




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 118-133.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2025.0044
• 智慧农业 农机装备 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-01-20
接受日期:2025-07-10
出版日期:2025-10-15
发布日期:2025-10-15
通讯作者:
崔艳荣
作者简介:黄志豪 E-mail:2023710688@yangtzeu.edu.cn;
基金资助:
Zhihao HUANG( ), Chengfang LU, Yanrong CUI(
), Chengfang LU, Yanrong CUI( ), Ronghua HU
), Ronghua HU
Received:2025-01-20
Accepted:2025-07-10
Online:2025-10-15
Published:2025-10-15
Contact:
Yanrong CUI
摘要:
针对果园环境下苹果果实目标重叠、光照不均且尺度不一等复杂场景特点,同时为满足模型落地部署时检测精度与计算资源之间的平衡需求,提出一种基于YOLO11n改进的轻量化苹果果实检测模型YOLO-AP。首先,结合幽灵卷积与动态卷积改进特征提取模块,提出一种GD_C3K2模块,增强模型特征提取能力的同时降低模型复杂度;设计一种全局-局部双流特征融合网络,通过简化双向特征金字塔网络与自适应下采样模块对颈部网络进行重构,并在网络首部上引入全局到局部空间聚合模块进一步增强模型全局和局部空间建模能力;结合坐标注意力机制和重参数化卷积构建轻量化共享卷积头RepCoord-LDH,减少模型复杂度的同时维持高检测精度;最后,引入WiseIOUv3作为模型边界框损失函数,优化边界框回归性能。结果表明,YOLO-AP的精确率、召回率和平均精确率分别达到89.1%、88.9%和96.1%,相较于基线模型YOLO11n分别提升0.5、0.1和1.0百分点,同时模型的参数量和浮点运算量分别为1.4 M和3.6 G,仅为基线模型的53.8%和54.5%。与主流检测算法对比,YOLO-AP在模型检测性能和复杂度等指标中也优于其他算法。综上所述,YOLO-AP模型可为复杂环境下的苹果检测提供有效的技术支持。
中图分类号:
黄志豪, 卢承方, 崔艳荣, 胡蓉华. YOLO-AP:基于改进YOLO11n的轻量级苹果果实检测算法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(10): 118-133.
Zhihao HUANG, Chengfang LU, Yanrong CUI, Ronghua HU. YOLO-AP: a Lightweight Apple Fruit Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLO11n[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(10): 118-133.

图5 GL-DSFN结构注:蓝色块表示输入特征图,绿色块和黄色块分别表示经过上采样和ADown下采样后的中间结果与最终输出结果。
Fig. 5 GL-DSFN structureNote:The blue block represents the input feature map, while the green and yellow blocks denote the intermediate results and final output results after upsampling and ADown downsampling, respectively.
| 参数Parameter | 数值Value | 参数Parameter | 数值Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 随机种子Random seed | 0 | 训练轮数Epoch | 300 |
| 输入图像大小Input size | 640×640 | 训练批次Batchsize | 32 |
| 初始学习率Orignal learn rate | 10-2 | 动量因子Momentum factor | 0.937 |
| 优化器Optimizer | SGD | 早停次数Early stop | 100 |
表1 训练超参数设置
Table 1 Training hyperparameter settings
| 参数Parameter | 数值Value | 参数Parameter | 数值Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 随机种子Random seed | 0 | 训练轮数Epoch | 300 |
| 输入图像大小Input size | 640×640 | 训练批次Batchsize | 32 |
| 初始学习率Orignal learn rate | 10-2 | 动量因子Momentum factor | 0.937 |
| 优化器Optimizer | SGD | 早停次数Early stop | 100 |
编号 Number | C3K2模块 C3K2 module | 颈部网络 Neck network | 检测头 Detect head | 损失函数 Loss function | 参数量 Params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall /% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD-C3K2 | GL-DSFN | RepCoord-LDH | WiseIOUv3 | ||||||
| 1 | - | - | - | - | 2.6 | 6.6 | 88.6 | 89.0 | 95.1 |
| 2 | √ | - | - | - | 2.3 | 5.5 | 89.2 | 89.7 | 95.4 |
| 3 | √ | √ | - | - | 1.5 | 4.4 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 95.8 |
