




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 69-76.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0172
收稿日期:2021-03-02
接受日期:2021-06-19
出版日期:2022-07-15
发布日期:2022-08-15
通讯作者:
闫伟
作者简介:郝艳玲E-mail:hyluuu@163.com;
基金资助:Received:2021-03-02
Accepted:2021-06-19
Online:2022-07-15
Published:2022-08-15
Contact:
Wei YAN
摘要:
为揭示混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗形态及生理指标的影响,以白榆幼苗为试验材料,采用盆栽法,设置6个混合盐(等浓度NaCl和NaHCO3溶液)浓度[0(CK)、10(T1)、30(T2)、50(T3)、70(T4)、100(T5) mmol·L-1]对白榆幼苗进行不同时间胁迫处理,分析混合盐胁迫下白榆幼苗的生长及生理指标的变化。结果表明,白榆幼苗生长对盐胁迫反应敏感,当盐浓度(10 mmol·L-1)较低时即表现出明显的抑制作用,胁迫35 d后,随着盐浓度的升高,白榆幼苗的总生物量、株高及地径增长量均显著降低,当混合盐浓度高于50 mmol·L-1时,各处理间降幅趋于稳定。不同盐浓度胁迫下,根冠比值均大于对照组;随着盐胁迫程度的加剧,丙二醛含量和相对电导率在不同处理时间下均逐渐增大,而可溶性糖、过氧化物酶及超氧化物歧化酶均呈现先升高后降低的趋势;不同处理时间下,叶绿素含量随着盐胁迫浓度的增加显著降低,混合盐浓度为100 mmol·L-1时,不同处理时间下叶绿素含量均为最小值。混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗的生长具有一定程度的抑制作用,但白榆幼苗可通过渗透调节及提高保护酶活性主动适应逆境,从而表现出较强的抗盐能力。研究结果旨在为白榆在盐碱地区的种植提供理论依据和技术参考。
中图分类号:
郝艳玲, 闫伟. 混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗形态及生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 69-76.
Yanling HAO, Wei YAN. Effects of Mixed Salt Stress on Morphological and Physiological Indexes of Ulmus pumila Seedlings[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 69-76.

图1 混合盐胁迫下白榆幼苗的株高增长量和地径增长量注:柱形图标上方不同小写字母表示不同处理在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.1 Plant height growth and ground diameter growth of Ulmus pumila seedlings under mixed salt stressNote: Different small letters above bar indicate significant difference among the different treatments at the P<0.05 level.
| 处理 Treatment | 总生物量 Total biomass/g | 根部干重 Root dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio | 盐耐受系数 Salt tolerance coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.43±0.05 a | 1.29±0.03 a | 1.13±0.01 a | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T1 | 1.72±0.14 b | 0.96±0.11 b | 1.28±0.12 a | 0.71±0.04 b |
| T2 | 1.27±0.12 c | 0.70±0.07 c | 1.22±0.03 a | 0.52±0.06 c |
| T3 | 1.12±0.09 c | 0.65±0.08 c | 1.37±0.21 a | 0.46±0.03 c |
| T4 | 1.08±0.18 c | 0.63±0.09 c | 1.42±0.08 a | 0.45±0.08 c |
| T5 | 0.97±0.02 c | 0.55±0.03 c | 1.31±0.13 a | 0.40±0.02 c |
表1 混合盐胁迫下白榆幼苗的生物量和盐耐受系数
Table1 Biomass and salt tolerance coefficient of Ulmus pumila seedlings under different mixed salt stress
| 处理 Treatment | 总生物量 Total biomass/g | 根部干重 Root dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio | 盐耐受系数 Salt tolerance coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.43±0.05 a | 1.29±0.03 a | 1.13±0.01 a | 1.00±0.00 a |
| T1 | 1.72±0.14 b | 0.96±0.11 b | 1.28±0.12 a | 0.71±0.04 b |
| T2 | 1.27±0.12 c | 0.70±0.07 c | 1.22±0.03 a | 0.52±0.06 c |
| T3 | 1.12±0.09 c | 0.65±0.08 c | 1.37±0.21 a | 0.46±0.03 c |
| T4 | 1.08±0.18 c | 0.63±0.09 c | 1.42±0.08 a | 0.45±0.08 c |
| T5 | 0.97±0.02 c | 0.55±0.03 c | 1.31±0.13 a | 0.40±0.02 c |

图2 混合盐胁迫下白榆幼苗MDA含量及SS含量的变化注:不同小写字母表示同一时间不同处理在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.2 Changes of MDA content and SS content of Ulmus pumila seedlings under mixed salt stressNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among the different treatments of the same time at the P<0.05 level.

