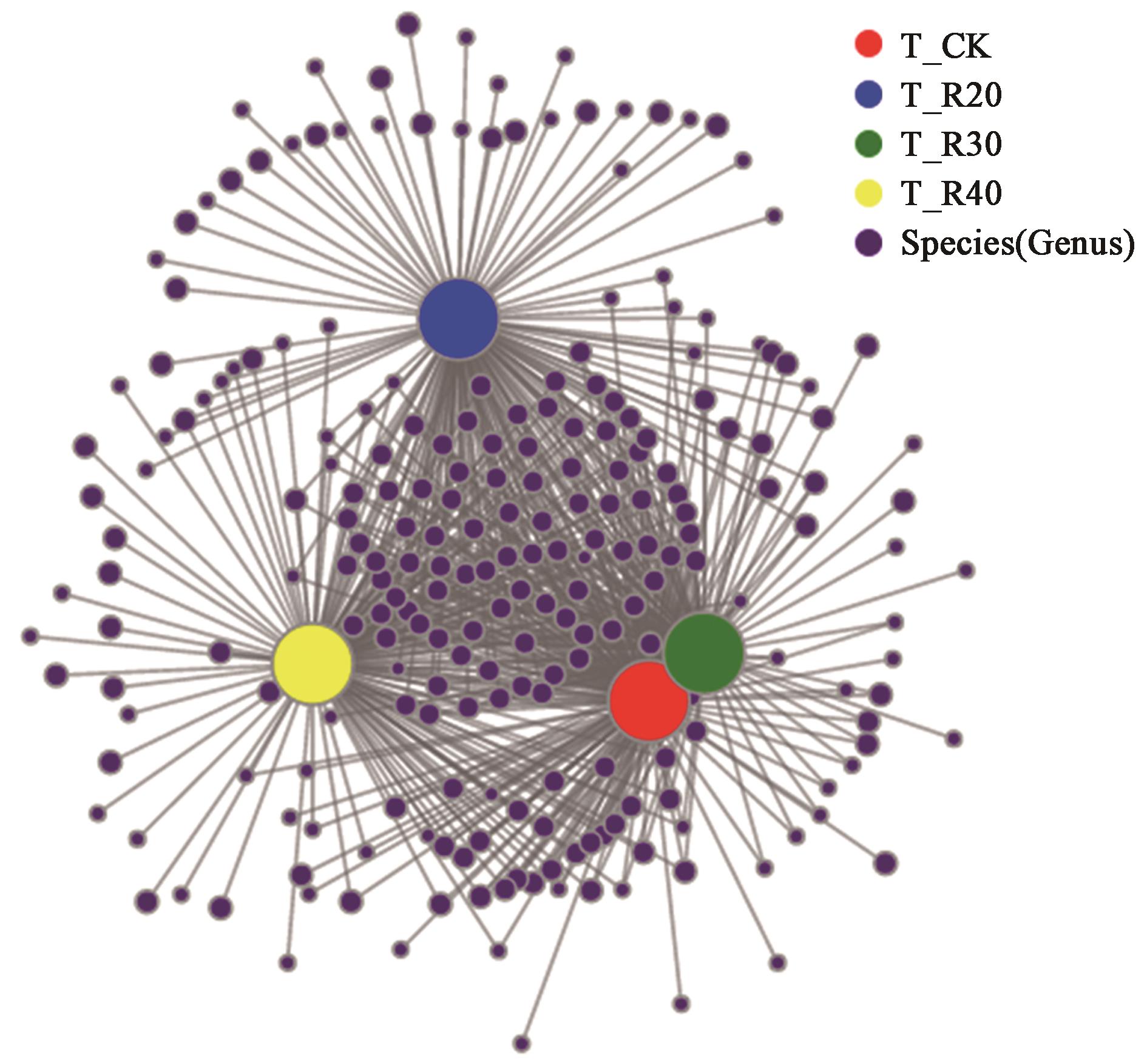
图8 细菌群落在属水平的网络分析注:图中默认显示丰度大于50%的物种。
Fig. 8 Network analysis of bacteria on Genus levelNote: Species with abundance greater than 50% are shown by default.
