




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 181-192.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2025.0141
仝姗姗1( ), 金锋1, 杨清竹1, 张瑞芳2,3, 王鑫鑫2, 王红1,2,3(
), 金锋1, 杨清竹1, 张瑞芳2,3, 王鑫鑫2, 王红1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-02
接受日期:2025-03-25
出版日期:2025-09-15
发布日期:2025-09-24
通讯作者:
王红
作者简介:仝姗姗 E-mail:2309728554@qq.com;
基金资助:
Shanshan TONG1( ), Feng JIN1, Qingzhu YANG1, Ruifang ZHANG2,3, Xinxin WANG2, Hong WANG1,2,3(
), Feng JIN1, Qingzhu YANG1, Ruifang ZHANG2,3, Xinxin WANG2, Hong WANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-02
Accepted:2025-03-25
Online:2025-09-15
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
Hong WANG
摘要:
为揭示膜下滴灌条件下,片麻岩山坡地新成土梨园土壤养分随施肥年限的垂直分布规律,以整地后8年内未施肥、未种植作物的地块为对照,研究不同膜下滴灌施肥年限(3~8年)下,不同土层(0—20、20—40、40—60 cm)梨园土壤的养分积累与分布。结果表明,施肥年限显著影响梨园土壤养分含量,除pH外,各养分因子均以施肥8年处理最高。与对照相比,膜下滴灌配施有机肥处理显著提高梨园土壤的有机质、阳离子交换量、水解氮、有效磷、速效钾含量,增幅为6.87%~691.60%;同时,梨园不同土层土壤中的微量元素含量也随施肥年限的延长呈增加趋势,增幅为122.00%~258.00%。随着施肥年限的增加,存在较长施肥年限40—60 cm土层中水解氮、有效磷等含量高于较短施肥年限0—20 cm土层养分含量现象,其中,施肥8年处理的40—60 cm土壤水解性氮和有效磷含量较施肥3年处理0—20 cm土壤分别增加24.3%和31.45%,由此表明,长期施肥驱动养分向深层迁移。土壤各养分含量整体呈现表聚现象,以施肥第5年为养分垂直迁移拐点,此后深层土壤的有效磷、速效钾累积速率加快,表聚系数降低。综上表明,膜下滴灌施肥与有机肥配施可高效提升片麻岩山地梨园全剖面土壤肥力,但长期施用(>5年)将导致速效养分突破淋失风险阈值,因此需结合深根作物调控或优化施肥频次。
中图分类号:
仝姗姗, 金锋, 杨清竹, 张瑞芳, 王鑫鑫, 王红. 膜下滴灌施肥对片麻岩新生土梨园土壤养分积累与分布的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 181-192.
Shanshan TONG, Feng JIN, Qingzhu YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Xinxin WANG, Hong WANG. Effects of Fertilization by Mulched Drip Irrigation on Soil Nutrient Accumulation and Distribution in Pear Orchards on Gneiss Mountain Slopes[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 181-192.
指标 Index | 施肥年限 Fertilization year | 土壤深度 Soil depth | 施肥年限×土壤深度 Fertilization years×soil depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质Organic matter | 32.098*** | 85.951*** | 3.123** |
| 水解性氮Alkali-hydrolyzable N | 19.422*** | 31.203*** | 2.323* |
| 有效磷Available P | 24.601*** | 101.699*** | 12.396*** |
| 速效钾Available K | 45.374*** | 190.960*** | 18.455*** |
| pH | 0.268 | 0.059 | 0.223 |
| 全盐Full salt | 21.247*** | 17.829*** | 6.578*** |
| 阳离子交换量Cation exchange | 9.985*** | 3.142 | 2.228* |
| 交换性钙Exchangeable Ca | 8.789*** | 10.234** | 5.285*** |
| 交换性镁Exchangeable Mg | 18.790*** | 18.448*** | 1.874 |
| 有效硫Available S | 77.511*** | 37.805*** | 50.142*** |
| 有效铁Available Fe | 32.541*** | 20.059*** | 3.186** |
| 有效锰Available Mn | 28.665*** | 17.086*** | 2.944** |
| 有效铜Available Cu | 20.937*** | 10.827*** | 2.747** |
| 有效锌Available Zn | 64.530*** | 30.250*** | 10.922*** |
表1 梨园不同施肥年限土壤垂直分布方差分析
Table 1 Analysis of variance in vertical distribution of soil in pear orchard with different fertilization years
指标 Index | 施肥年限 Fertilization year | 土壤深度 Soil depth | 施肥年限×土壤深度 Fertilization years×soil depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质Organic matter | 32.098*** | 85.951*** | 3.123** |
| 水解性氮Alkali-hydrolyzable N | 19.422*** | 31.203*** | 2.323* |
| 有效磷Available P | 24.601*** | 101.699*** | 12.396*** |
| 速效钾Available K | 45.374*** | 190.960*** | 18.455*** |
| pH | 0.268 | 0.059 | 0.223 |
| 全盐Full salt | 21.247*** | 17.829*** | 6.578*** |
| 阳离子交换量Cation exchange | 9.985*** | 3.142 | 2.228* |
| 交换性钙Exchangeable Ca | 8.789*** | 10.234** | 5.285*** |
| 交换性镁Exchangeable Mg | 18.790*** | 18.448*** | 1.874 |
| 有效硫Available S | 77.511*** | 37.805*** | 50.142*** |
| 有效铁Available Fe | 32.541*** | 20.059*** | 3.186** |
| 有效锰Available Mn | 28.665*** | 17.086*** | 2.944** |
| 有效铜Available Cu | 20.937*** | 10.827*** | 2.747** |
| 有效锌Available Zn | 64.530*** | 30.250*** | 10.922*** |

图1 梨园不同施肥年限下不同土层土壤的理化性质注:不同英文字母表示同一土层不同施肥年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示相同施肥年限不同土层间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Soil physicochemical properties in different soil layers of pear orchards under different fertilization yearsNote:Different English letters indicate significant differences between different fertilization years in same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers of same fertilization year at P<0.05 level.
