




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 186-194.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0715
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Lixia YI1( ), Yong ZHOU2, Wei YANG1, Lai YAO1(
), Yong ZHOU2, Wei YANG1, Lai YAO1( ), Mengdie JIANG1, Jiangwen NIE1, Bo ZHU1, Zhangyong LIU1
), Mengdie JIANG1, Jiangwen NIE1, Bo ZHU1, Zhangyong LIU1
Received:2024-09-02
Accepted:2025-05-07
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2025-11-17
Contact:
Lai YAO
易丽霞1( ), 周勇2, 杨伟1, 姚涞1(
), 周勇2, 杨伟1, 姚涞1( ), 蒋梦蝶1, 聂江文1, 朱波1, 刘章勇1
), 蒋梦蝶1, 聂江文1, 朱波1, 刘章勇1
通讯作者:
姚涞
作者简介:易丽霞 E-mail:yilixia525@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lixia YI, Yong ZHOU, Wei YANG, Lai YAO, Mengdie JIANG, Jiangwen NIE, Bo ZHU, Zhangyong LIU. Effect of Ryegrass Return to Field as Substitute for Urea on Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(11): 186-194.
易丽霞, 周勇, 杨伟, 姚涞, 蒋梦蝶, 聂江文, 朱波, 刘章勇. 黑麦草还田替代尿素对稻田土壤氨挥发的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(11): 186-194.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0715
处理 Treatment | 尿素总量 Total urea amount/(g·m-2) | 绿肥量 Green fertilizer amount/(g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| CF | 0.64 | 0.0 |
| 25%RG | 0.48 | 7.2 |
| 50%RG | 0.32 | 14.3 |
| 75%RG | 0.16 | 21.5 |
| 100%RG | 0.00 | 28.7 |
Table 1 Fertilizer application rate for each treatment
处理 Treatment | 尿素总量 Total urea amount/(g·m-2) | 绿肥量 Green fertilizer amount/(g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| CF | 0.64 | 0.0 |
| 25%RG | 0.48 | 7.2 |
| 50%RG | 0.32 | 14.3 |
| 75%RG | 0.16 | 21.5 |
| 100%RG | 0.00 | 28.7 |
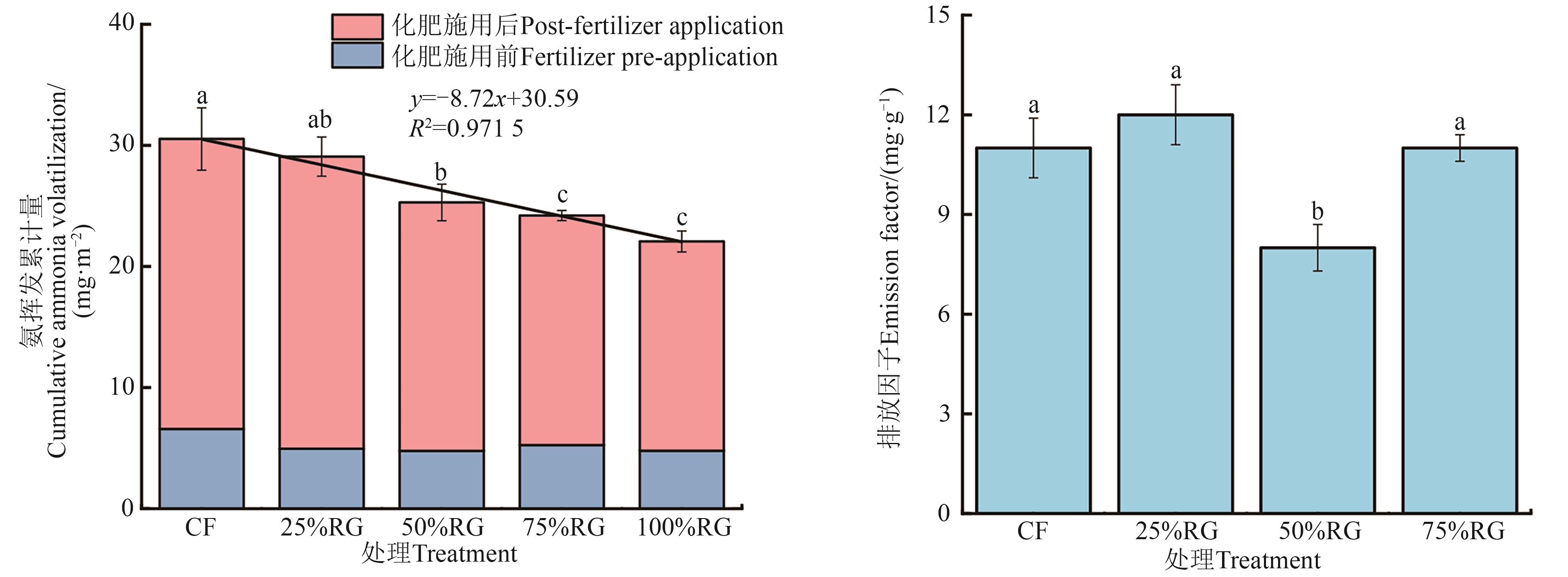
Fig. 2 Cumulative ammonia volatilization and ammonia emission factors under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 头季First season | 再生季Regeneration season | 总产量 Total output/(g·m-2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling/% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling /% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | ||
| CF | 9 a | 798 a | 91.5 a | 28.3 a | 719.6 a | 5 a | 92 a | 72.8 a | 26.2 a | 76.7 a | 796.3 a |
| 25%RG | 8 ab | 743 b | 92.2 a | 29.4 a | 695.8 a | 4 a | 93 a | 71.9 a | 26.3 a | 77.9 a | 773.7 a |
| 50%RG | 8 ab | 733 c | 85.6 ab | 28.6 a | 667.6 a | 4 a | 91 a | 67.9 b | 27.5 a | 79.6 a | 747.2 a |
| 75%RG | 6 c | 558 c | 87.0 a | 31.6 a | 560.0 b | 3 a | 89 a | 67.6 b | 27.6 a | 78.3 a | 639.2 b |
| 100%RG | 4 c | 536 c | 81.7 b | 30.1 a | 513.8 b | 5 a | 90 a | 72.4 a | 28.3 a | 81.1 a | 594.9 b |
Table 2 Rice yield under different fertilization ratios
| 处理Treatment | 头季First season | 再生季Regeneration season | 总产量 Total output/(g·m-2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling/% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | 穗数Number of ears | 总粒数Total grains | 结实率 Grain filling /% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量Yield/(g·m-2) | ||
