




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 133-144.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0695
收稿日期:2021-08-13
接受日期:2021-11-27
出版日期:2022-06-15
发布日期:2022-06-21
通讯作者:
李琼
作者简介:闫宁 E-mail:3355316860@qq.com;
基金资助:
Ning YAN( ), Yu ZHAN, Xinyue MIAO, Ergang WANG, Changbao CHEN, Qiong LI(
), Yu ZHAN, Xinyue MIAO, Ergang WANG, Changbao CHEN, Qiong LI( )
)
Received:2021-08-13
Accepted:2021-11-27
Online:2022-06-15
Published:2022-06-21
Contact:
Qiong LI
摘要:
强还原土壤灭菌(reductive soil disinfestation,RSD)和土壤熏蒸(soil fumigation,SF)是缓解人参连作障碍的常用方法。为研究2种方法对土壤细菌群落和土壤酶活性的影响,采用高通量测序技术和化学分析方法对强还原土壤灭菌加氯化苦熏蒸(RSD+SF)、强还原土壤灭菌加复合菌(RSD+F)、氯化苦熏蒸加复合菌(SF+F)3种方式改良的土壤细菌群落和土壤酶活性进行分析。结果表明,RSD+F组细菌群落多样性与丰富度均最高,SF+F组均最低,3组拥有相同细菌菌属431个。RSD+SF组中,丰富度最高的细菌为Gemmatimonas,其丰富度为9.17%;RSD+F组中丰富度最高的细菌为norank_f_noranko_Gaiellales,其丰富度为8.72%;RSD+F组中丰富度最高的细菌为Bacillus,其丰富度为9.16%;Bacillus为3种方式改良土壤前10种优势菌群中共有的优势菌群。土壤酶活性与土壤细菌群落结构存在显著性关系,随着生长时间的增加,不同方式改良后的连作人参土壤酶活性均具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。由此可知,3种土壤改良方式均能在不同程度地增加有益细菌属的丰富度并提高土壤酶活性,其中RSD+SF组和RSD+F组的有益细菌属数量及土壤酶活性均高于SF+F组。
中图分类号:
闫宁, 战宇, 苗馨月, 王二刚, 陈长宝, 李琼. 强还原土壤灭菌处理对人参连作土壤细菌群落结构及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 133-144.