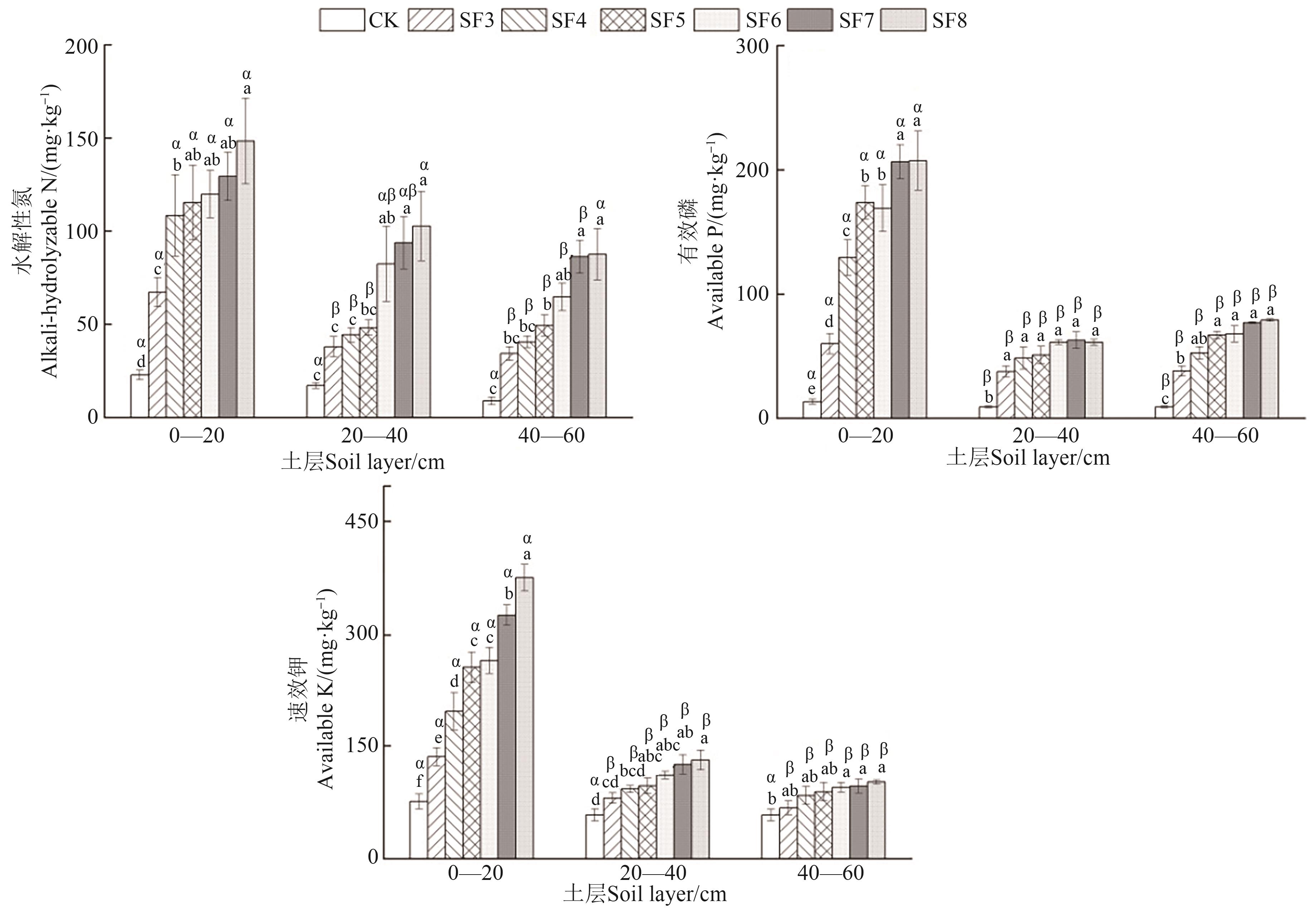
图2 梨园不同施肥年限下不同土层土壤的大量元素含量注:不同英文字母表示同一土层不同施肥年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示相同施肥年限不同土层间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Major elements in different soil layers of pear orchards under different fertilization yearsNote:Different English letters indicate significant differences between different fertilization years in same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers of same fertilization year at P<0.05 level.