| 1 | 张福锁.科学认识化肥的作用[J].中国农技推广,2017,33(1):16-19. |
| ZHANG F S. Scientific understanding of the role of chemical fertilizer [J]. Chin. Agric. Technol. Extension, 2017, 33(1):16-19. | |
| 2 | 杨吉祥,马平平.浅谈农药化肥的负面作用及对策[J].中国园艺文摘,2009(6):158-160. |
| YANG J X, MA P P. Discussion on the negative effects and countermeasures of pesticide and chemical fertilizer [J]. Chin. Hortic. Abstracts, 2009(6):158-160. | |
| 3 | 张迎春,颉建明,李静,等.生物有机肥部分替代化肥对莴笋及土壤理化性质和微生物的影响[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(4):196-205. |
| ZHANG Y C, XIE J M, LI J, et al.. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by bioorganic fertilizer on asparagus lettuce and soil physical chemical properties and microorganisms [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 33(4):196-205. | |
| 4 | 姜利红,谢桂先,刘强,等.有机无机肥配施对双季稻田土壤微生物和碳库的影响[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,44(3):295-300. |
| JIANG L H, XIE G X, LIU Q, et al.. Effect of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial and carbon pool in double rice paddy field [J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2018, 44(3):295-300. | |
| 5 | 祝英,王治业,彭轶楠,等.有机肥替代部分化肥对土壤肥力和微生物特征的影响[J].土壤通报,2015,46(5):1161-1167. |
| ZHU Y, WANG Z Y, PENG Y N, et al.. Changes of soil nutrients and microbial communities under the condition of organic fertilizers replacing part of chemical fertilizers [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2015, 46(5):1161-1167. | |
| 6 | 李杰,贾豪语,颉建明,等.生物肥部分替代化肥对花椰菜产量、品质、光合特性及肥料利用率的影响[J].草业学报,2015,24(1):47-55. |
| LI J, JIA H Y, XIE J M, et al.. Effects of partial substitution of mineral fertilizer by bio-fertilizer on yield, quality, photosynthesis and fertilizer utilization rate in broccoli [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2015, 24(1):47-55. | |
| 7 | 牛振明,张国斌,刘赵帆,等.生物肥部分替代化肥对甘蓝(Brassica oleracea)养分吸收、光合作用以及品质的影响[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(2):464-471. |
| NIU Z M, ZHANG G B, LIU Z F, et al.. Effect of partial replacement of chemical fertilizer by bio-fertilizer on nutrient uptake photosynthesis and quality of Brassica oleracea [J]. J. Desert Res., 2014, 34(2):464-471. | |
| 8 | 徐全辉,高仰,赵强,等.活性腐殖酸有机肥对水稻产量、养分吸收的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2010(8):3951-3952. |
| XU Q H, GAO Y, ZHAO Q, et al.. Effect of humic acid fertilizer on rice yield and nutrient uptake [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2010, 38(8):3951-3952. | |
| 9 | 沈渊,沈新芬,姚明军.复合微生物液态有机肥在滴灌玉米上的应用效果研究[J].现代农业科技, 2020(15):9-11 |
| SHEN Y, SHEN X F, YAO M J. Study on application effect of compound microbial liquid organic fertilizer on drip irrigation corn [J]. Modern Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020(15):9-11. | |
| 10 | 徐海东,董合林,苏丽丽,等.液态有机肥对滴灌棉花光合特性及产量形成规律的影响[J].中国农学通报, 2017,33(20):71-77. |
| XU H D, DONG H L, SU L L, et al.. Effects of liquid organic fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics and yield formation of cotton under drip irrigation [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2017, 33(20):71-77. | |
| 11 | 熊湖,郑顺林,龚静 等.液态有机肥对酚酸胁迫下马铃薯生长发育和土壤酶活性影响[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(3):254-259, 267. |
| XIONG H, ZHENG S L, GONG J, et al.. Effects of liquid organic soil enzyme activities fertilizer on potato growth and under phenolic acid stress [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 33(3):254-259, 267. | |
| 12 | 席天元,刘庆华,雷逢进,等.有机肥液态施入对番茄产量和品质的影响[J].山西农业科学,2014,42(7):697-700. |
