




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 72-79.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0266
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xuewen XU1,2( ), Xingpeng WANG1,2,3,4, Hongbo WANG1,2,3, Zhenxi CAO1,2,3(
), Xingpeng WANG1,2,3,4, Hongbo WANG1,2,3, Zhenxi CAO1,2,3( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Accepted:2023-06-19
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
Zhenxi CAO
徐雪雯1,2( ), 王兴鹏1,2,3,4, 王洪博1,2,3, 曹振玺1,2,3(
), 王兴鹏1,2,3,4, 王洪博1,2,3, 曹振玺1,2,3( )
)
通讯作者:
曹振玺
作者简介:徐雪雯 E-mail: 1726477971@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xuewen XU, Xingpeng WANG, Hongbo WANG, Zhenxi CAO. Physiological Regulation of Growth of Cotton Seedlings Under Salt Stress by Rhamnolipids[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 72-79.
徐雪雯, 王兴鹏, 王洪博, 曹振玺. 鼠李糖脂对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗根系生长的调控作用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 72-79.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://nkdb.magtechjournal.com/EN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0266
处理 Treatment | 根系总长度 Total root length/cm | 根系表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 体积 Volume/cm3 | 平均直径 Mean diameter/mm | 根尖数 Root tip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 62.72±2.72 a | 46.58±1.25 a | 2.55±0.24 a | 2.40±0.02 a | 55.00±3.61 a |
| T1R1 | 51.05±3.49 bc | 36.53±1.50 bc | 1.83±0.10 cd | 1.82±0.12 c | 44.00±2.65 b |
| T1R2 | 54.60±2.66 b | 39.10±3.34 b | 2.24±0.09 b | 2.14±0.16 b | 51.33±1.53 a |
| T1R3 | 45.54±2.08 d | 33.24±2.11 cd | 1.56±0.09 e | 1.78±0.05 c | 39.33±3.06 c |
| T1R0 | 47.25±2.40 cd | 31.49±2.04 d | 1.97±0.17 c | 1.88±0.03 c | 44.67±3.51 b |
| T2R1 | 45.75±1.68 d | 26.93±2.16 e | 1.69±0.11 de | 1.68±0.10 cd | 38.33±1.53 c |
| T2R2 | 40.78±1.61 e | 24.99±1.70 e | 1.31±0.08 f | 1.27±0.08 e | 35.00±2.00 c |
| T2R3 | 36.47±2.82 e | 17.63±0.99 f | 1.05±0.05 g | 1.27±0.23 e | 30.33±2.08 d |
| T2R0 | 37.22±2.35 e | 23.45±1.74 e | 1.20±0.06 fg | 1.53±0.23 d | 28.33±1.53 d |
Table 1 Morphological indexes of cotton seedlings at different salt stress under RLS application
处理 Treatment | 根系总长度 Total root length/cm | 根系表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 体积 Volume/cm3 | 平均直径 Mean diameter/mm | 根尖数 Root tip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 62.72±2.72 a | 46.58±1.25 a | 2.55±0.24 a | 2.40±0.02 a | 55.00±3.61 a |
| T1R1 | 51.05±3.49 bc | 36.53±1.50 bc | 1.83±0.10 cd | 1.82±0.12 c | 44.00±2.65 b |
| T1R2 | 54.60±2.66 b | 39.10±3.34 b | 2.24±0.09 b | 2.14±0.16 b | 51.33±1.53 a |
| T1R3 | 45.54±2.08 d | 33.24±2.11 cd | 1.56±0.09 e | 1.78±0.05 c | 39.33±3.06 c |
| T1R0 | 47.25±2.40 cd | 31.49±2.04 d | 1.97±0.17 c | 1.88±0.03 c | 44.67±3.51 b |
| T2R1 | 45.75±1.68 d | 26.93±2.16 e | 1.69±0.11 de | 1.68±0.10 cd | 38.33±1.53 c |
| T2R2 | 40.78±1.61 e | 24.99±1.70 e | 1.31±0.08 f | 1.27±0.08 e | 35.00±2.00 c |
| T2R3 | 36.47±2.82 e | 17.63±0.99 f | 1.05±0.05 g | 1.27±0.23 e | 30.33±2.08 d |
| T2R0 | 37.22±2.35 e | 23.45±1.74 e | 1.20±0.06 fg | 1.53±0.23 d | 28.33±1.53 d |
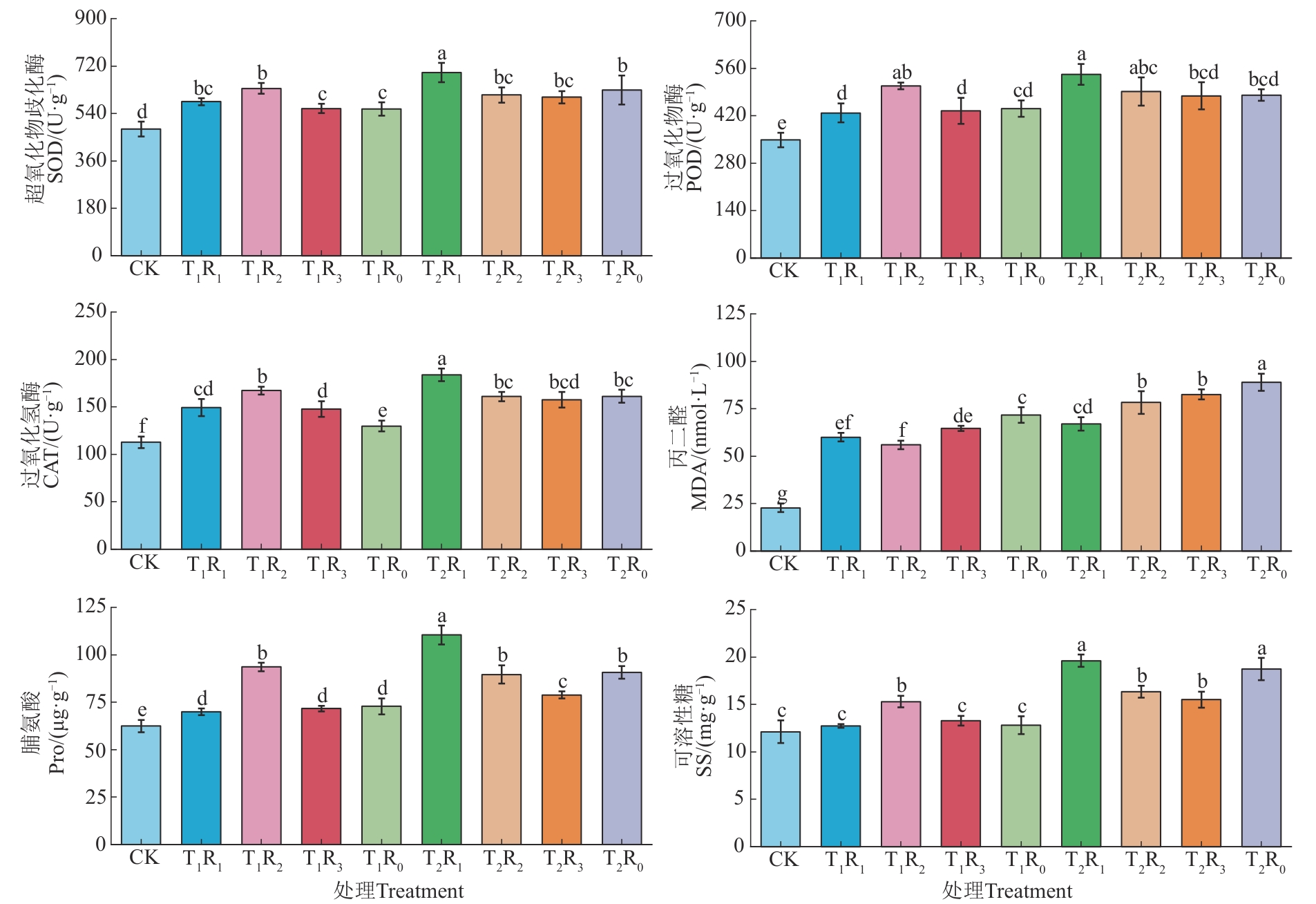
