




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 46-54.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0835
孙鲁鹏1( ), 杨洋1, 王卫超1, 傅廷栋2, 周广生2, 张凤华1(
), 杨洋1, 王卫超1, 傅廷栋2, 周广生2, 张凤华1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-25
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-13
通讯作者:
张凤华
作者简介:孙鲁鹏 E-mail:190508751@qq.com;
基金资助:
Lupeng SUN1( ), Yang YANG1, Weichao WANG1, Tingdong FU2, Guangsheng ZHOU2, Fenghua ZHANG1(
), Yang YANG1, Weichao WANG1, Tingdong FU2, Guangsheng ZHOU2, Fenghua ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2021-09-25
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Fenghua ZHANG
摘要:
为探究油菜苗期不同生长阶段(苗前期与苗后期)体内离子吸收及分配对复合盐碱胁迫的响应机制,以‘华油杂62号’为材料,采用盆栽方法,分析复合盐碱胁迫下离子(Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+)在油菜苗期不同器官吸收及分布的变化。结果表明,油菜苗前期在中度、重度盐碱处理下,根冠比较轻度处理分别增加16.47%、48.83%,而苗后期分别降低9.06%、45.49%;随盐碱程度的增加,油菜苗期各部位Na+含量均呈增加趋势,重度盐碱处理下Na+含量均显著高于轻度和中度处理,且苗前期Na+主要积累于茎叶,苗后期主要积累于根部;根中Na+含量在苗后期显著大于苗前期,分别增加1.80(轻度)、1.80(中度)和1.17倍(重度);K+主要积累于根部,苗后期根中的K+含量显著低于苗前期,分别降低65.7%(轻度)、83.1%(中度)和67.3%(重度);选择性运输系数
中图分类号:
孙鲁鹏, 杨洋, 王卫超, 傅廷栋, 周广生, 张凤华. 油菜苗期对盐碱胁迫的离子响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 46-54.
Lupeng SUN, Yang YANG, Weichao WANG, Tingdong FU, Guangsheng ZHOU, Fenghua ZHANG. Ion Response Mechanism of Canola Seedlings to Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 46-54.
电导率 Conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | pH | Na+含量 Na+ content/(mg·g-1) | Cl-含量 Cl- content/(mg·g-1) | SO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.70 | 7.41 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 3.80 |
表1 供试土壤主要参数
Table 1 Main soil parameters
电导率 Conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | pH | Na+含量 Na+ content/(mg·g-1) | Cl-含量 Cl- content/(mg·g-1) | SO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.70 | 7.41 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 3.80 |
处理 Treatment | 含量Content/(g·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Na2SO4 | NaHCO3 | Na2CO3 | |
| 轻度Low | 0.76 | 1.39 | 0.73 | 0.12 |
| 中度Moderate | 1.27 | 2.32 | 1.22 | 0.19 |
| 重度High | 2.55 | 4.63 | 2.44 | 0.38 |
表2 复合盐碱盐分种类及含量
Table 2 Salt types and content of combined saline-alkali salt