图3 混合盐胁迫下白榆幼苗SOD活性及POD活性的变化注:不同小写字母表示同一时间不同处理在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.3 Changes of SOD and POD activities of Ulmus pumila seedlings under mixed salt stressNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among the different treatments of the same time at the P<0.05 level.
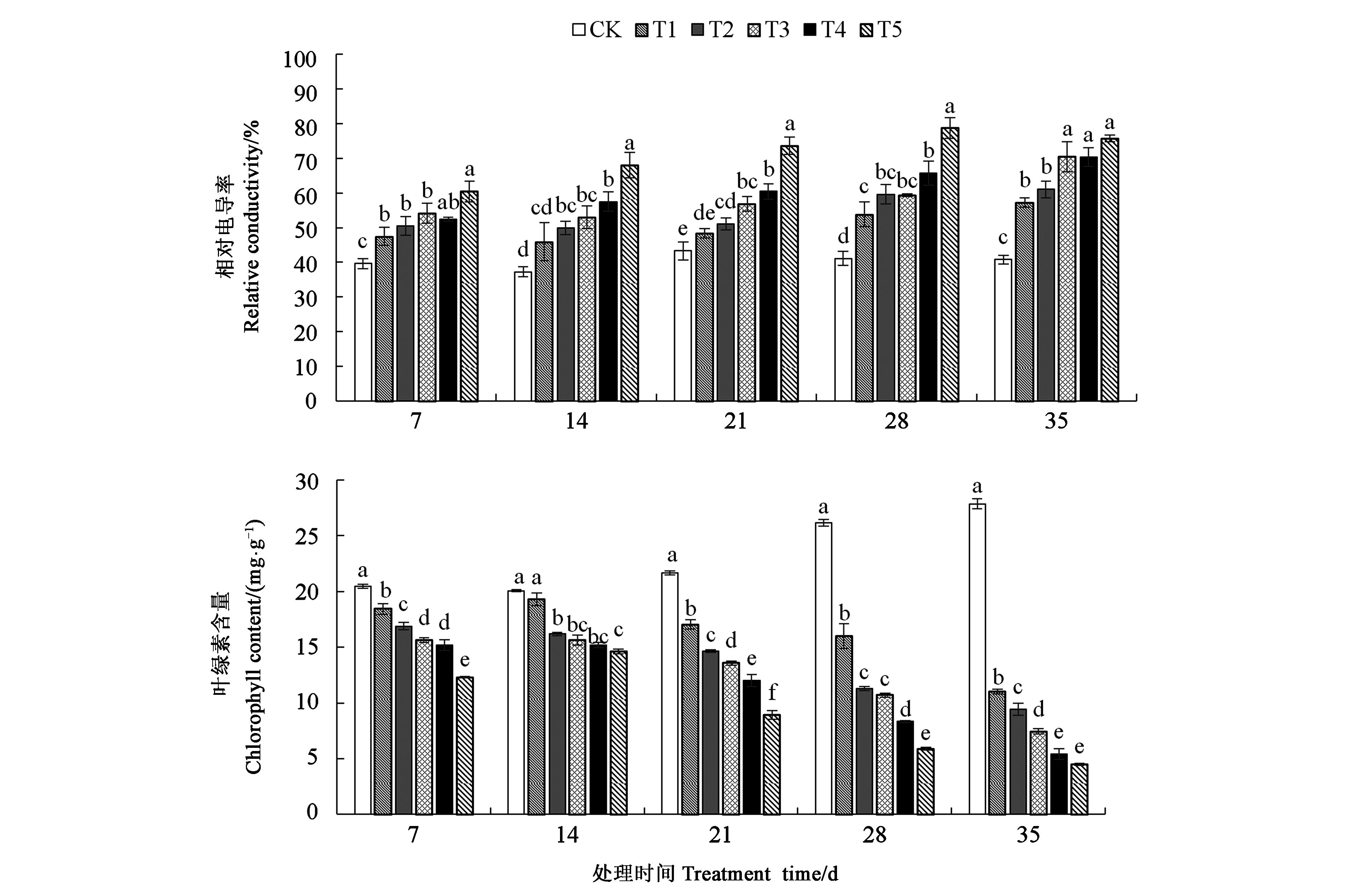
图4 混合盐胁迫下白榆幼苗相对电导率及叶绿素含量的变化注:不同小写字母表示同一时间不同处理在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.4 Changes of relative conductivity and chlorophyll content of Ulmus pumila seedlings under mixed salt stressNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among the different treatments of the same time at the P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 谭舒心.混合盐胁迫下藜麦生理特性的研究[D].长春:东北师范大学,2017. |
| TAN S X. Research on physiological characteristics of Chenopodium quinoa wild. under salt-alkali stress [D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2017. | |
| 2 | 黎雅楠.藜麦在盐碱地改良中的应用前景[J].绿色科技,2018(21):104-105. |
| LI Y N. Application prospect of Chenopodium quinoa wild in the improvement of saline-alkali land [J]. Green Tech., 2018(21): 104-105. | |
| 3 | MOUNGAR A, BADAOUI H, ABRI M. 16-channels wavelength efficient demultiplexing around 1.31/1.55 μm in 2D photonic crystal slab [J/OL]. Optik, 2019, 193: 162685 [2022-03-03]. . |
| 4 | 张梦璇,董智,李红丽,等.不同白榆品系对滨海盐碱地的改良效果及盐分离子的分布与吸收[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(6):340-345. |
| ZHANG M X, DONG Z, LI H L, et al.. Improvement effects of different Ulmus Pumila strains on coastal saline alkali soil and distribution and absorption of salt ions [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2018, 32(6): 340-345. | |
| 5 | 张磊,侯云鹏,王立春.盐碱胁迫对植物的影响及提高植物耐盐碱性的方法[J].东北农业科学,2018,43(4):11-16. |
| ZHANG L, HOU Y P, WANG L C. Effect of alkaline salt stress on plant and method of enhancing saline-alkali resistance [J]. Northeast Agric. Sci., 2018, 43(4): 11-16. | |
| 6 | 杨伟,王坚强,刘勇,等.植物盐胁迫研究进展[J].园艺与种苗,2018,38(5):55-57. |
| YANG W, WANG J Q, LIU Y, et al.. Research progress of plant salt stress [J]. Gard. Seedl., 2018, 38(5): 55-57. | |
| 7 | 张翼夫,李问盈,胡红,等.盐碱地改良研究现状及展望[J].江苏农业科学,2017,45(18):7-10. |
| 8 | 水润廷.世界四大行道树之一——七叶树[J].中国果菜,2009(8):41. |
| 9 | 梓叶.中国森林认证体系(CFCS)与森林认证体系认可计划(PEFC)实现互认[J].中国人造板,2014,21(4):43. |
| 10 | 慕德宇.白榆无性系耐盐性评价及耐盐机理研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2016. |
| MW D Y. Study on salt tolerance evaluation and salt tolerance mechanism of Ulmus pumila clone [D]. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2016. | |