Ning YAN, Yu ZHAN, Xinyue MIAO, Ergang WANG, Changbao CHEN, Qiong LI. Effects of Reductive Soil Disinfestation on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Enzyme Activity in Continuous Cropping of Ginseng[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 133-144.
处理组别 Treatment group | 指数Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | Chao | Shannon | Simpson | |
| RSD+SF | 643.59 b | 643.85 b | 4.57 b | 0.024 b |
| RSD+F | 719.21 a | 743.30 a | 4.79 a | 0.010 c |
| SF+F | 555.29 c | 564.38 c | 4.40 c | 0.027 a |
表1 土壤细菌多样性指数
Table 1 Diversity index of soil bacteria
处理组别 Treatment group | 指数Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | Chao | Shannon | Simpson | |
| RSD+SF | 643.59 b | 643.85 b | 4.57 b | 0.024 b |
| RSD+F | 719.21 a | 743.30 a | 4.79 a | 0.010 c |
| SF+F | 555.29 c | 564.38 c | 4.40 c | 0.027 a |
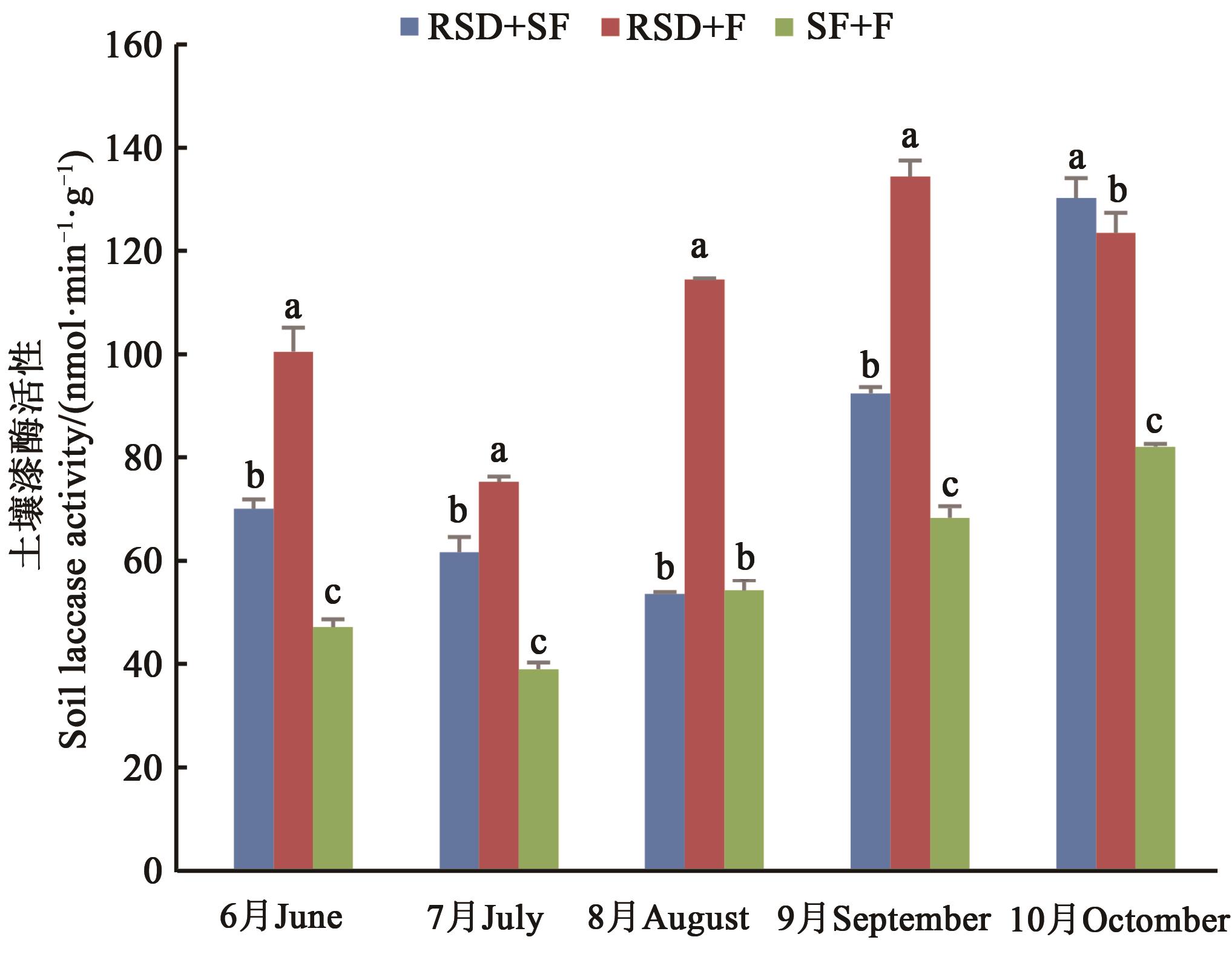
图5 不同方式改良处理人参土壤不同月份的漆酶活性注:同一月份不同小写字母表示P<0.05显著差异。
Fig. 5 Laccase activity in different months of Ginseng soil improved by different methodsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same month indicate significant differences of P<0.05.
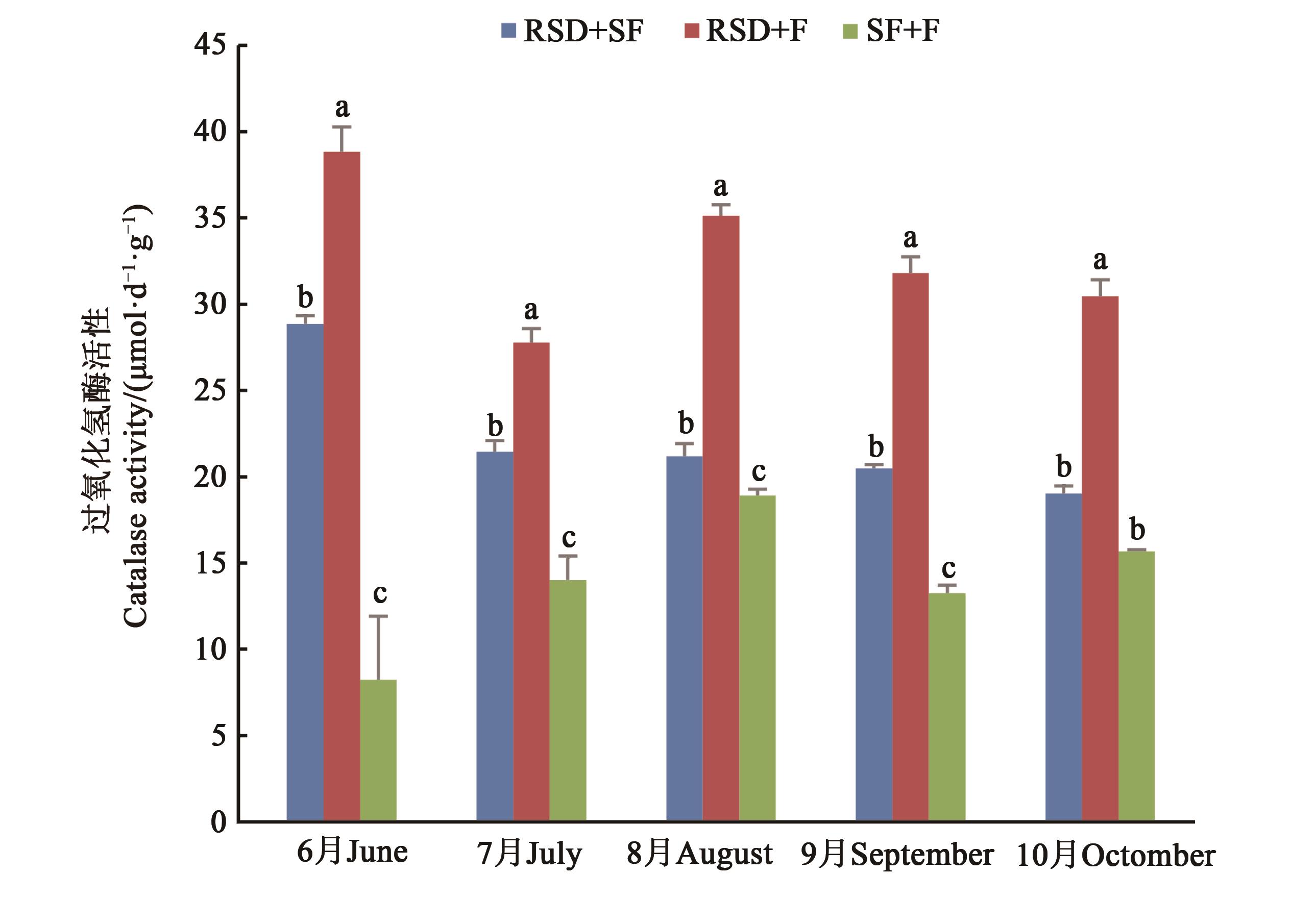
图6 不同方式改良后人参土壤不同月份的过氧化氢酶活性注:同一月份不同小写字母表示P<0.05显著差异。
Fig. 6 Catalase activity in different months of Ginseng soil improved by different methodsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same month indicate significant differences of P<0.05.