Fig. 2 Physiological parameters of cotton seedlings at salt stress under different RLS contentNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 根系总长度 Total root length | 根系表面积Root surface area | 体积Volume | 平均直径 Mean diameter | 根尖数Root tip number | 主根长Primary root length | 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 丙二醛MDA | 脯氨酸Pro | 可溶性糖SS | 贡献率Contribution rate/% | 累积 贡献率Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
主成分1 PC1 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 0.93 | -0.40 | -0.43 | -0.43 | -0.86 | -0.40 | -0.71 | 58.67 | 58.67 |
主成分2 PC2 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.85 | -0.35 | 0.90 | 0.66 | 35.01 | 93.68 |
Table 2 Component scoring coefficient matrix and contribution rates
指标 Index | 根系总长度 Total root length | 根系表面积Root surface area | 体积Volume | 平均直径 Mean diameter | 根尖数Root tip number | 主根长Primary root length | 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 丙二醛MDA | 脯氨酸Pro | 可溶性糖SS | 贡献率Contribution rate/% | 累积 贡献率Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
主成分1 PC1 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 0.93 | -0.40 | -0.43 | -0.43 | -0.86 | -0.40 | -0.71 | 58.67 | 58.67 |
主成分2 PC2 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.85 | -0.35 | 0.90 | 0.66 | 35.01 | 93.68 |
指标 Index | 根系总长度Total root length | 根系 表面积 Root surface area | 体积Volume | 平均 直径 Mean diameter | 根尖数 Root tip number | 主根长Primary root length | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 丙二醛MDA | 脯氨酸Pro | 可溶性糖SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
得分系数1 Scoring factor 1 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.35 | -0.15 | -0.16 | -0.16 | -0.32 | -0.15 | -0.27 |
得分系数2 Scoring factor 2 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.41 | -0.17 | 0.44 | 0.32 |
Table 3 Coefficients of principal component scores
指标 Index | 根系总长度Total root length | 根系 表面积 Root surface area | 体积Volume | 平均 直径 Mean diameter | 根尖数 Root tip number | 主根长Primary root length | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 丙二醛MDA | 脯氨酸Pro | 可溶性糖SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
得分系数1 Scoring factor 1 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.35 | -0.15 | -0.16 | -0.16 | -0.32 | -0.15 | -0.27 |
得分系数2 Scoring factor 2 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.41 | -0.17 | 0.44 | 0.32 |
综合评价 Comprehensive assessment | 处理 Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1R1 | T1R2 | T1R3 | T1R0 | T2R1 | T2R2 | T2R3 | T2R0 | |
得分1 Score 1(Y1) | 2.69 | 3.26 | 1.29 | 2.32 | -1.52 | -2.07 | -3.06 | -2.91 |
得分2 Score 2(Y2) | -0.93 | 2.70 | -1.66 | -1.73 | 3.59 | -0.26 | -1.56 | -0.14 |
综合得分 Composite score(Y) | 1.25 | 2.86 | 0.17 | 0.76 | 0.36 | -1.30 | -2.34 | -1.76 |
排序 Sort | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 7 |
Table 4 Composite score of principal component analysis
综合评价 Comprehensive assessment | 处理 Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1R1 | T1R2 | T1R3 | T1R0 | T2R1 | T2R2 | T2R3 | T2R0 | |
得分1 Score 1(Y1) | 2.69 | 3.26 | 1.29 | 2.32 | -1.52 | -2.07 | -3.06 | -2.91 |
得分2 Score 2(Y2) | -0.93 | 2.70 | -1.66 | -1.73 | 3.59 | -0.26 | -1.56 | -0.14 |
综合得分 Composite score(Y) | 1.25 | 2.86 | 0.17 | 0.76 | 0.36 | -1.30 | -2.34 | -1.76 |
排序 Sort | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 7 |