处理 Treatment | 含量Content/(g·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Na2SO4 | NaHCO3 | Na2CO3 | |
| 轻度Low | 0.76 | 1.39 | 0.73 | 0.12 |
| 中度Moderate | 1.27 | 2.32 | 1.22 | 0.19 |
| 重度High | 2.55 | 4.63 | 2.44 | 0.38 |
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 干重Dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root/shoot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
茎叶 Stem and leaf | 根 Root | |||
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.34±0.05 a | 0.02±0.00 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.23±0.06 b | 0.02±0.01 b | 0.07±0.02 a | |
| 重度High | 0.08±0.01 c | 0.01±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.83±0.01 a | 0.14±0.02 a | 0.17±0.02 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.58±0.00 b | 0.09±0.01 b | 0.15±0.01 a | |
| 重度High | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.02±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 b | |
表3 复合盐碱胁迫下油菜苗期不同生长阶段的生物量和根冠比
Table 3 Biomass and root/shoot ratio of canola at different seedling stages under combined saline-alkali salt stress
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 干重Dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root/shoot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
茎叶 Stem and leaf | 根 Root | |||
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.34±0.05 a | 0.02±0.00 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.23±0.06 b | 0.02±0.01 b | 0.07±0.02 a | |
| 重度High | 0.08±0.01 c | 0.01±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.83±0.01 a | 0.14±0.02 a | 0.17±0.02 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.58±0.00 b | 0.09±0.01 b | 0.15±0.01 a | |
| 重度High | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.02±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 b | |
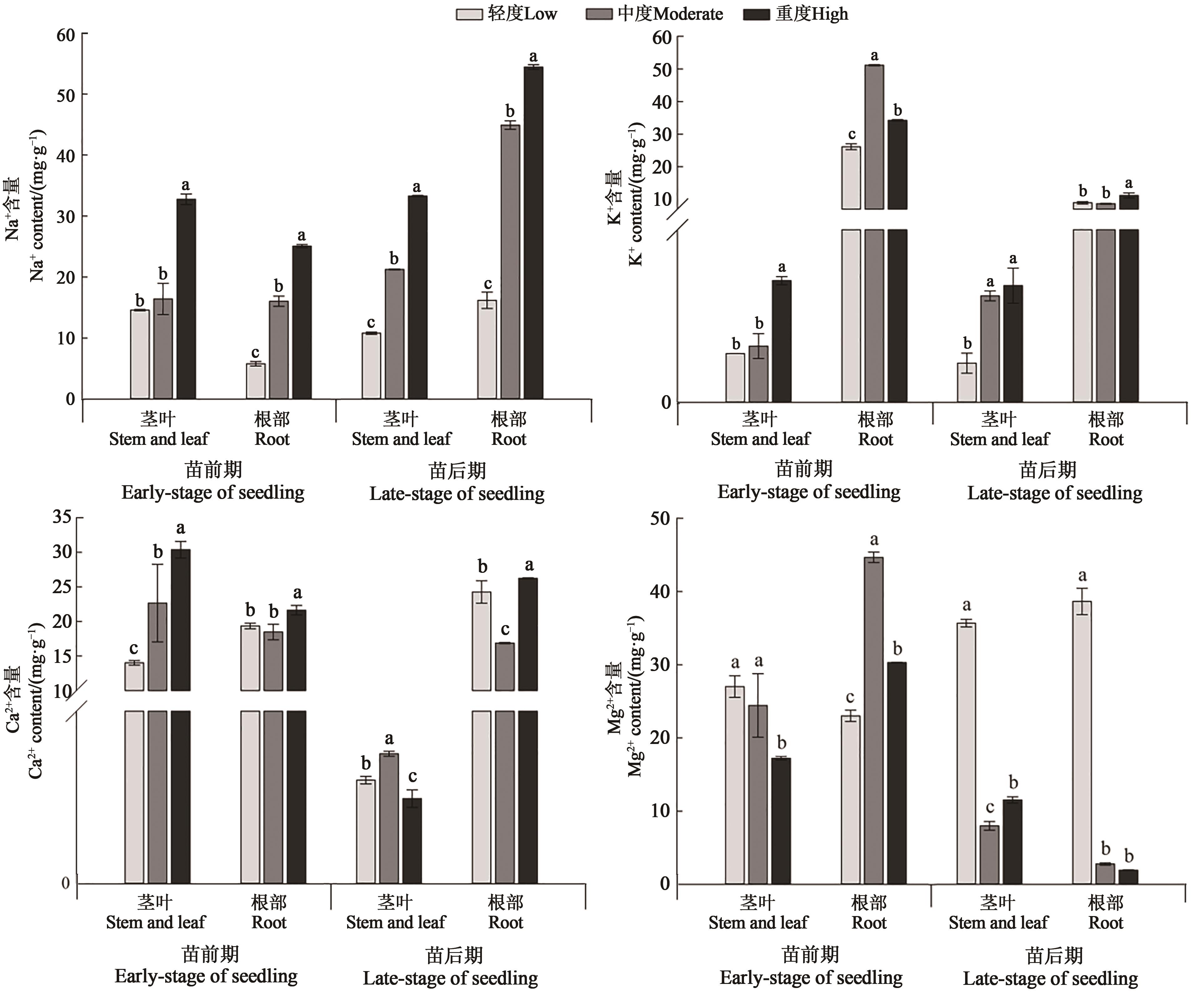
图1 复合盐碱胁迫下油菜苗期不同生长阶段的Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+含量注:不同小写字母表示同一时期不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Na+,K+,Ca2+,Mg2+ contents of canola seedling in different growth stages under combined saline-alkali stressNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.