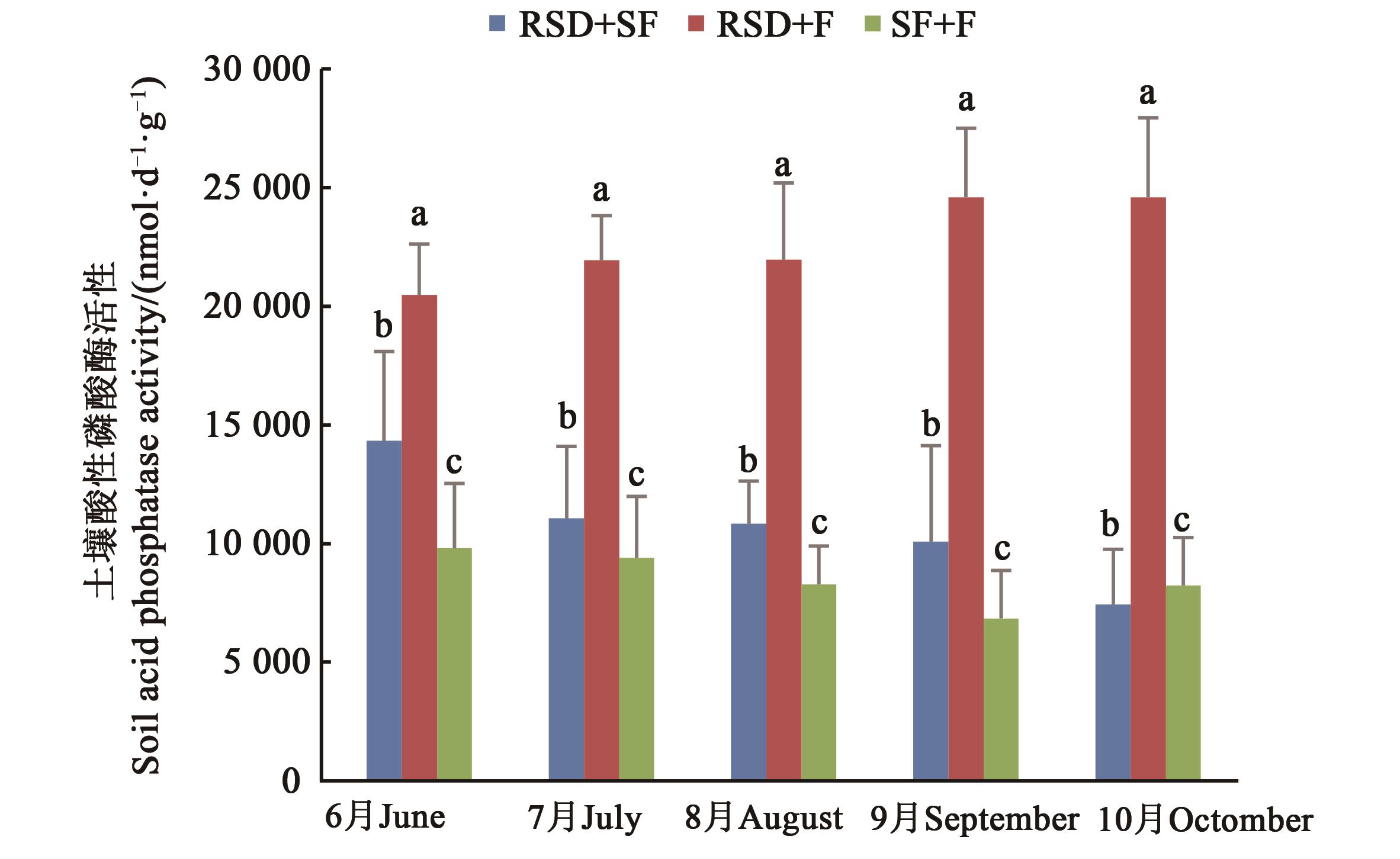
图7 不同方式改良后的人参土壤不同月份的酸性磷酸酶活性注:同一月份不同小写字母表示P<0.05显著差异。
Fig. 7 Acid phosphatase activity in different months of Ginseng soil improved by different methodsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same month indicate significant differences of P<0.05.