| 1 | 王兴鹏. 冬春灌对南疆土壤水盐动态和棉花生长的影响研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2018. |
| WANG X P. Effects of winter-spring irrigation on soil water-salt dynamics and cotton growth [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. | |
| 2 | 王海江, 王开勇, 刘玉国, 等. 膜下滴灌棉田不同土层盐分变化及其对棉花生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(10): 2381-2385. |
| WANG H J, WANG K Y, LIU Y G, et al.. Effects on cotton growth and salinity changes in different soil depth of drip irrigation in cotton field [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2010, 19 (10): 2381-2385. | |
| 3 | 段文静, 孟妍君, 江丹, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗形态及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(1): 92-104. |
| DUAN W J, MENG Y J, JIANG D,et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on the morphology and antioxidant enzyme activities of cotton seedlings under salt stress [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30 (1):92-104. | |
| 4 | WANG S L, ZHAO Z Y, GE S Q, et al.. Root morphology and rhizosphere characteristics are related to salt tolerance of Suaeda salsa and Beta vulgaris L. [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2021, 12:677767 [2023-03-06]. . |
| 5 | WEI Z Z, SHI X J, WEI F, et al.. The cotton endocycle-involved protein SPO11-3 functions in salt stress via integrating leaf stomatal response, ROS scavenging and root growth [J]. Physiol. Plant., 2019, 167(1): 127-141. |
| 6 | RANDHAWA K K S, RAHMAN P K S M. Rhamnolipid biosurfactants-past, present, and future scenario of global market [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2014, 5: 454 [2023-03-06]. . |
| 7 | INVALLY K, JU L K. Biolytic effect of rhamnolipid biosurfactant and dodecyl sulfate ggainst phagotrophic alga ochromonas danica [J]. J. Surfactants Detergents, 2017, 20(5): 1161-1171. |
| 8 | MIAO S D, DASHTBOZORG S S, CALLOW N V, et al.. Rhamnolipids as platform molecules for production of potential anti-zoospore agrochemicals [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2015, 63(13): 3367-3376. |
| 9 | 杨莹攀. 鼠李糖脂对盐渍化棉田土壤理化特性及棉花生长的影响[D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学, 2021. |
| YANG Y P. Effects of rhamnolipids on the physical and chemical properties of salted cotton field soil and cotton growth [D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2021. | |
| 10 | BURKETOVA L, TRDA L, OTT P G, et al.. Bio-based resistance inducers for sustainable plant protection against pathogens [J]. Biotechnol. Adv., 2015, 33(6): 994-1004. |
| 11 | SANCHETI A, JU L K. Eco-friendly rhamnolipid based fungicides for protection of soybeans from Phytophthora sojae [J]. Pest Manage. Sci., 2019, 75(11): 3031-3038. |
| 12 | 孟蝶, 万金忠, 张胜田, 等. 鼠李糖脂对林丹-重金属复合污染土壤的同步淋洗效果研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(1): 229-237. |
| MENG D, WAN J Z, ZHANG S T, et al.. Simultaneous removal of lindane and heavy metals from contaminated soils by rhamnolipids enhanced washing [J]. Acta Sci. Circumst., 2014, 34(1): 229-237. | |
| 13 | 刘雅, 蔡光容, 于伟, 等. 生物表面活性剂鼠李糖脂对大豆叶面肥喷施效果的影响[J]. 大豆科学, 2018, 37(3): 378-384. |
| LIU Y, CAI G R, YU W, et al.. Effect of biosurfactant rhamnolipid on the spraying efficiency of soybean foliar fertilizer [J]. Soybean Sci., 2018, 37(3):378-384. | |