| 4 | √ | √ | √ | - | 1.4 | 3.6 | 88.9 | 88.8 | 95.7 |
| 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.4 | 3.6 | 89.1 | 88.9 | 96.1 |
表2 消融试验结果
Table 2 Results of ablation experiments
编号 Number | C3K2模块 C3K2 module | 颈部网络 Neck network | 检测头 Detect head | 损失函数 Loss function | 参数量 Params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall /% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD-C3K2 | GL-DSFN | RepCoord-LDH | WiseIOUv3 | ||||||
| 1 | - | - | - | - | 2.6 | 6.6 | 88.6 | 89.0 | 95.1 |
| 2 | √ | - | - | - | 2.3 | 5.5 | 89.2 | 89.7 | 95.4 |
| 3 | √ | √ | - | - | 1.5 | 4.4 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 95.8 |
| 4 | √ | √ | √ | - | 1.4 | 3.6 | 88.9 | 88.8 | 95.7 |
| 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.4 | 3.6 | 89.1 | 88.9 | 96.1 |
颈部网络 Neck network | 参数量 Params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall /% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANet(YOLO11n) | 2.3 | 5.5 | 89.2 | 89.7 | 95.4 |
| BiFPN | 1.8 | 5.7 | 88.9 | 89.4 | 94.9 |
| SlimNeck | 2.4 | 5.6 | 88.5 | 89.2 | 95.3 |
| AFPN | 1.9 | 5.9 | 89.0 | 89.1 | 95.1 |
| GL-DSFN | 1.5 | 4.4 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 95.8 |
表3 颈部网络不同特征融合方式对比试验结果
Table 3 Comparison of different feature fusion methods in neck network
颈部网络 Neck network | 参数量 Params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall /% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANet(YOLO11n) | 2.3 | 5.5 | 89.2 | 89.7 | 95.4 |
| BiFPN | 1.8 | 5.7 | 88.9 | 89.4 | 94.9 |
| SlimNeck | 2.4 | 5.6 | 88.5 | 89.2 | 95.3 |
| AFPN | 1.9 | 5.9 | 89.0 | 89.1 | 95.1 |
| GL-DSFN | 1.5 | 4.4 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 95.8 |
检测头 Detect head | 参数量 params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO11-Head | 2.6 | 6.6 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 95.8 |
| DyHead | 2.3 | 5.5 | 88.3 | 88.4 | 95.5 |
| LM-YOLO | 1.4 | 3.7 | 88.1 | 87.2 | 95.1 |
| RepCoord-LDH | 1.4 | 3.6 | 88.9 | 88.8 | 95.7 |
表4 轻量化检测头对比结果
Table 4 Comparison result of lightweight detection head
检测头 Detect head | 参数量 params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO11-Head | 2.6 | 6.6 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 95.8 |
| DyHead | 2.3 | 5.5 | 88.3 | 88.4 | 95.5 |
| LM-YOLO | 1.4 | 3.7 | 88.1 | 87.2 | 95.1 |
| RepCoord-LDH | 1.4 | 3.6 | 88.9 | 88.8 | 95.7 |
损失函数 Loss function | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall /% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIoU(YOLO11n) | 88.8 | 88.6 | 95.7 |
| DIoU | 87.7 | 88.1 | 95.3 |
| GIoU | 88.8 | 85.5 | 95.2 |
| WiseIoUv3 | 89.1 | 88.9 | 96.1 |
表5 损失函数对比结果
Table 5 Comparison result of loss functions