| CF | 9 a | 798 a | 91.5 a | 28.3 a | 719.6 a | 5 a | 92 a | 72.8 a | 26.2 a | 76.7 a | 796.3 a |
| 25%RG | 8 ab | 743 b | 92.2 a | 29.4 a | 695.8 a | 4 a | 93 a | 71.9 a | 26.3 a | 77.9 a | 773.7 a |
| 50%RG | 8 ab | 733 c | 85.6 ab | 28.6 a | 667.6 a | 4 a | 91 a | 67.9 b | 27.5 a | 79.6 a | 747.2 a |
| 75%RG | 6 c | 558 c | 87.0 a | 31.6 a | 560.0 b | 3 a | 89 a | 67.6 b | 27.6 a | 78.3 a | 639.2 b |
| 100%RG | 4 c | 536 c | 81.7 b | 30.1 a | 513.8 b | 5 a | 90 a | 72.4 a | 28.3 a | 81.1 a | 594.9 b |
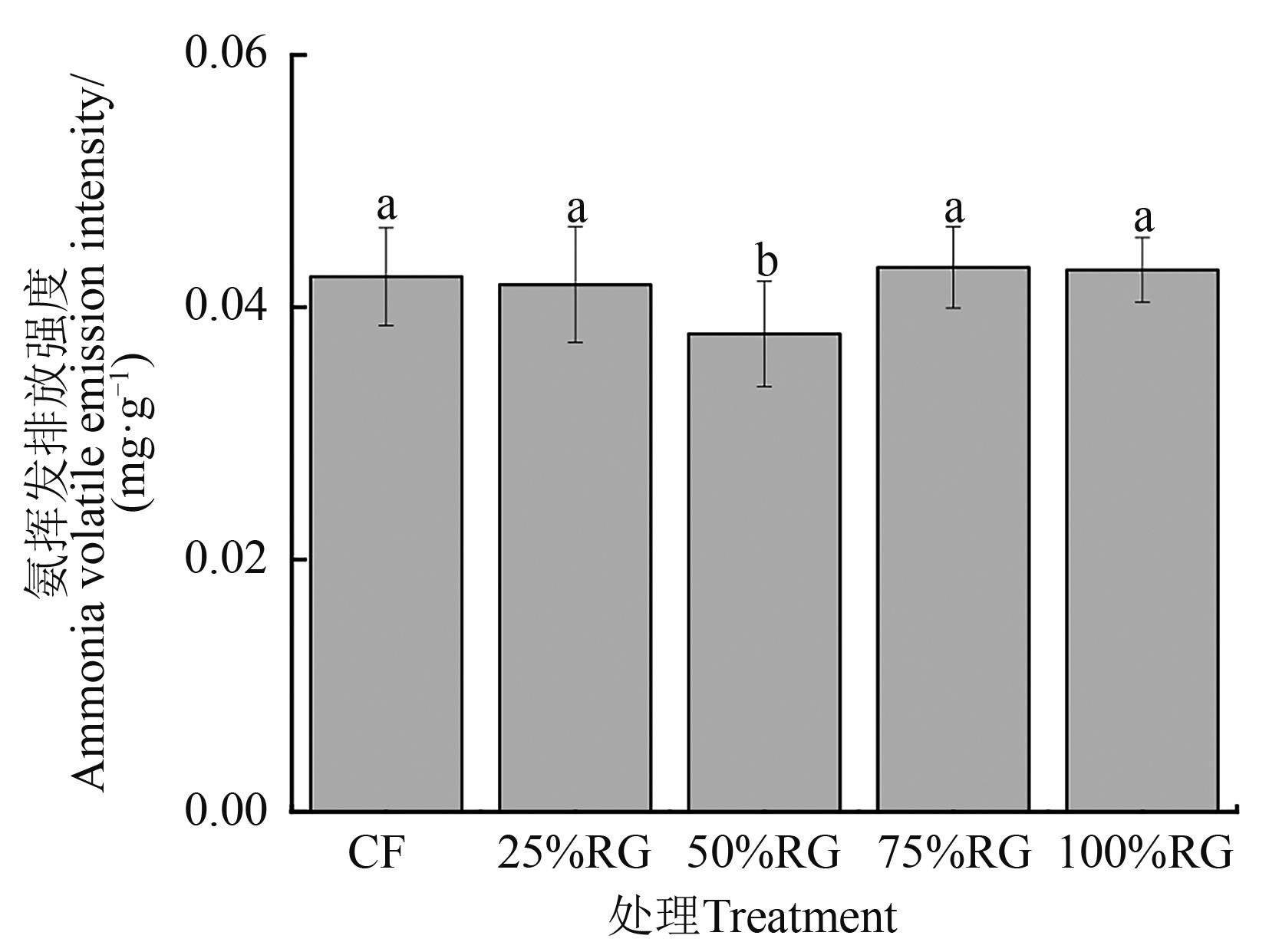
Fig. 3 Emission intensity of ammon ia volatilization under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| [1] | PENG X L, MAHARJAN B, YU C L, et al.. A laboratory evaluation of ammonia volatilization and nitrate leaching following nitrogen fertilizer application on a coarse-textured soil [J]. Agron. J., 2015, 107(3): 871-879. |
| [2] | 曹玉博,邢晓旭,柏兆海,等.农牧系统氨挥发减排技术研究进展[J].中国农业科学, 2018, 51(3): 566-580. |
| CAO Y B, XING X X, BAI Z H, et al.. Review on ammonia emission mitigation techniques of crop-livestock production system [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2018, 51(3): 566-580. | |
| [3] | 刘学军,沙志鹏,宋宇,等.我国大气氨的排放特征、减排技术与政策建议[J].环境科学研究, 2021, 34(1): 149-157. |
| LIU X J, SHA Z P, SONG Y, et al.. China’s atmospheric ammonia emission characteristics, mitigation options and policy recommendations [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2021, 34(1):149-157. | |
| [4] | 龚苏宁,王业明,刘荣桂.我国将加强氨排放治理[J].生态经济, 2020(11): 9-12. |
| [5] | 谢梓豪,樊品镐,武华,等.基于氨挥发因子方法的中国农田氨排放量估算[J].环境科学学报, 2020, 40(11): 4180-4188. |
| XIE Z H, FAN P H, WU H, et al.. Deriving volatile factors and estimating direct ammonia emissions for crop cultivation in China [J]. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(11): 4180-4188. | |
| [6] | LIAO B, LIAO P, HU R G, et al.. Mitigating ammonia volatilization in rice cultivation:the impact of partial organic fertilizer substitution [J/OL].Chemosphere,2023,344:140326 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [7] | 万雪薇,丁紫娟,聂江文,等.不同施肥方式对再生稻田氨挥发及氮肥利用率的影响[J].南方农业学报,2023, 54(12):3550-3560. |
| WAN X W, DING Z J, NIE J W, et al.. Effects of different fertilizer application methods on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate in regenerating rice fields [J].J. South. Agric., 2023, 54(12): 3550-3560. | |
| [8] | SUN L Y, WU Z, MA Y C, et al.. Ammonia volatilization and atmospheric N deposition following straw and urea application from a rice-wheat rotation in southeastern China [J]. Atmos.Environ., 2018, 181: 97-105. |
| [9] | WANG B, LI R, WAN Y F, et al.. Air warming and CO2 enrichment cause more ammonia volatilization from rice paddies:an OTC field study [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021,752:142071 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [10] | 朱晓琦,胡正义,王惠惠,等.滇池柴河流域蔬菜地土壤施用控释尿素与普通尿素的氮损失比较[J].中国农业科技导报,2014,16(6):109-116. |