生长阶段 Growth stage | 器官 Organ | 处理 Treatment | Na+/K+ | Na+/Ca2+ | Na+/Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 25.70±0.18 aα | 1.04±0.03 aβ | 0.54±0.03 bα |
| 中度Moderate | 25.39±1.79 aα | 0.73±0.08 bβ | 0.70±0.25 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 23.24±0.50 bα | 1.08±0.07 aβ | 1.90±0.03 aβ | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 0.22±0.02 cβ | 0.30±0.02 cβ | 0.25±0.03 cβ | |
| 中度Moderate | 0.31±0.02 bβ | 0.87±0.01 bβ | 0.36±0.02 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 0.73±0.01 aβ | 1.16±0.03 aβ | 0.83±0.01 aβ | ||
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 24.83±6.48 aα | 9.00±0.44 cα | 0.30±0.00 bβ |
| 中度Moderate | 17.25±0.87 aβ | 14.11±0.29 bα | 2.67±0.20 aα | ||
| 重度High | 25.00±3.94 aα | 33.98±3.56 aα | 2.89±0.11 aα | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 1.80±0.08 bα | 0.67±0.05 cα | 0.42±0.03 cα | |
| 中度Moderate | 5.19±0.15 aα | 2.66±0.03 aα | 16.19±1.08 bα | ||
| 重度High | 4.87±0.36 aα | 2.07±0.02 bα | 28.22±0.61 aα |
表4 油菜幼苗不同生长阶段的离子比
Table 4 Ion ratio in canola seedlings at different growth stages under combined saline-alkali stress
生长阶段 Growth stage | 器官 Organ | 处理 Treatment | Na+/K+ | Na+/Ca2+ | Na+/Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 25.70±0.18 aα | 1.04±0.03 aβ | 0.54±0.03 bα |
| 中度Moderate | 25.39±1.79 aα | 0.73±0.08 bβ | 0.70±0.25 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 23.24±0.50 bα | 1.08±0.07 aβ | 1.90±0.03 aβ | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 0.22±0.02 cβ | 0.30±0.02 cβ | 0.25±0.03 cβ | |
| 中度Moderate | 0.31±0.02 bβ | 0.87±0.01 bβ | 0.36±0.02 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 0.73±0.01 aβ | 1.16±0.03 aβ | 0.83±0.01 aβ | ||
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 24.83±6.48 aα | 9.00±0.44 cα | 0.30±0.00 bβ |
| 中度Moderate | 17.25±0.87 aβ | 14.11±0.29 bα | 2.67±0.20 aα | ||
| 重度High | 25.00±3.94 aα | 33.98±3.56 aα | 2.89±0.11 aα | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 1.80±0.08 bα | 0.67±0.05 cα | 0.42±0.03 cα | |
| 中度Moderate | 5.19±0.15 aα | 2.66±0.03 aα | 16.19±1.08 bα | ||
| 重度High | 4.87±0.36 aα | 2.07±0.02 bα | 28.22±0.61 aα |
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.009±0.001 c | 0.288±0.020 b | 0.467±0.026 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.012±0.002 b | 1.190±0.117 a | 0.547±0.150 a | |
| 重度High | 0.031±0.001 a | 1.076±0.052 a | 0.435±0.009 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.076±0.021 c | 0.074±0.006 b | 1.386±0.101 c |
| 中度Moderate | 0.302±0.022 a | 0.189±0.005 a | 6.080±0.565 b | |
| 重度High | 0.198±0.039 b | 0.062±0.007 c | 9.762±0.225 a |
表5 复合盐碱胁迫下油菜苗期不同生长阶段的离子选择性运输系数
Table 5 Ion selective transport coefficient of canola seedling at different growth stages combined saline-alkali stress
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.009±0.001 c | 0.288±0.020 b | 0.467±0.026 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.012±0.002 b | 1.190±0.117 a | 0.547±0.150 a | |
| 重度High | 0.031±0.001 a | 1.076±0.052 a | 0.435±0.009 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.076±0.021 c | 0.074±0.006 b | 1.386±0.101 c |
| 中度Moderate | 0.302±0.022 a | 0.189±0.005 a | 6.080±0.565 b | |
| 重度High | 0.198±0.039 b | 0.062±0.007 c | 9.762±0.225 a |
| 1 | YANG J Y, ZHENG W, TIAN Y, et al.. Effects of various mixed salt-alkaline stresses on growth, photosynthesis, and photosynthetic pigment concentrations of Medicago rutheniumca seedlings [J]. Photosynthetic, 2011, 49:275-284. |