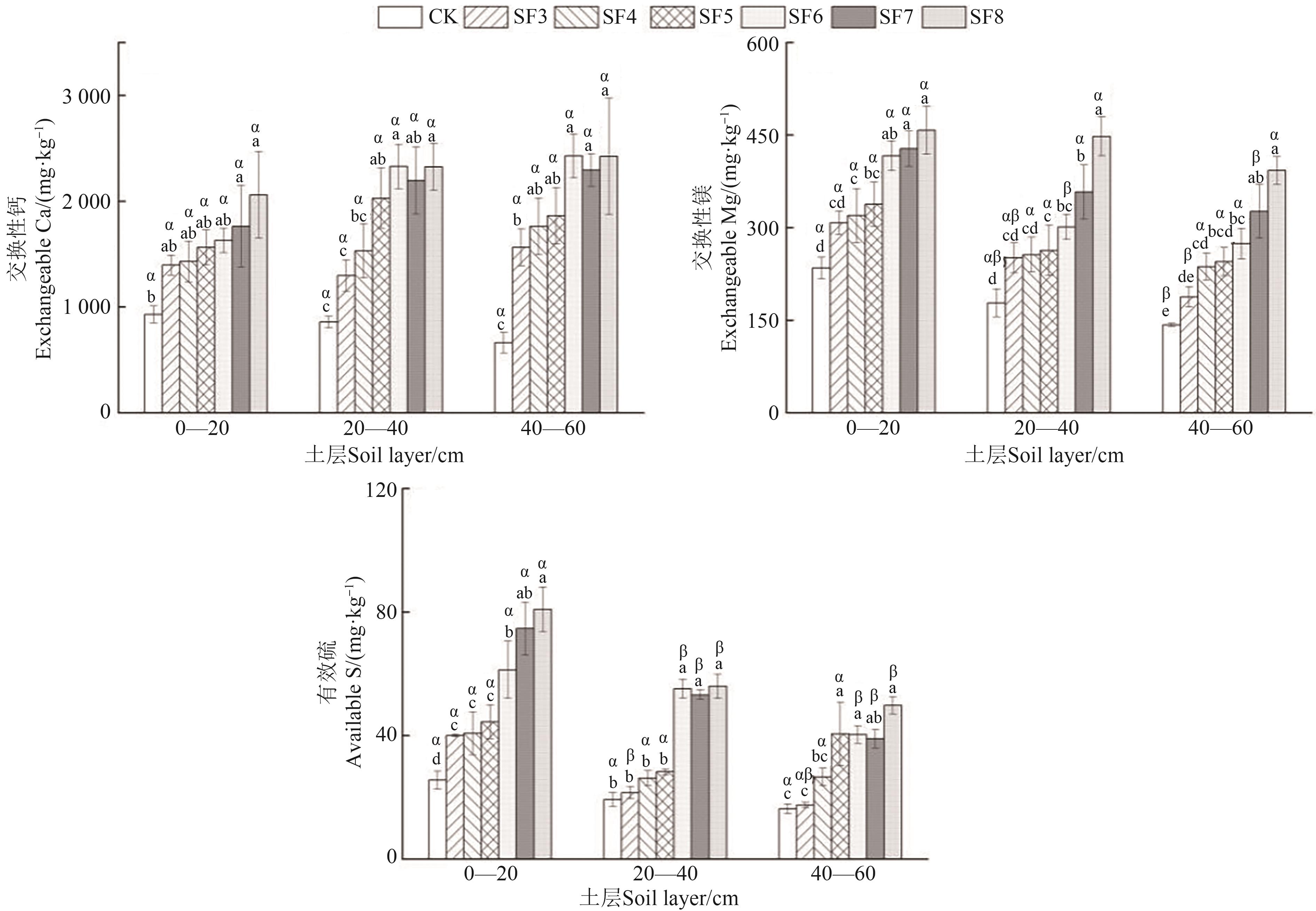
图3 梨园不同施肥年限下不同土层土壤的中量元素注:不同英文字母表示同一土层不同施肥年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示相同施肥年限不同土层间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Medium elements in different soil layers of pear orchards under different fertilizer yearsNote:Different English letters indicate significant differences between different fertilization years in same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers of same fertilization year at P<0.05 level.