| ZHU X Q, HU Z Y, WANG H H, et al.. Comparison of nitrogen loss between controlled release urea and common urea in vegetable soils at Chaihe Catchment of Dianchi Lake [J]. J.Agric. Sci. Technol., 2014,16(6):109-116. | |
| [11] | 卢丽丽,吴根义.农田氨排放影响因素研究进展[J].中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24(1):149-162. |
| LU L L, WU G Y. Advances in affecting factors of ammonia emission in farmland [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2019,24(1):149-162. | |
| [12] | 常菲,红梅,武岩,等.灌溉方式和改良措施对河套灌区盐渍土氨挥发的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2019(2):38-45. |
| CHANG F, HONG M, WU Y, et al.. Effects of irrigation methods and improvement measures on ammonia volatilization of saline soil in Hetao Irrigation Area [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China,2019(2): 38-45. | |
| [13] | 许云翔,何莉莉,陈金媛,等.生物炭对农田土壤氨挥发的影响机制研究进展[J].应用生态学报, 2020, 31(12): 4312-4320. |
| XU Y X, HE L L, CHEN J Y, et al.. Effects of biochar on ammonia volatilization from farmland soil: a review [J]. Chin. J.Appl. Ecol., 2020, 31(12): 4312-4320. | |
| [14] | DENG X Z, XU T T, XUE L X, et al..Effects of warming and fertilization on paddy N2O emissions and ammonia volatilization [J/OL]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2023,347:108361 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [15] | 张靖,朱潇,沈健林,等.生物有机肥与化肥配施对稻田氨挥发的影响[J].中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(1):15-25. |
| ZHANG J, ZHU X, SHEN J L, et al.. Effects of combined application of microbial organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer on ammonia volatilization in a paddy field with double rice cropping [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30(1):15-25. | |
| [16] | 梁琴,周泽弘,马雪清,等.绿肥翻压与氮肥减施对水稻产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(10):124-130. |
| LIANG Q, ZHOU Z H, MA X Q, et al.. Effects of green manure turning over and nitrogen reducing on rice yield,quality and soil fertility [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(10):124-130. | |
| [17] | 赵炯平,邓小华,江智敏,等.不同绿肥翻压还土后植烟土壤主要养分动态变化[J].作物研究, 2015, 29(2):161-165. |
| ZHAO J P, DENG X H, JIANG Z M, et al.. Dynamic changes of main nutrients in tobacco-planting soil under different green manure application [J]. Crop Res., 2015, 29(2):161-165. | |
| [18] | ZHANG X X, ZHANG R J, GAO J S, et al.. Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017, 104: 208-217. |
| [19] | 乔伟艳,顾洪如,沈益新.稻茬种植多花黑麦草对土壤肥力和微生物组成的影响[J].草业科学,2017,34(2): 240-245. |
| QIAO W Y, GU H R, SHEN Y X. Effects of planting Italian ryegrass in winter fallow fields on soil fertility and microorganisms [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2017, 34(2):240-245. | |