损失函数 Loss function | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall /% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIoU(YOLO11n) | 88.8 | 88.6 | 95.7 |
| DIoU | 87.7 | 88.1 | 95.3 |
| GIoU | 88.8 | 85.5 | 95.2 |
| WiseIoUv3 | 89.1 | 88.9 | 96.1 |
模型名称 Model name | 参数量 Params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% | 单批次帧 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 60.1 | 246.3 | 82.1 | 86.2 | 88.7 | 39.5 |
| SSD | 26.3 | 99.5 | 83.6 | 85.3 | 89.4 | 70.1 |
| RT-DETR-R18 | 20.1 | 58.6 | 89.6 | 88.6 | 94.6 | 110.6 |
| YOLOv5n | 1.9 | 4.5 | 88.2 | 87.9 | 94.5 | 193.8 |
| YOLOv6n | 4.6 | 11.3 | 88.7 | 88.4 | 93.1 | 98.6 |
| YOLOv7tiny | 5.7 | 13.0 | 89.0 | 87.2 | 92.4 | 167.5 |
| YOLOv8n | 3.1 | 8.1 | 87.7 | 89.2 | 94.6 | 284.5 |
| YOLOv9tiny | 2.2 | 7.8 | 88.3 | 88.4 | 94.1 | 116.5 |
| YOLOv10n | 2.6 | 8.2 | 89.2 | 88.0 | 94.9 | 149.8 |
| YOLO11n | 2.6 | 6.6 | 88.6 | 89.0 | 95.1 | 181.2 |
| YOLO-AP | 1.4 | 3.6 | 89.1 | 88.9 | 96.1 | 189.6 |
表6 检测模型对比
Table 6 Comparison of detection models
模型名称 Model name | 参数量 Params/M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% | 单批次帧 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 60.1 | 246.3 | 82.1 | 86.2 | 88.7 | 39.5 |
| SSD | 26.3 | 99.5 | 83.6 | 85.3 | 89.4 | 70.1 |
| RT-DETR-R18 | 20.1 | 58.6 | 89.6 | 88.6 | 94.6 | 110.6 |
| YOLOv5n | 1.9 | 4.5 | 88.2 | 87.9 | 94.5 | 193.8 |
| YOLOv6n | 4.6 | 11.3 | 88.7 | 88.4 | 93.1 | 98.6 |
| YOLOv7tiny | 5.7 | 13.0 | 89.0 | 87.2 | 92.4 | 167.5 |
| YOLOv8n | 3.1 | 8.1 | 87.7 | 89.2 | 94.6 | 284.5 |
| YOLOv9tiny | 2.2 | 7.8 | 88.3 | 88.4 | 94.1 | 116.5 |
| YOLOv10n | 2.6 | 8.2 | 89.2 | 88.0 | 94.9 | 149.8 |
| YOLO11n | 2.6 | 6.6 | 88.6 | 89.0 | 95.1 | 181.2 |
| YOLO-AP | 1.4 | 3.6 | 89.1 | 88.9 | 96.1 | 189.6 |
模型 Model | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO11n | 68.5 | 63.0 | 68.3 |
| YOLO-AP | 69.0 | 66.1 | 69.2 |
表7 MinneApple数据集泛化性对比试验结果
Table 7 Generalization comparison test results of MinneApple datasetom
模型 Model | 精确率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | 平均精确率 mAP50/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO11n | 68.5 | 63.0 | 68.3 |
| YOLO-AP | 69.0 | 66.1 | 69.2 |
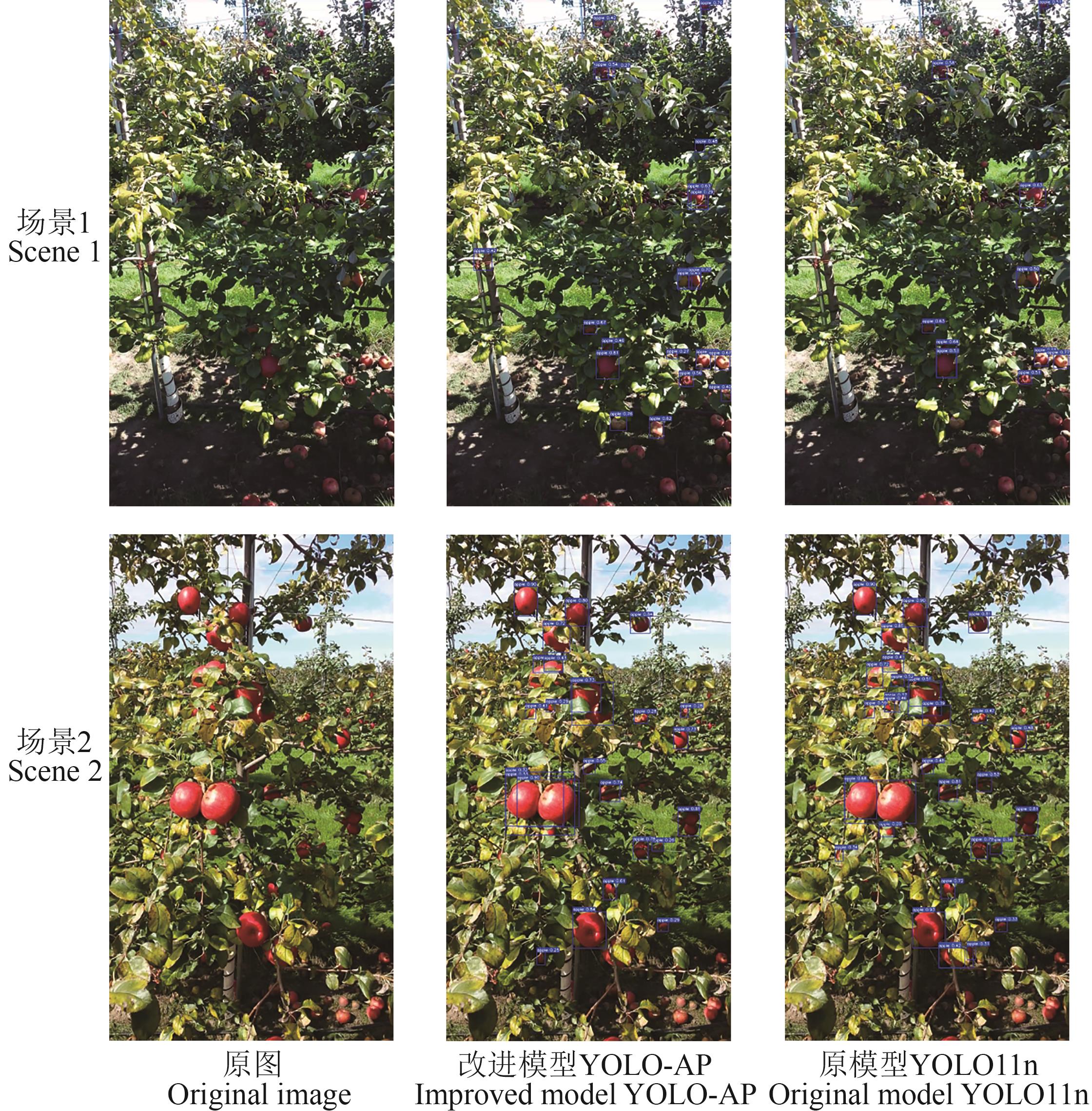
图13 泛化数据集可视化结果比较注:MinneApple数据集对落地苹果不进行标签化。
Fig.13 Comparison of visualization results of generalized datasetsNote:MinneApple dataset does not label fallen apples.
| [1] | 张放.2023年我国主要水果产量再创新高[J]. 中国果业信息, 2024, 41(6): 55. |
| [2] | 陈青, 吴玄博, 殷程凯, 等. 苹果机械化采收技术与装备研究现状[J]. 林业工程学报, 2025, 10(3): 13-24. |
| CHEN Q, WU X B, YIN CHENG K, et al.. Research status of apple mechanized harvesting technology and equipment [J]. J. For. Eng., 2025, 10(3): 13-24. | |
| [3] | 马锋旺. 中国苹果产业发展的思考:现状、问题与出路[J]. 落叶果树, 2023, 55(4): 1-4. |