| XI T Y, LIU Q H, LEI F J, et al.. Impact of organic fertilizer drip fertigationed to tomato yield and quality [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2014, 42(7):697-700. | |
| 13 | 陶瑞,李锐,谭亮,等.减少化肥配施有机肥对滴灌棉花N、P吸收和产量的影响[J].棉花学报,2014,26(4):342-349. |
| TAO R, LI R, TAN L, et al.. Effects of application of different organic manures with chemical fertilizer on cotton yield, N and P utilization efficiency under drip irrigation [J]. J. Cotton, 2014, 26(4):342-349. | |
| 14 | 孟琳,张小莉,蒋小芳,等.有机肥料氮替代部分化肥氮对稻谷产量的影响及替代率[J].中国农业科学,2009,42(2):532-542. |
| MENG L, ZHANG X L, JIANG X F, et al.. Effects of partial mineral nitrogen substitution by organic fertilizer nitrogen on the yields of rice grains and their proper substitution rate [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2009, 42(2):532-542. | |
| 15 | 刘森.施肥年限对泡桐人工林土壤微生物群落结构和多样性的影响[D].昆明:中南林业科技大学,2017. |
| LIU S. Effects of fertilization length on soil microbial community structure and diversity in paulownia plantations [D]. Kunming: Central south university of forestry and technology, 2017. | |
| 16 | CHEN S F, ZHOU Y Q, CHEN Y R, et al.. An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor [J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17):884-890. |
| 17 | MAGOČ T, SALZBERG S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies [J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(21):2957-2963. |
| 18 | EDGAR RC. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads [J]. Nat. Methods., 2013, 10(10):996-998. |
| 19 | STACKEBRANDT E, GOEBEL B M. Taxonomic Note: A place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology [J]. Int. J. System. Bacteriol., 1994, 44(4):846-849. |
| 20 | WANG Q, GARRITY G M, TIEDJE J M, et al.. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2007, 73(16):5261-5267. |
| 21 | HUANG L F, SONG L X, XIA X J, et al.. Plant-soil feedbacks and soil sickness: from mechanisms to application in agriculture [J]. J. Chem. Ecol., 2013, 39(2):232-242. |
| 22 | BERENDSEN R L, PIETERSE C M J, BAKKER P A H M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2012, 17(8):478-486. |
| 23 | 张凯煜,谷洁,王小娟,等.微生物有机肥对樱桃园土壤细菌群落的影响[J].中国环境科学,2019, 39(3):1245-1252. |
| ZHANG K Y, GU J, WANG X J, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on the soil bacterial community in a cherry orchard [J]. Chin. Environ. Sci., 2019, 39(3):1245-1252. | |
| 24 | 樊晓刚,金轲,李兆君,等.不同施肥和耕作制度下土壤微生物多样性研究进展[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2010,16(3):744-751. |
| FAN X G, JIN K, LI Z J, et al.. Soil microbial diversity under different fertilization and tillage practices: A review [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2010, 16(3):744-751. | |
| 25 | 王宁,南宏宇,冯克云.化肥减量配施有机肥对棉田土壤微生物生物量、酶活性和棉花产量的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2020,31(1):173-181. |
| WANG N, NAN H Y, FENG K Y. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application on soil microbial bio-mass, enzyme activity and cotton yield [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, 31(1):173-181. | |
| 26 | 白亚丽.日光温室果菜有机肥替代及化肥减施对其生长和土壤环境的影响[D].郑州:河南农业大学,2019. |
| BAI L Y. 2020, The effects on fruit vegetables growth and the soil environment with replacement of organic fertilizer and fertilizer application in solar greenhouse [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 27 | 王慧颖,徐明岗,周宝库,等.黑土细菌及真菌群落对长期施肥响应的差异及其驱动因素[J].中国农业科学,2018,51(5):914-925. |
| WANG H Y, XU M G, ZHOU B K, et al.. Response and driving factors of bacterial and fungal community to long-term fertilization in black soil [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2018, 51(5):914-925. | |