| 11 | 田志和,董健.白榆种源和种源内家系综合选择及早期选择的研究[J].辽宁林业科技,1990(2):3-5. |
| 12 | 刘炳响.白榆耐盐生理生态机制研究[D].保定:河北农业大学,2012. |
| LIU B X. Research on the physiological-ecological mechanism of salt tolerance in Ulmus pumila [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 13 | 夏尚光.美国岩榆的引种育苗技术与耐盐耐旱特性研究[D].南京:南京林业大学,2005. |
| XIA S G. Study on introduction and seedling-breeding of rock elms from America and its physiological characters under water-and-salt stress [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2005. | |
| 14 | 李庆贱,李悦,陈志强,等.盐碱胁迫下白榆苗期遗传变异与优良家系选择[J].北京林业大学学报,2012,34(3):53-57. |
| LI Q J, LI Y, CHEN Z Q, et al. Genetic variation and selection of fine families of Ulmus pumila L.in seedling stage under saline-alkali stress [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2012, 34(3): 53-57. | |
| 15 | 夏尚光,张金池,梁淑英.NaCl胁迫对3种榆树幼苗生理特性的影响[J].河北农业大学学报,2008(2):52-56. |
| XIA S G, ZHANG J C, LIANG S Y. Effect of NaCl stress on physiological characteristics of three elm species seedlings [J]. J. Hebei Agric.Univ., 2008(2): 52-56. | |
| 16 | 刘炳响,王志刚,梁海永,等.盐胁迫对不同生境白榆生理特性与耐盐性的影响[J].应用生态学报,2012,23(6):1481-1489. |
| LIU B X, WANG Z G, LIANG H Y, et al.. Effects of salt stress on physiological characters and salt-tolerance of Ulmus pumila in different habitats [J]. J. Applied Ecol., 2012, 23(6): 1481-1489. | |
| 17 | 宋庆云,黄圣,吕艳伟.盐碱胁迫对白榆种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J].种子,2018,37(7):15-18. |
| SONG Q Y, HUANG S, LYU Y W. Effect of saline-alkali stress on seed germination and seeding growth of Ulmus pumila L. [J]. Seed, 2018, 37(7): 15-18. | |
| 18 | 闫晶秋子,李钢铁,王月林,等.盐胁迫对蒙桑种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2020,22(1):28-37. |
| YAN J Q Z, LI G T, WANG Y L, et al.. Effect of salt stress on seed germination and seeding physiological characteristics of Morus mongolica [J]. China Agric. Sci. Tech. Review, 2020, 22(1): 28-37. | |
| 19 | 张晓晓.3个白榆品系耐盐特性比较研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2017. |
| ZHANG X X. A comparative study on the salt tolerance characteristics of three white elm strains[D].Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 20 | 王学奎.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2006:280-282. |
| 21 | 张雪,贺康宁,史常青,等.盐胁迫对柽柳和白刺幼苗生长与生理特性的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2017,45(1):105-111. |
| ZHANG X, HE K N, SHI C Q, et al.. Effects of salt stress on growth and physiological characteristics of Tamarix chinensis and Nitraria tangutorum seedlings [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat.Sci.), 2017, 45(1): 105-111. | |