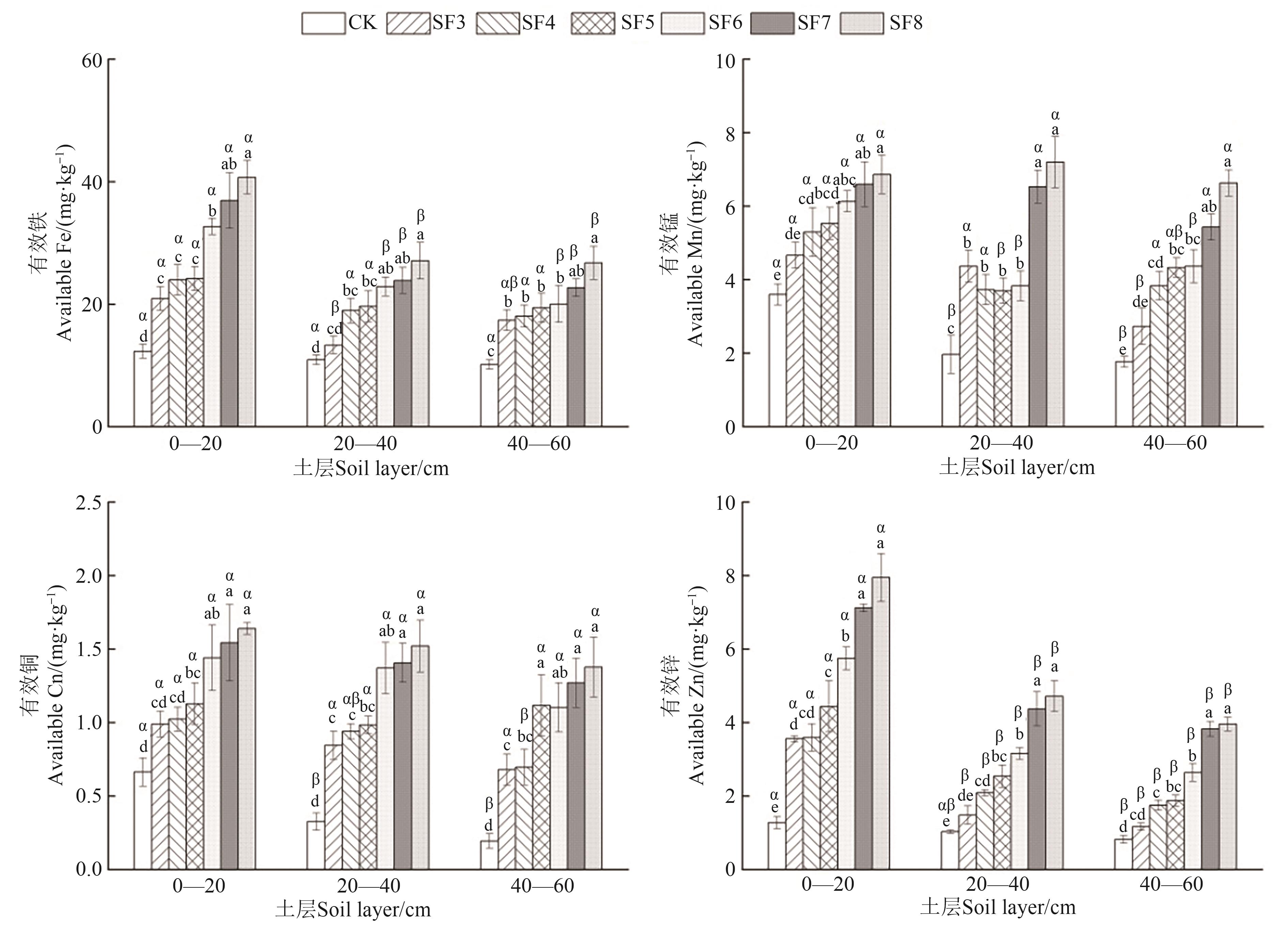
图4 梨园不同施肥年限下不同土层土壤的微量元素含量注:不同英文字母表示同一土层不同施肥年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示相同施肥年限不同土层间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Trace elements contents in different soil layers of pear orchards under different fertilization yearsNote:Different English letters indicate significant differences between different fertilization years in same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers of same fertilization year at P<0.05 level.