| 14 | SILVA V L D, LOVAGLIO R B, TOZZI H H, et al.. Rhamnolipids: a new application in seeds development [J]. J. Med. Biol. Sci. Res., 2015, 1(8): 100-106. |
| 15 | 王敏鸽, 刘艺文, 张丹丹, 等. 鼠李糖脂改性生物炭对盐渍土小白菜抗性及氮素吸收的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2022, 40(5): 81-87, 93. |
| WANG M G, LIU Y W, ZHANG D D, et al.. Effects of rhamnolipid modified biochar on resistance and nitrogen absorption of Chinese cabbage in saline soil [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2022, 40(5): 81-87, 93. | |
| 16 | 赵栗. 外源调节剂对棉花根系生长特性及酶活性的影响[D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2021. |
| ZHAO L. Effects of exogenous regulators on root growth characteristics andenzyme activities of cotton [D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2021. | |
| 17 | 王洪博, 付媛媛, 杨鸿基, 等. 基于隶属函数法对不同基因型棉种萌发期抗氧化能力的综合评价[J]. 棉花学报, 2021, 33(5): 393-403. |
| WANG H B, FU Y Y, YANG H J, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of antioxidant ability of different genotypes of cotton in germination period based on subordinate function method [J]. Cott. Sci., 2021, 33 (5): 393-403. | |
| 18 | 郑曦, 魏臻武, 武自念, 等. 不同燕麦品种(系)在扬州地区的适应性评价[J]. 草地学报, 2013, 21(2): 272-279. |
| ZHENG X, WEI Z W, WU Z N, et al.. Adaptability evaluation of different avena sativa varieties in Yangzhou area [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2013, 21(2): 272-279. | |
| 19 | 冯春晓, 郝志军, 高健民, 等. 干旱胁迫下NaCl对棉花幼苗抗氧化酶活性及水分特征的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(6): 98-103. |
| FENG C X, HAO Z J, GAO J M, et al.. Effect of NaCl on antioxidant enzyme activities and water status in cotton seedling under drought stress [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2018, 36(6): 98-103. | |
| 20 | WANG Q S, LIU N, YANG X Y, et al.. Small RNA-mediated responses to low- and high-temperature stresses in cotton [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1): 35558 [2023-03-06]. . |
| 21 | JADIDI O, ETMINAN A, AZIZI-NEZHAD R, et al.. Physiological and molecular responses of barley genotypes to salinity stress [J/OL]. Genes, 2022, 13(11): 2040 [2023-03-06]. . |
| 22 | CORTI E, FALSINI S, SCHIFF S, et al.. Saline stress impairs lipid storage mobilization during germination in eruca sativa [J/OL]. Plants, 2023, 12(2): 366 [2023-03-06]. . |
| 23 | KHAN M A H, MIA B M A, QUDDUS M A, et al.. Salinity-induced physiological changes in Pea (Pisum sativum L .): rategermination, accumulationbiomass, relative water content, seedling vigor and salt tolerance index [J/OL]. Plants, 2022, 11(24): 3493 [2023-03-06]. . |
| 24 | 郭家鑫, 鲁晓宇, 陶一凡, 等. 棉花在盐碱胁迫下代谢产物及通路的分析[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(8): 2100-2114. |
| GUO J X, LU X Y, TAO Y F, et al.. Analysis of metabolites and pathways in cotton under salt and alkali stresses [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2022, 48(8): 2100-2114. | |
| 25 | 王庆惠, 韩伟, 侯银莹, 等. 不同耐盐品种棉花根系主要指标对盐分胁迫的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(3): 865-873. |
| WANG Q H, HAN W, HOU Y Y, et al.. Responses of main characters of root system to salt stress among cotton varieties with different salt tolerance [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2018, 29(3): 865-873. | |