| [20] | CAO M Y, XIANG Y, HE H B, et al.. Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.)-rice (Oryza sativaL.) rotation promotes the nitrogen cycle in the rice rhizosphere through dominant ammonia-oxidizing bacteria [J/OL].Appl.Soil Ecol.,2024,193: 105121 [2024-08-06]. . |
| [21] | 龙莉,杨旭初,熊斌,等.冬作物秸秆还田对双季稻产量和土壤肥力的影响[J].作物研究,2019,33(2):104-109. |
| LONG L, YANG X C, XIONG B, et al.. Effect of winter crops straw returning on yield and soil fertility in a double cropping rice paddy [J]. Crop Res., 2019, 33(2):104-109. | |
| [22] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版. 北京:中国农业出版社,2000: 1-495. |
| [23] | 沈仕洲,杨艳,王瑞琦,等.施肥对云南洱海流域蒜田土壤氨挥发和大蒜产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(3): 470-479. |
| SHEN S Z, YANG Y, WANG R Q, et al.. Effects of fertilization on ammonia volatilization and garlic yield in Erhai Lake Basin of Yunnan province [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2021,27(3):470-479. | |
| [24] | ZHANG T, LIU H B, LUO J F, et al.. Long-term manure application increased greenhouse gas emissions but had no effect on ammonia volatilization in a Northern China upland field [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 633: 230-239. |
| [25] | 李诗豪,刘天奇,马玉华,等.耕作方式与氮肥类型对稻田氨挥发、氮肥利用率和水稻产量的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2018, 35(5): 447-454. |
| LI S H, LIU T Q, MA Y H, et al.. Effects of tillage practices and nitrogen sources on NH3 volatilization,nitrogen use efficiency and yield in paddy fields in Central China [J]. J.Agric. Resour. Environ., 2018, 35(5): 447-454. | |
| [26] | 唐良梁,李艳,李恋卿,等.不同施氮量对稻田氨挥发的影响及阈值探究[J].土壤通报, 2015, 46(5):1232-1239. |
| TANG L L, LI Y, LI L Q, et al.. Effect of different nitrogen application rate on paddy ammonia volatilization and nitrogen threshold [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2015, 46(5): 1232-1239. | |
| [27] | 易宗建,靳拓,袁沛,等.有机肥氮替代比例对双季稻氮肥利用率及氨挥发特征的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2024(10):172-181. |
| YI Z J, JIN T, YUAN P, et al.. Effects of organic fertilizer nitrogen replacement ratio on nitrogen use efficiency and ammonia volatilization of double-crop rice [J]. Soil Fert. Sci.China, 2024(10): 172-181. | |
| [28] | 卢丽兰,甘炳春,许明会,等.不同施肥与灌水量对槟榔土壤氨挥发的影响[J].生态学报, 2011, 31(15): 4477-4484. |
| LU L L, GAN B C, XU M H, et al.. Effect of different fertilization and irrigation practices on soil ammonia volatilization of Arecanut (Areca catechu L.) [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin.,2011, 31(15): 4477-4484. | |
| [29] | 赵淼,田玉华,张敏,等.改善农学管理措施减少太湖稻麦轮作NH3和NO排放[J].土壤, 2015, 47(5): 836-841. |
| ZHAO M, TIAN Y H, ZHANG M, et al.. Improving agronomic practices to reduce ammonia and nitric oxide emissions from rice-wheat rotation field in Tai Lake Region, China [J]. Soils,2015, 47(5): 836-841. | |