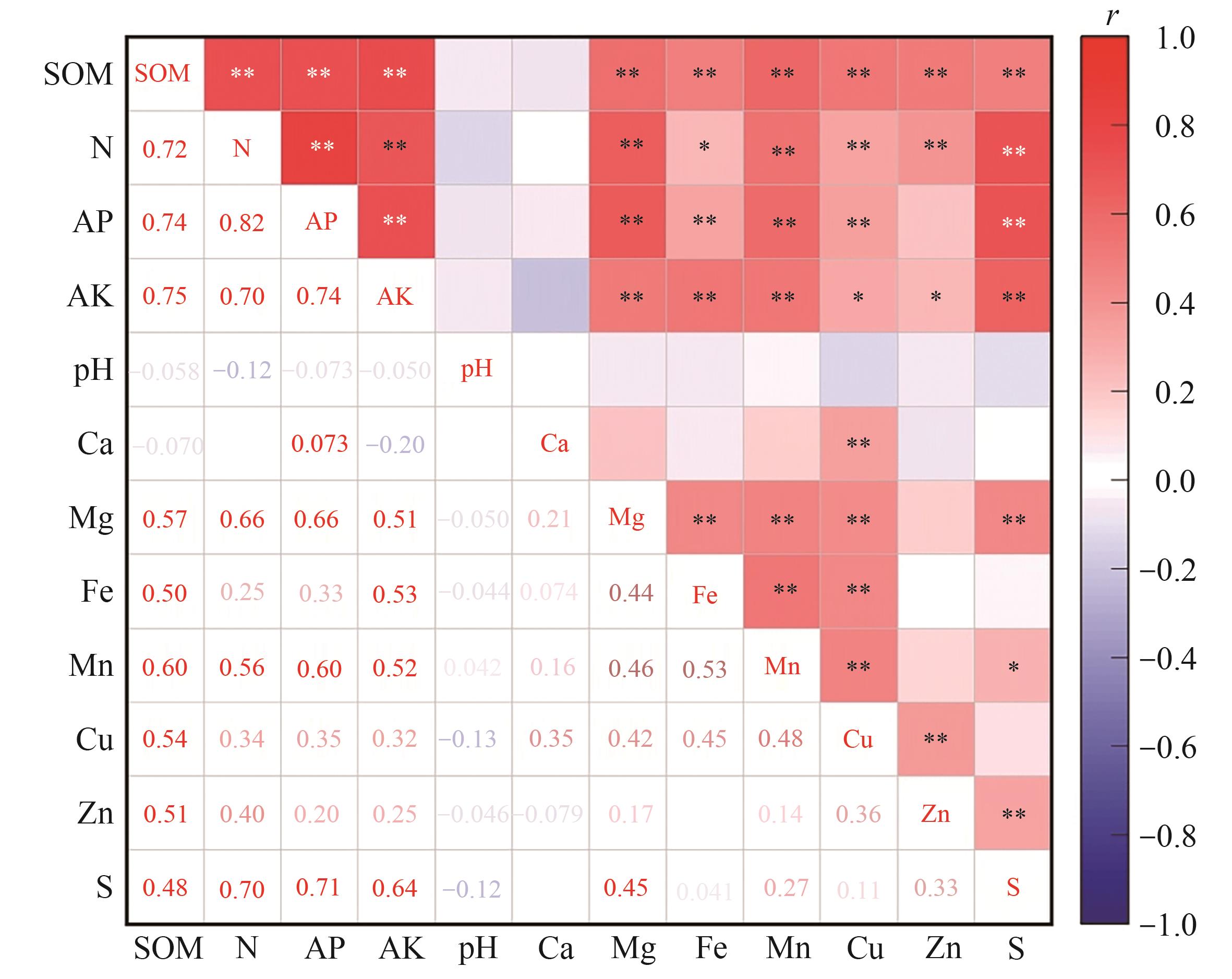
图5 梨园土壤养分指标相关性分析注:*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。AK—土壤速效钾;AP—土壤有效磷;N—土壤水解性氮;SOM—土壤有机质;pH—土壤pH;Ca—交换性钙;Mg—交换性镁;S—有效硫;Fe—有效铁;Mn—有效锰;Cu —有效铜;Zn—有效锌。
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis of soil nutrient indexes in pear orchardsNote: * and ** indicate significant correlation at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels; respectively. AK—Available K; AP—Available P; N—Alkali-hydrolyzable N; SOM—Organic matter; pH—Soil pH; Ca—Exchangeable Ca; Mg—Exchangeable Mg; S—Available S; Fe—Available Fe; Mn—Available Mn; Cu—Available Cu; Zn—Available Zn.