| 2 | PAZ R C, REINOSO H, ESPASABDIN F D, et al.. Akaline saline and mixed saline alkaline induce physiologicaland morphoanatomical changes in Lotus tenuis shoots [J]. Plant Biol., 2014, 16(6):1042-1049. |
| 3 | 乌凤章,王贺新.盐胁迫对高丛越橘幼苗生长及离子平衡的影响[J].生态学杂志,2019,38(11):3335-3341. |
| WU F Z, WANG H X. Effects of salt stress on growth and ion homeostasis of highbush blueberry seedlings [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2019, 38(11):3335-3341. | |
| 4 | ZHU X J, YANG J S, LIANG Y C, et al.. Effects of exogenous calcium on photosynthesis and its related physiological characteristics of rice seedlings under salt stress [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2004, 37(10):1497-1503. |
| 5 | LOUPASSAKI M H, CHARTZOULAKIS K S, DIGALAKI N B, et al.. Effects of salt stress on concentration of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sodium in leaves, shoots, and roots of six olive cultivars [J]. J. Plant Nutr., 2002, 25(11):2457-2482. |
| 6 | ZHANG J L, FLOWERS T J, WANG S M. Mechanisme of sodium up take by roots of higher plants [J]. Plant Soil, 2010, 326:45-60. |
| 7 | 韩志平,郭世荣,郑瑞娜,等.盐胁迫对小型西瓜幼苗体内离子分布的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(4):908-917. |
| HAN Z P, GUO S R, ZHENG R N, et al.. Effect of salinity on distribution of ions in mini-watermelon seedlings [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2013, 19(4):908-917. | |
| 8 | 熊韬,胡国智,吴海波,等.盐碱胁迫对甜瓜幼苗离子吸收和分配的影响[J].新疆农业科学,2019,56(7):1258-1266. |
| XIONG T, HU G Z, WU H B, et al.. Effects of saline-alkali stress on ion absorption and distribution in melon seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2019, 56(7):1258-1266. | |
| 9 | PAN J W, LI Z, DAI S J, et al.. Integrative analyses of transcriptomics and metabolomics upon seed germination of foxtail millet in response to salinity [J]. Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1):12700-12712. |
| 10 | 黎咏蜀.饲用油菜栽培技术及营养价值研究[D].重庆:西南大学, 2014. |
| LI Y S. Research on cultivation techniques and nutritional value of forage oilseed [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2014. | |
| 11 | 张哲,殷艳,刘芳,等.我国油菜多功能开发利用现状及发展对策[J].中国油料作物学报,2018,40(5):618-623. |
| ZHANG Z, YIN Y, LIU F, et al.. Current situation and development countermeasures of Chinese rapeseed multifunctional development and utilization [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2018, 40(5):618-623. | |
| 12 | 郭丛阳,王天河,杨文元,等.河西地区麦后复种饲用(绿肥)油菜栽培技术及效益分析[J].草业科学,2008,25(3):90-92. |
| GUO C Y, WANG T H, YANG W Y, et al.. Growing technology and profit analyzation of grazing (or green manure) Brassica napus grown after harvesting wheat in Hexi Corridor [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2008, 25(3):90-92. | |
| 13 | 油菜品种华油杂62[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2010, 49(11):2770. |
| 14 | 李惠英,陈良.盐胁迫对草坪草萌发生长及代谢的影响[J].草业科学,2018,35(11):2584-2592. |
| LI H Y, CHEN L. Effect of salt stress on turfgrass growth and metabolism [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2018, 35(11):2584-2592. | |
| 15 | 史晓艳,李维弟,余露,等.玛纳斯河流域农灌区土壤盐渍化遥感定量评价[J].灌溉排水学报,2018,37(11):69-75, 83. |
| SHI X Y, LI W D, YU L, et al.. Using remote sensing to evaluate soil salinization distribution over the irrigation areas in the Manas river basin [J]. J. Irrigat. Drain., 2018,37(11):69-75, 83. | |
| 16 | 罗家雄.新疆垦区盐碱地改良[M].北京:水利电力出版社,1985:1-128. |
| 17 | 郁万文,曹福亮,蔡金峰,等.盐碱胁迫对喜树幼苗生长及体内离子选择性运输的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2015,43(11):1-5. |