| 28 | 曾希柏,王亚男,王玉忠,等.不同施肥模式对设施菜地细菌群落结构及丰度的影响[J].中国农业科学,2013,46(1):69-79. |
| ZENG X B, WANG Y N, WANG Y Z, et al.. Effects of different fertilization regimes on abundance and composition of the bacterial community in greenhouse vegetable soils [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2013, 46(1):69-79. | |
| 29 | 马晓英,马琨,周艳,等.土壤细菌群落组成对有机与无机培肥措施的响应[J].西北农业学报,2019,28(10):1698-1707. |
| MA X Y, MA K, ZHOU Y, et al.. Response of Soil Bacteria Community Structure to Application of Inorganic and organic fertilizer [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2019, 28(10):1698-1707. | |
| 30 | 赵立君,刘云根,王妍,等.典型高原湖滨带底泥细菌群落结构及多样性特征[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(2):401-410. |
| ZHAO L J, LIU Y G, WANG Y, et al.. Bacterial community structure and diversity of sediments in a typical plateau lakeshore [J]. Microbiol. China, 2020, 47(2):401-410. | |
| 31 | 王光华,刘俊杰,于镇华,等.土壤酸杆菌门细菌生态学研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2016,32(2):14-20. |
| WANG G H, LIU J J, YU Z H, et al.. Research progress of Acidobacteria ecology in soils [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2016, 32(2):14-20. | |
| 32 | 于淑池.植物真菌病害生防芽孢杆菌的研究进展[J].通化师范学院学报,2007,28(8):52-54. |
| YU S C. Research review of biocontrol bacillus for plant fungous diseases [J]. J. Tonghua Norm. Univ., 2007, 28(8):52-54. | |
| 33 | 陈志谊,张荣胜,刘邮洲,等.植物病害生防芽孢杆菌研究进展[J].江苏农业学报,2012,28(5):999-1006. |
| CHEN Z Y, ZHANG R S, LIU Y Z, et al.. Research progress in biocontrol of Bacillus spp. against plant diseases [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2012, 28(5):999-1006. |
| [1] | 张曦瑜, 沈幸, 李伟, 谢文歌, 李杰, 杨昌浩, 柴仲平. 氮肥减量配施有机肥对库尔勒香梨园土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 217-228. |
| [2] | 蓝江林, 肖荣凤, 王阶平, 张海峰, 刘波. 整合微生物组菌剂对番茄植株生长及根际细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 173-181. |
| [3] | 王二刚, 吕朋元, 周一, 战宇, 何贵祥, 王丽翔, 苗馨月, 陈长宝, 李琼. 生防细菌对人参连作土壤性质及细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 140-148. |
| [4] | 金若珩, 李晓宇, 姚经武, 王蓓蓓, 曹春霞, 黄大野. 苏云金芽孢杆菌对茶尺蠖肠道细菌多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 141-149. |
| [5] | 季梦婷, 朱玲, 罗晓华, 郑钰婷, 肖顺, 胡方平, 蔡学清. 福建无花果细菌性叶斑病的症状及病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 147-154. |
| [6] | 王兴松, 王娜, 杜宇, 周鹏, 王戈, 贾孟, 徐照丽, 白羽祥. 有机肥对玉溪植烟土壤有机质组分和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 201-212. |
| [7] | 刘霏霏, 何万荣, 孙强, 席琳乔, 廖结安, 韩路. 苜蓿绿肥对塔里木盆地苹果园土壤细菌多样性和功能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 223-233. |
| [8] | 杨娅琳, 吴峰婧琳, 陈健鑫, 武自强, 刘丽, 张东华, 马焕成, 伍建榕. 油茶根腐病根际土壤、根系内真菌群落结构和多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 121-135. |
| [9] | 李海利, 徐引弟, 王治方, 朱文豪, 张立宪, 马春江. 一株多重耐药大肠杆菌全基因组测序及其耐药性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 113-121. |
| [10] | 季梦婷, 陈长江, 罗流河, 林志坚, 詹梦琳, 杨丙烨, 胡方平, 蔡学清. 福建猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病的病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 144-152. |
| [11] | 李鹏声, 黄清泰, 范咏梅, 王萌, 杨叶. 海南省东方市甜瓜细菌性果斑病病原鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 117-123. |
| [12] | 刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225. |
| [13] | 李慧君, 张伟健, 吴伟健, 李高洋, 陈艺杰, 黄枫城, 黄永相, 蔺中, 甄珍. 种植海水稻对滨海盐土化学性质和微生物群落影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [14] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [15] | 靳建刚, 田再芳, 郑敏娜, 康佳惠. 不同施肥措施对饲用燕麦土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 152-160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||