处理 Treatment | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 等级Grade | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter | 水解性氮Alkali-hydrolyzable N | 有效磷Available P | 速效钾Available K | 有效铁Available Fe | 有效锰Available Mn | 有效铜Available Cu | 有效锌Available Zn | ||
| CK | 0—20 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| 20—40 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| 40—60 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| SF3 | 0—20 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| SF4 | 0—20 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| SF5 | 0—20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| SF6 | 0—20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| SF7 | 0—20 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| SF8 | 0—20 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
表2 不同施肥年限下梨园不同土层土壤养分等级
Table 2 Soil nutrient grade in different soil layers of pear orchards under different fertilization years
处理 Treatment | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 等级Grade | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter | 水解性氮Alkali-hydrolyzable N | 有效磷Available P | 速效钾Available K | 有效铁Available Fe | 有效锰Available Mn | 有效铜Available Cu | 有效锌Available Zn | ||
| CK | 0—20 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| 20—40 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| 40—60 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| SF3 | 0—20 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| SF4 | 0—20 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| SF5 | 0—20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| SF6 | 0—20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| SF7 | 0—20 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| SF8 | 0—20 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 20—40 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40—60 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
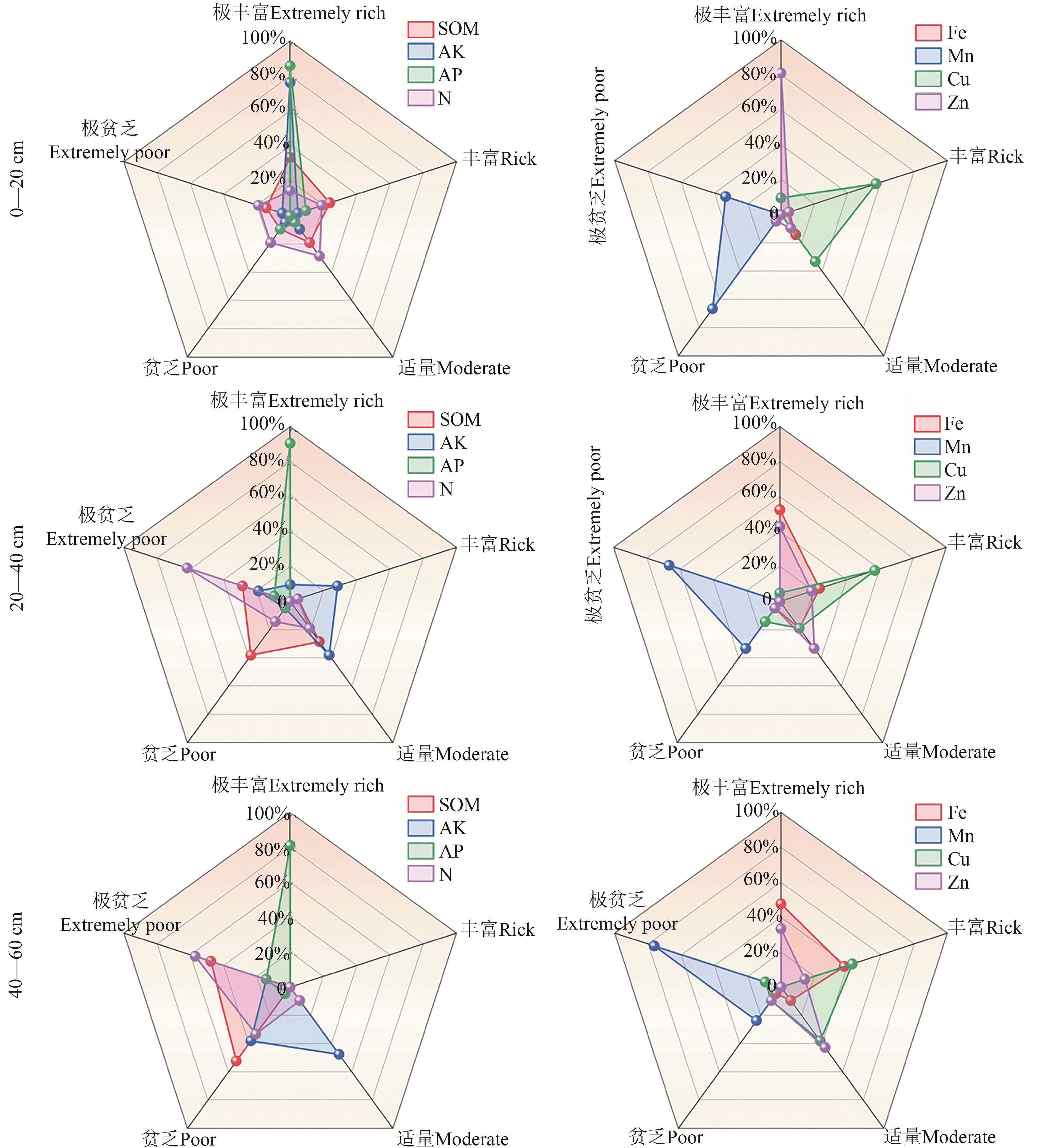
图6 梨园土壤养分等级评价注:AK—速效钾;AP—有效磷;N—水解氮;SOM—有机质;Fe—有效铁;Mn—有效锰;Cu—有效铜;Zn—有效锌。
Fig. 6 Soil nutrient grade evaluation of pear orchardNote:AK—Available K; AP—Available P; N—Alkali-hydrolyzable N; SOM—Organic matter; Fe—Available Fe; Mn—Available Mn; Cu—Available Cu; Zn—Available Zn.