| 26 | 郭建荣, 郑聪聪, 李艳迪, 等. NaCl处理对真盐生植物盐地碱蓬根系特征及活力的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(1): 63-70. |
| GUO J R, ZHENG C C, LI Y D, et al.. Effects of NaCl treatment on root system characteristics and activity of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2017, 53(1): 63-70. | |
| 27 | 逯亚玲, 王灵婧, 王宁, 等. 外源水杨酸对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2017, 25(6): 1265-1273. |
| LU Y L, WANG L J, WANG N, et al.. Effects of salicylic acid on physiological characteristics and growth of alfalfa seedling under NaCl stress [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2017, 25 (6): 1265-1273. | |
| 28 | 刘广明, 李金彪, 王秀萍, 等. 外源水杨酸对黑麦草幼苗盐胁迫的缓解效应研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(4): 995-1002. |
| LIU G M, LI J B, WANG X P, et al.. Effect of extraneous salicylic acid mitigating salt stress on ryegrass (Lolium perenne) seedlings [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2016, 53(4): 995-1002. | |
| 29 | 吴莺, 张淑英, 陈明媛, 等. SNP对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗光合抑制及氧化损伤的缓解效应[J]. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(4): 757-766. |
| WU Y, ZHANG S Y, CHEN M Y, et al.. The mitigative effect of SNP on photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage of cotton seedlings under salt stress [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2022, 58 (4): 757-766. | |
| 30 | LI J T, QIU Z B, ZHANG X W, et al.. Exogenous hydrogen peroxide can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2011, 33(3): 835-842. |
| 31 | 张倩, 李笑佳, 张淑英. 硅对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗生长和渗透调节系统的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(6): 110-117. |
| ZHANG Q, LI X J, ZHANG S Y. Effects of silicon on growth and osmotic regulation of cotton deedlings under salt stress [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2019, 34(6): 110-117. | |
| 32 | 山雨思, 代欢欢, 何潇, 等. 外源茉莉酸甲酯和水杨酸对盐胁迫下颠茄生理特性和次生代谢的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2019, 55(9): 1335-1346. |
| SHAN Y S, DAI H H, HE X, et al.. Effects of exogenous methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid on physiological characteristics and secondary metabolism of Atropa belladonna under NaCl stress [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2019, 55 (9): 1335-1346. | |
| 33 | 束红梅, 郭书巧, 巩元勇, 等. 油菜素内酯对NaCl胁迫下棉花叶片生理特征和基因表达谱的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1): 150-156. |
| SHU H M, GUO S Q, GONG Y Y, et al.. Effects of brassinolide on leaf physiological characteristics and differential gene expression profiles of NaCl-stressed cotton [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2016, 27(1): 150-156. | |
| 34 | 李国瑞, 李朝苏, 吴春, 等. 西南地区小麦品种萌发期抗旱性分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(4): 212-219. |
| LI G R, LI Z S, WU C, et al.. The analysis of drought resistance in different wheat varieties during germination in southwest area of China [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2015, 33(4): 212-219. |