| 22 | 刘盛波,张伟,杜尚嘉,等.NaCl胁迫对降香黄檀种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J].种子,2016,35(6):22-26. |
| LIU S B, ZHANG W, DU S J, et al.. Research on the seed germination and seedling growth of Dalbergia oderifera under NaCl stress [J]. Seed, 2016, 35(6): 22-26. | |
| 23 | SALTER J, MORRIS K, BAILEY P, et al.. Interactive effects of salinity and water depth on the growth of Melaleuca ericifolia Sm.(Swamp paperbark) seedlings[J]. Aquatic Bot., 2007, 86(3): 213-222. |
| 24 | 成广雷,张海娇,赵久然,等.临界胁迫贮藏条件下不同基因型玉米种子活力及生理变化[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(1):33-42. |
| CHENG G L, ZHANG H J, ZHAO J R, et al.. Vigor and physiological changes of different genotypes ofmaize seed (Zea mays L.) under critical stress storage conditions [J]. China Agric. Sci., 2015, 48(1): 33-42. | |
| 25 | LIU R. Comparative siological analysis of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) cultivars in response to salt stress and cloning of NnCIPK genes [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2014, 173(1): 29-36. |
| 26 | 薄鹏飞,孙秀玲,孙同虎,等.NaCl胁迫对海滨木槿抗氧化系统和渗透调节的影响[J].西北植物学报,2008(1):113-118. |
| BO P F, SUN X L, SUN T H, et al.. Antioxidative system and osmotic regulation in seedlings of annual Hibiscus syriacus under salt stress [J]. Northwest Bot., 2008(1): 113-118. | |
| 27 | 刘一明,程凤枝,王齐,等.四种暖季型草坪植物的盐胁迫反应及其耐盐阈值[J].草业学报,2009,18(3):192-199. |
| LIU Y M, CHENG F Z, WANG Q, et al.. Salinity stress responses and tolerance thresholds in four warm-season turfgrasses [J]. Acta Prata. Sin., 2009, 18(3): 192-199. | |
| 28 | 黄相玲,林妃妃,张明月,等.盐胁迫对小叶榄仁幼苗生长和渗透调节物质含量的影响[J].南方农业学报,2018,49(7):1364-1369. |
| HUANG X L, LIN F F, ZHANG M Y, et al.. Effects of salt stress on growth and osmoregulatory substances in Terminalia neotaliala Capuron seedlings [J]. Southern Agric. J., 2018, 49(7): 1364-1369. | |
| 29 | 张华新,宋丹,刘正祥.盐胁迫下11个树种生理特性及其耐盐性研究[J].林业科学研究,2008(2):168-175. |
| ZHANG H X, SONG D, LIU Z X. Study on physiological characteristics and salt tolerance for seedlings of 11 tree species [J]. For. Sci. Res., 2008(2): 168-175. | |
| 30 | 林兴生,林占熺,林冬梅,等.5种菌草苗期抗盐性的评价[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2013,42(2):195-201. |
| LIN X S, LIN Z X, LIN D M,et al.. Assessment on sail resistance at seedling stage of 5 species of juncao under NaCl stress[J]. J. Fujian Agric. Fore. Univ. (Nat. Sci. ED.), 2013, 42(2): 195-201. | |
| 31 | 韩志平,张海霞,周桂伶,李侠.混合盐胁迫下黄花菜生长和生理特性的变化[J].河南农业科学,2020,49(2):116-122. |