| MA F W. Reflections on the development of China’s apple industry: current situation, problems, and solutions [J]. Deciduous Fruits, 2023, 55(4): 1-4. | |
| [4] | 王艳,祁萌.基于遗传算法和阈值分割的夜间苹果识别方法[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2020, 36(3): 220-225, 233. |
| WANG Y, QI M. Apple recognition at night based on genetic algorithm and threshold segmentation [J]. Mach. Des.Res.,2020, 36(3): 220-225, 233. | |
| [5] | 林海波, 卢元栋, 丁荣诚, 等. 基于图像处理与改进SVM的苹果多特征融合分级方法[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(6):141-149. |
| LIN H B, LU Y D, DING R C, et al.. A multi-feature fusion classification method for apple based on image processing and improved SVM [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2022, 54(6): 141-149. | |
| [6] | 于慧杰, 李大华, 高强, 等. 自然环境中重叠与遮挡绿苹果图像的识别[J]. 激光杂志, 2020(2): 20-24. |
| YU H J, LI D H, GAO Q, et al.. Recognition of overlapping and occluding green apple images in natural environment [J]. Laser J., 2020(2): 20-24. | |
| [7] | GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2014: 580-587. |
| [8] | GIRSHICK R.Fast R-CNN [C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).IEEE, 2015:1440-1448. |
| [9] | TIAN Z, SHEN C, CHEN H, et al.. FCOS:a simple and strong anchor-free object detector [J].IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2022, 44(4): 1922-1933. |
| [10] | REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al.. You only look once:unified, real-time object detection [C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).IEEE,2016: 779-788. |
| [11] | REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2017: 6517-6525. |
| [12] | FARHADI A, REDMON J. Yolov3: an incremental improvement [C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Springer, 2018, 1804: 1-6. |
| [13] | 石展鲲, 杨风, 韩建宁, 等. 基于Faster-RCNN的自然环境下苹果识别[J]. 计算机与现代化, 2023(2): 62-65. |
| SHI Z K, YANG F, HAN J N,et al.. Apples recognition in natural environment based on faster-RCNN [J]. Comput. Mod., 2023(2): 62-65. | |
| [14] | LIU Y K, YANG G P, HUANG Y W, et al.. SE-mask R-CNN:an improved mask R-CNN for apple detection and segmentation [J]. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst., 2021, 41(6): 6715-6725. |
| [15] | WU L, MA J, ZHAO Y H, et al.. Apple detection in complex scene using the improved YOLOv4 model [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(3): 476 [2024-12-28].. |
| [16] | SUN L J, HU G R, CHEN C, et al.. Lightweight apple detection in complex orchards using YOLOV5-PRE [J/OL].Horticulturae, 2022, 8(12): 1169 [2024-12-28]. . |
| [17] | CHEN C Y, LIU M-Y, TUZEL O, et al.. R-CNN for small object detection [C]//Computer Vision-ACCV Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 214-230. |
| [18] | LIU S, QI L, QIN H F, et al.. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation [C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2018: 8759-8768. |