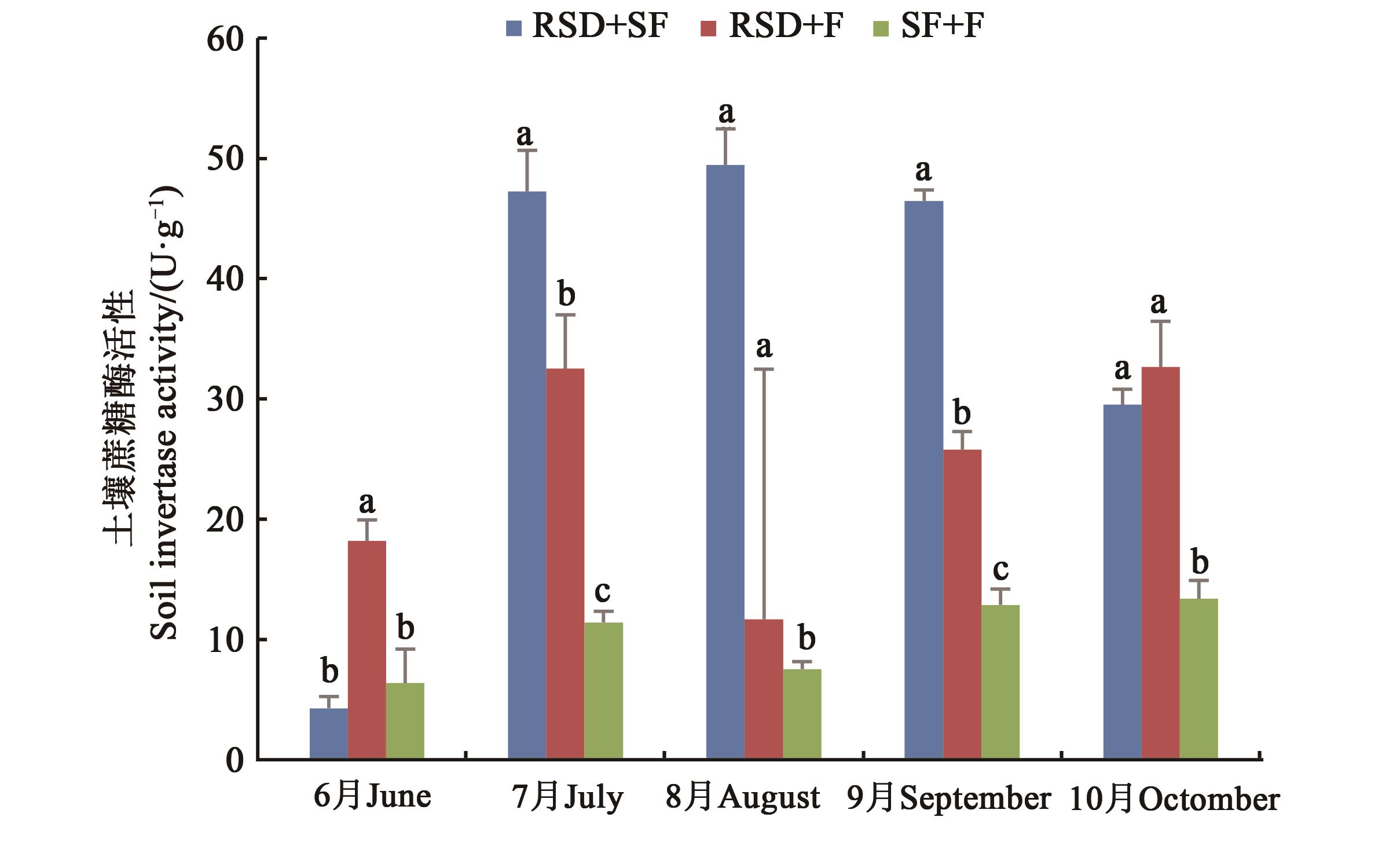
图8 不同方式改良后的人参土壤不同月份的蔗糖酶活性注:同一月份不同小写字母表示P<0.05显著差异。
Fig. 8 Sucrase activity in different months of Ginseng soil improved by different methodsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same month indicate significant differences of P<0.05.