| [1] | 明健.平山片麻岩微立地划分、植被特征及植物配置研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学,2019. |
| MING J. Study on micro-site division, vegetation characteristics and optimal allocation of Pingshan gneiss [D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019. | |
| [2] | 史薪钰,陈梦华,齐国辉,等.片麻岩山地土壤团聚体分布及养分特征[J].水土保持学报, 2015, 29(5): 172-175. |
| SHI X Y, CHEN M H, QI G H, et al.. Distribution and nutrient charicteristics of soil aggregates in gneiss mountainous region [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2015, 29(5): 172-175. | |
| [3] | 袁振,魏松坡,贾黎明,等.河北平山片麻岩山区微地形表层土壤养分异质性分析[J].水土保持研究, 2017, 24(6): 84-90. |
| YUAN Z, WEI S P, JIA L M, et al.. Heterogeneity analysis of micro-topography surface soil nutrients in Pingshan gneiss mountain area, Hebei province [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 24(6): 84-90. | |
| [4] | 王冲,秦亚旭,张珂,等.渭北旱塬矮化苹果园滴灌下土壤剖面水分和养分时空分布特征[J].水土保持学报,2020,34(5):343-348. |
| WANG C, QIN Y X, ZHANG K, et al.. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of water and nutrients in soil profile under drip irrigation in dwarf apple orchard in Weibei dryland [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2020, 34(5): 343-348. | |
| [5] | WANG L, WU W, XIAO J, et al.. Effects of different drip irrigation modes on water use efficiency of pear trees in Northern China [J/OL]. Agric. Water Manage., 2021, 245: 106660 [2025-02-10]. . |
| [6] | 韩哲群,高奇奇,贾昂元,等.智能滴灌水肥一体化下有机物料对盐碱地土壤性状与向日葵产量的影响[J/OL].中国土壤与肥料, 2024: 1-17[2025-02-10].. |
| HAN Z Q, GAO Q Q, JIA A Y, et al.. Effects of organic materials on soil properties and sunflower yield in saline-alkali soil under intelligent drip irrigation and water and fertilizer integration [J/OL]. China Soils Fert., 2024:1-17 [2025-02-10]. . | |
| [7] | SONG K, QIN Q, YANG Y F, et al.. Drip fertigation and plant hedgerows significantly reduce nitrogen and phosphorus losses and maintain high fruit yields in intensive orchards [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2023, 22(2): 598-610. |
| [8] | TITA V, NIJLOVEANU D, ANASTASIU P D, et al.. Study on the efficiency of the design of the drip irrigation management system using plastics [J]. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst., 2022, 43(2):1697-1705. |
| [9] | 刘子君,叶赟,王丽,等.滴喷灌施肥方式对土壤养分空间分异及茶苗根系生长的影响[J].水土保持学报,2022,36(6):330-339. |
| LIU Z J, YE Y, WANG L, et al.. Effects of drip irrigation fertilization methods on spatial differentiation of soil nutrients and root growth of tea seedlings [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2022, 36(6): 330-339. | |
| [10] | ZHANG X, LIU Y, ZHANG Z, et al.. Soil moisture influences wheat yield by affecting root growth and the composition of microbial communities under drip fertigation [J/OL]. Agric. Water Manage., 2024, 305: 109102 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [11] | MAHMOOD F, KHAN I, ASHRAF U, et al.. Effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their residual impact on soil physico-chemical properties [J/OL]. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2017, 17(ahead):2 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [12] | 马常宝,薛彦东,徐明岗,等. 耕地质量监测技术规程 [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2019. |
| [13] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| [14] | LI Z, MAO C, WU Q, et al.. Temporal variations in aboveground biomass, nutrient content, and ecological stoichiometry in young and middle-aged stands of Chinese fir forests [J/OL]. Plants (Basel), 2024, 13(13): 1877 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [15] | AFATA T N, MEKONEN S, SOGN T A, et al.. Examining the effect of agrochemicals on soil microbiological activity, availabilitymicronutrient, and uptake by maize (Zea mays L.) plants [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2024, 14(6):1321 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [16] | MORASH J, PAMURU S T, LEA-COX J D, et al.. Using organic amendments in disturbed soil to enhance soil organic matter, nutrient content and turfgrass establishment [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2024, 945: 174033 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [17] | 王英凡,何永涛,孙维,等.长期不同施肥模式对拉萨河谷农田土壤养分的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2024(9):228-237. |
| WANG Y F, HE Y T, SUN W, et al.. Effects of long-term different fertilization on farmland soil nutrients in the Lhasa River Valley [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2024(9): 228-237. | |
| [18] | 张玉星.果树栽培学各论:北方本[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2003:1-461. |