| [30] | WANG S W, SHAN J, XIA Y Q, et al.. Different effects of biochar and a nitrification inhibitor application on paddy soil denitrification:a field experiment over two consecutive rice-growing seasons [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2017, 593: 347-356. |
| [31] | 彭玉净,田玉华,尹斌.添加脲酶抑制剂NBPT对麦秆还田稻田氨挥发的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2012,20(1):19-23. |
| PENG Y J, TIAN Y H, YIN B. Effects of NBPT urease inhibitor on ammonia volatilization in paddy fields with wheat straw application [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2012,20(1):19-23. | |
| [32] | 山楠,毕晓庆,杜连凤,等.基施氮肥对麦田冬前氨挥发损失的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2013(6): 47-51. |
| SHAN N, BI X Q, DU L F, et al.. Effect of basal nitrogen fertilization on cornfield ammonia volatilization loss ahead of winter in-site conditions [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2013(6):47-51. | |
| [33] | 山楠,杜连凤,毕晓庆,等.用15N肥料标记法研究潮土中玉米氮肥的利用率与去向[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2016,22(4):930-936. |
| SHAN N, DU L F, BI X Q, et al.. Nitrogen use efficiency and behavior studied with 15N labeled fertilizer in maize in fluvo-aquic soils [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2016, 22(4): 930-936. | |
| [34] | 黄思怡,田昌,谢桂先,等.控释尿素减少双季稻田氨挥发的主要机理和适宜用量[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(12):2102-2112. |
| HUANG S Y, TIAN C, XIE G X, et al.. Mechanism and suitable application dosage of controlled-release urea effectively reducing ammonia volatilization in double-cropping paddy fields [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2019, 25(12): 2102-2112. | |
| [35] | ZHANG Y S, LUAN S J, CHEN L L, et al.. Estimating the volatilization of ammonia from synthetic nitrogenous fertilizers used in China [J]. J. Environ. Manage., 2011,92(3):480-493. |
| [36] | NDEGWA P M, HRISTOV A N, AROGO J, et al.. A review of ammonia emission mitigation techniques for concentrated animal feeding operations [J]. Biosyst. Eng., 2008,100(4):453-469. |
| [37] | 万伟帆,李斐,红梅,等.氮肥用量和脲酶抑制剂对滴灌马铃薯田氧化亚氮排放和氨挥发的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(3):693-702. |
| WAN W F, LI F, HONG M, et al.. Effects of nitrogen rate and urease inhibitor on N2O emission and NH3 volatilization in drip irrigated potato fields [J].J. Plant Nutr.Fert.,2018,24(3):693-702. | |
| [38] | 宋涛,尹俊慧,胡兆平,等.脲酶/硝化抑制剂减少农田土壤氮素损失的作用特征[J].农业资源与环境学报,2021,38(4):585-597. |
| SONG T, YIN J H, HU Z P, et al.. Characteristics of urease/nitrification inhibitors in reducing nitrogen losses in farmland soils [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2021, 38(4): 585-597. | |
| [39] | 黄立华,杨易,刘伯顺,等.苏打盐碱化稻田土壤反硝化和氨挥发特征及主要影响因子[J].农业环境科学学报,2023:42(8): 1748-1757. |
| HUANG L H, YANG Y, LIU B S, et al.. Characteristics and main influencing factors of denitrification and ammonia volatilization in saline-sodic paddy soils [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2023, 42(8): 1748-1757. | |