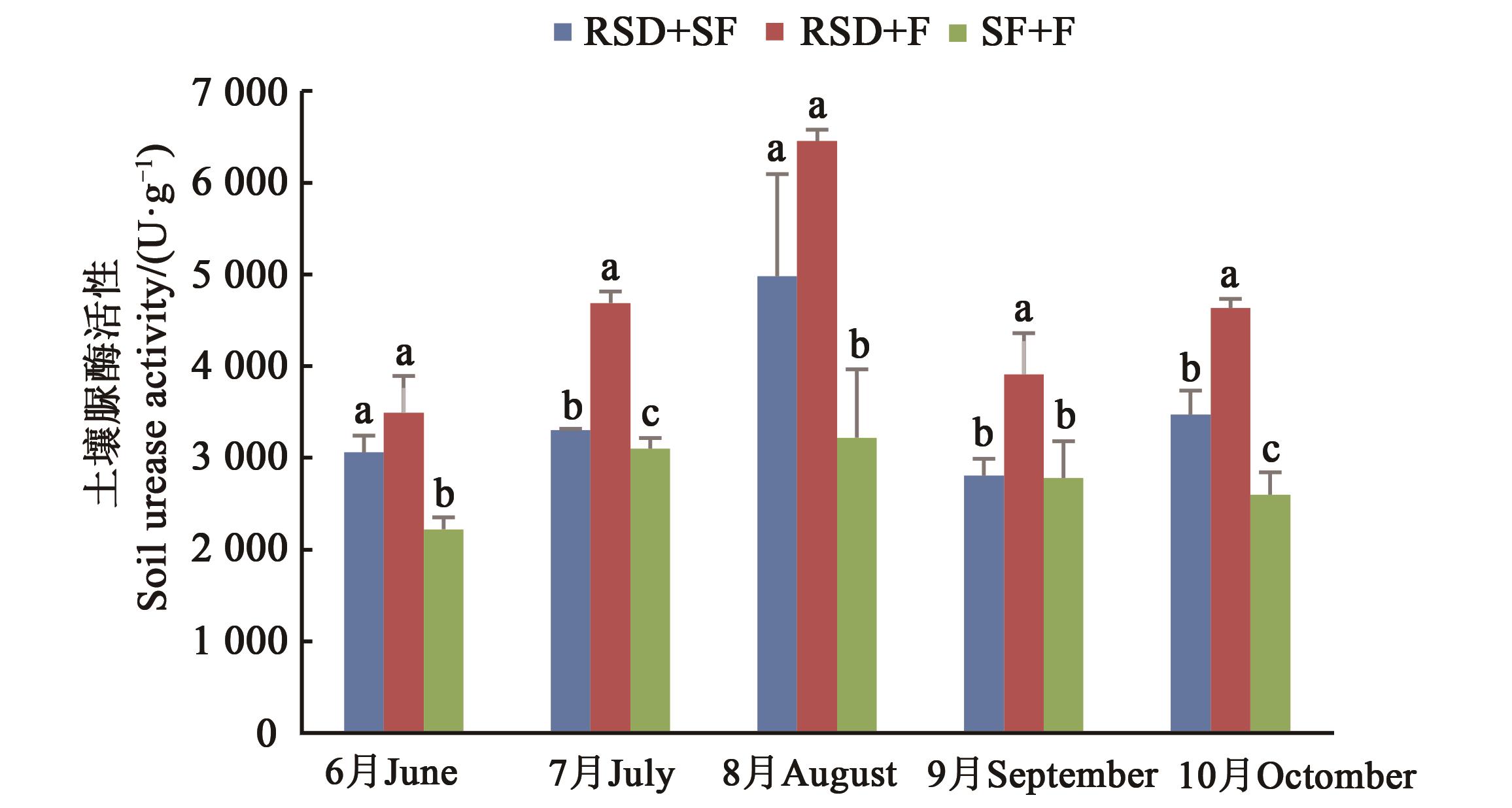
图9 不同方式改良后的人参土壤在不同月份的脲酶活性比较注:同一月份不同小写字母表示P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 9 Urease activity in different months of Ginseng soil improved by different methodsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same month indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
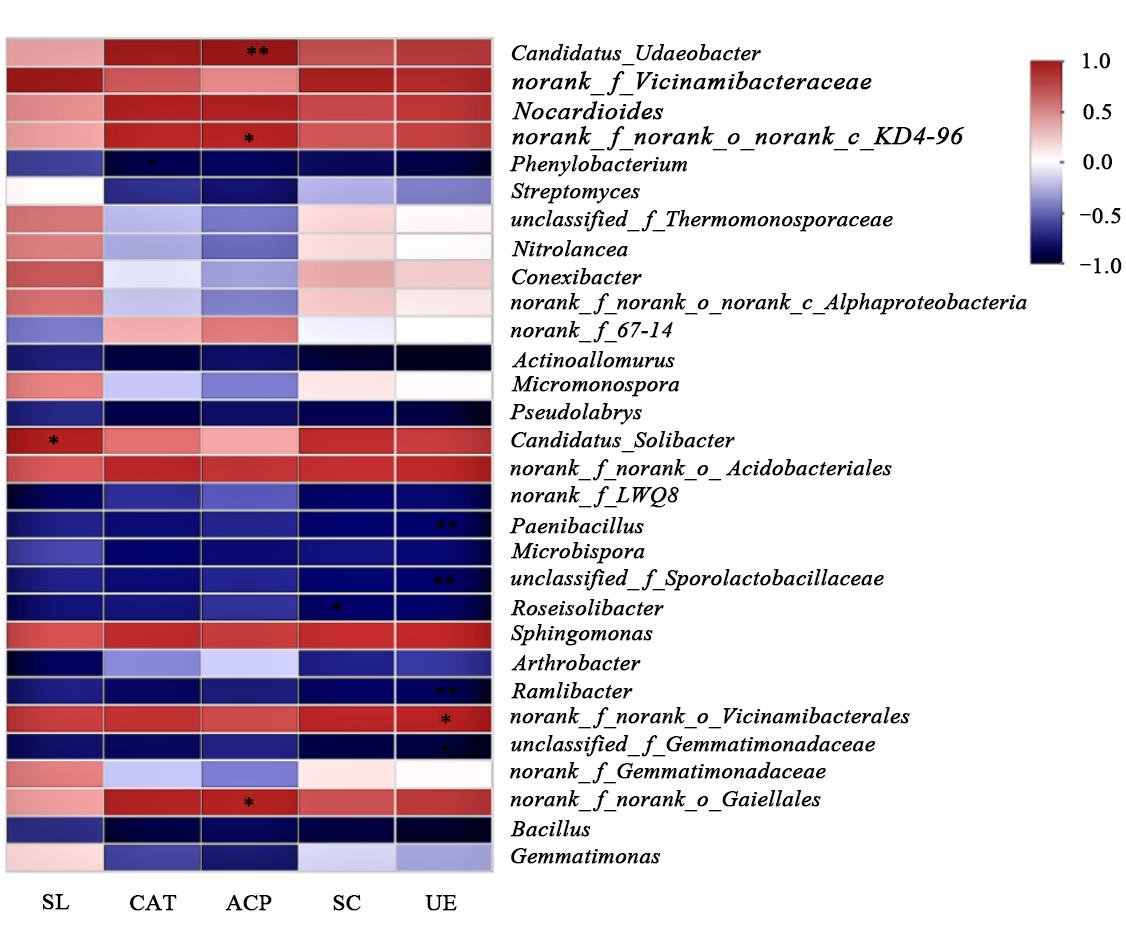
图10 土壤细菌群落与土壤酶活性相关性注:*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 10 Correlation between soil bacterial community and soil enzyme activityNote:* and ** indicate significant difference at P <0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respertively.