| [19] | HAN K, WANG Y, GUO J, et al.. ParameterNet: parameters are all you need for large-scale visual pretraining of mobile networks [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024: 15751-15761. |
| [20] | TAN M, PANG R, LE Q V. Efficientdet: scalable and efficient object detection [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2020: 10781-10790. |
| [21] | WANG C Y, YEH I H, MARK LIAO H Y. YOLOv9:learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information [C]// Proceedings of Computer Vision-ECCV 2024.Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 1-21. |
| [22] | LI X R, XU G X, ZHAO M, et al.. Encoder activation diffusion and decoder transformer fusion network for medical image segmentation [C]//Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision.Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2023: 185-197. |
| [23] | HOU Q B, ZHOU D Q, FENG J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design [C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2021: 13708-13717. |
| [24] | DING X H, ZHANG X Y, MA N N, et al.. RepVGG:making VGG-style ConvNets great again [C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).IEEE, 2021: 13728-13737. |
| [25] | TONG Z, CHEN Y, XU Z, et al.. Wise-IoU: bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism [J/OL]. arXiv Preprint arXiv, 2023, 2301: 10051 [2024-12-28]. . |
| [26] | 王娜, 陈勇, 崔艳荣, 等. 基于改进轻量化YOLO v5n的番茄叶片病害识别方法[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(8): 192-199. |
| [27] | 王志东, 陈晨阳, 刘晓明. 基于自适应特征提取的通信光缆缺陷检测方法[J]. 图学学报, 2025, 46(2): 241-248. |
| WANG Z D, CHEN C Y, LIU X M. Defect detection method of communication optical cable based on adaptive feature extraction [J]. J. Graph., 2025, 46(2): 241-248. | |
| [28] | 闫建红, 冉同霄. 基于YOLOv8的轻量化无人机图像目标检测算法[J]. 图学学报, 2024, 45(6): 1328-1337. |
| YAN J H, RAN T X. Lightweight UAV image target detection algorithm based on YOLOv8 [J]. J. Graph., 2024, 45(6): 1328-1337. | |
| [29] | LI H, LI J, WEI H, et al.. Slim-neck by GSConv: a better design paradigm of detector architectures for autonomous vehicles [J/OL]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 2022, 2206: 02424 [2024-12-28]. . |
| [30] | YANG G Y, LEI J, ZHU Z K, et al.. AFPN:asymptotic feature pyramid network for object detection [C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). IEEE, 2023: 2184-2189. |
| [31] | DAI X Y, CHEN Y P, XIAO B,et al.. Dynamic head:unifying object detection heads with attentions [C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2021: 7369-7378. |
| [32] | LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D,et al.. SSD:single shot MultiBox detector [C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016.Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 21-37. |