| YU W W, CAO F L, CAI J F, et al.. Effects of saline and alkali stresses in growth and mineral nutrition selective transportation of Camptotheca acuminate Decne [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2015, 43(11):1-5. | |
| 18 | 周琦,祝遵凌. NaCl胁迫对2种鹅耳枥幼苗生长及离子吸收、分配与运输的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2015,37(12):7-16. |
| ZHOU Q, ZHU Z L. Effects of NaCl stress on seedling growth and mineral ions uptake, distribution and transportation of two varieties of Carpinus L. [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2015, 37(12):7-16. | |
| 19 | WANG S F, HU Y X, LI Z L, et al.. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and mineral ion uptake, transportation and distribution of Quercus virginiana [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010, 30(17):4609-4616. |
| 20 | 李先婷,曹靖,魏晓娟,等.NaCl渐进胁迫对啤酒大麦幼苗生长、离子分配和光合特性的影响[J].草业学报,2013,22(6):108-116. |
| LI X T, CAO J, WEI X J, et al.. Effect of extended exposure to NaCl stress on the growth, ion distribution and photosynthetic characteristics of malting barley (Hordeum vulgare) [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2013, 22(6):108-116. | |
| 21 | 朱义,谭贵娥,何池全,等.盐胁迫对高羊茅(Festuca arundinacea)幼苗生长和离子分布的影响[J].生态学报,2007, 27(12):5447-5454. |
| ZHU Y, TAN G E, HE C Q, et al.. Effect of salinization on growth and ion homeostasis in seedlings of Festuca arundinacea [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2007, 27(12):5447-5454. | |
| 22 | 王薇薇,祖艳侠,吴永成,等.盐胁迫对豇豆幼苗离子分布的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2019,47(12):161-164. |
| 23 | 张继伟,赵昕,石勇,等.盐胁迫下沙米(Agriophyllum squarrosum)矿质离子吸收与分配特征[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(3):702-707. |
| ZHANG J W, ZHAO X, SHI Y, et al.. Ion absorption and distribution of Agriophyllum squarrosum seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. J. Desert Res., 2016, 36(3):702-707. | |
| 24 | 李玉梅,郭修武,姜云天.牛叠肚幼苗对盐胁迫的离子响应[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(2):353-361. |
| LI Y M, GUO X W, JIANG Y T. Response of ions in Rubus crataegifolius seedlings to salt stress [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2016, 33(2):353-361. | |
| 25 | YANG Y, ZHENG Q S, LIU M, et al.. Difference in sodium spatial distribution in the shoot of two canola cultivars under saline stress [J]. Narnia, 2012, 53(6):1083-1092. |
| 26 | 徐靖宇.盐胁迫下野大豆(Glycine soja)光合特性、离子动态平衡及其相关关系研究[D].长春:东北师范大学, 2016. |
| XU J Y. The photosynthetic characteristics, ion homeostasis and the correlation between them in Glycine soja under salt stress [D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2016. | |
| 27 | MOLLER I S, GILLIHAM M, JHA D, et al.. Shoot Na+ exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na+ transport in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(7):2163-2178. |
| 28 | WU H, SHABALA L, LIU X, et al.. Linking salinity stress tolerance with tissue specific Na+ sequestration in wheat roots [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2015, 6:71 [2021-09-05]. . |
| 29 | 车永梅,唐静,陈康,等.一氧化氮对盐胁迫下玉米幼苗叶绿素荧光参数和光合特性的影响[J].玉米科学,2009,17(3):91-94. |
| CHE Y M, TANG J, CHEN K, et al.. Effects of nitric oxide on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and photosynthetic characteristics of maize seedling under salt stress [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2009, 17(3):91-94. | |
| 30 | 马琛,乙引,张习敏,等.钙离子在植物生理调节中的作用[J].贵州农业科学,2010,38(2):36-41. |