| HAN Z P, ZHANG HX, ZHOU G L. Change of growth and physiological characteristics of daylily under mixed salt stress[J]. Henan Agric. Sci., 2020, 49(2): 116-122. | |
| 32 | 于兆友,闫海冰,张慧芳 等.不同盐分胁迫对皂荚种子萌发及幼苗生理特征的影响[J].东北农业大学学报,2020,51(10):28-35. |
| YU Z Y, YAN H B, ZHANG H F, et al.. Effect of different salt stresses on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of Gleditsia sinensis [J]. J. Northeast Agric.Univ., 2020, 51(10): 28-35. | |
| 33 | 高汝勇.混合盐碱胁迫对大白菜种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J].河南农业科学,2011,40(1):121-123. |
| GAO R Y. Effects of three salt stresses on the seed sprouting and seedling growth of cabbage [J]. Henan Agric. Sci., 2011, 40(1): 121-123. |
| [1] | 刘雪晴, 王静, 阳宜, 吴慧琴, 王延宏, 王麓尧, 路佳伟, 张凯璇, 翟源, 成妍. 外源乙烯利对色素辣椒脱叶及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 36-46. |
| [2] | 张余莽, 陈贵娟, 常洪艳, 王永恒, 刘淑霞, 应允秀. 水分胁迫下新型土壤保水剂对玉米苗期发育的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 201-210. |
| [3] | 黄丽芳, 龙宇宙, 李金芹, 董云萍, 王晓阳, 陈鹏, 王宪文, 闫林. 低温胁迫对小粒种咖啡幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 60-67. |
| [4] | 陈炟, 巨吉生, 马麒, 徐守振, 刘娟娟, 袁文敏, 李吉莲, 王彩香, 宿俊吉. FeNPs对苗期棉花根系生长及其对干旱响应的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 49-57. |
| [5] | 崔宏亮, 宋晓晓, 姚庆, 安万刚, 邢宝, 秦培友. 伊犁河谷不同藜麦品种对盐胁迫的生理响应及耐盐评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 32-45. |
| [6] | 彭田伟, 谢会雅, 李思军, 刘怡轩, 帅开峰, 彭媛媛, 王青, 李迪秦. 复硝酚钠和枯草芽孢杆菌复配对烟苗生长和生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 154-161. |
| [7] | 郭瑞锋, 任月梅, 杨忠, 刘贵山, 任广兵, 张绶, 朱文娟. 草甘膦铵盐诱导谷子雄性不育的转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 35-43. |
| [8] | 王东1,曹源倍2,吉遥芳3,傅渝亮3*. 不同滴灌量对红寺堡区酿酒葡萄生长和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 154-161. |
| [9] | 杨瑞萍1,刘瑞香1,马迎梅1*,郭占斌2,张宏武2,白宇1,赵新宇1. 不同藜麦资源的抗旱性评价及渗透调节剂对其抗旱性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 52-60. |
| [10] | 张嘉雯,卢绍浩,赵喆,赵铭钦*. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下烟草幼苗生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 78-86. |
| [11] | 张琛,韩婷,马洁,杨涓,刘根红,郑国琦* . 起垄高度对黑果枸杞生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 153-161. |
| [12] | 胡博,闫伟*,刘宇,郝艳玲. 三种桑生理特性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(4): 61-67. |
| [13] | 田梅§,曹慧雅§,张明烁§,张子璇,杨冬月,李浩然,马春英*. 红花在萌发期和幼苗期对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(5): 49-54. |
| [14] | 秦岭,陈二影,杨延兵,张艳亭,孔清华,张华文,王海莲,王润丰,管延安*. 干旱和复水对不同耐旱型谷子品种苗期生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3): 146-151. |
| [15] | 王梦园1,杜延全2,朱建强1*. 复合促生菌对小麦苗期生长和土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 98-106. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