| [19] | BHAGAT R, WALIA S S, DHERI G S, et al.. Pear (Pyrus communis)-based agroecosystem improves soil nutrient dynamics, microbial biomass, enzymatic activity, farm productivity and profitability [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2024, 336:113398 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [20] | ZHANG J, CAI J, XU D, et al.. Soil salinization poses greater effects than soil moisture on field crop growth and yield in arid farming areas with intense irrigation [J/OL]. J. Clean. Prod., 2024, 451: 142007 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [21] | 丛萍,李玉义,高志娟,等.秸秆颗粒化高量还田快速提高土壤有机碳含量及小麦玉米产量[J].农业工程学报,2019,35(1):148-156. |
| CONG P, LI Y Y, GAO Z J, et al.. High-volume straw granulation returning to field to quickly increase soil organic carbon content and wheat and maize yield [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2019, 35(1): 148-156. | |
| [22] | GUO J, WANG B, WANG G, et al.. Effects of three cropland afforestation practices on the vertical distribution of soil organic carbon pools and nutrients in Eastern China [J/OL]. Glob. Ecol. Conserv., 2020, 22: e00913 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [23] | 陈伟,王红阳,王志坚,等.黄土丘陵区香梨园土壤水分、养分分布特征及其与产量的关系[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(9):3159-3166. |
| CHEN W, WANG H Y, WANG Z J, et al.. Distribution characteristics of soil moisture and nutrients and their relationship with yield in pear orchard in Loess Hilly Region [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2021, 32(9): 3159-3166. | |
| [24] | 张加良,孔涛,高熙梣,等.辽西北沙地苹果-农作物间作对土壤养分分布和收益的影响[J].生态学杂志,2024,43(5):1314-1323. |
| ZHANG J L, KONG T, GAO X C, et al.. Effects of apple-crop intercropping on soil nutrient distribution and income in sandy land of northwest Liaoning province [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2024, 43(5): 1314-1323. | |
| [25] | 张玲,褚杰,孙昊,等.北京市大兴区不同类型果园土壤肥力和环境质量研究[J].中国土壤与肥料,2023(8):14-22. |
| ZHANG L, CHU J, SUN H, et al.. Study on soil fertility and environmental quality of different orchards in Daxing district of Beijing [J]. Soils Fert. Sci. China, 2023(8): 14-22. | |
| [26] | 李祥,宁琪,周佳逸,等.长期定位施肥对甘薯-小麦体系剖面土壤质量的影响[J].土壤,2024,56(6):1214-1221. |
| LI X, NING Q, ZHOU J Y, et al.. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil quality of sweet potato-wheat system profile [J]. Soils, 2024, 56(6): 1214-1221. | |
| [27] | JAKHRO M I, LI Z. Organic fertilization and its effects on storage of carbon and nitrogen in apple orchard soil: a meta-analysis [J]. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2025, 25(1): 53-66. |
| [28] | 吴昊,葛梅红,王烁衡,等.化肥优化减施杧果园磷钾养分平衡与环境风险[J].西南农业学报,2022,35(6):1355-1364. |
| WU H, GE M H, WANG S H, et al.. Optimization of chemical fertilizers and reduction of phosphorus and potassium nutrient balance and environmental risks in Castanopsis kawakamii orchard [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2022, 35(6): 1355-1364. | |
| [29] | LIU B, XIA H, JIANG C, et al.. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2022, 841: 156608 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [30] | CHEN J, RAN W, ZHAO Y, et al.. Effects of fertilization on soil ecological stoichiometry and fruit quality in Karst pitaya orchard [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2024, 14(1): 18307 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [31] | WOJCIECH K, DARIUSZ W, SEBASTIAN P. Effect of nitrogen fertilization of apple orchard on soil mineral nitrogen content, yielding of the apple trees and nutritional status of leaves and fruits [J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(12): 2169-2178. |
| [32] | 汪宗兰.库尔勒典型香梨种植区土壤质量空间变异性分析及评价[D].石河子:石河子大学,2023. |
| WANG Z L. Spatial variability of soil quality in typical Korla fragrant pear growing areas in Korla analysis and evaluation [D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2023. | |
| [33] | ZHANG J, LIN G, ZENG D H. Long-term nitrogen addition modifies fine root growth and vertical distribution by affecting soil nutrient availability in a Mongolian pine plantation [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2024, 921: 171168 [2025-02-20]. . |
| [34] | 谢昶琰,王迪,安祥瑞,等.滴灌减量施肥对梨树体养分及果实产量、品质的影响[J].江苏农业学报,2021,37(6):1526-1533. |
| [35] | AHMAD R, GAO J, LI W, et al.. Response of soil nutrients, enzyme activities, and fungal communities to biochar availability in the rhizosphere of mountainous apple trees [J]. Plant Soil, 2023, 489(1): 277-293. |
| [36] | 徐永杰,姜德志,李莉,等.不同类型有机肥对核桃园土壤、生长结果特性和坚果品质的影响[J].果树学报,2025,42(1):141-150. |
| XU Y J, JIANG D Z, LI L, et al.. Effects of different types of organic fertilizers on soil, growth and fruiting characteristics and nut quality in walnut orchard [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2025, 42(1): 141-150. |
| [1] | 马彦霞, 陈静茹, 王晓巍, 张玉鑫, 张俊峰, 蒯佳琳. 灌水下限和施肥量对膜下滴灌小型大白菜耗水及光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 239-249. |
| [2] | 吴梅, 张金珠, 王振华, 刘健, 温越, 李宣志. 水气互作对膜下滴灌玉米生理生长及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 189-200. |
| [3] | 贾莉, 陈娟, 雍山玉, 李效文, 梁伟琴. 半干旱区膜下滴灌量与滴灌次数对马铃薯生长及水分利用效率影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 176-184. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||