| MA C, YI Y, ZHANG X M, et al.. Effect of the regulation of plant physiology on calcium ion [J]. Guizhou Agric. Sci., 2010, 38(2):36-41. | |
| 31 | 周艳.GSH缓解番茄幼苗盐胁迫的耐盐机制研究[D].石河子:石河子大学,2019. |
| ZHOU Y. Salt-tolerant mechanism of GSH alleciates salt-induced stress in tomato seedlings [D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2019. | |
| 32 | 张科,张道远,王雷,等.自然生境下盐角草的离子吸收、运输特征[J].干旱区研究,2007,24(4):480-486. |
| ZHANG K, ZHANG D Y, WANG L, et al.. Study on the ionic absorption and transport in Salicornia europaea L. growing in natural habitas in Xinjiang [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2007, 24 (4):480-486. | |
| 33 | 王佺珍,刘倩,高娅妮,等.植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J].生态学报,2017,37(16):5565-5577. |
| WANG Q Z, LIU Q, GAO Y N, et al.. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(16):5565-5577. | |
| 34 | 刘正祥,张华新,杨秀艳,等.NaCl胁迫下沙枣幼苗生长和阳离子吸收、运输与分配特性[J].生态学报,2014,34(2):326-336. |
| LIU Z X, ZHANG H X, YANG X Y, et al.. Growth, and cationic absorption, transportation and allocation of Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2014, 34(2):326-336. | |
| 35 | 王龙强,米永伟,蔺海明.盐胁迫对枸杞属两种植物幼苗离子吸收和分配的影响[J].草业学报,2011,20(4):129-136. |
| WANG L Q, MI Y W, LIN H M. Effect of salt stress on ion absorption and distribution of two Lycium seedlings [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2011, 20(4):129-136. | |
| 36 | 萨如拉,刘景辉,刘伟,等.燕麦对碱胁迫的阳离子响应机制[J].作物学报,2014,40 (2):362-368. |
| SA R L, LIU J H, LIU W, et al.. Cation-responsive mechanisms of oats to alkali stress [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2014, 40 (2):362-368. | |
| 37 | TEAKLE N L, FLOWERS T J, REAL D, et al.. Lotus tenuis tolerates the interactive effects of salinity and waterlogging by 'excluding' Na+ and Cl- from the xylem [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2007, 58(8):2169-2180. |
| 38 | 乌凤章,朱心慰,胡锐锋,等.NaCl胁迫对2个蓝莓品种幼苗生长及离子吸收、运输和分配的影响[J].林业科学,2017,53(10):40-49. |
| WU F Z, ZHU X W, HU R F, et al.. Effects of NaCl stress on growth ion uptake, transportation and distribution of two blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) cultivars seedlings [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin., 2017, 53(10):40-49. |
| [1] | 关永旭, 孙志成, 王研, 李媛, 孙晓丽, 贾博为, 孙明哲. 拟南芥AtCHX19基因在盐碱胁迫应答中的功能解析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 60-72. |
| [2] | 凌磊, 蒋慧欣, 李铭婧, 殷亚杰, 陈乃钰, 赵晓菊. 盐碱胁迫下燕麦蛋白组及代谢组联合分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 61-71. |
| [3] | 闫敏, 王艳, 王程成, 郭松超, 卢登洋, 吴翠云. 混合盐碱胁迫对骏枣叶片结构和光合荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 57-65. |
| [4] | 邓玉荣, 韩联, 王金龙, 韦兴翰, 王旭东, 赵颖, 魏小红, 李朝周. 藜麦SOD家族基因的鉴定及其对混合盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 28-39. |
| [5] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [6] | 梁培鑫, 唐榕, 刘建国. 混合盐碱胁迫对油莎豆光合生理及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 195-204. |
| [7] | 万何平, 张浩, 余忆, 陈敬东, 曾长立, 赵伦, 文静, 沈金雄, 傅廷栋. 油菜耐盐碱研究与应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(12): 59-67. |
| [8] | 李媛媛1,陈博2,姚立蓉2,翟雪婷1,司二静2,汪军成2,马小乐2,孟亚雄2,王化俊2,李葆春1*,杨亮1. 283份小麦品种(系)萌发期耐盐碱性评价及种质筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 25-33. |
| [9] | 王俊铎1,曾辉2,龚照龙1,梁亚军1,艾先涛1,郭江平1,莫明1,李雪源1,郑巨云1*. 陆地棉品种资源耐复合盐碱性综合评价分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 1-11. |
| [10] | 景宇鹏1,2,连海飞1,李焕春1,史培1,杜超3,刘梅4,常新娟5. 玉米耐盐碱能力及评价指标筛选研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(11): 94-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||