| [33] | ZHAO Y A, LYU W Y, XU S L, et al..DETRs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection [C]//2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2024: 16965-16974. |
| [34] | SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al.. Grad-CAM:visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization [C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, 2017: 618-626. |
| [35] | HANI N, ROY P, ISLER V. MinneApple: a benchmark dataset for apple detection and segmentation [J]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett., 2020, 5(2): 852-858. |
| [36] | 魏晓宇. 苹果采摘目标检测与机械臂路径规划技术研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2024. |
| WEI X Y. Research on apple picking object detection and path planning technology of manipulator [D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2024. |
| [1] | 黄梦真, 李皞, 胡桓浚, 李梓芃, 盛钟尹, 刘义凡, 夏震言, 郑奥运. 融合亮度自适应模块的端到端低光环境黑猪检测技术研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 113-125. |
| [2] | 李广瑶, 杨胜龙, 程田飞, 崔雪森, 周为峰, 张胜茂. 中西太平洋金枪鱼渔场环境特征及预报现状分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 203-221. |
| [3] | 陈自立, 林卫, 贺佳, 王来刚, 郑国清, 彭一龙, 焦家东, 郭燕. 基于卷积神经网络的农作物病害识别研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 99-109. |
| [4] | 邢卓冉, 丁松爽, 张凯, 马明, 郭文龙, 刘旭东, 时向东. 计算机视觉与深度学习技术在烟叶生产上的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 96-106. |
| [5] | 胡国玉, 董娅兰, 古丽巴哈尔·托乎提, 刘广, 周建平. 基于机器视觉的葡萄藤结构分割方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 105-111. |
| [6] | 熊晓菲, 王秀琴, 庄翠珍, 郭家贤, 谢新锐, 吴建伟, 李奇峰. 基于ROI融合特征的柑橘炭疽病诊断方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 83-92. |
| [7] | 金慧萍, 牟海雯, 刘腾, 于佳琳, 金小俊. 基于深度卷积神经网络的青菜和杂草识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 122-130. |
| [8] | 帖军, 赵捷, 郑禄, 吴立锋, 洪博文. 改进YOLOv5 模型在自然环境下柑橘识别的应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 111-120. |
| [9] | 黄诗锐, 王天一, 文韬, 周江龙. 基于改进YOLOv7的农作物虫害识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 107-116. |
| [10] | 朱芷芫, 王海峰, 李斌, 赵文文, 朱君, 贾楠, 赵宇亮. 深度学习在畜禽典型行为识别中的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 110-124. |
| [11] | 郑果, 姜玉松. 基于多任务学习农作物叶片病害诊断方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 89-98. |
| [12] | 林开颜, 梅飞, 吴军辉, 郭文刚, 陈杰, 司慧萍. 基于计算机视觉的作物病害监测服务平台设计与研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 89-96. |
| [13] | 杨超, 韩海斌, 韦波, 张衡, 商宸, 苏冰, 刘思源, 蒋沛雯, 相德龙. 北太平洋远东拟沙丁鱼年龄鉴定方法的构建[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 225-233. |
| [14] | 赵越, 卫勇, 单慧勇, 穆志民, 张健欣, 吴海云, 赵辉, 胡建龙. 基于深度学习的高分辨率麦穗图像检测方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 96-105. |
| [15] | 刘海涛, 韩鑫, 兰玉彬, 伊丽丽, 王宝聚, 崔立华. 基于YOLOv4网络的棉花顶芽精准识别方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 99-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||