| 1 | 孙宝良,孙希.人参栽培技术[J].林业勘查设计, 2017 (1):66-68. |
| SUN B L, SUN X. Ginseng cultivation techniques [J]. For. Exploration Design, 2017(1): 66-68. | |
| 2 | 王一鸣,王兴录.人参多糖提取分离及药理作用研究进展[J].东北农业科学,2021,46(2):103-107. |
| WANG Y M, WANG X L. Research progress on extraction, isolation and pharmacological effects of ginseng polysaccharides [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Sci., 2021,46(2):103-107. | |
| 3 | 刘莹,孙文松,李玲,等.人参连作障碍及防治措施研究进展[J].园艺与种苗,2020,40(7):26-29. |
| LIU Y, SUN W S, LI L, et al.. Research progress on continuous cropping obstacles and control measures of ginseng [J]. Hortic. Seedlings, 2020,40 (7): 26-29. | |
| 4 | 王玲玲.人参连作障碍影响因素及土壤改良技术研究[D].烟台:烟台大学,2016. |
| WANG L L. Study on influencing factors of continuous cropping obstacles of ginseng and soil improvement technology [D]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2016. | |
| 5 | SUN, JUSHENG, GAO, et al.. Parental material and cultivation determine soil bacterial community structure and fertility [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2015. |
| 6 | 卢宝慧,高成林,赵玥, 等.运用高通量测序技术分析人参不同栽培模式根际土壤微生物多样性[J].东北林业大学学报,2021,49(3):113-119. |
| LU B H, GAO C L, ZHAO Y, et al. Analysis of rhizosphere soil microbial diversity in different cultivation modes of Ginseng by high throughput sequencing [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2021,49 (3): 113-119. | |
| 7 | LI Y, FANG F, WEI J, et al.. Humic acid fertilizer improved soil properties and soil microbial diversity of continuous cropping peanut: a three-year experiment [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(10):12014 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 8 | GAO Z, HU Y, HAN M, et al.. Effects of continuous cropping of sweet potatoes on the bacterial community structure in rhizospheric soil [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10:1-11 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 9 | ZHAO J, ZHANG D, YANG Y, et al.. Dissecting the effect of continuous cropping of potato on soil bacterial communities as revealed by high-throughput sequencing [J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(5): e0233356. |
| 10 | ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, XIA P, et al.. Impact of continuous Panax notoginseng plantation on soil microbial and biochemical properties [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1): 13205 [2021-05-06]. . |
| 11 | 王俊仙.基于有机农业种植技术方法和措施分析[J].种子科技,2019,37(11):14-15. |
| WANG J X. Analysis of planting methods and measures based on organic agriculture [J]. Seed Sci. Technol., 2019,37(11):14-15. | |
| 12 | 宋时丽,吴昊,黄鹏伟,等.秸秆还田土壤改良培肥基质和复合菌剂配施对土壤生态的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(11):4562-4576. |
| SONG S L, WU H, HUANG P W, et al. Effects of straw returning to field soil improvement and fertilization matrix and compound bacterial agent on soil ecology [J]. J. Ecol., 2021,41 (11): 4562-4576. | |
| 13 | HUANG B, YAN D, OUYANG C, et al. Chloropicrin fumigation alters the soil phosphorus and the composition of the encoding alkaline phosphatase PhoD gene microbial community [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 711:135080 [2021-11-12]. . |
| 14 | ZHAO J, LIU S, ZHOU X, et al.. Reductive soil disinfestation incorporated with organic residue combination significantly improves soil microbial activity and functional diversity than sole residue incorporation [J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2020, 104(7):1-16. |
| 15 | 朱文娟,王小国.强还原土壤灭菌研究进展[J].土壤,2020,52(2):223-233. |
| ZHU W J, WANG X G. Research progress of strong reduction soil sterilization [J]. Soils, 2020,52(2): 223-233. | |
| 16 | 郭晨曦,周桂芳,陈碧华,等.强还原土壤灭菌法(RSD)对大棚连续三茬蔬菜生长、产量和病虫害的影响[J].河南农业科学,2020,49(11):98-109. |
| GUO C X, ZHOU G F, CHEN B H, et al., Effects of strong reduction soil sterilization (RSD) on growth, yield and diseases and pests of three consecutive crops of vegetables in greenhouse [J]. Henan Agric. Sci., 2020,49 (11): 98-109. | |
| 17 | 刘亮亮,黄新琦,朱睿,等.强还原土壤对尖孢镰刀菌的抑制及微生物区系的影响[J].土壤,2016,48(1):88-94. |
| LIU L L, HUANG X Q, ZHU R, et al.. Influences of reductive soil disinfestation of Fusarium oxysporum and soil microbiome [J]. Soils, 2016,48(1):88-94. | |