| [40] | 王吕,吴玉红,秦宇航,等.紫云英稻秆联合还田与氮肥减量对水稻产量及氨挥发的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2024,43(2): 462-472. |
| WANG L, WU Y H, QIN Y H, et al.. Effects of rice stalk mulching combined with green manure retention and nitrogen reduction on rice yield and ammonia emission [J]. J. Agro- Environ. Sci., 2024,43(2): 462-472. | |
| [41] | 王昱杭,唐旭,姜振辉,等.不同比例有机无机氮配施对长期稻麦轮作体系中水稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J].土壤通报, 2024, 55(2): 401-411. |
| WANG Y H, TANG X, JIANG Z H, et al.. Effects of long-term combined application of organic-inorganic fertilizers on rice yield,nitrogen uptake and utilization in a rice-wheat rotation system [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2024, 55(2): 401-411. | |
| [42] | 刘汝亮,张爱平,李友宏,等.长期配施有机肥对宁夏引黄灌区水稻产量和稻田氮素淋失及平衡特征的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5): 947-954. |
| LIU R L, ZHANG A P, LI Y H, et al.. Rice yield,nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and nitrogen leaching losses as affected by long-term combined applications of manure and chemical fertilizers in Yellow River irrigated region of Ningxia,China [J].J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(5): 947-954. | |
| [43] | 文春燕,熊运华,王萍,等.减施化肥配施不同有机肥对优质籼稻产量和品质的影响[J].土壤,2023,55(2):280-287. |
| WEN C Y, XIONG Y H, WANG P, et al.. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application on yield and quality of high-quality indica rice [J]. Soils, 2023, 55(2):280-287. |
| [1] | Yan WU, Leping ZOU, Huijie SONG, Dandan HU, Kailou LIU, Wanli LIANG. Effect of Controlled-release Nitrogen Fertilizer Combined Urea on Ammonium Nitrogen of Surface Water and Early Rice Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 192-200. |
| [2] | Wenxuan SHI, Jinfang TAN, Qian ZHANG, Lantao LI, Yilun WANG. Effect of One-off Fertilization on Yield and Nitrogen Fertilizer Efficiency of Summer Maize in Different Ecological Regions [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 193-202. |
| [3] | Qiaoyi HUANG, Yongpei WU, Xu HUANG, Ping LI, Hongting FU, Mu ZHANG, Yuwan PANG, Zhaobing ZENG, Shuanhu TANG. Impact of Controlled-release Urea Combined with Conventional Urea on Yield and Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency of Spring Sweet Corn Under One-off Application [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 163-173. |
| [4] | Yi DANG, Jianjun ZHANG, Gang ZHAO, Tinglu FAN, Lei WANG, Shangzhong LI, Gang ZHOU. Effects of Mixed Applying of Controlled-release Urea and Conventional Urea on Yield,Water and Nitrogen Utilization of Maize in Dryland [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 156-165. |
| [5] | Yuan YI, Huiyun ZHANG, Liwei LIU, Jing WANG, Xuecheng ZHU, Na ZHAO, Guohua FENG. Effects of Slow-released Fertilizer Compound Humic Acid Instead of Urea on Grain Yield and Population Quality in Xumai New Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 144-153. |