| [1] | Hao JIA, Hongzhe WANG, Zhengwen SUN, Qishen GU, Dongmei ZHANG, Xingyi WANG, Yan ZHANG, Huaiyu LU, Zhiying MA, Xingfen WANG. Genome-wide Identification of VOZ Genes Family in Cotton and Study on Salt Tolerance Function of GhVOZ1 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 58-68. |
| [2] | Yueriyeti Sali, Nuerbiye Yisimayi, Aliya Waili, Lingna CHEN, Yongkun CHEN. Heterologous Expression of PaMT3-1 Gene from Phytolacca americana Enhances Salt and Osmotic Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 92-98. |
| [3] | Huanbin ZHENG, Ming LI, Suxin YANG, Weilin WU. Alkaline Tolerance Screening and Evaluation Analysis of Soybean Germplasm Resources at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 54-71. |
| [4] | Jilin SUN, Jiaqi ZHANG, Fansen MENG, Silong SUN. Genome-wide Identification and Tissue Expression Pattern Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Thinopyrum elongatum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 28-38. |
| [5] | Zhiduo DONG, Qiuping FU, Jian HUANG, Tong QI, Yanbo FU, Kuerban Kaisaier. Analysis of Salt Tolerance Capacity of Xinjiang Cotton Guring Germination [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 57-67. |
| [6] | Gang LEI, Rong FANG, Kunhua ZHOU, Xuejun CHEN, Xinjie YUAN, Yueqin HUANG, Gege LI, Yuanyuan XIE, Xiaomin SONG. Establishment of Comprehensive Evaluation System of Pepper Germplasm Resources on Heat Tolerance at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 60-70. |
| [7] | Qiang WU, Conglian WU, Xiaoyun WU, Jian WU, Xuanmei XU, Junsheng LAI, Weiyun HU, Bangchu GONG, Xibing JIANG. Effect of Different Fertilization Treatments on Yield and Fruit Quality of Castanea henryi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 228-237. |
| [8] | Tingting MA, Yanrong ZHAO, Yuqing WEI, Yuejuan WANG, Xuefei WANG, Erdong ZHANG. Dynamic Characteristics of Stem Growth and Sugar Accumulation of Sweet Sorghum at Late Growth Stage Under Soil Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 42-50. |
| [9] | Shixu QU, Yu SUN, Yizhen SUO, Haipeng YUAN, Yuhong ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Physiological Characteristics and Secondary Metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 80-88. |
| [10] | Ting WANG, Jinghan DU, Guangdi ZHANG, Jianglong WANG, Yinan JIA, Yu WANG, Wenyi BAO. Study on Quality and Volatile Substances of New Excellent Cabbage Varieties in Mountainous Area of Southern Ningxia [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 165-180. |
| [11] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [12] | Shuang LI, Aiying WANG, Zhen JIAO, Qing CHI, Hao SUN, Tao JIAO. Physiological and Chemical Characteristics and Transcriptome Analysis of Different Type of Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [13] | Panpan MENG, Haiyan HE, Yuxin CAO, Lixin ZHANG, Qinghao LYU, Ruilin QI, Hongrui ZHANG. Comprehensive Evaluation of 5 Cultivation Types of Medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. at Branching Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 90-99. |
| [14] | Xuemin JIANG, Xiangqian CHEN, Hongyan LI, Qiyan JIANG. Metabolomic Analysis of Wheat Response to Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [15] | Yulu WU, Jiaxin HU, Yuxi CHEN, Bingsong ZHENG, DaoLiang YAN. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号