| 18 | HUANG X, LIU L, WEN T, et al.. Changes in the soil microbial community after reductive soil disinfestation and cucumber seedling cultivation [J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2016 100(12):5581-5593. |
| 19 | HUANG X, WEN T, ZHANG J, et al.. Toxic organic acids produced in biological soil disinfestation mainly caused the suppression of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense [J]. BioControl, 2015, 60(1):113-124. |
| 20 | MOMMA N, MMOMMAet al K.. Fe2+ and Mn2+, potential agents to induce suppression of Fusarium oxysporum for biological soil disinfestation [J]. J. Gen. Plant Pathol., 2011, 77(6):331-335. |
| 21 | HUANG X, LIU L, WEN T, et al.. Illumina MiSeq investigations on the changes of microbial community in the Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense infected soil during and after reductive soil disinfestation [J]. Microbiol. Res., 2015, 181:33-42. |
| 22 | 檀兴燕.强还原土壤灭菌法缓解番茄连作障碍的效果及其土壤微生物群落的响应机制[D].安徽淮北:淮北师范大学,2019. |
| TAN X Y. Effect of strong reduction soil sterilization on alleviating continuous cropping obstacle of tomato and its response mechanism of soil microbial community [D]. Anhui Huaibei: Huaibei Normal University, 2019. | |
| 23 | 蔡祖聪,张金波,黄新琦,等.强还原土壤灭菌防控作物土传病的应用研究[J].土壤学报,2015,52(3):469-476. |
| CAI Z C, ZHANG J B, HUANG X Q, et al.. Application of strong reduction soil sterilization to prevent and control crop soil borne diseases [J]. J. Soil, 2015,52 (3): 469-476. | |
| 24 | 韩晓磊,严莲荷,周申范.漆酶分泌及其活性影响因素综述[J].化学与生物工程,2005(7):10-13. |
| HAN X L, YAN L H, ZHOU S F. The influences on the production and activity of laccase: a review [J]. Chem. Bioeng., 2005(7):10-13. | |
| 25 | 李冰,李玉双,陈琳,等.沈北新区不同土地利用类型土壤过氧化氢酶活性特征及其影响因素分析[J].沈阳大学学报(自然科学版),2019,31(6):465-473. |
| LI B, LI Y S, CHEN L, et al.. Activity and influencing factors of soils CAT in different utilization types of land in Shenbei area [J]. J. Shenyang Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2019,31(6):465-473. | |
| 26 | 王涵,王果,黄颖颖,等.pH变化对酸性土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态环境,2008,17(6):2401-2406. |
| WANG H, WANG G, HUANG Y Y, et al.. The effects of pH change on the activities of enzymes in an acid soil [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2008,17(6):2401-2406. | |
| 27 | 谢洪宝,于贺,陈一民,等.秸秆深埋对不同氮肥水平土壤蔗糖酶活性的影响[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(24):79-83. |
| XIE H B, YU H, CHEN Y M, et al.. Effects of straw deep burial on soil invertase activity at different nitrogen levels [J]. Chin. Agron. Bull., 2021,37 (24): 79-83. | |
| 28 | 郭继勋,姜世成,林海俊,等.不同草原植被碱化草甸土的酶活性[J].应用生态学报,1997(4):412-416. |
| GUO J X, JIANG S C, LIN H J, et al.. Enzyme activities in alkalized meadow soil of different steppe vegetation [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol.,1997(4):412-416. | |
| 29 | 李琼.人参皂苷对连作土壤锈腐病趋重发生的作用及其机理[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2020. |
| LI Q. Effect and mechanism of Ginsenoside on the aggravation of soil rust rot in continuous cropping [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 30 | ALI A, GHANI M I, LI Y, et al.. Hiseq base molecular characterization of soil microbial community, diversity structure, and predictive functional profiling in continuous cucumber planted soil affected by diverse cropping systems in an intensive greenhouse region of Northern China [J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20(11): 1-22. |
| 31 | 刘海娇,苏应威,方岚,等.茴香轮作调控土壤细菌群落缓解三七连作障碍的效应及机制[J].中国生物防治学报,2021,37(1):139-149. |
| LIU H J, SU Y W, FANG L, et al. Effect and mechanism of fennel rotation on regulating soil bacterial community and alleviating continuous cropping obstacle of Panax notoginseng [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Control, 2021,37 (1): 139-149. | |
| 32 | SAXENA A K, KUMAR M, CHAKDAR H, et al. Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition [J]. Appl. Microbiol., 2020, 128(6):1583-1594. |
| 33 | GOSWAMI D, THAKKER J N, DHANDHUKIA P C, et al. Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): a review [J/OL]. Cogent Food Agric., 2016, 2(1):1127500 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 34 | MELO A L, SOCCOL V T, SOCCOL C R. Bacillus thuringiensis: mechanism of action, resistance, and new applications: a review [J]. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 2016, 36(2):317-326. |