| [6] | WENG Wenan, CHENG Shuang, LI Shaoping, TIAN Jinyu, TAO Yu, HU Qun, HU Yajie, GUO Baowei, WEI Haiyan, XING Zhipeng, ZHANG Hongcheng. Effects of One-off Nitrogen Basal Fertilization on Yield of Direct Seeding Conventional Japonica Rice Under Different Panicle Formation Types [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 163-172. |
| [7] | ZHOU Xuan, KANG Xingrong, PENG Jianwei, YANG Xiangdong, ZHONG Xuemei, HU Wenfeng, LONG Junyou. Effects of Reduction Application of Polyurethane Coated Urea on Growth, Yield and Economic Benefit of Double-cropping Early Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 153-161. |
| [8] | ZHANG Mao, XU Yanhong, XI Yi*, PEI Yingjie, HUANG Benyong, YANG Kechao, LI Jinmeng. Effects of Pb2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ on Growth, Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Perennial Ryegrass [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 41-50. |
| [9] | WU Tianqi1, LIU Lang1, BIAN Chuanfei1, TAN Jingai2, SHI Xugen2*, LI Baotong1*. Effects of Cultivation Patterns and Nitrogen Application on the Rice False Smut and Yield of Double Cropping Late Japonica Rice in Jiangxi Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 159-169. |
| [10] | YIN Huanli1, YUE Yanjun2, CHANG Feng1, WANG Haibiao1, MIAO Yuhong1, WANG Yilun1*. Effects of Newtype Urea on Yield, Nutrient Absorption and Utilization of Winter Wheat [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(5): 145-152. |
| [11] | WANG Haibiao, ZHANG Bo, CHANG Feng, TAO Jingjing, LIU Pei, WANG Yilun*. Effects of Combined Application of Coated Urea and Common Urea on Summer Maize Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(7): 98-105. |
| [12] | GUO Shijia1, DUAN Yu2*, ZHANG Jun2, ZHANG Runsheng1, SHI Youguo3. Influence of Different Types of Urea on the Yield, Quality and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Processing Tomato [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(6): 96-103. |
| [13] | WANG Wujing1, WANG Mingli2*. Analysis of Ryegrass Planting Technical Efficiency and Technological Progress Contribution in Southwest China——Taking Sichuan Province as an Example [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(6): 21-28. |
| [14] | XUE Hailong1,2, XU Wennian1,2,3, LIU Daxiang2,3*, XIA Zhenyao2,3. Studies on Preparation and Evaluation Method of Several Polymeric Materials Coated Urea [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(4): 92-99. |
| [15] | QIN Miaojing1§, YANG Yang2§, CAO Fengqiu3, YANG Chao4, LI Changjun4, . Impact of OsUreD Mutation on Rice Growth Phenotype and Nitrogen Nutritional Physiology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(3): 9-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号