| 35 | QIN S, YEBOAH S, CAO L, et al.. Breaking continuous potato cropping with legumes improves soil microbial communities, enzyme activities and tuber yield [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5):e0175934 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 36 | SINGH R, CABRERA M, RADCLIFFE D E,et al.. Laccase mediated transformation of 17 beta-estradiol in soil [J]. Environ. Poll., 2015, 197: 28-35. |
| 37 | FENG S, SU Y, DONG M,et al.. Laccase activity is proportional to the abundance of bacterial laccase-like genes in soil from subtropical arable land [J]. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 31(12):2039-2045. |
| 38 | 朱文娟,王小国.强还原土壤灭菌研究进展[J].土壤,2020,52(2):223-233. |
| ZHU W J, WANG X G. Research progress of strong reduction soil sterilization [J]. Soils, 2020,52 (2): 223-233. | |
| 39 | 刘晨阳,高成林,赵玥,等.农田栽参土壤改良中肥料对土壤元素及酶活性的影响[J].生态科学,2021,40(2):40-47. |
| LIU C Y, GAO C L, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of fertilizer on soil elements and enzyme activities in farmland Ginseng soil improvement [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2021,40 (2): 40-47. | |
| 40 | 黄雪琳,杨静,贺宇纯.土壤酶活性的主要影响因素分析[J].现代园艺,2018(11):92-93. |
| Huang X L, Yang J, HE Y C. Analysis of main factors affecting soil enzyme activity [J]. Modern Hortic.,2018(11): 92-93. | |
| 41 | 黄宇,张海伟,徐芳森.植物酸性磷酸酶的研究进展[J].华中农业大学学报,2008(1):148-154. |
| HUANG Y, ZHANG H W, XU F S. Research progress on plant acid phosphatase [J]. J. Huazhong Agric.Univ., 2008(1):148-154. | |
| 42 | 骆爱兰,余向阳.氟啶胺对土壤中蔗糖酶活性及呼吸作用的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2011,19(4):902-906. |
| 43 | LUO A L, YU X Y. Effects of haloperidol on invertase activity and respiration in soil [J]. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric., 2011,19 (4): 902-906. |
| 44 | 王启宇,吕怡颖,杨敏,等.烤烟根结线虫病发生与土壤酶活性的相关性研究[J].湖南农业科学,2021(8):32-35. |
| 45 | WANG Q Y, LYU Y Y, YANG M, et al.. Study on the correlation between the occurrence of flue-cured tobacco root knot nematode and soil enzyme activity [J]. Hunan Agric. Sci., 2021 (8): 32-35. |
| 46 | 焦治芳.长期施肥对黄土高原小麦农田土壤酶活性的影响[D].兰州:兰州大学,2010. |
| JIAO Z F. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil enzyme activity of wheat farmland in the loess plateau [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. | |
| 47 | 徐彬,徐健,祁建杭,等.枯草芽孢杆菌1013对连作障碍土壤的改良及对番茄的促生作用[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2021,42(2):111-116. |
| XU B, XU J, QI J H, et al. Improvement of continuous cropping barrier soil and growth promoting effect of Bacillus subtilis 1013 on tomato [J]. J. Yangzhou Univ (Agric. Life Sci.), 2021,42 (2): 111-116. |
| [1] | 周琦, 刘强, 张靖, 邓超超, 王振龙, 柳洋, 吴芳, 常浩, 周彦芳, 宿翠翠, 施志国, 高正睿, 马凤捷. 有机肥替代化肥对土壤生物学特性及南瓜产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 190-203. |
| [2] | 王二刚, 吕朋元, 周一, 战宇, 何贵祥, 王丽翔, 苗馨月, 陈长宝, 李琼. 生防细菌对人参连作土壤性质及细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 140-148. |
| [3] | 李大荣, 李小玲, 周武先, 张美德, 蒋小刚, 由金文, 王华. 有机肥替代部分化肥对湖北贝母生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 216-226. |
| [4] | 马振华, 时倩茹, 宁欣杰, 魏宏杨, 王璨, 张静静, 张彪, 杨素勤. 生物质炭对镉铅污染土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 201-210. |
| [5] | 徐哲丰, 刘春铄, 廖旭东, 隋佳宏, 陈雨秋, 陈长宝, 张涛, 魏丽娜. 生态因子对林地参和农田参质量差异的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 213-223. |
| [6] | 刘霏霏, 何万荣, 孙强, 席琳乔, 廖结安, 韩路. 苜蓿绿肥对塔里木盆地苹果园土壤细菌多样性和功能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 223-233. |
| [7] | 谢勇俊, 潘小卓, 陈福慧, 尹凯波, 金嘉悦, 王一兵. 人参酚酸类自毒物质降解菌的筛选鉴定及生防研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 147-155. |
| [8] | 杜洋洋, 包媛媛, 刘项宇, 张新永. 荞麦轮作对云南栽培马铃薯根际土壤酶活和微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 192-200. |
| [9] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [10] | 周旭东, 韩天华, 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 贺彪, 杨明英, 裴卫华, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 4种轮作模式下长期连作烟田土壤微生态的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 174-187. |
| [11] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [12] | 方泰军, 侯璐, 白露超. 柴达木地区患根腐病枸杞根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [13] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [14] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [15] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||